Sandbox:Sahar: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Replaced content with "__NOTOC__ ==Images== ===Example #1=== The patient presented with S.O.B. one year after hysterectomy for a leiomyomatous uterus. <div align="left"> <gallery heights="175"...") Tag: Replaced |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Images== | ==Images== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! rowspan="2" |Organ System Involvement | |||
!Differential Diagnosis | |||
!Causes | |||
!Clinical Features | |||
!Laboratory Findings | |||
!Gold Standard Test | |||
!Therapy | |||
|- | |||
!'''Secondary (AA) Amyloidosis''' | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
! | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="8" |Nephrotic Syndrome and Real Failure | |||
|Primary (AL) Amyloidosis | |||
| | |||
* [[Monoclonal]] [[plasma cell]] proliferation | |||
* Extracellular [[amyloid]] [[fibril]] deposition | |||
| | |||
* [[Anasarca]] | |||
* [[Bleeding tendency]] | |||
* Swelling of [[lower limbs]] | |||
* Frothy [[urine]] | |||
* [[Chest pain]] | |||
* [[Numbness]] or [[tingling]] | |||
* [[Early satiety]] | |||
* [[Joint pains]] | |||
* [[Macroglossia|Enlarged tongue]] | |||
* [[Taste loss]] | |||
* [[Hoarseness|Hoarseness of voice]] | |||
* [[Alopecia|Hair loss]] | |||
| | |||
* Increased [[erythrocyte sedimentation rate]] ([[ESR]]) | |||
* Increased [[Alanine aminotransferase|alanine aminotrasnferase]] ([[Alanine transaminase|ALT]]) and [[Aspartate aminotransferase|aspartate aminotrasnferase]] ([[Aspartate transaminase|AST]]) | |||
* Increased [[Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and T (cTnT)|cardiac troponins]] | |||
* Increased [[brain natriuretic peptide]] ([[BNP]]) | |||
* Increased [[blood urea nitrogen]] ([[BUN]]) and [[creatinine]] | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* Urinary [[Hyaline cast|hyaline]] and fatty casts | |||
* [[Hypercholesterolemia]] | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** Diffuse glomerular deposition of amorphous [[hyaline]] material (nodular pattern - 8 to15 nm in diameter), in [[mesangium]] (weakly staining with [[Periodic acid-Schiff stain|periodic acid-Schiff]] ([[Periodic acid-Schiff stain|PAS]]) | |||
| | |||
* [[Melphalan]]-[[prednisone]]/[[dexamethasone]] | |||
* [[Dexamethasone]] plus [[Cyclophosphamide]]-[[thalidomide]] | |||
* [[Stem cell transplantation]] | |||
* [[Kidney transplantation]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Diabetic nephropathy|Diabetic Nephropathy]] | |||
| | |||
* Hyperfiltration | |||
* Constriction of [[efferent arteriole]] | |||
* [[Microalbuminuria]] | |||
* [[Mesangial cell|Mesangial]] proliferation | |||
| | |||
* [[Nocturia]] | |||
* [[Fatigue]] | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
* [[Peripheral edema]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Hyperglycemia]] (random plasma glucose ≥200 mg/dL) | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* [[Glucosuria]] | |||
* [[Glycosylated hemoglobin|HbA1C]] ≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol).<br /> | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** [[Periodic acid-Schiff stain|PAS]] positive [[Kimmelstiel-Wilson syndrome|Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules]] | |||
** [[Glomerulosclerosis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[ACE inhibitor|ACE inhibitors]] | |||
* [[Angiotensin receptor blockers]] | |||
* [[Glycemic]] control | |||
|- | |||
|[[Minimal change disease|Minimal Change Disease]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Upper respiratory tract infection]] | |||
* [[Allergy]] to bee sting | |||
* [[Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug|NSAID]] | |||
* [[Gold]] | |||
* [[Penicillamine]] | |||
* [[Ampicillin]] | |||
* [[Mercury (element)|Mercury]] | |||
* [[Hodgkin's lymphoma|Hodgkin's]] and [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma|non-Hodgkin's lymphoma]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Peripheral edema]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Peripheral edema]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Hyperlipidemia]] | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* [[Microscopic hematuria]] | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** Fused [[podocytes]]/effacement | |||
| | |||
* [[Prednisone]] with taper | |||
* [[ACE inhibitor|ACE inhibitors]] | |||
* [[Angiotensin receptor blockers]] | |||
* Salt restriction | |||
|- | |||
|[[Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis|Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[HIV]] | |||
* [[Parvovirus B19]] | |||
* [[Cytomegalovirus]] | |||
* [[Heroin]] | |||
* [[Interferon alpha]] | |||
* [[Lithium]] | |||
* [[Pamidronate]]/aledronate | |||
* [[Anabolic steroids]] | |||
* [[Diabetes mellitus]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Obesity]] | |||
* [[Congenital heart disease cyanotic|Cyanotic congenital heart disease]] | |||
* [[Sickle cell anemia]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Peripheral edema]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Peripheral edema]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Hyperlipidemia]] | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* [[Microscopic hematuria]] | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** [[Podocytes|Podocyte]] foot process effacement | |||
** [[Capillary]] lumen abolished by the segmental increase in matrix<br /> | |||
| | |||
* [[Prednisone]] | |||
* [[Calcineurin inhibitor|Calcineurin inhibitors]] ([[Cyclosporine|Cyclosporin]], [[tacrolimus]]) | |||
* [[Rituximab]] | |||
* [[Cyclophosphamide]]/[[chlorambucil]] | |||
* [[Mycophenolate|Mycophenolate motefil]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Fabry's disease|Fabry's Disease]] | |||
| | |||
* Deficient alpha galactosidase A | |||
| | |||
* [[Abdominal pain]] | |||
* [[Arthralgia]] | |||
* [[Febrile]] episodes | |||
* [[Angiokeratomas]] | |||
* Burning pain and tingling ([[Peripheral neuropathy|peripheral neuropathy)]] | |||
* [[Hypohidrosis]] | |||
* [[X-linked recessive]] inheritance | |||
| | |||
* Deficient alpha galactosidase A | |||
* Increased ceramide trihexoside ([[Globotriaosylceramide 3-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase|globotriaosylceramide]]) | |||
| | |||
* Alpha-galactosidase A activity | |||
* [[GLA|GLA gene]] analysis for [[Heterozygote|heterozygotes]] | |||
| | |||
* Enzyme replacement therapy | |||
* [[ACE inhibitor|ACE inhibitors]] | |||
* [[Gabapentin]], [[carbamazepine]] | |||
* [[Migalastat]] | |||
|- | |||
|Light Chain Deposition Disease | |||
| | |||
* [[Multiple myeloma]] | |||
* [[Waldenström's macroglobulinemia]] | |||
* [[Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Asymptomatic]] | |||
* [[Fatigue]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
* [[Dyspnea]] | |||
* [[Peripheral edema]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* [[Portal hypertension]] | |||
* Increased [[Alanine transaminase|ALT]], [[Aspartate transaminase|AST]] | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** Non-amyloid granules | |||
| | |||
* [[Bortezomib]] | |||
* Autologous [[stem cell transplantation]] | |||
* Immunomodulatory drugs | |||
* [[Kidney transplantation|Kidney transplant]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Membranous glomerulonephritis|Membranous Glomerulonephritis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Hepatitis B]] and [[Hepatitis C|C]] | |||
* [[HIV]] | |||
* [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin`s lymphoma]] | |||
* [[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]] | |||
* [[Hodgkin lymphoma|Hodgkin`s lymphoma]] | |||
* Solid tissue tumors | |||
* [[Schistosomiasis]] | |||
* [[Leprosy]] | |||
* [[Hydatid disease]] | |||
* [[Loaiasis]] (filaria) | |||
* [[Malaria|Quartan malaria]] | |||
* [[Systemic lupus erythematosis]] ([[SLE]])<br /> | |||
| | |||
* [[Headache]] | |||
* [[Edema]] affecting any area of the body | |||
* Foamy appearance of urine | |||
* [[Weight gain]] | |||
* [[Poor appetite]] | |||
* [[Nocturia]] | |||
* [[Fatigue]] | |||
* [[Hematuria]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Hyperlipidemia]] | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* Microscopic or gross hematuria | |||
* [[Hypoalbuminemia]] | |||
* [[Antinuclear antibodies|ANA]] and [[Anti-dsDNA antibody|anti-dsDNA]] positivity | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** [[Immunoglobulin G|IgG]] and [[C3 (complement)|C3]] deposits with thickened [[basement membrane]] with spikes and vacuolization | |||
** [[Glomerulosclerosis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Prednisone]] | |||
* [[Methylprednisolone]] with [[cyclophosphamide]] | |||
* [[Tacrolimus]] with a six-month taper | |||
* [[Rituximab]] | |||
|- | |||
|Fibrillary-Immunotactoid Glomerulopathy | |||
| | |||
* [[Idiopathic]] | |||
* [[Hepatitis C]] | |||
| | |||
* Microscopic or [[Hematuria|gross hematuria]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Proteinuria]] | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* Increased [[blood urea nitrogen]] ([[Blood urea nitrogen|BUN]]) and [[creatinine]] | |||
| | |||
* Biopsy: | |||
** Polycloncal [[Immunoglobulin G|IgG]] deposits | |||
** Infiltration of glomerular structures by amorphous acellular material (nonbranching fibrils 12-24nm in diameter) | |||
** Ig heavy-chain and one light-chain subclass | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
!Organ System Involvement | |||
!Differential Diagnosis | |||
!Causes | |||
!Clinical Features | |||
!Laboratory Findings | |||
!Gold Standard Test | |||
!Therapy | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="6" |''Polyneuropathy'' | |||
|'''[[POEMS syndrome]] (Demyelinating)''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Monoclonal]] [[plasma cell]] proliferation | |||
* [[Cytokine]] storm ([[IL-1]], [[Interleukin 6|IL-6]], [[Interleukin 12|IL-12]], [[TNF alpha]], [[VEGF]]) | |||
| | |||
* Symmetrical, ascending chronic progressive [[polyneuropathy]] with both [[Sensory system|sensory]] (pin-prick and vibration) and [[Motor skill|motor]] disability ([[Motor skill|motor]] > [[sensory]]) | |||
* Generalized/extermity [[pain]] | |||
* [[Areflexia]] | |||
| | |||
* Increased number of [[Platelet|thrombocytes]] | |||
* Increased number of [[Red blood cell|erythrocytes]] | |||
* Elevated [[Cerebrospinal fluid|cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)]] [[protein]] content | |||
* Increased number of [[White blood cells|leukocytes]] | |||
* High levels of [[Immunoglobulin G|IgG]] lambda or [[Immunoglobulin A|IgA]] lambda [[M protein|M-protein]] in the [[serum]] | |||
* Increased number of [[Plasma cell|plasma cells]] in the [[bone marrow]] | |||
* Increased serum [[Vascular endothelial growth factor|VEGF]] level | |||
* Elevated levels of antitiroglobulin [[antibody]] and antithyroid peroxydase [[antibody]] | |||
| | |||
* [[POEMS syndrome diagnostic criteria|International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) clinical and laboratory diagnostic criteria]] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Metabolic syndrome|Metabolic Syndrome]] (Axonal pathology)''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| | |||
* Symmetric sensorimotor distal polyneuropathy | |||
* Asymmetric proximal neuropathy | |||
* [[Oculomotor nerve palsy|3rd nerve palsy]] | |||
* [[Carpal tunnel syndrome|Carpel tunnel syndrome]] | |||
* [[Autonomic neuropathy]] | |||
* "Glove and stocking" type pain | |||
* [[Muscle wasting]] | |||
* [[Hammer toe|Hammer toes]] | |||
* [[Polyuria]] | |||
* [[Polydipsia]] | |||
| | |||
* Uncontrolled [[hyperglycemia]] | |||
* Slowed [[Nerve conduction study|nerve conduction]] | |||
* [[Small fiber peripheral neuropathy|Small fiber dysfunction]] | |||
* [[Monofilament|Monofilament testing]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Fasting blood sugar|Fasting blood sugar level]] greater than equal to 126 mg/dl on 2 separate occasions | |||
| | |||
* [[Diabetes mellitus medical therapy|Anti-diabetic therapy]] | |||
* [[Gabapentin]] | |||
* [[Carbamazepine]] | |||
* [[Foot care]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Vitamin deficiencies|Vitamin Deficiencies]] (Axonal Pathology)''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Vitamin B12 deficiency]] (Decreased [[S-Adenosyl methionine|S-adenosyl methionine]]) | |||
* [[Thiamine deficiency|Vitamin B1 deficiency]] | |||
| | |||
* Primarily [[sensory]] deficits | |||
* Vibration and [[proprioception]] affected | |||
* [[Gait abnormality|Gait abnormalities]] | |||
* [[Cognitive impairment]] | |||
* [[Irritability]] | |||
* [[Glossitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Anemia]] ([[Megaloblastic Anemias|megaloblastic]] in case of [[Vitamin B12 deficiency|B12 deficiency]]) | |||
* Decreased [[serum]] [[Vitamin B12]] levels (< 200 pg/ml) | |||
* [[Methylmalonic acidemia|Elevated methylmalonic acid]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Serum]] [[Vitamin B12]] levels | |||
* [[Methylmalonic acid|Methylmalonic acid levels]] | |||
* [[Intrinsic factor|Intrinsic factor antibodies]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Vitamin B12]] supplement ([[parenteral]]) | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Guillain-Barré syndrome|Guillain-Barre Syndrome]] (Demyelinating)''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Anti-ganglioside antibodies|Anti-ganglioside]] and anti-[[myelin]] antibodies | |||
* [[Viral]] infections: | |||
** [[Epstein Barr virus]] | |||
** [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]] | |||
** [[Cytomegalovirus]] | |||
** [[Varicella Zoster Virus|Varicella Zoster virus]] | |||
* [[Bacterial]] infections: | |||
** [[Campylobacter]] infection | |||
** [[Mycoplasma pneumoniae]] | |||
| | |||
* Rapid onset and quick progression | |||
* Progression stops after 2-3 weeks | |||
* Bilateral ascending [[Paraesthesia|paraesthesias]] and [[paralysis]] (generalized) | |||
* [[Muscle weakness|Weakness]] | |||
* [[Ataxia]] | |||
* [[Areflexia]] | |||
* No fever | |||
* 4 sub-types: | |||
** [[Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy]] | |||
** [[Acute motor axonal neuropathy]] | |||
** Acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy | |||
** [[Miller Fisher syndrome]] | |||
| | |||
* Delayed F waves | |||
| | |||
* Clinical diagnostic criteria (progressive weakness of more than two [[limbs]], [[areflexia]], and progression for no more than four weeks) | |||
| | |||
* [[Intravenous]] [[immunoglobulins]] | |||
* [[Plasma]] exchange | |||
* [[Mechanical ventilation|Respiratory support]] | |||
* [[DVT]]/[[PE]] [[prevention]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy|Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy]] (CIDP) (Mixed axonal and demyelinatiing)''' | |||
| | |||
* Abnormal [[immune response]] (both [[Immunoglobulin G|IgG]] based [[Humoral immunity|humoral]] and [[Cell mediated immunity|T-Cell mediated]]) response to unknown [[antigen]] (possible culprits include [[myelin]] [[proteins]] P0, P2 and PMP22) | |||
| | |||
* Slow onset and gradual progression | |||
* [[Relapse|Relapsing]] and remitting course | |||
* Symmetrical [[Proximal muscle weakness|proximal]] and [[Distal muscle weakness|distal motor]] and [[Sensory system|sensory weakness]] (legs>arms) | |||
* [[Foot drop]] | |||
* [[Numbness]], [[tingling]] and [[pain]] | |||
* [[Areflexia]] | |||
| | |||
* Elevated [[CSF]] [[protein]] ([[oligoclonal bands]] with normal [[White blood cells|WBCs]]) | |||
* Slowed [[Nerve conduction study|motor nerve conduction velocities]] | |||
* Prolonged distal [[Motor skill|motor]] latencies (period between F wave and initial stimulation) | |||
* Delayed F wave latencies (recorded from the [[feet]], hence called "F" waves) | |||
* [[MRI]] contrast enhancement and enlargement of [[Vertebra|T2]] [[spinal segments]] | |||
| | |||
* EFNS/PNS criteria | |||
* Koski criteria | |||
| | |||
* [[Corticosteroids]] | |||
* [[Intravenous immunoglobulin]] ([[IVIG]]) | |||
* [[Immunosupressive drug|Immunosupressants]] ([[Alemtuzumab|Alemtuzemab]] [[Azathioprine]] [[Cyclophosphamide]] [[Cyclosporine|Cyclosporin]] [[Etanercept]] [[Interferon-alpha]]) | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Multifocal motor neuropathy|Multifocal Motor Neuropathy]]''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Immune response|Abnormal immune response]] ([[Anti-ganglioside antibodies|Anti ganglioside]] [[Anti-ganglioside antibodies|GM-1]] [[IgM]] [[antibodies]]) | |||
| | |||
* Progressive, asymmetric, distal and upper [[Limb (anatomy)|limb]] predominant weakness | |||
* No significant [[sensory]] abnormalities | |||
* [[Areflexia]] | |||
| | |||
* Elevated [[CSF]] [[protein]] | |||
| | |||
* Clinical criteria (EFNS/PNS): | |||
** Slowly progressive or step-wise progressive, focal, asymmetric [[limb]] weakness; i.e., [[Motor skill|motor]] involvement in the [[motor nerve]] distribution of at least two nerves for > 1 month. | |||
** No objective [[Sensory system|sensory]] abnormalities except for minor vibration sense abnormalities in the [[lower limbs]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Intravenous immunoglobulin|Intravenous immunoglobulins]] | |||
* [[Cyclophosphamide]] | |||
* [[Rituximab]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''Organ System Involvement''' | |||
|'''Differential Diagnosis''' | |||
|'''Causes''' | |||
|'''Features''' | |||
|'''Laboratory Findings''' | |||
|'''Gold Standard Test''' | |||
|'''Therapy''' | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="7" |''Organomegaly (Hepatosplenomegaly and Lymphadenopathy)'' | |||
|'''[[Malaria]]''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Plasmodium falciparum]] | |||
* [[Plasmodium ovale|P. ovale]] | |||
* [[P. malariae]] | |||
* [[Plasmodium knowlesi|P. knowlesi]] | |||
| | |||
* Tertian ([[Plasmodium vivax|vivax]], [[Plasmodium ovale|ovale]], [[Plasmodium falciparum|falciparum]]), quartan (malariae), quotidian fever ([[Plasmodium knowlesi|knowlesi]]) | |||
* [[Vector]] is female [[Anopheles]] mosquito | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Jaundice]] | |||
* [[Icterus (medicine)|Icterus]] | |||
* [[Tachycardia]] | |||
* [[Tachypnea]] | |||
* [[Productive cough]] | |||
* [[Hematuria]] | |||
* [[Altered mental status]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Microcytic anemia]] | |||
* [[Malaria differential diagnosis|Thick and thin blood films]] ([[Giemsa stain|Giemsa staining]]) | |||
* Rapid diagnostic test ([[antigen]] detection | |||
* [[Polymerase chain reaction]] ([[Polymerase chain reaction|PCR]]) | |||
* [[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay]] ([[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|ELISA]]) | |||
| | |||
* [[Malaria differential diagnosis|Thick and thin films]] | |||
| | |||
* Non-[[Plasmodium falciparum|falciparum]] species: | |||
** [[Chloroquine]] (in susceptible) | |||
** [[Artemisinin]] plus [[Mefloquine|mefloquin]] or [[lumefantrine]] (in [[chloroquine]] resistant) | |||
* [[Plasmodium falciparum|Falciparum]] species: | |||
** [[Chloroquine]] (in susceptible) | |||
** [[Artemether]] plus [[lumefantrine]] (in [[Chloroquine|chloroquin]] resistant) OR | |||
** [[Artesunate]] plus [[Mefloquine|mefloquin]] OR | |||
** [[Artesunate]] plus [[Sulfadoxine|sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine]] | |||
** [[Atovaquone-Proguanil|Atovaquone plus proguanil]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Kala-azar]]''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Leishmaniasis|Leshmania donovani]] | |||
* L. infantum | |||
* L. chagasi | |||
| | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* Vector is [[sandfly]] | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Hyperpigmentation]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
* [[Direct agglutination test]] (DAT) | |||
* rk39 dipstick | |||
* [[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|ELISA]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Splenic]] aspiration | |||
| | |||
* [[Liposomal amphotericin B]] | |||
* [[Sodium stibogluconate]] | |||
* [[Pentamidine]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Hepatitis|Infective Hepatitis]]''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Hepatitis A virus|Hepatitis A virus (HAV)]] | |||
* [[HBV]] | |||
* [[Hepatitis C|HCV]] | |||
* [[Hepatitis D|HDV]] (co-infection with [[HBV]]) | |||
* [[Hepatitis E|HEV]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* Transmitted via [[fecal-oral route]] ([[Hepatitis A|HAV]], [[Hepatitis B virus|HBV]], [[HDV]], [[HEV]]), infected sera ([[HCV]]), [[sexual contact]] with infected individuals | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] (may become shrunken in cases of [[cirrhosis]] due to chronic infection) | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Jaundice]] | |||
* [[Palmar erythema]] | |||
* [[Spider angiomata]] | |||
* [[Gynecomastia]] | |||
* [[Arthritis-dermatitis syndrome]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Antigen]] and [[antibody]] detection | |||
* Total and direct [[bilirubin]] (increased) | |||
* Severe disease is often associated with persistent [[bilirubin]] levels >340 mmol/L | |||
* [[ALT]] and [[AST]] (increased) | |||
* [[Alkaline phosphatase]] (normal or mildly elevated) | |||
* [[Prothrombin time]] (prolonged from synthetic defect, caused by hepatocellular [[necrosis]]) | |||
* [[Total protein]] (decreased) | |||
* [[Globulin]] (mildly elevated) | |||
* Initial [[lymphopenia]] and [[neutropenia]], followed by relative [[lymphocytosis]] | |||
* [[Anemia|Low hemoglobin]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Antigen]] and [[antibody]] detection | |||
| | |||
* [[Interferon]] ([[IFN]]) | |||
* [[Antivirals|Nucleoside analogs]] | |||
* [[Antivirals|Nucleotide analogs]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Chronic myelogenous leukemia|Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia]] (CML)''' | |||
| | |||
* [[Philadelphia chromosome|BCR/ABL gene]] fusion product due to [[Chromosomal translocation|translocation]] [[mutation]] [[Philadelphia chromosome|t(9;22)]](q34;q11) | |||
| | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Bruises]] | |||
* [[Petechiae]] | |||
* [[Ulcers]] | |||
* [[Vesicles]] | |||
* [[Malaise]] | |||
* [[Early satiety]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] (median of 100,000/µL) with a [[left shift]] | |||
* [[Thrombocytosis]] | |||
* [[Blast|Blasts]] usually <2% | |||
* Absolute [[basophilia]] | |||
* Absolute [[eosinophilia]] | |||
* [[Monocytosis]] | |||
* [[Thrombocytosis]] | |||
* [[Thrombocytopenia]] suggests an alternative diagnosis or the presence of advanced stage | |||
* Elevated [[uric acid]] | |||
* Elevated [[histamine]] levels | |||
| | |||
* [[Fluorescence in situ hybridization|Fluoroscent insitu hybridization (FISH)]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Imatinib]] | |||
* [[Dasatinib]] | |||
* [[Nilotinib]] | |||
* [[Bosutinib]] | |||
* [[Ponatinib]] | |||
* [[Cytarabine]] | |||
* [[Cytarabine|HDAC]] (high-dose [[cytarabine]]) | |||
* [[Hydroxyurea]] | |||
* [[Busulfan]] | |||
* [[Busulfex]] | |||
* [[Stem cell transplantation]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Lymphoma]]''' | |||
| | |||
* Various causes based on type: | |||
** [[Hodgkin's lymphoma|Hodgkin's]] | |||
** [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin's]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | |||
* [[Night sweats]], constant [[fatigue]] | |||
* Purplish scaly rash in cases of [[cutaneous lymphoma]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|Elevated ESR]] | |||
* [[C-reactive protein|Increased CRP]] | |||
* [[Lactate dehydrogenase|Increased LDH]] | |||
* [[Anemia of chronic disease]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Lymph node biopsy]] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Primary amyloidosis|Primary (AL) Amyloidosis]]''' | |||
| | |||
* Aggregation and deposition of [[immunoglobulin light chains]] that are usually produced by [[plasma cell]] clones | |||
| | |||
* [[Nephrotic syndrome]] ([[peripheral edema]]) | |||
* [[Restrictive cardiomyopathy]] ([[fatigue]], [[dyspnea]], [[syncope]]) | |||
* [[Peripheral neuropathy]] ([[numbness]], [[tingling]]) | |||
* [[Hepatomegaly]] with elevated [[liver enzymes]] | |||
* [[Macroglossia]] | |||
* [[Purpura]] | |||
* [[Bleeding diathesis]] | |||
| | |||
* Typical green birefringence under polarized light after Congo red staining (appears in red under normal light) | |||
| | |||
* Congo red staining | |||
| | |||
* Melphalan-prednisone/dexamethasone | |||
* Dexamethasone plus Cyclophosphamide-thalidomide | |||
* Stem cell transplantation | |||
|- | |||
|'''[[Gaucher's disease|Gaucher's Disease]]''' | |||
| | |||
* [[GBA (gene)|GBA gene]] [[mutation]] | |||
* Aberrant metabolism of [[glucocerebroside]] ([[lipid]]) | |||
| | |||
* [[Hydrops fetalis]] | |||
* Dry, scaly skin ([[ichthyosis]]) or other [[skin]] abnormalities | |||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | |||
* Distinctive facial features | |||
* [[Neurological disorder|Neurological problems]] | |||
* [[Gall stones]] | |||
* [[Growth retardation]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Hypocholesterolemia]] | |||
* [[Splenic]] nodules | |||
* [[Cytopenias]] (especially [[thrombocytopenia]]) | |||
* Increased [[ferritin]] levels | |||
* Increased tartarate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) levels | |||
| | |||
* Enzyme assay for [[glucocerebrosidase]] | |||
* [[DNA|DNA analysis]] for [[GBA (gene)|GBA mutation]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Enzyme replacement therapy|Enzyme replacement]] | |||
* [[Splenectomy]] | |||
* [[Blood transfusion]] | |||
|} | |||
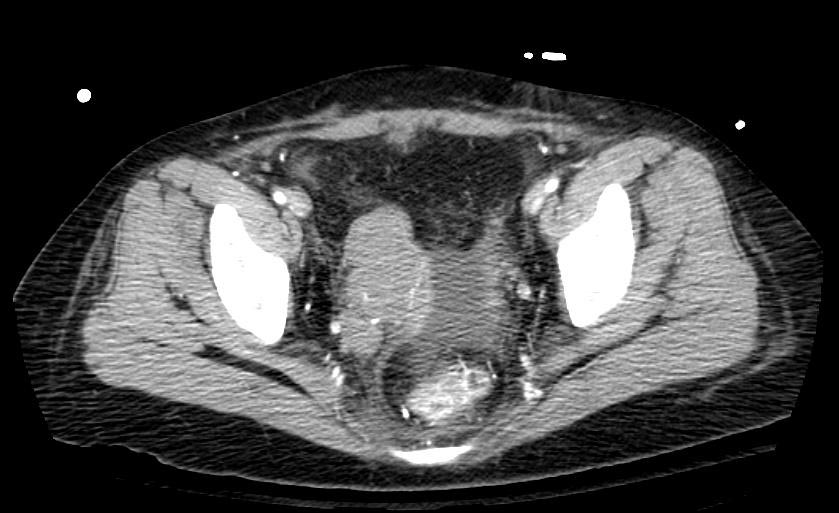
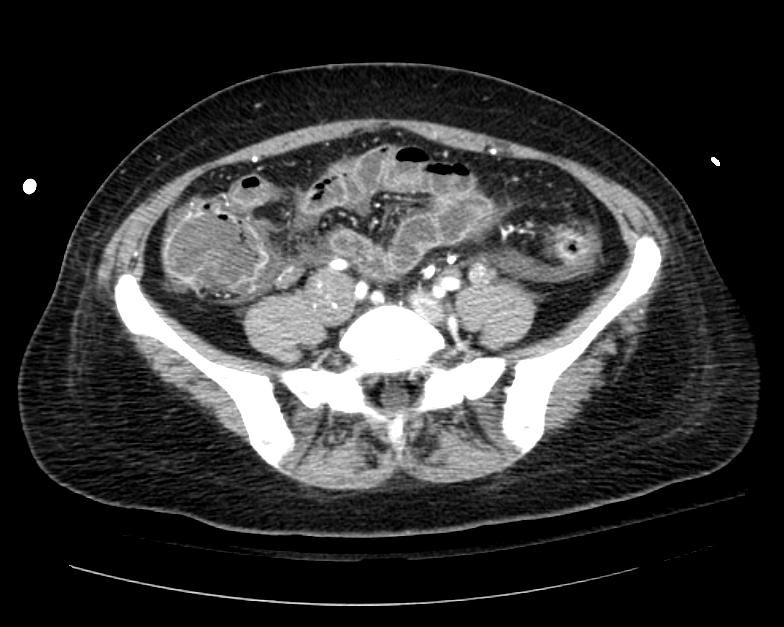
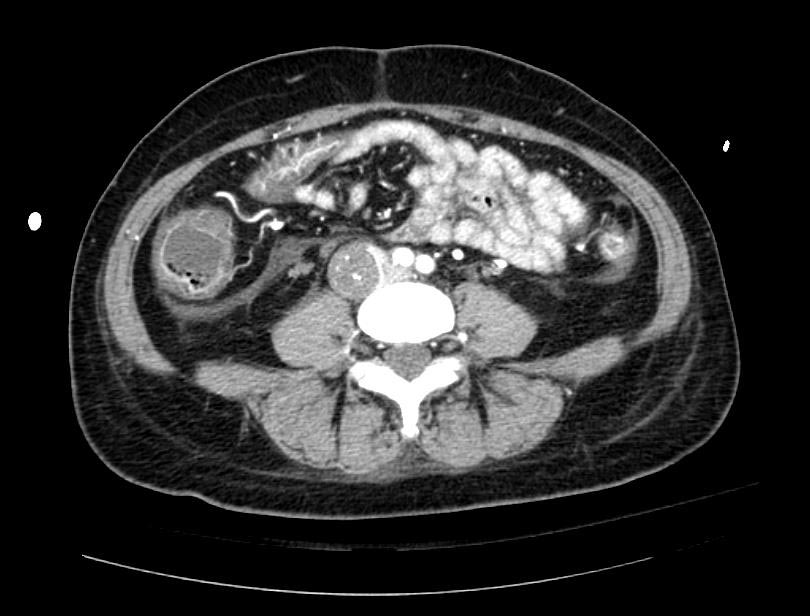
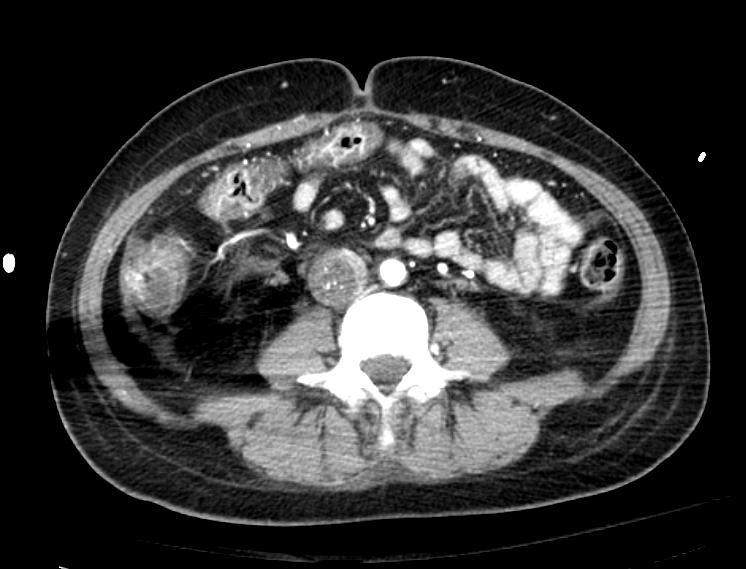
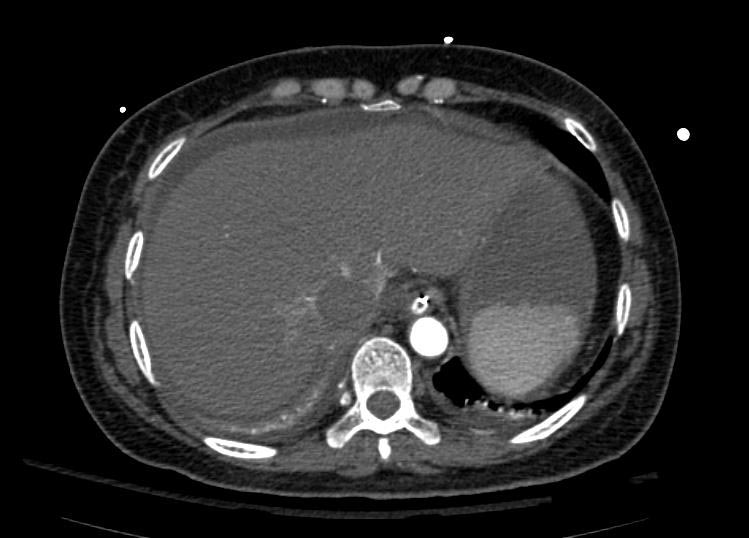
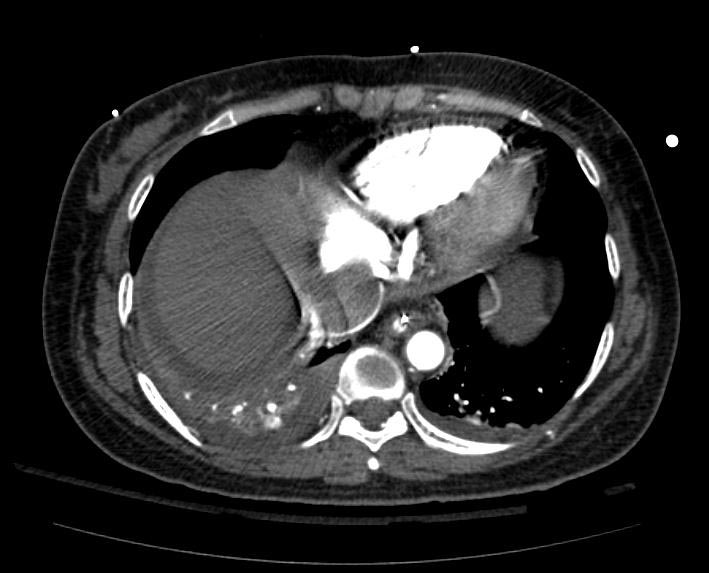
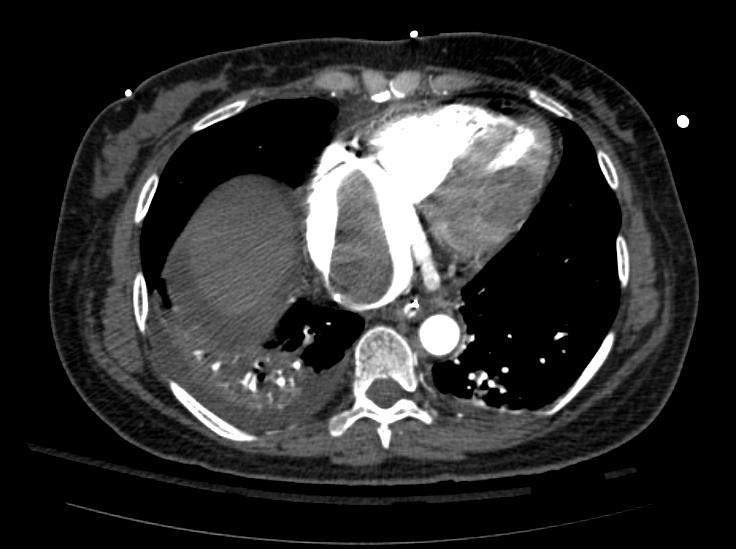
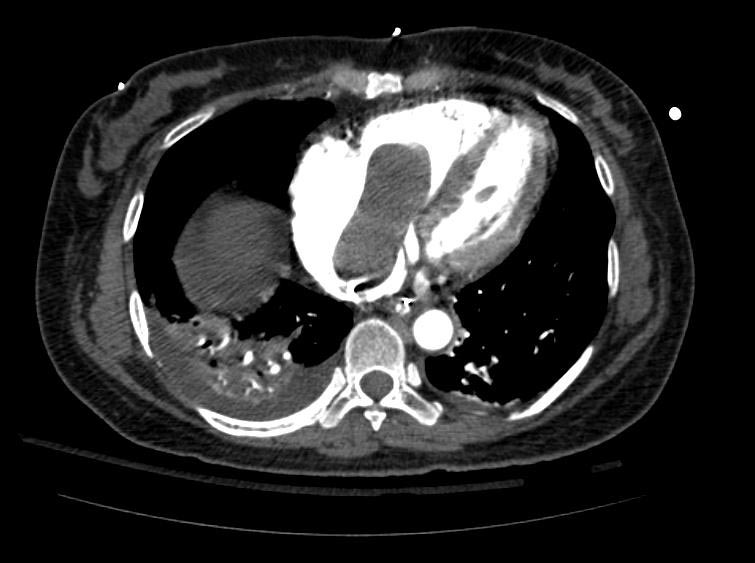
===Example #1=== | ===Example #1=== | ||
The patient presented with S.O.B. one year after hysterectomy for a leiomyomatous uterus. | The patient presented with S.O.B. one year after hysterectomy for a leiomyomatous uterus. | ||
Revision as of 20:56, 4 November 2019
Images
| Organ System Involvement | Differential Diagnosis | Causes | Clinical Features | Laboratory Findings | Gold Standard Test | Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary (AA) Amyloidosis | ||||||
| Nephrotic Syndrome and Real Failure | Primary (AL) Amyloidosis |
|
|
|
||
| Diabetic Nephropathy |
|
|
|
|||
| Minimal Change Disease |
|
| ||||
| Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis | ||||||
| Fabry's Disease |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Light Chain Deposition Disease |
|
|
| |||
| Membranous Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Fibrillary-Immunotactoid Glomerulopathy |
|
|
|
|||
| Organ System Involvement | Differential Diagnosis | Causes | Clinical Features | Laboratory Findings | Gold Standard Test | Therapy |
| Polyneuropathy | POEMS syndrome (Demyelinating) |
|
|
|||
| Metabolic Syndrome (Axonal pathology) |
|
|
|
|||
| Vitamin Deficiencies (Axonal Pathology) |
|
|
|
| ||
| Guillain-Barre Syndrome (Demyelinating) |
|
|
|
|||
| Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) (Mixed axonal and demyelinatiing) |
|
|
|
|
||
| Multifocal Motor Neuropathy |
|
|||||
| Organ System Involvement | Differential Diagnosis | Causes | Features | Laboratory Findings | Gold Standard Test | Therapy |
| Organomegaly (Hepatosplenomegaly and Lymphadenopathy) | Malaria |
|
|
| ||
| Kala-azar |
|
|
|
|||
| Infective Hepatitis |
|
|
||||
| Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) |
|
|
||||
| Lymphoma |
|
|
||||
| Primary (AL) Amyloidosis |
|
|
|
| ||
| Gaucher's Disease |
|
|
|
|
Example #1
The patient presented with S.O.B. one year after hysterectomy for a leiomyomatous uterus.