GTF3C2
| General transcription factor IIIC, polypeptide 2, beta 110kDa | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | GTF3C2 ; KIAA0011; TFIIIC-BETA; TFIIIC110 | ||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 37490 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
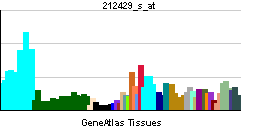
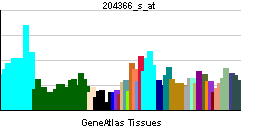
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
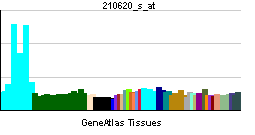 | |||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
General transcription factor IIIC, polypeptide 2, beta 110kDa, also known as GTF3C2, is a human gene.[1]
References
Further reading
- Jang KL, Collins MK, Latchman DS (1992). "The human immunodeficiency virus tat protein increases the transcription of human Alu repeated sequences by increasing the activity of the cellular transcription factor TFIIIC". J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 5 (11): 1142–7. PMID 1403646.
- Nomura N, Miyajima N, Sazuka T; et al. (1995). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. I. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0001-KIAA0040) deduced by analysis of randomly sampled cDNA clones from human immature myeloid cell line KG-1". DNA Res. 1 (1): 27–35. PMID 7584026.
- Nomura N, Miyajima N, Sazuka T; et al. (1995). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. I. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0001-KIAA0040) deduced by analysis of randomly sampled cDNA clones from human immature myeloid cell line KG-1 (supplement)". DNA Res. 1 (1): 47–56. PMID 7584028.
- Sinn E, Wang Z, Kovelman R, Roeder RG (1995). "Cloning and characterization of a TFIIIC2 subunit (TFIIIC beta) whose presence correlates with activation of RNA polymerase III-mediated transcription by adenovirus E1A expression and serum factors". Genes Dev. 9 (6): 675–85. PMID 7729686.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY; et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC; et al. (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. PMID 9110174.
- Chu WM, Wang Z, Roeder RG, Schmid CW (1997). "RNA polymerase III transcription repressed by Rb through its interactions with TFIIIB and TFIIIC2". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (23): 14755–61. PMID 9169441.
- Oettel S, Härtel F, Kober I; et al. (1997). "Human transcription factors IIIC2 , IIIC1 and a novel component IIIC0 fulfil different aspects of DNA binding to various pol III genes". Nucleic Acids Res. 25 (12): 2440–7. PMID 9171097.
- Wang Z, Roeder RG (1998). "DNA topoisomerase I and PC4 can interact with human TFIIIC to promote both accurate termination and transcription reinitiation by RNA polymerase III". Mol. Cell. 1 (5): 749–57. PMID 9660958.
- Hsieh YJ, Wang Z, Kovelman R, Roeder RG (1999). "Cloning and characterization of two evolutionarily conserved subunits (TFIIIC102 and TFIIIC63) of human TFIIIC and their involvement in functional interactions with TFIIIB and RNA polymerase III". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (7): 4944–52. PMID 10373544.
- Hsieh YJ, Kundu TK, Wang Z; et al. (1999). "The TFIIIC90 subunit of TFIIIC interacts with multiple components of the RNA polymerase III machinery and contains a histone-specific acetyltransferase activity". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (11): 7697–704. PMID 10523658.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Suzuki Y, Yamashita R, Shirota M; et al. (2004). "Sequence comparison of human and mouse genes reveals a homologous block structure in the promoter regions". Genome Res. 14 (9): 1711–8. doi:10.1101/gr.2435604. PMID 15342556.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA; et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T; et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Innes F, Ramsbottom B, White RJ (2006). "A test of the model that RNA polymerase III transcription is regulated by selective induction of the 110 kDa subunit of TFIIIC". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (11): 3399–407. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl432. PMID 16822860.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA; et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F; et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Dumay-Odelot H, Marck C, Durrieu-Gaillard S; et al. (2007). "Identification, molecular cloning, and characterization of the sixth subunit of human transcription factor TFIIIC". J. Biol. Chem. 282 (23): 17179–89. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611542200. PMID 17409385.
External links
- GTF3C2+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.