IFI16
| Interferon, gamma-inducible protein 16 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 2oq0. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | IFI16 ; IFNGIP1; MGC9466; PYHIN2 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 48354 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
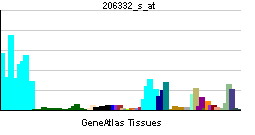
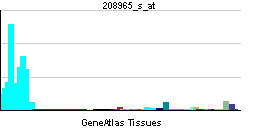
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Interferon, gamma-inducible protein 16, also known as IFI16, is a human gene.[1]
This gene encodes a member of the HIN-200 (hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear antigens with 200 amino acid repeats) family of cytokines. The encoded protein contains domains involved in DNA binding, transcriptional regulation, and protein-protein interactions. The protein localizes to the nucleoplasm and nucleoli, and interacts with p53 and retinoblastoma-1. It modulates p53 function, and inhibits cell growth in the Ras/Raf signaling pathway.[1]
References
Further reading
- Trapani JA, Browne KA, Dawson MJ; et al. (1992). "A novel gene constitutively expressed in human lymphoid cells is inducible with interferon-gamma in myeloid cells". Immunogenetics. 36 (6): 369–76. PMID 1526658.
- Dawson MJ, Trapani JA (1995). "IFI 16 gene encodes a nuclear protein whose expression is induced by interferons in human myeloid leukaemia cell lines". J. Cell. Biochem. 57 (1): 39–51. doi:10.1002/jcb.240570106. PMID 7536752.
- Dawson MJ, Trapani JA, Briggs RC; et al. (1995). "The closely linked genes encoding the myeloid nuclear differentiation antigen (MNDA) and IFI16 exhibit contrasting haemopoietic expression". Immunogenetics. 41 (1): 40–3. PMID 7806273.
- Trapani JA, Dawson M, Apostolidis VA, Browne KA (1994). "Genomic organization of IFI16, an interferon-inducible gene whose expression is associated with human myeloid cell differentiation: correlation of predicted protein domains with exon organization". Immunogenetics. 40 (6): 415–24. PMID 7959953.
- Johnstone RW, Kerry JA, Trapani JA (1998). "The human interferon-inducible protein, IFI 16, is a repressor of transcription". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (27): 17172–7. PMID 9642285.
- Johnstone RW, Kershaw MH, Trapani JA (1998). "Isotypic variants of the interferon-inducible transcriptional repressor IFI 16 arise through differential mRNA splicing". Biochemistry. 37 (34): 11924–31. doi:10.1021/bi981069a. PMID 9718316.
- Dawson MJ, Elwood NJ, Johnstone RW, Trapani JA (1998). "The IFN-inducible nucleoprotein IFI 16 is expressed in cells of the monocyte lineage, but is rapidly and markedly down-regulated in other myeloid precursor populations". J. Leukoc. Biol. 64 (4): 546–54. PMID 9766636.
- Briggs LJ, Johnstone RW, Elliot RM; et al. (2001). "Novel properties of the protein kinase CK2-site-regulated nuclear- localization sequence of the interferon-induced nuclear factor IFI 16". Biochem. J. 353 (Pt 1): 69–77. PMID 11115400.
- Johnstone RW, Wei W, Greenway A, Trapani JA (2001). "Functional interaction between p53 and the interferon-inducible nucleoprotein IFI 16". Oncogene. 19 (52): 6033–42. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204005. PMID 11146555.
- Gariglio M, Azzimonti B, Pagano M; et al. (2003). "Immunohistochemical expression analysis of the human interferon-inducible gene IFI16, a member of the HIN200 family, not restricted to hematopoietic cells". J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 22 (7): 815–21. doi:10.1089/107999002320271413. PMID 12184920.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Izmailova E, Bertley FM, Huang Q; et al. (2003). "HIV-1 Tat reprograms immature dendritic cells to express chemoattractants for activated T cells and macrophages". Nat. Med. 9 (2): 191–7. doi:10.1038/nm822. PMID 12539042.
- Clarke CJ, Apostolidis V, Hii LL; et al. (2003). "Critical role of the transcription factor AP-1 for the constitutive and interferon-induced expression of IFI 16". J. Cell. Biochem. 89 (1): 80–93. doi:10.1002/jcb.10475. PMID 12682910.
- Xin H, Curry J, Johnstone RW; et al. (2003). "Role of IFI 16, a member of the interferon-inducible p200-protein family, in prostate epithelial cellular senescence". Oncogene. 22 (31): 4831–40. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206754. PMID 12894224.
- Kwak JC, Ongusaha PP, Ouchi T, Lee SW (2003). "IFI16 as a negative regulator in the regulation of p53 and p21(Waf1)". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (42): 40899–904. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308012200. PMID 12925527.
- Aglipay JA, Lee SW, Okada S; et al. (2004). "A member of the Pyrin family, IFI16, is a novel BRCA1-associated protein involved in the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway". Oncogene. 22 (55): 8931–8. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207057. PMID 14654789.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T; et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Raffaella R, Gioia D, De Andrea M; et al. (2004). "The interferon-inducible IFI16 gene inhibits tube morphogenesis and proliferation of primary, but not HPV16 E6/E7-immortalized human endothelial cells". Exp. Cell Res. 293 (2): 331–45. PMID 14729471.
- Fujiuchi N, Aglipay JA, Ohtsuka T; et al. (2004). "Requirement of IFI16 for the maximal activation of p53 induced by ionizing radiation". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (19): 20339–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400344200. PMID 14990579.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D; et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMID 15302935.
External links
- IFI16+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.