Cannabis (drug) cultivation
Cannabis, also known as marijuana[1] or ganja (from Hindi/Sanskrit: गांजा gānjā),[2] is a psychoactive product of the plant Cannabis sativa. The herbal form of the drug consists of dried mature flowers and subtending leaves of pistillate ("female") plants. The resinous form, known as hashish,[3] consists primarily of glandular trichomes collected from the same plant material.

The major biologically active chemical compound in cannabis is Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), commonly referred to as THC.
Humans have been consuming cannabis since prehistory,[4] although in the 20th century there was a rise in its use for recreational, religious or spiritual, and medicinal purposes. It is estimated that about four percent [5] of the world's adult population use cannabis annually and 0.6 percent daily. The possession, use, or sale of psychoactive cannabis products became illegal in most parts of the world in the early 20th century. Since then, some countries have intensified the enforcement of cannabis prohibition while others have reduced the priority of enforcement.
History

Evidence of the inhalation of cannabis smoke can be found as far back as the Neolithic age, as indicated by charred cannabis seeds found in a ritual brazier at an ancient burial site in present day Romania.[4] The most famous users of cannabis were the ancient Hindus of India and Nepal. The herb was called ganjika in Sanskrit (गांजा/গাঁজা ganja in modern Indic languages).[6][7] The ancient drug soma, mentioned in the Vedas as a sacred intoxicating hallucinogen, was sometimes associated with cannabis.[8]
Cannabis was also known to the Assyrians, who discovered its psychoactive properties through the Aryans.[9] Using it in some religious ceremonies, they called it qunubu (meaning "way to produce smoke"), a probable origin of the modern word 'Cannabis'.[10] Cannabis was also introduced by the Aryans to the Scythians and Thracians/Dacians, whose shamans (the kapnobatai—“those who walk on smoke/clouds”) burned cannabis flowers to induce a state of trance.[11] Members of the cult of Dionysus, believed to have originated in Thrace, are also thought to have inhaled cannabis smoke. In 2003, a leather basket filled with cannabis leaf fragments and seeds was found next to a 2,500- to 2,800-year-old mummified shaman in the northwestern Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China.[12][13]
Cannabis has an ancient history of ritual use and is found in pharmacological cults around the world. Hemp seeds discovered by archaeologists at Pazyryk suggest early ceremonial practices like eating by the Scythians occurred during the 5th to 2nd century BCE, confirming previous historical reports by Herodotus.[14] Some historians and etymologists have claimed that cannabis was used as a religious sacrament by ancient Jews and early Christians.[15] It was also used by Muslims in various Sufi orders as early as the Mamluk period, for example by the Qalandars.[16] In India and Nepal, it has been used by some of the wandering spiritual sadhus for centuries, and in modern times the Rastafari movement has embraced it as a sacrament.[17] Elders of the modern religious movement known as the Ethiopian Zion Coptic Church consider cannabis to be the Eucharist, claiming it as an oral tradition from Ethiopia dating back to the time of Christ, even though the movement was founded in the United States in 1975 and has no ties to either Ethiopia or the Coptic Church.[18] Like the Rastafari, some modern Gnostic Christian sects have asserted that cannabis is the Tree of Life.[19][20] Other organized religions founded in the past century that treat cannabis as a sacrament are the THC Ministry,[21] the Way of Infinite Harmony, Cantheism,[22] the Cannabis Assembly[23] and the Church of Cognizance.
The production of cannabis for drug use remains illegal throughout most of the world through for ex. International Opium Convention of 1925, the Marijuana Tax Act of 1937, the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, and the 1988 United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, while simple possession of small quantities is either legal, or treated as an addiction rather than a criminal offense in a few countries.[citation needed][dubious ]
Medical use
A synthetic form of one chemical in marijuana, Delta-9 Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is a controversial treatment for medical use. The American Marijuana Policy Project, a pro-cannabis organization, claims that cannabis is an ideal therapeutic drug for cancer and AIDS patients, who often suffer from clinical depression, and from nausea and resulting weight loss due to chemotherapy and other aggressive treatments.Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag Other medical uses may included fighting cancer, according to an isolated study by scientists in Italy. This study states that cannabidiol (CBD), a chemical found in marijuana, inhibits growth of cancer cells in animals.[24]
The FDA and comparable authorities in Western Europe, including the Netherlands, have not approved smoked marijuana for any condition or disease. The current view of the United States Food and Drug Administration is that if there is any future of marijuana as a medicine, it lies in its isolated components, the cannabinoids and their synthetic derivatives.[25]
A synthetic version of the cannabinoid THC named Dronabinol has been shown to relieve symptoms of anorexia and reduce agitation in elderly Alzheimer's patients.[26] Dronabinol has been approved for use with anorexia in patients with HIV/AIDS and chemotherapy-related nausea. This drug, while demonstrating the effectiveness of cannabis at combating several disorders, is more expensive and less available than "pot" and has not been shown to be effective or safe.[27]
Glaucoma, a condition of increased pressure within the eyeball causing gradual loss of sight, can be treated with medical marijuana to decrease this intraocular pressure. There has been debate for 25 years on the subject. Some data exist, showing a reduction of IOP in glaucoma patients who smoke marijuana,[28] but the effects are short-lived, and the frequency of doses needed to sustain a decreased IOP can cause systemic toxicity. There is also some concern over its use since it can also decrease blood flow to the optic nerve. Marijuana lowers IOP by acting on a cannabinoid receptor on the ciliary body called the CB receptor.[29] Although marijuana is not a good therapeutic choice for glaucoma patients, it may lead researchers to more effective, safer treatments. A promising study shows that agents targeted to ocular CB receptors can reduce IOP in glaucoma patients who have failed other therapies.[30]
Medical marijuana is used for analgesia, or pain relief. “Marijuana is used for analgesia only in the context of a handful of illnesses (e.g., headache, dysentery, menstrual cramps, and depression) that are often cited by marijuana advocates as medical reasons to justify the drug being available as a prescription medication.”[31] It is also reported to be beneficial for treating certain neurological illnesses such as epilepsy, and bipolar disorder.[32] Case reports have found that cannabis can relieve tics in people with obsessive compulsive disorder and Tourette syndrome. Patients treated with tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive chemical found in cannabis, reported a significant decrease in both motor and vocal tics, some of 50% or more.[33][34][35] Some decrease in obsessive-compulsive behavior was also found.[33] A recent study has also concluded that cannabinoids found in cannabis might have the ability to prevent Alzheimer's disease.[36] THC has been shown to reduce arterial blockages.[37]
Another use for medical marijuana is movement disorders. Marijuana is frequently reported to reduce the muscle spasms associated with multiple sclerosis; this has been acknowledged by the Institute of Medicine, but it noted that these abundant anecdotal reports are not well-supported by clinical data. Evidence from animal studies suggests that there is a possible role for cannabinoids in the treatment of certain types of epileptic seizures.[38] Marijuana "numbs" the nervous system slightly, possibly preventing shock. A synthetic version of the major active compound in cannabis, THC, is available in capsule form as the prescription drug dronabinol (Marinol) in many countries. The prescription drug Sativex, an extract of cannabis administered as a sublingual spray, has been approved in Canada for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.[39]
New breeding and cultivation techniques

It is often claimed by growers and breeders of herbal cannabis that advances in breeding and cultivation techniques have increased the potency of cannabis since the late 1960s and early '70s, when delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol was discovered and understood. However, potent seedless marijuana such as "Thai sticks" were already available at that time. In fact, the sinsemilla technique of producing high-potency marijuana has been practiced in India for centuries[citation needed]. Sinsemilla (Spanish for "without seed") is the dried, seedless inflorescences of female cannabis plants. Because THC production drops off once pollination occurs, the male plants (which produce little THC themselves) are eliminated before they shed pollen to prevent pollination. Advanced cultivation techniques such as hydroponics, cloning, high-intensity artificial lighting, and the sea of green method are frequently employed as a response (in part) to prohibition enforcement efforts that make outdoor cultivation more risky. These intensive horticultural techniques have led to fewer seeds being present in cannabis and a general increase in potency over the past 20 years. The average levels of THC in marijuana sold in United States rose from 3.5% in 1988 to 7% in 2003 and 8.5% in 2006.[40]
"Skunk" cannabis is a potent strain of cannabis, grown through selective breeding and usually hydroponics, that is a cross-breed of Cannabis sativa and C. indica. Skunk cannabis potency ranges usually from 6% to 15% and rarely as high as 20%. The average THC level in coffeehouses in the Netherlands is about 18–19%.[41]
The average THC content of Skunk #1 is 8.2%; it is a 4-way combination of the cannabis strains Afghani indica, Mexican Gold, Colombian Gold, and Thai: 75% sativa, 25% indica.[citation needed] This was done via extensive breeding by cultivators in California in the 1970s using the traditional outdoor cropping methods used for centuries.[citation needed]
In proposed revisions to cannabis rescheduling in the UK, the government is considering rescheduling cannabis back from C to B. One of the reasons is the high-potency marijuana.[42]
A Dutch double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study examining male volunteers aged 18–45 years with a self-reported history of regular cannabis use concluded that smoking of cannabis with high THC levels (marijuana with 9–23% THC), as currently sold in coffee shops in the Netherlands, may lead to higher THC blood-serum concentrations. This is reflected by an increase of the occurrence of impaired psychomotor skills, particularly among younger or inexperienced cannabis smokers, who do not adapt their smoking-style to the higher THC content.[43] High THC concentrations in cannabis was associated with a dose-related increase of physical effects (such as increase of heart rate, and decrease of blood pressure) and psychomotor effects (such as reacting more slowly, being less concentrated, making more mistakes during performance testing, having less motor control, and experiencing drowsiness). It was also observed during the study that the effects from a single joint lasted for more than eight hours. Reaction times remained impaired five hours after smoking, when the THC serum concentrations were significantly reduced, but still present. When subjects smoke on several occasions per day, accumulation of THC in blood-serum may occur.
Another study showed that consumption of 15 mg of Delta(9)-THC resulted in no learning whatsoever occurring over a three-trial selective reminding task after two hours. In several tasks, delta(9)-THC increased both speed and error rates, reflecting “riskier” speed–accuracy trade-offs.[44]
Legal status

Since the beginning of the 20th century, most countries have enacted laws against the cultivation, possession, or transfer of cannabis for recreational use. These laws have impacted adversely on the cannabis plant's cultivation for non-recreational purposes, but there are many regions where, under certain circumstances, handling of cannabis is legal or licensed. Many jurisdictions have lessened the penalties for possession of small quantities of cannabis, so that it is punished by confiscation or a fine, rather than imprisonment, focusing more on those who traffic the drug on the black market. There are also changes in a more restrictive direction such as the closing of coffee shops in the Netherlands, the closing of the open drug market in Christiania, Copenhagen, the Gonzales v. Raich rule in 2005 that the Commerce Clause of the United States Constitution allow the federal government to ban the use of marijuana, including medical use anywhere in the United States.
Some jurisdictions use free voluntary treatment programs and/or mandatory treatment programs for frequent known users. Simple possession can carry long prison terms in some countries, particularly in East Asia, where the sale of cannabis may lead to a sentence of life in prison or even execution.
Effects
Cannabis has psychoactive and physiological effects when consumed, usually by smoking or ingestion. The minimum amount of THC required to have a perceptible psychoactive effect is about 10 micrograms per kilogram of body weight[45] (which, in practical terms, is a varying amount, dependent upon potency). A related compound, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin, also known as THCV, is produced in appreciable amounts by certain drug strains. This cannabinoid has been described in the popular literature as having shorter-acting, flashier effects than THC, but recent studies suggest that it may actually inhibit the effects of THC. Relatively high levels of THCV are common in African dagga (marijuana), and in hashish from the northwest Himalayas.[citation needed]
Health issues
A recent study by the Canadian government found cannabis contained more toxic substances than tobacco smoke.[46] The study determined that marijuana smoke contained 20 times more ammonia, and five times more hydrogen cyanide and nitrous oxides than tobacco smoke. In spite of this, a recent large-scale study found no correlation between heavy marijuana use and lung cancer, despite noting that cannabis contains the same carcinogens as tobacco. The same study found a 20-fold increase in lung-cancer rates of smokers who consumed two or more packs of cigarettes per day.[47] These researchers postulated that the THC present may have a "protective effect" by causing aging cells to die before they become cancerous.[48] Other recent research suggest the cannabinoid CBD may stop certain cancers from spreading, although not in concentrations consumed during smoking.[49]
In contrast, a study published in the January 2008 edition of the journal Respirology found that "regular" cannabis smokers who developed bullous lung disease[[2]] did so on average 24 years sooner than tobacco smoking counterparts.[50] Researchers attributed this to the inhalation of a larger volume of smoke, and typically holding it for four times longer than tobacco smokers. Bullous lung disease is considered an uncommon cause of respiratory distress.[51] In general, habitual inhalation of any kind of smoke is detrimental to lung health.[52]
Cannabis use has been linked to exacerbating the effects of depression, psychosis, schizophrenia, bronchitis, and emphysema by several peer-reviewed studies for those who are vulnerable to such illnesses based on personal or family history.[53] More recently, the Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study published research showing an increased risk of psychosis for cannabis users with a certain genetic predisposition, held by 25% of the population.[54]
In July 2007, British medical journal The Lancet published a study that indicates that cannabis users have, on average, a 41% greater risk of developing psychosis than non-users. The risk was most pronounced in cases with an existing risk of psychotic disorder, and was said to grow up to 200% for the most-frequent users.[55][56][57]
A 2008 study by the National Institutes of Health suggested a link between chronic marijuana smoking and increased risk of heart attack or stroke.[58]
Relationship with other drugs
Since its origin in the 1950s, the "gateway drug" hypothesis has been one of the central pillars of cannabis drug policy in the United States. One variant is that people, upon trying cannabis for the first time and not finding it dangerous, are then tempted to try other, harder drugs. These models of cause and effect has been debated.[59] A 2005 comprehensive review of the literature on the cannabis gateway hypothesis found that pre-existing traits may predispose users to addiction in general, the availability of multiple drugs in a given setting confounds predictive patterns in their usage, and drug sub-cultures are more influential than cannabis itself. The study called for further research on "social context, individual characteristics, and drug effects" to discover the actual relationships between cannabis and the use of other drugs.[60]
Some argue that the purported relationship between marijuana and more illicit drugs, as proposed by the "gateway theory", is methodologically flawed. A common argument is that a new user of cannabis who doesn't find it dangerous will see the difference between public information regarding the drug and their own experiences, and apply this distrust to public knowledge of other, more powerful drugs. Some studies support the "gateway drug" model.[61] An example from 2007: A stratified, random sample of 1943 adolescents was recruited from secondary schools across Victoria, Australia, at age 14–15 years. This cohort was interviewed on eight occasions until the age of 24–25 years. At age 24 years, 12% of the sample had used amphetamines in the past year, with 1–2% using at least weekly. Young adult amphetamine use was predicted strongly by adolescent drug use and was associated robustly with other drug use and dependence in young adulthood. Associations were stronger for more frequent users. Among young adults who had not been using amphetamines at age 20 years, the strongest predictor of use at age 24 years was the use of other drugs, particularly cannabis, at 20 years.[62] Those who were smoking cannabis at the age of 15 were as much as 15 times more likely to be using amphetamines in their early 20s.[63]
Analysts have hypothesized that the illegal status of cannabis is a possible cause of a gateway drug effect, reasoning that cannabis users are likely to become acquainted with people who use and sell other illegal drugs in order to acquire cannabis. But it is said that Marijuana is not as harmful or addicting as any other drug.[64][65] Some contend that by this argument, alcohol and tobacco may also be regarded as gateway drugs. Studies have shown that tobacco smoking is a better predictor of concurrent illicit hard drug use than smoking cannabis.[66]
A current doctoral thesis from Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, on the neurobiological effects of early life cannabis exposure, gives support for the cannabis gateway hypothesis in relation to adult opiate abuse. THC exposed rats showed increased motivation for opiate drug use under conditions of stress. However, the cannabis exposure did not correlate to amphetamine use.[67]
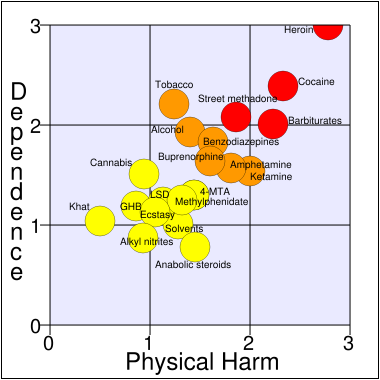
A study[68] published in The Lancet on 24 March 2007 was twenty drugs were assigned a risk from zero to three. Dr. David Nutt et al. asked medical, scientific and legal experts to rate 20 different drugs on nine parameters:
- Physical harm (Acute, Chronic, and Intravenous harm)
- Dependence (Intensity of pleasure, Psychological dependence, Physical dependence)
- Social harms (Intoxication, Other social harms, Health-care costs)
Cannabis was ranked seventeenth of twenty for mean physical harm score and eleventh for mean dependence score. Not shown is the mean social harm score, which rated ninth, in a tie with Amphetamine.
Poly drug use is not unusual among established users; statistics from Spain show that cannabis users aged 15 -34 also used amphetamine (9%), ecstasy (11%) or cocaine (18%) the same year.[69]
Classification
While many drugs clearly fall into the category of either Stimulant, Depressant, Hallucinogen, or Antipsychotic, cannabis, containing both THC and CBD, exhibits a mix of all sections, leaning towards the Hallucinogen section due to THC being the primary constituent.[70][71][72]
Methods of consumption

Cannabis is prepared for human consumption in several forms:[citation needed]
- Marijuana or ganja: the flowering tops of female plants, from less than 1% THC to 22% THC; the wide range is probably one of the reasons for the conflicting results from different studies.
- Hashish or charas: a concentrated resin composed of heated glandular trichomes that have been physically extracted, usually by rubbing, sifting, or with ice.
- Kief: (1) the chopped flowering tops of female cannabis plants, often mixed with tobacco; (2) Moroccan hashish produced in the Rif mountains;[73] (3) sifted cannabis trichomes consisting of only the glandular "heads" (often incorrectly referred to as "crystals" or "pollen"); (4) the crystal (trichomes) left at the bottom of a grinder after grinding marijuana, then smoked.
- Bhang: a beverage prepared by grinding cannabis leaves in milk and boiling with spices and other ingredients.
- Second Hand when marijuana is smoked in an enclosed area resulting in others to get "higher".

These forms are not exclusive, and mixtures of two or more different forms of cannabis are frequently consumed. Between the many different strains of cannabis and the various ways that it is prepared, there are innumerable variations similar to the wide variety of mixed alcoholic beverages that are consumed.
Smoking

Cannabis can be smoked in a variety of ways, some of which are more popular than others. The most common methods of smoking cannabis involve the use of implements such as bongs and smoking pipes, or rolling joints or blunts. These methods differ by: the preparation of the cannabis plant before use; the parts of the cannabis plant which is used; and the treatment of the smoke before inhalation.[citation needed]
Vaporization
A vaporizer heats herbal cannabis to 365–410 °F (185–210 °C), which turns the active ingredients into gas without burning the plant material (the boiling point of THC is 392 °F (200°C) at 0.02 mm Hg pressure, and somewhat higher at standard atmospheric pressure).[74][75] A lower proportion of toxic chemicals are released than by smoking, although this may vary depending on the design of the vaporizer and the temperature at which it is set. A MAPS-NORML study using a Volcano vaporizer reported 95% THC and no toxins delivered in the vapor.[76] However, an older study using less sophisticated vaporizers found more toxins.[77] The effects from a vaporizer are noticeably different to that of smoking cannabis. Users have reported a more euphoric hallucinogen type high, because the vapor contains more pure THC.[citation needed]
Eating
As an alternative to smoking, cannabis may be consumed orally.
Although hashish is sometimes eaten raw or mixed with water, THC and other cannabinoids are more efficiently absorbed into the bloodstream when dissolved in ethanol, or combined with butter or other lipids.[citation needed] The time to onset of effects is usually about an hour and may continue for a considerable length of time, whereas the effects of smoking herbal cannabis are almost immediate.[citation needed]
Smoking cannabis results in a significant loss of THC and other cannabinoids in the exhaled smoke, by decomposition on burning, and in smoke that is not inhaled. In contrast, all of the active constituents enter the body when cannabis is ingested. It has been shown that the primary active component of cannabis, Δ9-THC, is converted to the more psychoactive 11-hydroxy-THC by the liver.[78] Titration to the desired effect by ingestion is much more difficult than through inhalation.
Other methods
Cannabis material can be leached in high-proof spirits (often grain alcohol) to create “Green Dragon”. This process is often employed to make use of low-potency stems and leaves.[citation needed]
Cannabis can also be consumed as a tea. Although THC is lipophilic and only slightly water soluble (with a solubility of 2.8 grams per liter[79]), enough THC can be dissolved to make a mildly psychoactive tea. However, water-based infusions are generally considered to be an inefficient use of the herb.
Cannabis culture
Template:Unreferencedsection There are multiple drug subcultures based on the use of different drugs - the culture surrounding cannabis, for example, is very different from that of heroin, due to the different sort of experiences, sentiment amongst the crowd attracted to the drug in question, as well as the problems the users encounter. Template:Seealso Template:Seealso Template:Seealso
See also
- 1937 Marihuana Tax Act
- Cannabis political parties
- Cannabis use disorders
- Emerald Triangle
- Fitz Hugh Ludlow ("The Hasheesh Eater")
- Global Marijuana March
- Head shop
- International Opium Convention
- Legality of cannabis by country
- List of cannabis strains
- Marc Emery
- Marijuana Policy Project
- National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws
- Proposition 215
- Hemp
- Hemp oil
- THC
References
- ↑ Compact Oxford Ditctionary definition
- ↑ The Oxford English Dictionary. Any of various preparations of different parts of the hemp-plant which are smoked, chewed, sniffed or drunk for their intoxicating or hallucinogenic properties and were formerly used medicinally; bhang (marijuana), ganja, and charas (hashish) are different forms of these preparations." It is also notes that "cannabis" was elliptical reference (i.e. slang) for Cannabis sativa.
- ↑ Matthew J. Atha - Independent Drug Monitoring Unit. "Types of Cannabis Available in the UK". Retrieved 2007-09-13.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Rudgley, Richard (1999). Touchstone, ed. The Lost Civilizations of the Stone Age. ISBN 0-6848-5580-1.
- ↑ United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2006), "Cannabis: Why we should care" (PDF), World Drug Report, 1, ISBN 9-2114-8214-3, retrieved 2006-10-10 p.14
- ↑ Leary, Thimothy (1990). Tarcher/Putnam, ed. Flashbacks. ISBN 0-8747-7870-0.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.), 1911, retrieved 2006-06-15
- ↑ Rudgley, Richard (1998). Little, Brown and Company, ed. The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Substances. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
- ↑ Franck, Mel (1997). Marijuana Grower's Guide. Red Eye Press. ISBN 0-9293-4903-2. p.3
- ↑ Rubin, Vera D. (1976). Cannabis and Culture. Campus Verlag. ISBN 3-5933-7442-0. p.305
- ↑ Cunliffe, Barry W. (2001). The Oxford Illustrated History of Prehistoric Europe. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-1928-5441-0. p.405
- ↑ "Lab work to identify 2,800-year-old mummy of shaman". People's Daily Online. 2006. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
- ↑ Hong-En Jiang; et al. (2006). "A new insight into Cannabis sativa (Cannabaceae) utilization from 2500-year-old Yanghai tombs, Xinjiang, China". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 108 (3): 414–422. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
- ↑ Walton, Robert P. (1938). Marijuana, America's New Drug Problem. J. B. Lippincott. p.6
- ↑ "Cannabis linked to Biblical healing". Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ↑ Ibn Taymiyya. Le haschich et l'extase. ISBN 2-8416-1174-4.
- ↑ Joseph Owens. Dread, The Rastafarians of Jamaica. ISBN 0-4359-8650-3.
- ↑ The Ethiopian Zion Coptic Church. "Marijuana and the Bible". Schaffer Library of Drug Policy. Retrieved 2007-09-13.
- ↑ "Zion Light Ministry". Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ↑ Chris Bennett, Lynn & Osburn, Judy Osburn (1938). Green Gold: the Tree of LifeMarijuana in Magic & Religion. Access Unlimited. p. 418. ISBN 0-9629-8722-0.
- ↑ "The Hawai'i Cannabis Ministry". Retrieved 2007-09-13.
- ↑ "Cantheism". Retrieved 2007-09-13.
- ↑ "Cannabis Assembly". Retrieved 2007-09-13.
- ↑ "Cannabidiol Dramatically Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth, Study Says". Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ↑ Meyer, Robert J. "Testimony before the Subcommittee on Criminal Justice, Drug Policy, and Human Resources, Committee on Government Reform". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2007-09-15. line feed character in
|title=at position 22 (help) - ↑ "Cannabis lifts Alzheimer appetite". BBC. Retrieved 2007-09-15.
- ↑ Greenberg, Gary (2005-11-01). "Respectable Reefer". Mother Jones. Retrieved 2007-04-03. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Merritt JC, Crawford WJ, Alexander PC; et al. (1980). "Effect of marihuana on intraocular and blood pressure in glaucoma". Ophthalmol (87): 222–8. ISSN 0007-1161.
- ↑ "Factors associated with age-related macular degeneration". Am J Epidemiol (128): 700–10. 1988. Text "Goldberg J, Flowerdew G, Smith E, et al." ignored (help)
- ↑ Porcella A, Maxia C, Gessa GL, Pani L. (2001). "The synthetic cannabinoid WIN55212-2 decreases the intraocular pressure in human glaucoma resistant to conventional therapies". Eur J Neurosci (13): 409–12.
- ↑ Blanchard Randall (1992), Medical Use of Marijuana: Policy and Regulatory Issues, Library of Congress, Congressional Research Service
- ↑ "Review of Therapeutic Effects". Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 K.R. Muller, U. Schneider, H. Kolbe, H.M. Emrich (1999). "Treatment of Tourette's Syndrome With Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol". American Journal of Psychiatry. 156 (3). Retrieved 2007-09-15.
- ↑ K.R. Muller, U. Schneider, A. Koblenz, M. Jöbges, H. Kolbe, T. Daldrup, H.M. Emrich (2002). "Treatment of Tourette's Syndrome with Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): A Randomized Crossover Trial". Pharmacopsychiatry. 35 (2). Retrieved 2007-09-15.
- ↑ R. Sandyk, G. Awerbuch (1988). "Marijuana and Tourette's Syndrome". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 8 (6). Retrieved 2007-09-15.
- ↑ Ramíirez, B. G., C. Blázquez, T. Gómez del Pulgar, M. Guzmán, and M. L. de Ceballos (2005). "Prevention of Alzheimer's disease pathology by cannabinoids: neuroprotection mediated by blockade of microglial activation". Journal of Neuroscience. 25 (8^): 1904–1913. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ↑ Steffens, S.,Veillard, N.R.; et al. "Low dose oral cannabinoid therapy reduces progression of atherosclerosis in mice". Nature. 474 (7034): 782–786. Unknown parameter
|acecssdate=ignored (help) - ↑ Randall, Blanchard (1992). Medical use of marijuana policy and regulatory issues. Congressional Research Service, Library of Congress. OCLC 29975643.
- ↑ Koch, W. (23 June 2005). "Spray alternative to pot on the market in Canada". USA Today. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ↑ "Marijuana sold in U.S. stronger than ever". MSNBC. Retrieved 2007-09-21.
- ↑ "World Drug Report 2006". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Retrieved 2008-02-25. Ch. 2.3
- ↑ BBC: Cannabis laws to be strengthened.May 2008 20:55 UK
- ↑ Tj. T. Mensinga; et al., A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study on the pharmacokinetics and effects of cannabis (PDF), RIVM, retrieved 2007-09-21
- ↑ Curran H.V.; et al. (2002). "Cognitive and subjective dose-response effects". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2007-09-21.
- ↑ http://www.marijuanalibrary.org/brain2.txt
- ↑ "Cannabis smoke 'has more toxins'". BBC. 2007-12-19.
- ↑ "Study Finds No Link Between Marijuana Use And Lung Cancer". Science Daily. 2006-05-26. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Study Finds No Cancer-Marijuana Connection". Washington Post. [2006-5-26]. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Marijuana compound may stop spread of breast". Fox News. 2007-11-19. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ http://www.scienceedaily.com/releases/2008/01/080123104017.htm |publisher=Science Daily |date=2008-01-27 |title=Marijuana Smokers Face Rapid Lung Destruction -- As Much As 20 Years Ahead Of Tobacco Smokers}}
- ↑ Bullous Lung Disease
- ↑ [[1]]
- ↑ PII: S0140-6736(98)05021-1
- ↑ "Cannabis study finds gene linked to psychosis".
- ↑ "Cannabis could increase risk of psychotic illness later in life by 40%". The Lancet.
- ↑ "Prospective cohort study of cannabis use, predisposition for psychosis, and psychotic symptoms in young people". BMJ. line feed character in
|title=at position 61 (help) - ↑ "Marijuana may increase psychosis risk". CTV.
- ↑ "Heavy pot smoking could raise risk of heart attack, stroke". CBC.
- ↑ "RAND study casts doubt on claims that marijuana acts as "gateway" to the use of cocaine and heroin". RAND Corporation. 2002-12-02. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ↑ WAYNE D. HALL & MICHAEL LYNSKEY (January 2005). "Is cannabis a gateway drug? Testing hypotheses about the relationship between cannabis use and the use of other illicit drugs". 24 (1). Drug and Alcohol Review: 39 – 48.
- ↑ Saitz, Richard (2003-02-18). "Is marijuana a gateway drug?". Journal Watch. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ↑ Degenhardt, Louisa; et al. (2007). "Who are the new amphetamine users? A 10-year prospective study of young Australians". Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ↑ "Cannabis linked to use of amphetamines". ABC News Australia. 2007-07-18. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ↑ Morral AR, McCaffrey DF, Paddock SM (2002). "Reassessing the marijuana gateway effect". Addiction. 97 (12): 1493–504. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00280.x. PMID 12472629.
- ↑ "Marijuana Policy Project- FAQ". Retrieved 2006-12-24.
- ↑ Torabi MR, Bailey WJ, Majd-Jabbari M (1993). "Cigarette smoking as a predictor of alcohol and other drug use by children and adolescents: evidence of the "gateway drug effect"". The Journal of school health. 63 (7): 302–6. PMID 8246462.
- ↑ Ellgren, Maria (2007). "Neurobiological effects of early life cannabis exposure in relation to the gateway hypothesis". Karolinska Institutet. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ↑ Nutt D, King LA, Saulsbury W, Blakemore C (2007). "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse". Lancet. 369 (9566): 1047–53. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60464-4. PMID 17382831.
- ↑ EMCDDA Annual report 2006: the state of the drugs problem in Europe, ch. 8
- ↑ McKim, William A (2002). Drugs and Behavior: An Introduction to Behavioral Pharmacology (5th Edition). Prentice Hall. p. 400. ISBN 0-13-048118-1.
- ↑ "Information on Drugs of Abuse". Commonly Abused Drug Chart. Unknown parameter
|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help) - ↑ Stafford, Peter (1992). Psychedelics Encyclopedia. ISBN 0914171518.
- ↑ Zijlma, Anouk. "Smoking hashish in Morocco". About.com. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ↑ "Air Temperature Table" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-09-22.. Volcanotm Operating Manual. Storz & Bickel, Tuttlingen, Germany.
- ↑ 1989. The Merck Index, 11th ed., Merck & Co., Rahway, New Jersey
- ↑ Template:Cite journal)).
- ↑ Gieringer, Dale. "Marijuana Water Pipe and Vaporizer Study". Retrieved 2006-04-21.
- ↑ Paulo Borini; Romeu Cardoso Guimarães; Sabrina Bicalho Borini (2004). "Possible hepatotoxicity of chronic marijuana usage". Sao Paulo Medical Journal. 122 (3). doi:10.1590/S1516-31802004000300007. Retrieved 2006-05-02. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Akinde Omotayo. "The Medical Applications of Cannabinoids". Borough of Manhattan Community College. Retrieved 2006-09-15.
- [3] Marijuana Tax Act of 1937
Further reading
- Howard Markel (2002-10-27). "For Addicts, Relief May Be an Office Visit Away". New York Times. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - Louise Arsenault, Mary Cannon, Richie Poulton, Robin Murray, Avshalom Caspi, and Terrie E. Moffitt (2002). "Cannabis use in adolescence and risk for adult psychosis: longtudinal prospective study" (PDF). British Medical Journal. 325: 1212 &ndash, 1213.
- Avshalom Caspi, Terrie E. Moffitt, Mary Cannon, Joseph McClay, Robin Murray, HonaLee Harrington, Alan Taylor, Louise Arsenault, Ben Williams, Antony Braithwaite, Richie Poulton, and Ian W. Craig (2005). "Moderation of the effect of adult-onset cannabis use on adult psychosis by a functional polymorphism in the Catchol-O-Methyltransferase gene: Longitudinal evidence of a gene X environment interaction" (PDF). Biol Psychiatry. 25: 1117 &ndash, 1127.
- Henderson, Mark (2005-04-12). "One in four at risk of cannabis psychosis". The Times. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - Bruce Mirken and Neel Makwana (Aston Birmingham): "Psychosis, Hype And Baloney". AlterNet. 2005-03-07. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - James Huff and Po Chan (2000). "Antitumor Effects of THC". Environmental Health Perspectives. 108 (10): Correspondence. PMID 11097557. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - Booth, Martin (2005). Cannabis: A History. ISBN 0-312-32220-8.
- Long term impact of Cannabis use of 16 year olds "Long-term impact of the Gatehouse Project on Cannabis use of 16-year-olds in Australia. (Research Papers)". journal of school health. 2004-01-01. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
External links
- Marijuana in Jamaica
- Marijuana Policy Project
- National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws
- Wiktionary appendix of cannabis slang
- Various slang terms for cannabis
- Comprehensive Cannabis Faqs and Marijuana information
- Extensive list of notable cannabis users
- Debunking Myths about Marijuana Since 2002
- Research paper on the effects of marijuana
- The Report of the Canadian Government Commission of Inquiry into the Non-Medical Use of Drugs - 1972 - DRCNet Online Library of Drug Policy
- Marihuana Medical Access Regulations in Canada
- Pot Shrinks Tumors; Government Knew in '74
- University of Maryland, CECAR: Marijuana
- www.whitehousedrugpolicy.gov/drugfact/marijuana
Template:WH
Template:WS
bg:Марихуана
cs:Marihuana
cy:Cannabis (cyffur)
de:Marihuana
eo:Mariĥuano
gl:Cannabis (droga)
ko:대마초
hr:Marihuana
id:Ganja
it:Marijuana
he:מריחואנה
lv:Marihuāna
lt:Marihuana
jbo:marna snexu'i
mk:Марихуана
ml:കഞ്ചാവ്
ms:Ganja
nl:Marihuana
no:Cannabis (rusmiddel)
sk:Marihuana
sl:Marihuana
sr:Уживалачка употреба конопље
fi:Kannabis
sv:Cannabis
tt:Kinder
uk:Марихуана
vls:Marihuana
- Pages with reference errors
- CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al.
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- CS1 errors: invisible characters
- CS1 errors: dates
- Pages with citations using unnamed parameters
- Pages with citations using unsupported parameters
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2008
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- All accuracy disputes
- Articles with disputed statements from April 2008
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2008
- Psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants
- Medicinal use of cannabis
- Cannabis