Constipation: Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
DiseasesDB = 3080 | | DiseasesDB = 3080 | | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Constipation}} | ||
{{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{MUT}} | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{MUT}} | ||
Revision as of 18:37, 4 September 2012
For patient information click here
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
|
Constipation Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Constipation On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Constipation |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: M.Umer Tariq [2]
Overview
Constipation or irregularity, is a condition of the digestive system where a person (or animal) experiences hard feces that are difficult to egest. It may be extremely painful, and in severe cases (fecal impaction) lead to symptoms of bowel obstruction. The term obstipation is used for severe constipation. Causes of constipation may be dietary, hormonal, anatomical, a side effect of medications (e.g. some painkillers), or an illness or disorder. Treatments consist of changes in dietary and exercise habits, the use of laxatives, and other medical interventions depending on the underlying cause.
Signs and symptoms
-
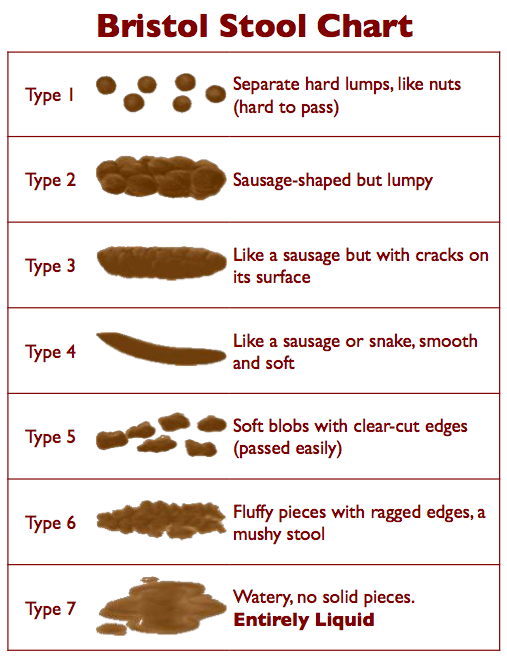
Types 1 and 2 on the Bristol Stool Chart indicate constipation
Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints. It varies greatly between different people, as each person's bowel movements differ. Rate of defecation is not in itself a problem, as infrequent defecation without problems is not abnormal. Constipation is most common in children and older people, and affects women more than men. In children, constipation can lead to soiling (enuresis and encopresis). [1]
In common constipation, the stool is hard and difficult and painful to pass. Usually, there is an infrequent urge to void. Straining to pass stool may cause hemorrhoids and anal fissures, which are themselves painful. In later stages of constipation, the abdomen may become distended and diffusely tender and crampy, occasionally with enhanced bowel sounds.
The definition of constipation includes the following:[2]
- infrequent bowel movements (typically 3 times or less per week)
- difficulty during defecation (straining during more than 25% of bowel movements or a subjective sensation of hard stools), or
- the sensation of incomplete bowel evacuation.
Severe cases ("fecal impaction") may feature symptoms of bowel obstruction (vomiting, very tender abdomen) and "paradoxical diarrhea", where soft stool from the small intestine bypasses the impacted matter in the colon.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is essentially made from the patient's description of the symptoms. Bowel movements that are difficult to pass, very firm, or made up of small rabbit-like pellets qualify as constipation, even if they occur every day. Other symptoms related to constipation can include bloating, distention, abdominal pain, or a sense of incomplete emptying.
Inquiring about dietary habits may reveal a low intake of dietary fiber or inadequate amounts of fluids. Constipation as a result of poor ambulation or immobility should be considered in the elderly. Constipation may arise as a side effect of medications (especially antidepressants and opiates). Rarely, other symptoms suggestive of hypothyroidism may be elicited.
During physical examination, scybala (manually palpable lumps of stool) may be detected on palpation of the abdomen. Rectal examination gives an impression of the anal sphincter tone and whether the lower rectum contains any feces or not; if so, then suppositories or enemas may be considered. Otherwise, oral medication may be required. Rectal examination also gives information on the consistency of the stool, presence of hemorrhoids, admixture of blood and whether any tumors or abnormalities are present.
X-rays of the abdomen, generally only performed on hospitalized patients or if bowel obstruction is suspected, may reveal impacted fecal matter in the colon, and confirm or rule out other causes of similar symptoms.
Chronic constipation (symptoms present for more than 3 months at least 3 days per month) associated with abdominal discomfort is often diagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) when no obvious cause is found. Physicians caring for patients with chronic constipation are advised to rule out obvious causes through normal testing.[3]
Causes
The main causes of constipation include:
- Hardening of the feces
- Improper mastication (chewing) of food
- Insufficient intake of dietary fiber
- Dehydration from any cause or inadequate fluid intake
- Medication, e.g. diuretics and those containing iron, calcium, aluminium
- Paralysis or slowed transit, where peristaltic action is diminished or absent, so that feces are not moved along
- Hypothyroidism (slow-acting thyroid gland)
- Hypokalemia
- Injured anal sphincter (patulous anus)
- Medications, such as loperamide, opioids (e.g. codeine & morphine) and certain tricyclic antidepressants
- Severe illness due to other causes
- Acute porphyria (a rare inherited condition)
- Lead poisoning
- Dyschezia (usually the result of suppressing defecation)
- Constriction, where part of the intestine or rectum is narrowed or blocked, not allowing feces to pass
- Stenosis (Strictures)
- Diverticula
- Tumors, either of the bowel or surrounding tissues
- Retained foreign body or a bezoar
- Psychosomatic constipation, based on anxiety or unfamiliarity with surroundings.
- Functional constipation
- Constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome, characterized by a combination of constipation and abdominal discomfort and/or pain[4]
- Smoking cessation (tobacco smoking has a laxative effect)[5]
- Abdominal surgery, other types of surgery, childbirth
Complete Differential Diagnosis of the Causes of Constipation
(In alphabetical order)
Complete Differential Diagnosis of the Causes of Constipation
(By organ system)
Physical Examination
- Complete physical examination including thyroid examination
Abdomen
- Examination of abdomen:
- Palpate for masses
- Surgical scars
- Hernias
- Hepatosoplenomegaly
- Examination results are usually normal
Other
- Complete rectal examination with attention paid to:
- Presence of stool
- Masses
- Fistulas
- Hemorrhoids
- Abscesses
- Fissures
- Squeezing and resting of sphincter tone
- Palpable relaxation of anal tone and perineal descents
Laboratory Findings
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) / creatinine
- Phosphate
- Glucose
- Liver function tests (LFTs)
- Fecal occult blood test
- Thyroid function tests
- Calcium
Echocardiography or Ultrasound
- Ultrasound may be used to detect tumors, fibroids, ovarian cysts or pregnancy
Other Diagnostic Studies
- Colonoscopy for patients:
- Greater than 50 years old
- Present with constipation with no apparent cause
- Presence of blood in the stool
- Sigmoidoscopy for all other patients
- To rule out ova and parasites, a stool examination should be considered
Treatment
In people without medical problems, the main intervention is to increase the intake of fluids (preferably water) and dietary fiber. The latter may be achieved by consuming more vegetables and fruit and whole meal bread, and by adding linseeds to one's diet. The routine non-medical use of laxatives is to be discouraged as this may result in bowel action becoming dependent upon their use. Enemas can be used to provide a form of mechanical stimulation.
In alternative and traditional medicine, colonic irrigation, enemas, exercise, diet and herbs are used to treat constipation.
Laxatives
Laxatives may be necessary in people in whom dietary intervention is not effective or is inappropriate. Most laxatives can be safely used long-term, although some are associated with cramping and bloatedness and can cause the phenomenon of melanosis coli.
Physical intervention
Constipation that resists all the above measures requires physical intervention. Manual disimpaction (the physical removal of impacted stool) is done by patients who have lost control of their bowels secondary to spinal injuries. Manual disimpaction is also used by physicians and nurses to relieve rectal impactions. Finally, manual disimpaction can occasionally be done under sedation or a general anesthetic—this avoids pain and loosens the anal sphincter.
Many of the products are widely available over-the-counter. Enemas and clysters are a remedy occasionally used for hospitalized patients in whom the constipation has proven to be severe, dangerous in other ways, or resistant to laxatives. Sorbitol, glycerin and arachis oil suppositories can be used. Severe cases may require phosphate solutions introduced as enemas.
Prevention
Constipation is usually easier to prevent than to treat. The relief of constipation with osmotic agents, i.e. lactulose, polyethylene glycol (PEG), or magnesium salts, should immediately be followed with prevention using increased fiber (fruits, vegetables, and grains) and a nightly decreasing dose of osmotic laxative. With continuing narcotic use, for instance, nightly doses of osmotic agents can be given indefinitely (without harm) to cause a daily bowel movement.
Recent controlled studies have questioned the role of physical exercise in the prevention and management of chronic constipation, while exercise is often recommended by published materials on the subject.
In various conditions (such as the use of codeine or morphine), combinations of hydrating (e.g. lactulose or glycols), bulk-forming (e.g. psyllium) and stimulant agents may be necessary to prevent constipation.
Epidemiology
Depending on the definition employed, constipation occurs in 2% of the population; it is more common in women, the elderly and children [6]
In animals
Hibernating animals can experience tappens that are usually expelled in the spring. For example, bears eat many foods that create a "rectal plug" before hibernation.
See also
References
- ↑ NHS direct page on constipation.
- ↑ Emedicine, "constipation".
- ↑ Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC (2006). "Functional bowel disorders". Gastroenterology. 130 (5): 1480–91. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.061. PMID 16678561.
- ↑ Caldarella MP, Milano A, Laterza F; et al. (2005). "Visceral sensitivity and symptoms in patients with constipation- or diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): effect of a low-fat intraduodenal infusion". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 100 (2): 383–9. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.40100.x. PMID 15667496.
- ↑ "Nicotine withdrawal symptoms:Constipation". helpwithsmoking.com. 2005. Retrieved 2007-06-29.
- ↑ Sonnenberg A, Koch TR (1989). "Epidemiology of constipation in the United States". Dis. Colon Rectum. 32 (1): 1–8. PMID 2910654.