Mediastinal mass: Difference between revisions
Trushatank (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Trushatank (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
* [[Human foamy virus]] | * [[Human foamy virus]] | ||
* [[Epstein-Barr virus]] | * [[Epstein-Barr virus]] | ||
* Human T-cell lymphotropic virus | * [[HTLV|Human T-cell lymphotropic virus]] | ||
* [[MEN 1 syndrome]] | * [[MEN 1 syndrome]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
* [[Epithelium|Epithelial cells]] | * [[Epithelium|Epithelial cells]] | ||
* [[Lymphoblasts|Immature lymphocytes]] | * [[Lymphoblasts|Immature lymphocytes]] | ||
* Immature T cells | * [[T cell|Immature T cells]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Thymoma GIF final.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing presence of voluminous expansive lesion of 6 cm in the upper anterior mediastinum without infiltration of surrounding tissues signs with modest enhancement. Case courtesy of Dr. Domenico Nicoletti | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Thymoma GIF final.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing presence of voluminous expansive lesion of 6 cm in the upper anterior mediastinum without infiltration of surrounding tissues signs with modest enhancement. Case courtesy of Dr. Domenico Nicoletti | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/38443 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/38443 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |'''Associated condition''' | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |'''Associated condition''' | ||
* | * [[Neuromuscular]] | ||
** [[Myasthenia gravis]] | ** [[Myasthenia gravis]] | ||
** [[Neuromyotonia]] | ** [[Neuromyotonia]] | ||
** [[Rippling muscle disease]] | ** [[Rippling muscle disease]] | ||
** [[Polymyositis and dermatomyositis|Polymyositis/dermatomyositis]] | ** [[Polymyositis and dermatomyositis|Polymyositis/dermatomyositis]] | ||
** [[Encephalitis]] (limbic, cortical and | ** [[Encephalitis]] ([[Limbic system|limbic]], [[Cortical area|cortical]] and [[Brain stem|brainstem]]) | ||
** [[Intestinal pseudoobstruction]] | ** [[Intestinal pseudoobstruction]] | ||
* Hematological | * [[Hematological]] | ||
** [[Anemia]]: [[pure red cell aplasia]], [[pernicious anemia]], [[hemolytic anemia]], [[aplastic anemia]] | ** [[Anemia]]: [[pure red cell aplasia]], [[pernicious anemia]], [[hemolytic anemia]], [[aplastic anemia]] | ||
** Other isolated [[Cytopenia|cytopenias]]: [[eosinophils]], [[basophils]] [[neutrophils]] | ** Other isolated [[Cytopenia|cytopenias]]: [[eosinophils]], [[basophils]] [[neutrophils]] | ||
** Immunodeficiencies: [[Hypogammaglobulinaemia|hypogammaglobulinemia]]/- T-cell deficiencies [[Good syndrome|(Good syndrome)]] | ** [[Immunodeficiency|Immunodeficiencies]]: [[Hypogammaglobulinaemia|hypogammaglobulinemia]]/- T-cell deficiencies [[Good syndrome|(Good syndrome)]] | ||
* Dermatological | * [[Dermatology|Dermatological]] | ||
** [[Pemphigus]] ([[Pemphigus foliaceus|foliaceus]] or [[Paraneoplastic syndrome|paraneoplastic]]) | ** [[Pemphigus]] ([[Pemphigus foliaceus|foliaceus]] or [[Paraneoplastic syndrome|paraneoplastic]]) | ||
** [[Lichen planus]] | ** [[Lichen planus]] | ||
** [[Alopecia areata]] | ** [[Alopecia areata]] | ||
* Endocrine | * [[Endocrine system|Endocrine]] | ||
** [[Addison's disease|Addison disease]] | ** [[Addison's disease|Addison disease]] | ||
** [[Graves' disease|Grave's disease]] | ** [[Graves' disease|Grave's disease]] | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
** [[Glomerulonephritis]] | ** [[Glomerulonephritis]] | ||
** [[Autoimmune hepatitis]] | ** [[Autoimmune hepatitis]] | ||
* Systemic | * Systemic autoimmune diseases | ||
** [[SLE]] | ** [[SLE]] | ||
** [[Sjögren's syndrome]] | ** [[Sjögren's syndrome]] | ||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''Fatty mass''' | | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Lipoma|Fatty mass]]''' | ||
<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22021525">{{cite journal |vauthors=Molinari F, Bankier AA, Eisenberg RL |title=Fat-containing lesions in adult thoracic imaging |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=197 |issue=5 |pages=W795–813 |date=November 2011 |pmid=22021525 |doi=10.2214/AJR.11.6932 |url=}}</ref> | <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22021525">{{cite journal |vauthors=Molinari F, Bankier AA, Eisenberg RL |title=Fat-containing lesions in adult thoracic imaging |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=197 |issue=5 |pages=W795–813 |date=November 2011 |pmid=22021525 |doi=10.2214/AJR.11.6932 |url=}}</ref> | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* Steroid use | * [[Anabolic steroid|Steroid use]] | ||
* Cushing's syndrome | * [[Cushing's syndrome]] | ||
* | * [[Obesity]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* Mostly asymptomatic | * Mostly [[asymptomatic]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |MRI: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI:]] | ||
* Well-defined encapsulated | * Well-defined encapsulated mass | ||
* Extensive fat content | * Extensive [[fat]] content | ||
* Small amounts of solid areas | * Small amounts of solid areas | ||
* Fibrous septa | * [[Fibrous]] septa | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Mediastinal Lipoma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| Limited images of an MRI of the chest demonstrate the mass to be of fat density. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Mediastinal Lipoma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| Limited images of an MRI of the chest demonstrate the mass to be of fat density. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/20044 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/20044 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Fatty [[Tumor|mass]] can be: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Fat|Fatty]] [[Tumor|mass]] can be: | ||
* [[Lipoma]] | * [[Lipoma]] | ||
* [[Liposarcoma]] | * [[Liposarcoma]] | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
* Caucasians > African and Asian Americans | * Caucasians > African and Asian Americans | ||
* Positive family history of first degree relative | * Positive family history of first degree relative | ||
* [[B cell|B-cell]] activating autoimmune disorders | * [[B cell|B-cell]] activating [[autoimmune disorders]] | ||
* Radiation exposure | * [[Radioactive contamination|Radiation exposure]] | ||
* Infections | * [[Infection|Infections]] | ||
([[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]], [[Hepatitis C|Hep C]], [[Human T-lymphotropic virus|HTLV-1]], [[Epstein Barr virus|EBV]], [[Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus|HHV-8]], [[Helicobacter pylori|H. pylori]], [[psittacosis]], [[Campylobacter jejuni|Campylobacter jejuni)]] | ([[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]], [[Hepatitis C|Hep C]], [[Human T-lymphotropic virus|HTLV-1]], [[Epstein Barr virus|EBV]], [[Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus|HHV-8]], [[Helicobacter pylori|H. pylori]], [[psittacosis]], [[Campylobacter jejuni|Campylobacter jejuni)]] | ||
* Previous [[cancer]] treatment | * Previous [[cancer]] treatment | ||
* Exposure to chemicals and drugs | * [[Exposure effect|Exposure to chemicals and drugs]] | ||
([[Pesticide|pesticides]], [[methotrexate]], [[TNF inhibitor|TNF inhibitors]], [[trichloroethylene]]) | ([[Pesticide|pesticides]], [[methotrexate]], [[TNF inhibitor|TNF inhibitors]], [[trichloroethylene]]) | ||
* [[Smoking|Cigarette smoking]] for ≥ 40 years | * [[Smoking|Cigarette smoking]] for ≥ 40 years | ||
* BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | * [[Body mass index|BMI]] ≥30 kg/m2 | ||
* Diet | * [[Diet (nutrition)|Diet]] | ||
* Hair dyes | * Hair dyes | ||
* [[Breast implant|Breast implants]] | * [[Breast implant|Breast implants]] | ||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
* | * | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* | * [[lymphadenopathy|Painless lymphadenopathy]] | ||
* [[Fever]] | * [[Fever]] | ||
* [[Weight loss]] and [[Anorexia (symptom)|anorexia]] | * [[Weight loss]] and [[Anorexia (symptom)|anorexia]] | ||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
* [[Thrombocytopenia]], [[leukopenia]], or [[pancytopenia]] | * [[Thrombocytopenia]], [[leukopenia]], or [[pancytopenia]] | ||
* [[Lymphocytosis]] with [[malignant]] | * [[Lymphocytosis]] with [[Malignant|malignant cell]] | ||
* [[Thrombocytosis]] | * [[Thrombocytosis]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
}}</ref><ref name="pmid27365459">{{cite journal| author=Vardhana S, Younes A| title=The immune microenvironment in Hodgkin lymphoma: T cells, B cells, and immune checkpoints. | journal=Haematologica | year= 2016 | volume= 101 | issue= 7 | pages= 794-802 | pmid=27365459 | doi=10.3324/haematol.2015.132761 | pmc=5004458 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27365459 }}</ref><ref>Hodgkin-lymphoma. Canadian Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/hodgkin-lymphoma/diagnosis/?region=ab Accessed on September 11, 2015</ref> | }}</ref><ref name="pmid27365459">{{cite journal| author=Vardhana S, Younes A| title=The immune microenvironment in Hodgkin lymphoma: T cells, B cells, and immune checkpoints. | journal=Haematologica | year= 2016 | volume= 101 | issue= 7 | pages= 794-802 | pmid=27365459 | doi=10.3324/haematol.2015.132761 | pmc=5004458 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27365459 }}</ref><ref>Hodgkin-lymphoma. Canadian Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/hodgkin-lymphoma/diagnosis/?region=ab Accessed on September 11, 2015</ref> | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Epstein Barr virus|Epstein-Barr virus]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Epstein Barr virus|Epstein-Barr virus]] | ||
* A history of infection with the [[Epstein-Barr virus]] (EBV) | * A history of [[infection]] with the [[Epstein-Barr virus]] (EBV) | ||
[[Family history]] | [[Family history]] | ||
* First-degree relatives | * First-degree relatives | ||
* Siblings of the same sex | * Siblings of the same sex | ||
[[HIV AIDS|HIV infection]] | [[HIV AIDS|HIV infection]] | ||
* [[HIV]] | * [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV infection]] increases risk | ||
[[Autoimmune diseases]] | [[Autoimmune diseases]] | ||
* [[Rheumatoid arthritis]] | * [[Rheumatoid arthritis]] | ||
| Line 239: | Line 239: | ||
* [[Severe combined immunodeficiency]] ([[SCID]]) | * [[Severe combined immunodeficiency]] ([[SCID]]) | ||
* [[Hypogammaglobulinemia]] | * [[Hypogammaglobulinemia]] | ||
* [[Hyperimmunoglobulin M syndrome]] | * [[Hyper IgM syndrome|Hyperimmunoglobulin M syndrome]] | ||
* [[Primary immunodeficiency|Congenital immunodeficiency]] | * [[Primary immunodeficiency|Congenital immunodeficiency]] | ||
* [[Organ transplant]] or allogeneic [[bone marrow transplant]] | * [[Organ transplant]] or [[Allograft|allogeneic]] [[bone marrow transplant]] | ||
[[Tobacco smoking]] | [[Tobacco smoking]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* | * [[Lymphadenopathy|Painless lymphadenopathy]] with a rubbery consistency | ||
[[B symptoms|Systemic B symptoms]]: | [[B symptoms|Systemic B symptoms]]: | ||
* [[Fever]] ([[Pel-Ebstein fever]]): persistent temperature >38°C (>100.4°F) | * [[Fever]] ([[Pel-Ebstein fever]]): persistent temperature >38°C (>100.4°F) | ||
* | * [[night sweats]] | ||
* | * [[Weight loss]] >10% within the past 6 months | ||
Other | Other | ||
* [[Itch|Pruritus]] | * [[Itch|Pruritus]] | ||
* [[Fatigue]] | * [[Fatigue]] | ||
Mass effect | [[Mass effect (medicine)|Mass effect]] | ||
* [[Chest pain]] | * [[Chest pain]] | ||
* [[Cough]] | * [[Cough]] | ||
* [[Pain]] or | * [[Pain]] or [[Satiety|fullness]] below the [[Rib|ribs]] due to [[Splenomegaly|swollen spleen]] or [[Hepatomegaly|liver]] | ||
* [[Pain]] in [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] after drinking alcohol | * [[Pain]] in [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] after drinking [[alcohol]] | ||
* [[Skin]] [[blushing]] or [[flushing]] | * [[Skin]] [[blushing]] or [[flushing]] | ||
* [[Bone pain]] | * [[Bone pain]] | ||
| Line 267: | Line 267: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Hodgkin's disease ant mediastinum GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing A large soft tissue attenuation mass occupying the anterior mediastinal displaying homogenous attenuation with low-density areas of cystic changes inside. It extends to the middle mediastinum to occupy the pretracheal space and involve the right hilum. Inferiorly it is inseparable from the anterior pericardium. Compression upon the SVC and encasement of the aorta and great vessels are noted. There is also mild right costal pleural thickening and enhancement suggesting infiltration with mild pleural effusion and abdominal retrocaval lymph nodes. Case courtesy of Dr Ahmed Abdrabou | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Hodgkin's disease ant mediastinum GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing A large soft tissue attenuation mass occupying the anterior mediastinal displaying homogenous attenuation with low-density areas of cystic changes inside. It extends to the middle mediastinum to occupy the pretracheal space and involve the right hilum. Inferiorly it is inseparable from the anterior pericardium. Compression upon the SVC and encasement of the aorta and great vessels are noted. There is also mild right costal pleural thickening and enhancement suggesting infiltration with mild pleural effusion and abdominal retrocaval lymph nodes. Case courtesy of Dr Ahmed Abdrabou | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/24432 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/24432 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Positron emission tomography | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Positron emission tomography|Positron emission tomography (PET)]] | ||
*Detect small deposits | *Detect small deposits | ||
*Monitor the response to treatment | *Monitor the response to treatment | ||
*Detect recurrences | *Detect recurrences | ||
*Quantitate the size of lymph nodes with precision | *Quantitate the size of [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] with precision | ||
*Assess for bone marrow involvement | *Assess for [[bone marrow]] involvement | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Mediastinal germ cell tumor]]''' | | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Mediastinal germ cell tumor]]''' | ||
| Line 304: | Line 304: | ||
* [[Hemorrhage]] and [[Necrosis|coagulation necrosis]] | * [[Hemorrhage]] and [[Necrosis|coagulation necrosis]] | ||
* [[Metastasis]] to [[Lymph node metastases|lymph nodes]] and [[Bone metastasis|bone]] | * [[Metastasis]] to [[Lymph node metastases|lymph nodes]] and [[Bone metastasis|bone]] | ||
* [[Germ cell tumors|Non-seminomatous germ cell tumors]] present as large masses with marked [[heterogeneous]] attenuation | * [[Germ cell tumors|Non-seminomatous germ cell tumors]] present as large [[Tumor|masses]] with marked [[heterogeneous]] attenuation | ||
* [[Invasive (medical)|Invasion]] of adjacent structures and [[Metastasis|distant metastasis]] | * [[Invasive (medical)|Invasion]] of adjacent structures and [[Metastasis|distant metastasis]] | ||
* [[Pleural effusion|Pleural]] and [[pericardial effusion]] | * [[Pleural effusion|Pleural]] and [[pericardial effusion]] | ||
| Line 315: | Line 315: | ||
* Benign equal in men and women | * Benign equal in men and women | ||
* [[Malignant]] more common in men | * [[Malignant]] more common in men | ||
* Pediatric population higher risk | * [[Pediatrics|Pediatric population]] higher risk | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Benign | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Benign]] | ||
* Asymptomatic | * [[Asymptomatic]] | ||
Malignant | [[Malignant]] | ||
* [[Cough]] | * [[Cough]] | ||
* [[Chest pain]] | * [[Chest pain]] | ||
| Line 354: | Line 354: | ||
* Unilocular | * Unilocular | ||
[[Acquired disorder|Acquired]] | [[Acquired disorder|Acquired]] | ||
* Multilocular | * Multilocular: | ||
** [[Teratoma]] | ** [[Teratoma]] | ||
** [[Lymphoma]] | ** [[Lymphoma]] | ||
| Line 360: | Line 360: | ||
** [[Autoimmune disorders]] | ** [[Autoimmune disorders]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* Asymptomatic | * [[Asymptomatic]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| Line 380: | Line 380: | ||
<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlBenign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview">{{cite web |url=http://endocrinediseases.org/thyroid/goiter.shtml |title=Benign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlBenign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview">{{cite web |url=http://endocrinediseases.org/thyroid/goiter.shtml |title=Benign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* [[Iodine]] | * [[Iodine deficiency]] | ||
* Female gender | * Female gender | ||
* Age over 50 years | * Age over 50 years | ||
| Line 391: | Line 391: | ||
* [[Radiation]] | * [[Radiation]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* | * [[swelling]] at the base of your [[neck]] | ||
* Tight feeling in [[throat]] | * Tight feeling in [[throat]] | ||
* [[Cough]] | * [[Cough]] | ||
| Line 402: | Line 402: | ||
* [[Nodule (medicine)|Nodules]] | * [[Nodule (medicine)|Nodules]] | ||
* Size | * Size | ||
* Function of the gland: ↑ or | * Function of the gland: [[Hyperthyroidism|↑ hyperthyroidism]], [[Hypothyroidism|↓ hypothyroidism]] or normal ([[euthyroid]]) | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Mediastinal goiter.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing A goitrous left lobe 9cm in its greatest dimension (craniocaudal) extending posterior to the great vessels, 3.4cm below the top of the manubrium. The tracheal axis is shifted to the right and about 2cm below the cricoid cartilage, the trachea is compresssed for a length of 5cm, causing approx. 40% tracheal lumen cross sectional narrowing. Case courtesy of Dr Varun Babu | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Mediastinal goiter.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing A goitrous left lobe 9cm in its greatest dimension (craniocaudal) extending posterior to the great vessels, 3.4cm below the top of the manubrium. The tracheal axis is shifted to the right and about 2cm below the cricoid cartilage, the trachea is compresssed for a length of 5cm, causing approx. 40% tracheal lumen cross sectional narrowing. Case courtesy of Dr Varun Babu | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17104 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/17104 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| Line 409: | Line 409: | ||
[[Hypothyroidism|Hypoactive gland (hypothyroid):]] | [[Hypothyroidism|Hypoactive gland (hypothyroid):]] | ||
* [[Hashimoto's thyroiditis|Hashimoto thyroiditis]] | * [[Hashimoto's thyroiditis|Hashimoto thyroiditis]] | ||
Normal functioning gland | Normal functioning [[Thyroid Gland|gland]] [[Euthyroid|(euthyroid):]] | ||
* Benign thyroid enlargement (non toxic multinodular goiter) | * Benign thyroid enlargement (non toxic multinodular goiter) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 482: | Line 482: | ||
* [[Electrical alternans]] | * [[Electrical alternans]] | ||
[[Echocardiography]]: | [[Echocardiography]]: | ||
* Presence of effusion | * Presence of [[Pericardial effusion|effusion]] | ||
* Reversal of [[Right atrium|RA]] and [[Right ventricle|RV]] [[Diastole|diastolic]] transmural pressures | * Reversal of [[Right atrium|RA]] and [[Right ventricle|RV]] [[Diastole|diastolic]] transmural pressures | ||
* [[Heart|Cardiac chamber]] indentation or [[Collapse (medical)|collapse]] | * [[Heart|Cardiac chamber]] indentation or [[Collapse (medical)|collapse]] | ||
* [[Respiratory]] variation of [[Heart valve|atrioventricular valves]] increased | * [[Respiratory]] variation of [[Heart valve|atrioventricular valves]] increased | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Aortic dissection]]''' | | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Aortic dissection]]''' | ||
| Line 534: | Line 534: | ||
[[CT angiography|CTA]]: | [[CT angiography|CTA]]: | ||
* Beak sign: An [[acute]] angle between the dissection flap and the [[Artery|arterial]] wall | * Beak sign: An [[acute]] angle between the dissection flap and the [[Artery|arterial]] wall | ||
* | * Aortic cobwebs: Fibroelastic bands | ||
* Size: [[False lumen]] larger than the true [[lumen]] | * Size: [[False lumen]] larger than the true [[lumen]] | ||
* Displaced [[Intima|intimal]] [[calcification]]: True lumen | * Displaced [[Intima|intimal]] [[calcification]]: True lumen | ||
| Line 580: | Line 580: | ||
* [[Dizziness]] | * [[Dizziness]] | ||
* [[Fainting]] | * [[Fainting]] | ||
* Sensation of [[head]] or [[ear]] "fullness" | * Sensation of [[Headache|head]] or [[ear]] "fullness" | ||
* Vision changes | * [[Visual disturbance|Vision changes]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | ||
| Line 589: | Line 589: | ||
* Superimposed [[thrombosis]] | * Superimposed [[thrombosis]] | ||
* Mediastinal mass or [[lymphadenopathy]] | * Mediastinal mass or [[lymphadenopathy]] | ||
* Collateral vessels and associated lung masses | * Collateral vessels and associated [[Lung mass|lung masses]] | ||
* | * | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:SVC obstruction GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a large right upper lobe mass abuts the right brachiocephalic vein and SVC. Case courtesy of Dr Henry Knipe | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:SVC obstruction GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a large right upper lobe mass abuts the right brachiocephalic vein and SVC. Case courtesy of Dr Henry Knipe | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/28046 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/28046 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Invasive [[contrast]] [[venography]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Invasive [[contrast]] [[venography]]: | ||
* Etiology of obstruction | * [[Superior vena cava syndrome causes|Etiology of obstruction]] | ||
* Exact location of the obstruction | * Exact location of the obstruction | ||
| Line 604: | Line 604: | ||
* Associated with an [[Atrial septal defect|ASD]] | * Associated with an [[Atrial septal defect|ASD]] | ||
* [[Turner's syndrome|Turner's syndrome (monosomy X)]] | * [[Turner's syndrome|Turner's syndrome (monosomy X)]] | ||
* | * [[scimitar syndrome|The scimitar syndrome]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* [[Asymptomatic]] | * [[Asymptomatic]] | ||
* | * [[dizziness|Exertional dizziness]] | ||
* [[Neck pain]] | * [[Neck pain]] | ||
* [[Diaphoresis]] | * [[Diaphoresis]] | ||
| Line 614: | Line 614: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI with contrast]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI with contrast]]: | ||
* Provide better anatomic definition | * Provide better [[Anatomical|anatomic]] definition | ||
* Associated defects | * Associated defects | ||
* Condition of heart chambers | * Condition of [[Heart chamber|heart chambers]] | ||
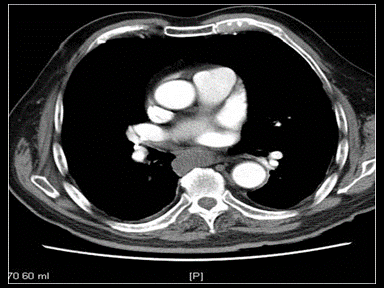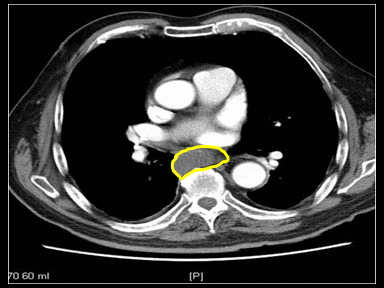
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:TAPVR GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing anomalous origin of right subclavian artery. traversing behind oesophagus as it crosses midline from left to right. Case courtesy of Dr Piyush P Siwach | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:TAPVR GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing anomalous origin of right subclavian artery. traversing behind oesophagus as it crosses midline from left to right. Case courtesy of Dr Piyush P Siwach | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/53955 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/53955 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Associated with | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Associated with | ||
* Adult onset [[Pulmonary hypertension|pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)]] | * Adult onset [[Pulmonary hypertension|pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)]] | ||
* [[Right | * [[Right heart failure|Right ventricular volume overload]] ([[Right heart failure|RV failure)]] | ||
[[Cardiac catheterization|Cardiac catheter]]: | [[Cardiac catheterization|Cardiac catheter]]: | ||
* Pressure and [[Oxygen saturation|O2 Sat]] in heart chambers | * Pressure and [[Oxygen saturation|O2 Sat]] in [[Heart chamber|heart chambers]] | ||
[[Spirometry|PFT]]: | [[Spirometry|PFT]]: | ||
* Normal despite of severe [[Dyspnea|SOB]] | * Normal despite of severe [[Dyspnea|SOB]] | ||
| Line 642: | Line 642: | ||
*[[Sarcoidosis ]] | *[[Sarcoidosis ]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* [[Dysphagia]] for solids and liquids | * [[Dysphagia]] for solids and liquids | ||
* [[Regurgitation]] of undigested food | * [[Regurgitation]] of undigested food | ||
* [[Cough]] | * [[Cough]] | ||
* [[Aspiration]] | * [[Aspiration]] | ||
* [[Weight loss]] | * [[Weight loss]] | ||
* [[Chest pain]], radiate to the back, jaw, neck, and arms | * [[Chest pain]], radiate to the [[Back pain|back]], [[Jaw pain|jaw]], [[Neck pain|neck]], and [[Arm pain|arms]] | ||
* [[Heartburn]] | * [[Heartburn]] | ||
* [[Hiccup]] | * [[Hiccup]] | ||
| Line 655: | Line 655: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[High resolution manometry|High resolution manometry (HRM)]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[High resolution manometry|High resolution manometry (HRM)]]: | ||
* Residual pressure of LES > 10 mmHg | * Residual pressure of [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]] > 10 mmHg | ||
* Incomplete relaxation of the [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]] | * Incomplete relaxation of the [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]] | ||
* Increased resting tone of [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]] | * Increased resting tone of [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]] | ||
* [[Aperistalsis]] | * [[Aperistalsis]] | ||
| Line 667: | Line 667: | ||
* Air fluid level due to absent [[peristalsis]] | * Air fluid level due to absent [[peristalsis]] | ||
* Absence of gastric air bubble | * Absence of gastric air bubble | ||
* In advanced achalasia - sigmoid appearance | * In advanced [[achalasia]] - sigmoid appearance | ||
[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | ||
* Dilatation of the esophagus | * Dilatation of the [[esophagus]] | ||
* Air fluid levels | * Air fluid levels | ||
* Exclude [[pseudoachalasia]] | * Exclude [[pseudoachalasia]] | ||
* | * [[Achalasia]] symptoms resulting from [[esophageal cancer]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease''' | ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease''' | ||
| Line 709: | Line 709: | ||
* [[Anorexia]] | * [[Anorexia]] | ||
* [[Regurgitation (digestion)|Regurgitation]] of food or saliva | * [[Regurgitation (digestion)|Regurgitation]] of food or [[saliva]] | ||
* [[Dysphonia|Hoarseness]] or loss of voice | * [[Dysphonia|Hoarseness]] or [[Voice disturbances|loss of voice]] | ||
* Intractable [[cough]] | * Intractable [[cough]] | ||
* [[Melena|Blood in stools]] | * [[Melena|Blood in stools]] | ||
| Line 720: | Line 720: | ||
* Friable lesion | * Friable lesion | ||
* Superficial [[Plaque|plaques]] | * Superficial [[Plaque|plaques]] | ||
* | * Superficial [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] | ||
* Superficial [[Ulcer|ulcerations]] | * Superficial [[Ulcer|ulcerations]] | ||
* [[Stenosis|Strictures]] | * [[Stenosis|Strictures]] | ||
* [[Ulcer|Ulcerated]] mass | * [[Ulcer|Ulcerated]] [[Tumor|mass]] | ||
* Circumferential masses | * Circumferential [[Tumor|masses]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Esophageal ca GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing irregular circumferential thickening of the mid oesophagus with oesophageal dilatation of the proximal segment, invasion of the adjacent right pleura, periosteal reaction without definite invasion of the right 2nd and 3rd ribs, subcarinal lymph node and multiple bilateral metastatic pulmonary nodules Case courtesy of Dr Ahmed Abdrabou | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Esophageal ca GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing irregular circumferential thickening of the mid oesophagus with oesophageal dilatation of the proximal segment, invasion of the adjacent right pleura, periosteal reaction without definite invasion of the right 2nd and 3rd ribs, subcarinal lymph node and multiple bilateral metastatic pulmonary nodules Case courtesy of Dr Ahmed Abdrabou | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29336 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29336 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Esophagogram|Barium swallow]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Esophagogram|Barium swallow]]: | ||
* Tapering stricture known as a "rat's tail" | * Tapering stricture known as a "rat's tail" | ||
* Irregular stricture | * [[Stenosis|Irregular stricture]] | ||
* Pre-stricture dilatation | * Pre-stricture dilatation | ||
* Shouldering | * Shouldering | ||
| Line 776: | Line 776: | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26240 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26240 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | ||
* Esophageal wall edema and thickening | * Esophageal wall [[edema]] and thickening | ||
* Peri-esophageal fluid | * Peri-esophageal fluid | ||
* [[Mediastinal widening]] | * [[Mediastinal widening]] | ||
| Line 815: | Line 815: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Ultrasound]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Ultrasound]]: | ||
* Location of [[gastroesophageal junction]] | * Location of [[gastroesophageal junction]] | ||
* Bowel diameter measured at the diaphragmatic hiatus | * [[Intestine|Bowel]] diameter measured at the [[Diaphragm (anatomy)|diaphragmatic hiatus]] | ||
[[Ultrasound]] in [[Pediatrics|pediatric]] population: | [[Ultrasound]] in [[Pediatrics|pediatric]] population: | ||
* Measurement of intra-abdominal [[esophagus]] which is less than 2 cm in diameter | * Measurement of intra-abdominal [[esophagus]] which is less than 2 cm in diameter | ||
| Line 859: | Line 859: | ||
*[[Fever]] | *[[Fever]] | ||
*[[Malaise]] | *[[Malaise]] | ||
*[[Flu]]- like illness | *[[Flu]]-like illness | ||
*[[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]] | *[[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]] | ||
*[[Night sweats]] | *[[Night sweats]] | ||
| Line 875: | Line 875: | ||
* Loss of fatty hilum | * Loss of fatty hilum | ||
* Focal [[necrosis]] | * Focal [[necrosis]] | ||
* Cystic necrotic nodes | * [[Lymphangioma|Cystic]] [[necrotic]] [[Lymph node|nodes]] | ||
* Long-to-short axis ratio (>2cm - usually [[benign]]) | * Long-to-short axis ratio (>2cm - usually [[benign]]) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 919: | Line 919: | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/18967 Radiopedia])]] | (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/18967 Radiopedia])]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Physical exam:]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Physical exam:]] | ||
*[[Mediastinal crunch]] or click on [[auscultation]] over the [[Apex of the heart|cardiac apex]] and the [[left sternal border]] synchronous with the [[Heart sounds|heart sound]] [[Hamman's sign|(Hamman's sign)]] | *[[Hamman's crunch|Mediastinal crunch]] or click on [[auscultation]] over the [[Apex of the heart|cardiac apex]] and the [[left sternal border]] synchronous with the [[Heart sounds|heart sound]] [[Hamman's sign|(Hamman's sign)]] | ||
*[[Subcutaneous emphysema physical examination|Subcutaneous crepitation]] | *[[Subcutaneous emphysema physical examination|Subcutaneous crepitation]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 945: | Line 945: | ||
* [[Löfgren syndrome|Lofgren's syndrome]], [[HLA-DRB1|HLA-DRB1*03]] is 4 times higher | * [[Löfgren syndrome|Lofgren's syndrome]], [[HLA-DRB1|HLA-DRB1*03]] is 4 times higher | ||
* [[BTNL2|BTNL-2 (butyrophilin-like 2)]] gene | * [[BTNL2|BTNL-2 (butyrophilin-like 2)]] gene | ||
Immune | Immune system | ||
* Higher expression of [[serum amyloid A]] | * Higher expression of [[serum amyloid A]] | ||
* Immune system exhaustion and failure of effective antigen clearence | * Immune system exhaustion and failure of effective antigen clearence | ||
Drug side effect | [[Adverse effect (medicine)|Drug side effect]] | ||
* [[Adalimumab]] | * [[Adalimumab]] | ||
* [[Etanercept]] | * [[Etanercept]] | ||
* [[Ipilimumab]] | * [[Ipilimumab]] | ||
* [[Infliximab]] | * [[Infliximab]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Sarcoidosis classification|Cutaneous sarcoidosis]] | ||
Cutaneous | |||
* [[Papule|Papular]], [[Nodular lesions|nodular]], [[Plaque|plaque-like]], [[lupus pernio]], [[erythema nodosum]], [[Subcutaneous tissue|subcutaneous]] [[sarcoidosis]] | * [[Papule|Papular]], [[Nodular lesions|nodular]], [[Plaque|plaque-like]], [[lupus pernio]], [[erythema nodosum]], [[Subcutaneous tissue|subcutaneous]] [[sarcoidosis]] | ||
[[Sarcoidosis classification|Ocular sarcoidosis]] | |||
* [[dry eye]], [[blurred vision]], [[photophobia]], [[red eye]], [[Eye pain|pain]] | * [[dry eye]], [[blurred vision]], [[photophobia]], [[red eye]], [[Eye pain|pain]] | ||
[[Upper respiratory tract]] | [[Upper respiratory tract]] | ||
* [[Cough]] | * [[Cough]] | ||
| Line 977: | Line 964: | ||
* [[epistaxis]] | * [[epistaxis]] | ||
* [[Nasal polyp|Nasal polyposis]] | * [[Nasal polyp|Nasal polyposis]] | ||
[[Sarcoidosis|Cardiac sarcoidosis]] | [[Sarcoidosis classification|Cardiac sarcoidosis]] | ||
* [[Palpitation|Palpitations]] | * [[Palpitation|Palpitations]] | ||
* [[syncope]] | * [[syncope]] | ||
| Line 986: | Line 973: | ||
* [[facial nerve palsy|Peripheral facial nerve palsy]] | * [[facial nerve palsy|Peripheral facial nerve palsy]] | ||
* [[Polyuria]] - [[polydipsia]] | * [[Polyuria]] - [[polydipsia]] | ||
* Disturbance in body temperature and [[libido]] due to [[hypothalamic inflammation]] | * Disturbance in [[Thermoregulation|body temperature]] and [[libido]] due to [[Encephalitis|hypothalamic inflammation]] | ||
* [[Seizure|Seizures]] | * [[Seizure|Seizures]] | ||
* [[Sleep disturbance|Impairment in sleep]] | * [[Sleep disturbance|Impairment in sleep]] | ||
| Line 994: | Line 981: | ||
* [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | * [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | ||
[[Musculocutaneous]] | [[Musculocutaneous]] | ||
* Acute [[sarcoid arthritis]] or [[Polyarthritis|acute polyarthritis]] | * Acute [[Sarcoidosis|sarcoid arthritis]] or [[Polyarthritis|acute polyarthritis]] | ||
* [[Arthritis|Chronic arthritis]] | * [[Arthritis|Chronic arthritis]] | ||
* [[Myopathy | * [[Myositis classification|Myopathy(diffuse granulomatous myositis)]] | ||
[[Löfgren syndrome|Lofgren syndrome]] | [[Löfgren syndrome|Lofgren syndrome]] | ||
* [[erythema nodosum]] | * [[erythema nodosum]] | ||
* [[hilar lymphadenopathy]] | * [[hilar lymphadenopathy]] | ||
* [[Migratory polyarthralgia]] | * [[Polyarthralgia|Migratory polyarthralgia]] | ||
* [[fever]] | * [[fever]] | ||
[[Exocrine gland|Exocrine glands]] | [[Exocrine gland|Exocrine glands]] | ||
| Line 1,013: | Line 1,000: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Endoscopy]] with [[biopsy]] and [[histopathology]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Endoscopy]] with [[biopsy]] and [[histopathology]] | ||
* Granulomas can be detected in any organ | * [[Granuloma|Granulomas]] can be detected in any organ | ||
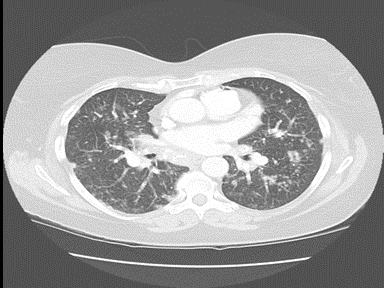
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Sarcoidosis lung.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows extensive calcified lymph | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Sarcoidosis lung.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows extensive calcified lymph nodiiniin mediastinum, extensive architectural distortion of lung tissue, associated with marked fibrosis. Multiple pulmonary nodules are present in both lungs. Case courtesy of Prof Oliver Hennessy (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/34388 Radiopedia])]] | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/34388 Radiopedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Laboratory]] findings: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Laboratory]] findings: | ||
* [[Angiotensin-converting enzyme|Serum ACE]] levels greater than two times the upper limit of normal | * [[Angiotensin-converting enzyme|Serum ACE]] levels greater than two times the upper limit of normal | ||
| Line 1,046: | Line 1,032: | ||
*''[[Candida albicans]]'' | *''[[Candida albicans]]'' | ||
Risk factors: | Risk factors: | ||
* Recent chest surgery | * [[Thoracic surgery|Recent chest surgery]] | ||
* [[Endoscopy]] | * [[Endoscopy]] | ||
* [[Obesity]] | * [[Obesity]] | ||
| Line 1,053: | Line 1,039: | ||
* [[Intensive care unit]] stay > 2 days | * [[Intensive care unit]] stay > 2 days | ||
* [[COPD]] | * [[COPD]] | ||
* Drug users | * [[Intravenous drug use|Drug users]] | ||
* [[Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes]] | ||
* [[Renal insufficiency|Kidney failure]] | * [[Renal insufficiency|Kidney failure]] | ||
| Line 1,071: | Line 1,057: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Growth medium|Culture]] and [[sensitivity]] of [[Mediastinal|mediastinal tissue]] collected by [[biopsy]]/[[Aspiration (medicine)|aspiration]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Growth medium|Culture]] and [[sensitivity]] of [[Mediastinal|mediastinal tissue]] collected by [[biopsy]]/[[Aspiration (medicine)|aspiration]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Sarcoidosis 01.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows airway narrowing of the right lower lobe bronchus. There is thickening of the right pleura and right interlobular septae. There are partially calcified right hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. Case courtesy of Dr Darel E Heitkamp | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Sarcoidosis 01.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows airway narrowing of the right lower lobe bronchus. There is thickening of the right pleura and right interlobular septae. There are partially calcified right hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. Case courtesy of Dr Darel E Heitkamp (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/34388 Radiopedia])]] | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/34388 Radiopedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Physical exam | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Physical exam | ||
*[[Chest wall]] tenderness | *[[Chest wall]] tenderness | ||
| Line 1,080: | Line 1,065: | ||
* [[Leukocytosis]] | * [[Leukocytosis]] | ||
[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | [[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | ||
* Mediastinal or [[ | * [[Mediastinal lymph node|Mediastinal]] or [[Hilar lymphadenopathy|hilar mass]] | ||
* Infiltrative region of soft-tissue attenuation which obliterates normal mediastinal fat planes and encases or invades adjacent structures | * Infiltrative region of soft-tissue attenuation which obliterates normal mediastinal fat planes and encases or invades adjacent structures | ||
* [[Calcification|Calcifications]] of the central mass or associated lymph nodes (especially if there has been preceding [[histoplasmosis]]) | * [[Calcification|Calcifications]] of the central [[Tumor|mass]] or associated [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] (especially if there has been preceding [[histoplasmosis]]) | ||
* [[Tracheobronchial]] narrowing | * [[Tracheobronchial]] narrowing | ||
* [[Pulmonary]] infiltrates | * [[Pulmonary]] infiltrates | ||
| Line 1,091: | Line 1,076: | ||
People at higher [[Risk factor|risk]] | People at higher [[Risk factor|risk]] | ||
* Veterinarians | * Veterinarians | ||
* Laboratory professionals dealing the bacteria | * Laboratory professionals dealing the [[bacteria]] | ||
* Health care workers | * Health care workers | ||
* Livestock producers | * Livestock producers | ||
| Line 1,105: | Line 1,090: | ||
* | * | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
Inhalation or | [[Inhalation anthrax|Inhalation]] or [[Inhalation anthrax|pulmonary anthrax]] | ||
* [[Fatigue]] | * [[Fatigue]] | ||
* [[Body aches|Body pain]] | * [[Body aches|Body pain]] | ||
| Line 1,122: | Line 1,107: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Culture and sensitivity: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Culture medium|Culture]] and sensitivity: | ||
* [[Serum]] | * [[Serum]] | ||
* [[Blood plasma|Plasma]] | * [[Blood plasma|Plasma]] | ||
| Line 1,128: | Line 1,113: | ||
* [[Pleural effusion|Pleural fluid]] | * [[Pleural effusion|Pleural fluid]] | ||
* [[CSF]] | * [[CSF]] | ||
* [[Biopsy]] | * [[Biopsy|Biopsy specimen]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Antrax GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows showing bilateral pulmonary consolidation (yellow arrows) and pleural effusions (blue arrows). Case courtesy and picture courtesy: [https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/7/6/01-0604-f4 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Antrax GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows showing bilateral pulmonary consolidation (yellow arrows) and pleural effusions (blue arrows). Case courtesy and picture courtesy: [https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/7/6/01-0604-f4 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | ||
* [[Mediastinal widening]] | * [[Mediastinal widening]] | ||
* Hyperdense [[lymph nodes]] in the [[mediastinum]] | * Hyperdense [[lymph nodes]] in the [[mediastinum]] | ||
* Lymph node [[hemorrhage]] and [[necrosis]] following [[spore]] | * Lymph node [[hemorrhage]] and [[necrosis]] following [[spore|spore germination]] and [[Vegetation (pathology)|vegetative growth]] with [[exotoxin]] elaboration | ||
* [[Edema]] of [[mediastinal]] fat | * [[Edema]] of [[mediastinal]] fat | ||
PCR | [[Polymerase chain reaction|PCR]] | ||
* Confirms [[virulence]] of [[Bacillus anthracis|organism]] by [[virulence factor]] [[genes]] | * Confirms [[virulence]] of [[Bacillus anthracis|organism]] by [[virulence factor]] [[genes]] | ||
| Line 1,149: | Line 1,134: | ||
* Elderly | * Elderly | ||
* Infants | * Infants | ||
* IV drug users | * [[Intravenous drug use (recreational)|IV drug users]] | ||
[[Immunosuppression]]: | [[Immunosuppression]]: | ||
* [[AIDS]] | * [[AIDS]] | ||
* [[Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes]] | ||
* [[Silicosis]] | * [[Silicosis]] | ||
* [[Malignancy]], such as head and neck cancers | * [[Malignancy]], such as [[Head and neck cancer|head and neck cancers]] | ||
* [[Hematology|Hematologic]] and [[Reticuloendothelial system|reticuloendothelial]] | * [[Hematology|Hematologic]] and [[Reticuloendothelial system|reticuloendothelial disease]] | ||
* [[End-stage kidney disease]] | * [[End-stage kidney disease]] | ||
* History of [[gastrectomy]] | * History of [[gastrectomy]] | ||
| Line 1,162: | Line 1,147: | ||
The risk of contracting [[TB]] increases in: | The risk of contracting [[TB]] increases in: | ||
* Frequent contact with people who have [[TB]] | * Frequent contact with people who have [[TB]] | ||
* | * [[Nutritional deficiencies|Poor nutrition]] | ||
* Smoking | * [[Smoking]] | ||
* Bad hygiene | * Bad hygiene | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* [[Cough]] (most common | * [[Cough]] (most common) | ||
* [[Fever]] | * [[Fever]] | ||
| Line 1,233: | Line 1,218: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Bronchogenic cyst GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows a large fluid density cystic structure abutting the right side of the superior mediastinum without evidence of invasion into either the mediastinum or the lung. It is well circumscribed and has appearances most consistent with a bronchogenic cyst. Case courtesy of Dr Gagandeep Choudhary | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Bronchogenic cyst GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows a large fluid density cystic structure abutting the right side of the superior mediastinum without evidence of invasion into either the mediastinum or the lung. It is well circumscribed and has appearances most consistent with a bronchogenic cyst. Case courtesy of Dr Gagandeep Choudhary (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/10946 Radiopedia])]] | ||
(Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/10946 Radiopedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan:]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan:]] | ||
* Spherical or oval [[Tumor|mass]] | * Spherical or oval [[Tumor|mass]] | ||
| Line 1,248: | Line 1,232: | ||
<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25184121">{{cite journal |vauthors=Liu R, Adler DG |title=Duplication cysts: Diagnosis, management, and the role of endoscopic ultrasound |journal=Endosc Ultrasound |volume=3 |issue=3 |pages=152–60 |date=July 2014 |pmid=25184121 |pmc=4145475 |doi=10.4103/2303-9027.138783 |url=}}</ref> | <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25184121">{{cite journal |vauthors=Liu R, Adler DG |title=Duplication cysts: Diagnosis, management, and the role of endoscopic ultrasound |journal=Endosc Ultrasound |volume=3 |issue=3 |pages=152–60 |date=July 2014 |pmid=25184121 |pmc=4145475 |doi=10.4103/2303-9027.138783 |url=}}</ref> | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* Rare congenital gastrointestinal malformation | * Rare [[Congenital malformations|congenital gastrointestinal malformation]] | ||
* | * | ||
| Line 1,278: | Line 1,262: | ||
* [[Cancer|Malignancy]] suspicion | * [[Cancer|Malignancy]] suspicion | ||
[[Endoscopy]] | [[Endoscopy]] | ||
* Indistinguishable from a [[lipoma]], [[leiomyoma]], a [[gastrointestinal stromal tumor | * Indistinguishable from a [[lipoma]], [[leiomyoma]], a [[gastrointestinal stromal tumor|gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)]], or other [[Submucosal|submucosal lesions]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease''' | ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease''' | ||
| Line 1,301: | Line 1,285: | ||
* [[Constipation]] | * [[Constipation]] | ||
* [[Failure to thrive]] | * [[Failure to thrive]] | ||
* Signs and symptoms of genetic defects | * Signs and symptoms of [[Genetic disorder|genetic defects]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | + | ||
| Line 1,321: | Line 1,305: | ||
<ref name="pmid14740430">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hellmich B, Ehlers S, Csernok E, Gross WL |title=Update on the pathogenesis of Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. |volume=21 |issue=6 Suppl 32 |pages=S69–77 |date=2003 |pmid=14740430 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid29240526">{{cite journal |vauthors=Safran T, Masckauchan M, Maj J, Green L |title=Wells syndrome secondary to influenza vaccination: A case report and review of the literature |journal=Hum Vaccin Immunother |volume= |issue= |pages=1–3 |date=December 2017 |pmid=29240526 |doi=10.1080/21645515.2017.1417714 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20623310">{{cite journal |vauthors=Szczeklik W, Sokołowska B, Mastalerz L, Grzanka P, Górka J, Pacułt K, Miszalski-Jamka T, Soja J, Musiał J |title=Pulmonary findings in Churg-Strauss syndrome in chest X-rays and high resolution computed tomography at the time of initial diagnosis |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=29 |issue=10 |pages=1127–34 |date=October 2010 |pmid=20623310 |doi=10.1007/s10067-010-1530-3 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15818205">{{cite journal |vauthors=Silva CI, Müller NL, Fujimoto K, Johkoh T, Ajzen SA, Churg A |title=Churg-Strauss syndrome: high resolution CT and pathologic findings |journal=J Thorac Imaging |volume=20 |issue=2 |pages=74–80 |date=May 2005 |pmid=15818205 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21496416">{{cite journal |vauthors=Feng RE, Xu WB, Shi JH, Mahmoudi A, Mu WB, Zheng WJ, Zhu YJ, Liu HR |title=Pathological and high resolution CT findings in Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Chin. Med. Sci. J. |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=1–8 |date=March 2011 |pmid=21496416 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | <ref name="pmid14740430">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hellmich B, Ehlers S, Csernok E, Gross WL |title=Update on the pathogenesis of Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. |volume=21 |issue=6 Suppl 32 |pages=S69–77 |date=2003 |pmid=14740430 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid29240526">{{cite journal |vauthors=Safran T, Masckauchan M, Maj J, Green L |title=Wells syndrome secondary to influenza vaccination: A case report and review of the literature |journal=Hum Vaccin Immunother |volume= |issue= |pages=1–3 |date=December 2017 |pmid=29240526 |doi=10.1080/21645515.2017.1417714 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20623310">{{cite journal |vauthors=Szczeklik W, Sokołowska B, Mastalerz L, Grzanka P, Górka J, Pacułt K, Miszalski-Jamka T, Soja J, Musiał J |title=Pulmonary findings in Churg-Strauss syndrome in chest X-rays and high resolution computed tomography at the time of initial diagnosis |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=29 |issue=10 |pages=1127–34 |date=October 2010 |pmid=20623310 |doi=10.1007/s10067-010-1530-3 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15818205">{{cite journal |vauthors=Silva CI, Müller NL, Fujimoto K, Johkoh T, Ajzen SA, Churg A |title=Churg-Strauss syndrome: high resolution CT and pathologic findings |journal=J Thorac Imaging |volume=20 |issue=2 |pages=74–80 |date=May 2005 |pmid=15818205 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21496416">{{cite journal |vauthors=Feng RE, Xu WB, Shi JH, Mahmoudi A, Mu WB, Zheng WJ, Zhu YJ, Liu HR |title=Pathological and high resolution CT findings in Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Chin. Med. Sci. J. |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=1–8 |date=March 2011 |pmid=21496416 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* [[ | * [[HLA-DRB1|HLA-DRB1*04]] and [[HLA-DRB1|*07]] | ||
* [[ | * [[HLA DRB4|HLA - DRB4]] | ||
* [[Allergen|Allergens]] | * [[Allergen|Allergens]] | ||
* [[Infection|Infections]] | * [[Infection|Infections]] | ||
* [[Vaccination|Vaccinations]] (eg, [[influenza]]) | * [[Vaccination|Vaccinations]] (eg, [[influenza]]) | ||
* [[:Category:Drugs|Drugs]]: | * [[:Category:Drugs|Drugs]]: | ||
** [[Leukotriene antagonist|Leukotriene receptor antagonists]]/ leukotriene modifying agents | ** [[Leukotriene antagonist|Leukotriene receptor antagonists]]/ [[Montelukast|leukotriene modifying agents]] | ||
** | ** [[Omalizumab|Anti IgE antibodies]] (eg, [[omalizumab]]) | ||
** [[Mesalazine]] | ** [[Mesalazine]] | ||
** [[Propylthiouracil]] | ** [[Propylthiouracil]] | ||
| Line 1,406: | Line 1,390: | ||
* [[Congenital anomalies of spine|Vertebral anomalies]] | * [[Congenital anomalies of spine|Vertebral anomalies]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Neurenteric Cyst new GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT showing a well-defined posterior mediastinal cystic lesion (highlight) is seen with air-fluid levels showing mucosal enhancement. A cystic mass is extending in between and is displacing descending thoracic aorta anteriorly (curved arrow), azygous vein posteriorly (straight arrow). | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Neurenteric Cyst new GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT showing a well-defined posterior mediastinal cystic lesion (highlight) is seen with air-fluid levels showing mucosal enhancement. A cystic mass is extending in between and is displacing descending thoracic aorta anteriorly (curved arrow), azygous vein posteriorly (straight arrow). [https://10.21699/ajcr.v7i4.454 Source: Case courtesy of Taruna Yadav et al]]] | ||
[https://10.21699/ajcr.v7i4.454 Source: Case courtesy of Taruna Yadav et al]]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Postnatal]] [[chest X-ray]]: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Postnatal]] [[chest X-ray]]: | ||
* [[Posterior mediastinum|Posterior mediastinal]] [[Tumor|mass]] with associated [[Congenital anomalies of spine|vertebral anomalies]] | * [[Posterior mediastinum|Posterior mediastinal]] [[Tumor|mass]] with associated [[Congenital anomalies of spine|vertebral anomalies]] | ||
| Line 1,420: | Line 1,403: | ||
* | * | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* [[Abdominal pain]] - constant [[pain]] or deep [[Abdominal pain|ache in the abdomen]] | * [[Abdominal pain]] - constant [[Abdominal pain|pain]] or deep [[Abdominal pain|ache in the abdomen]] | ||
* [[Back pain|Pain radiating to the back]] | * [[Back pain|Pain radiating to the back]] | ||
* [[Abdominal mass]] | * [[Abdominal mass]] | ||
* [[Bloating | * [[Bloating|Bloating of the abdomen]] | ||
* Difficulty eating | * Difficulty eating | ||
* [[Indigestion]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Histopathology]] and [[Cell biology|cytology]] of cyst and fluid content | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Histopathology]] and [[Cell biology|cytology]] of [[cyst]] and fluid content | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Mediastinal pancreatic pseudocyst.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a low attenuating thick walled peripherally enhancing cystic lesion, measuring approximately 5.2 x 2.8 cm noted in the lower aspect of posterior mediastinum and appears to arise adjacent to the esophageal hiatus and extending up to the carina. | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Mediastinal pancreatic pseudocyst.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a low attenuating thick walled peripherally enhancing cystic lesion, measuring approximately 5.2 x 2.8 cm noted in the lower aspect of posterior mediastinum and appears to arise adjacent to the esophageal hiatus and extending up to the carina. | ||
Case courtesy of Dr Prashant Mudgal | Case courtesy of Dr Prashant Mudgal | ||
| Line 1,434: | Line 1,418: | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]] | ||
* Thin-walled | * Thin-walled | ||
* Fluid-containing [[cyst]] within the posterior mediastinum | * Fluid-containing [[cyst]] within the [[posterior mediastinum]] | ||
* In continuity with the intrapancreatic or peripancreatic fluid collections | * In continuity with the intrapancreatic or peripancreatic fluid collections | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,458: | Line 1,442: | ||
* [[Alcohol abuse|Alcohol use]] | * [[Alcohol abuse|Alcohol use]] | ||
* [[Caffeine]] use | * [[Caffeine]] use | ||
* | * [[Folate deficiency|Low folate intake]] | ||
* Elevated glycaemic load or index | * Elevated glycaemic load or index | ||
* Low [[methionine]] intake | * Low [[methionine]] intake | ||
* Low serum [[choline]] level | * Low serum [[choline]] level | ||
* Low serum | * [[Vitamin B12 deficiency|Low serum vitamin B12 level]] | ||
* | * [[Vitamin C deficiency|Low vitamin C level]] | ||
* | * [[Zinc deficiency|Low zinc intake]] | ||
* [[Smoking]] | * [[Smoking]] | ||
* [[Hyperthermia]] | * [[Hyperthermia]] | ||
* | * [[Perinatal infection|Maternal infections]] and illnesses | ||
* Pregestational insulin-dependent | * [[diabetes|Pregestational insulin-dependent diabetes]] | ||
* | * [[obesity|Pregestational obesity]] | ||
* [[Psychosocial|Psychosocial stress]] | * [[Psychosocial|Psychosocial stress]] | ||
* [[Valproic acid]] use | * [[Valproic acid]] use | ||
2. Environmental factors: | 2. Environmental factors: | ||
* Ambient air pollution | * [[Air pollution|Ambient air pollution]] | ||
* Disinfectant by-products in drinking water | * Disinfectant by-products in drinking water | ||
* Indoor air pollution | * [[Air pollution|Indoor air pollution]] | ||
* Nitrate-related compounds | * Nitrate-related compounds | ||
* Organic solvents | * [[Solvent|Organic solvents]] | ||
* [[Pesticides]] | * [[Pesticides]] | ||
* [[Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons]] | * [[Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons]] | ||
| Line 1,485: | Line 1,469: | ||
* [[Bowel]] incontinence | * [[Bowel]] incontinence | ||
* [[Sensation]] problems in the [[lower extremity]] | * [[Sensation]] problems in the [[lower extremity]] | ||
* Motor problems in the lower extremity | * [[Motor skills disorder|Motor problems in the lower extremity]] | ||
* [[Headache]] | * [[Headache]] | ||
[[Orthopedic|Orthopedic abnormalities]]: | [[Orthopedic|Orthopedic abnormalities]]: | ||
| Line 1,497: | Line 1,481: | ||
* [[Memory]] | * [[Memory]] | ||
* [[Abstraction]] | * [[Abstraction]] | ||
* [[Attention|Attention problems]] | * [[Attention|Attention problems]] | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 18 February 2019
|
WikiDoc Resources for Mediastinal mass |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Mediastinal mass Most cited articles on Mediastinal mass |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Mediastinal mass |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Mediastinal mass at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Mediastinal mass Clinical Trials on Mediastinal mass at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Mediastinal mass NICE Guidance on Mediastinal mass
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Mediastinal mass Discussion groups on Mediastinal mass Patient Handouts on Mediastinal mass Directions to Hospitals Treating Mediastinal mass Risk calculators and risk factors for Mediastinal mass
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Mediastinal mass |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Trusha Tank, M.D.[2], Amr Marawan, M.D. [3]
Synonyms and keywords: Mediastinal enlargement; mass in the mediastinum
Differential diagnosis of mediastinal mass
Wide variety of medical conditions can present as a mediastinal mass on radiological imaging.
- Mediastinal mass may cause obstruction, entrapment or infiltration of other mediastinal organs such as: Trachea, bronchi, esophagus, aorta, superior vena cava (SVC) or heart.[1]
- Disorder caused by any kind of mediastinal mass is collectively known as: Mediastinal syndromes
- Mediastinal syndrome includes:
- Compression of the trachea: Dyspnea and respiratory insufficiency.
- Compression of the esophagus: Dysphagia.
- Compression of SVC causes superior vena cava syndrome: Vein distention, edema of the face or upper extremities and a positive Pemberton's sign.
- Pemberton's sign: Development of suffusion, plethora, or duskiness upon elevation of the arms above the head in patient
- Superior vena cava syndrome is the most severe complication of mediastinal syndrome and a medical emergency.
| ABBREVIATIONS: N/A: Not available, SOB: Shortness of breath, M/C: Most common, RI: Respiratory insufficiency, NM: Neuromuscular system, SVCS: Superior vena cava syndrome, SLE: Systemic lupus erythematosus disease, T3: Triiodothyronine, T4: Thyroxine, TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone, TFT: Thyroid function test | ||||||||
| Disease | Causes/risk factors | Clinical presentation | Paraclinical findings | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General symptoms | Mediastinal syndrome | |||||||
| Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings | |||
| Anterior mediastinal mass | ||||||||
| Tumors | ||||||||
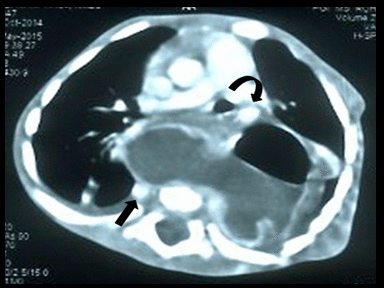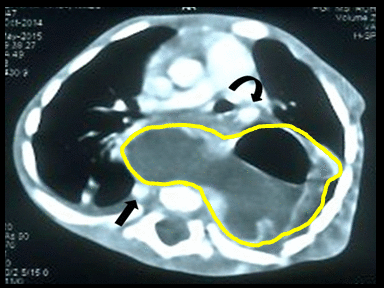
| Thymoma | + | + | + | Biopsy: | 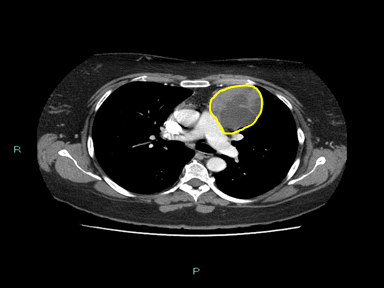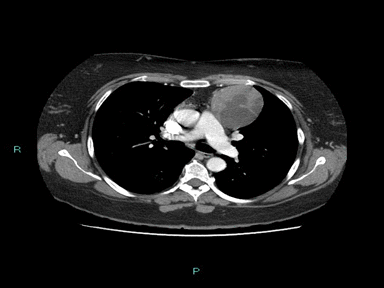 |
Associated condition
| ||
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Fatty mass |
|
- | - | - | MRI: | 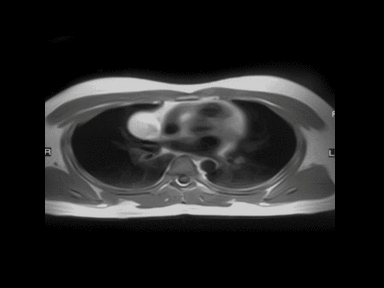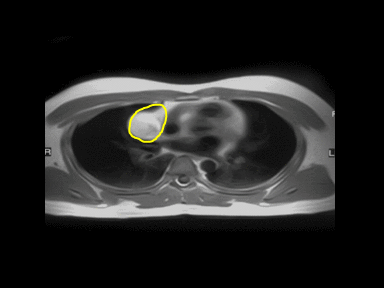 |
Fatty mass can be: | |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
(HIV, Hep C, HTLV-1, EBV, HHV-8, H. pylori, psittacosis, Campylobacter jejuni)
(pesticides, methotrexate, TNF inhibitors, trichloroethylene)
|
+/- | +/- | +/- | Excisional lymph node biopsy with immunohistochemical study
|
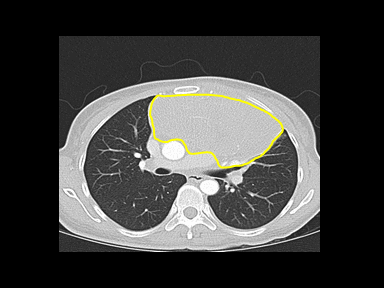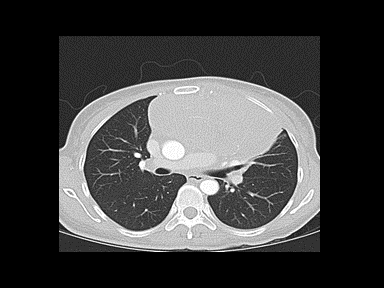 |
| |
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Hodgkin's lymphoma | Epstein-Barr virus
|
Other
|
+ | + | +/- | Lymph node biopsy with immunohistochemistry
|
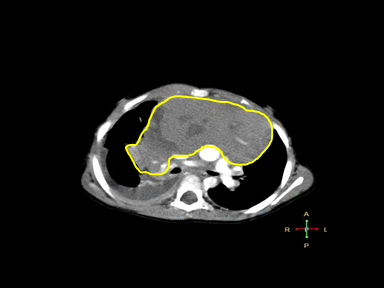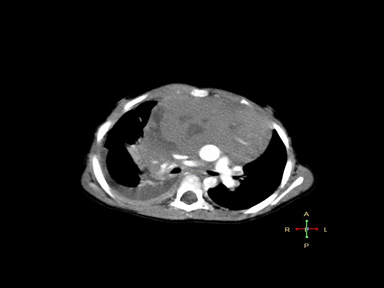 |
Positron emission tomography (PET)
|
| Mediastinal germ cell tumor
(Non-teratomatous) |
|
+ | - | - | Biopsy: | 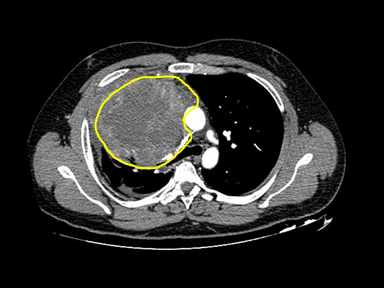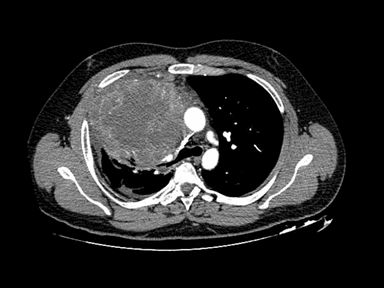 |
CT scan:
Laboratory finding: | |
| Teratoma |
|
Benign | +/- | +/- | +/- | Chest CT scan:
|
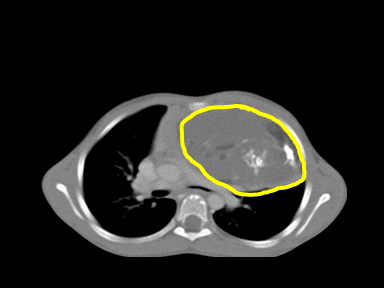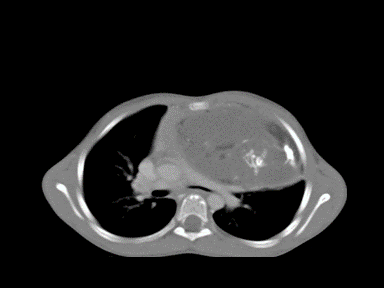 |
N/A |
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Cystic mass | ||||||||
| Thymic cyst | Congenital
|
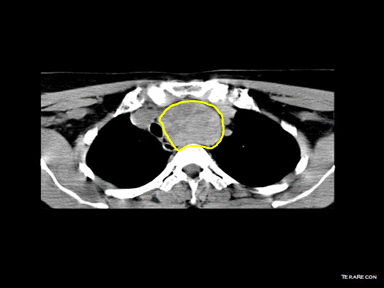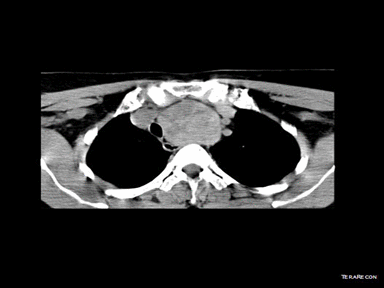
- | - | + | Biopsy with histopathology and cytology | 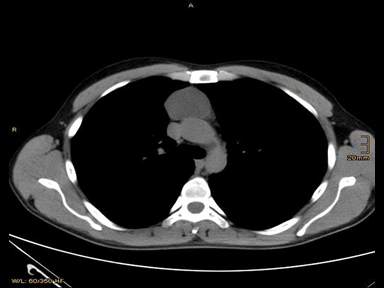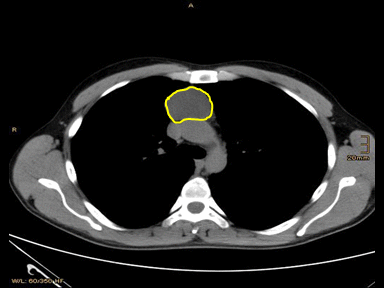 |
CT scan: | |
| Thyroid gland disease | ||||||||
| Mediastinal goiter |
|
+ | + | - | Radioactive iodine scan:
|
 |
Hyperactive gland (hyperthyroid):
Hypoactive gland (hypothyroid): Normal functioning gland (euthyroid):
| |
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Middle mediastinal mass | ||||||||
| Cardiovascular Disease | ||||||||
| Pericardial effusion |
|
|
+ | +/- | - | Echocardiography guided pericardiocentesis:
|
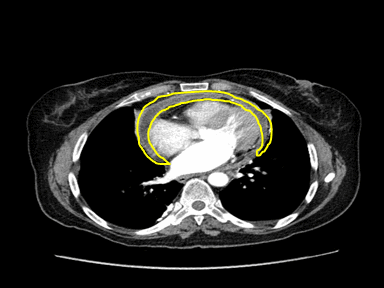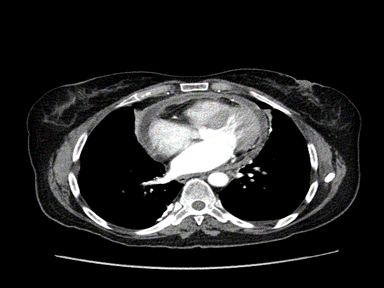 |
Physical findings:
EKG:
|
| Aortic dissection | + | +/- | + | MRI: | 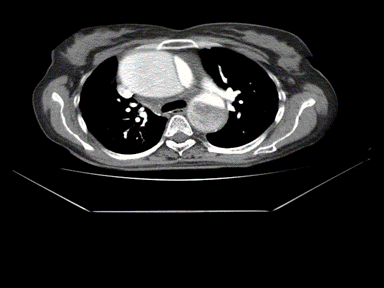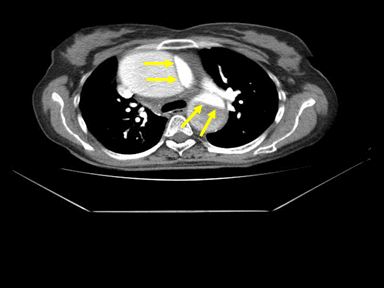 |
TEE:
CTA:
| ||
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Superior vena cava obstruction | Compression of SVC from: |
|
+ | + | ++ | Contrast-enhanced CT scan:
|
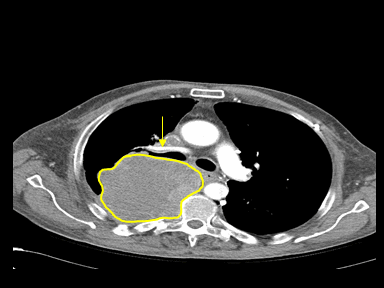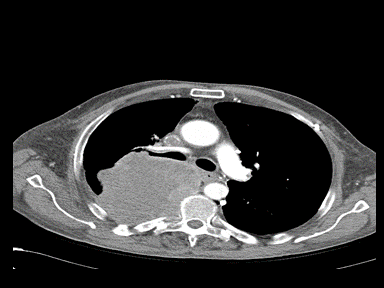 |
Invasive contrast venography:
|
| Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection |
|
+ | - | - | MRI with contrast:
|
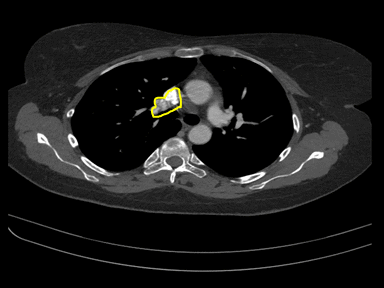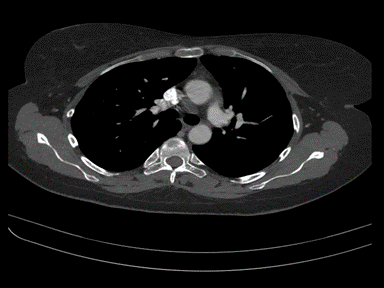 |
Associated with
PFT:
| |
| Gastrointestinal tract disease | ||||||||
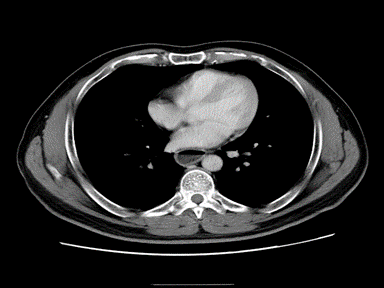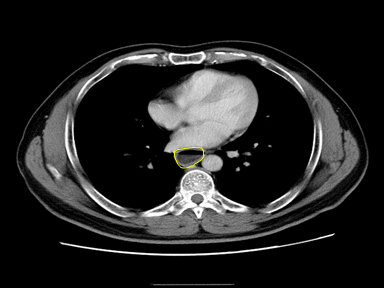
| Esophageal achalasia |
|
+ | + | - | High resolution manometry (HRM):
|
 |
X ray:
| |
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Esophageal cancer |
|
|
- | + | - | Endoscopy with biopsy:
|
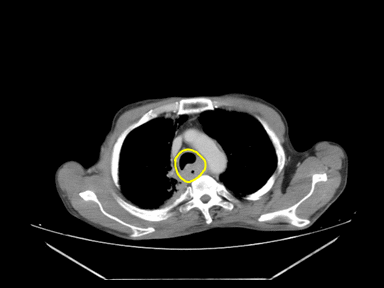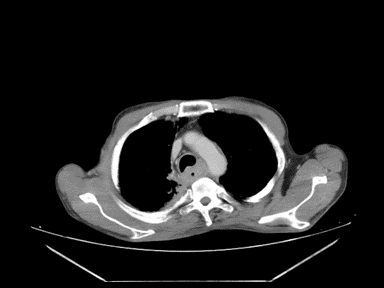 |
Barium swallow:
|
| Esophageal rupture |
|
Other: Patients with cervical perforations can present with
|
+ | + | - | Esophagogram:
|
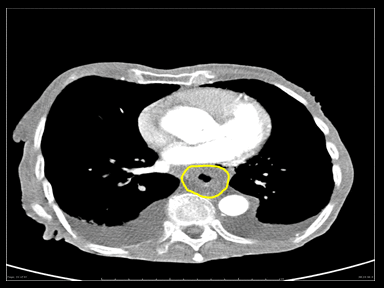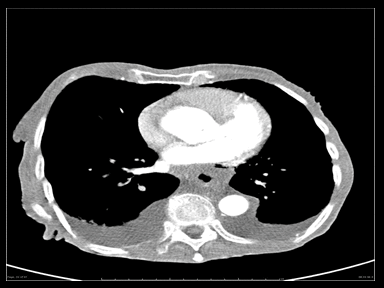 |
CT scan:
|
| Hiatus hernia |
|
- | + | - | High resolution manometry with esophageal pressure topography (EPT):
|
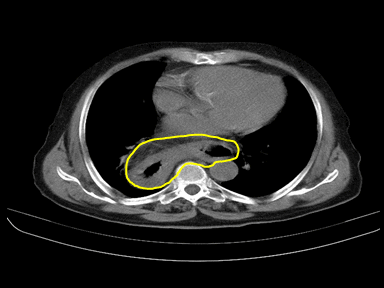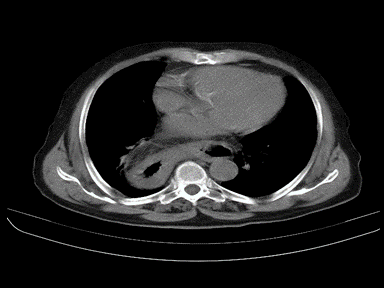 |
Ultrasound:
Ultrasound in pediatric population:
| |
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Pulmonary disease | ||||||||
| Hilar lymphadenopathy | Lymphadenopathy:
|
Constituitional symptoms like:
|
+ | - | - | Lymph node biopsy and histopathology | 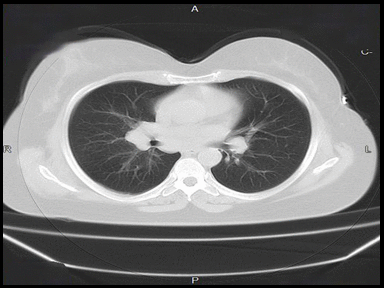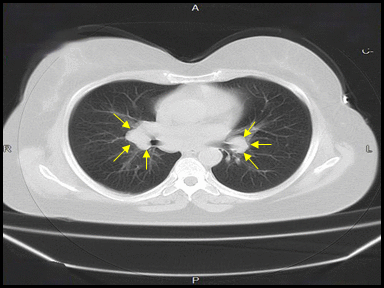 |
CT scan |
| Pneumomediastinum |
|
|
+ | - | - | CT scan:
Pediatric pneumomediastinum: |
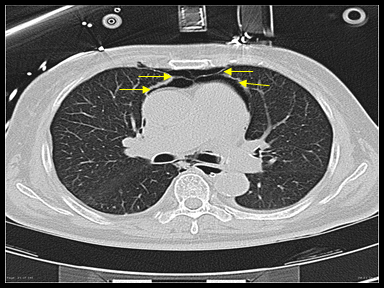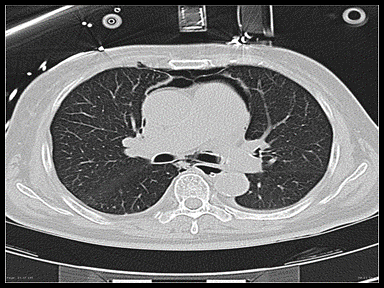 |
Physical exam:
|
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Sarcoidosis |
Immune system
|
Cutaneous sarcoidosis
Renal & electrolyte
|
+ | - | - | Endoscopy with biopsy and histopathology
|
 |
Laboratory findings:
|
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Infectious disease | ||||||||
| Mediastinitis |
Risk factors: |
+ | - | - | Culture and sensitivity of mediastinal tissue collected by biopsy/aspiration | 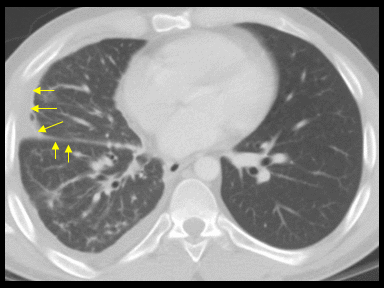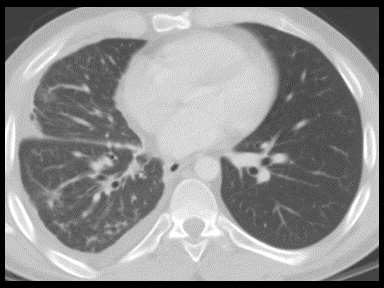 |
Physical exam
| |
| Anthrax | B. anthracis
People at higher risk
|
+ | - | - | Culture and sensitivity: | 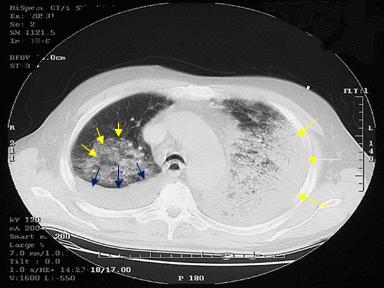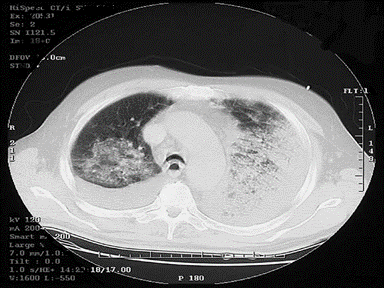 |
CT scan
| |
| Tuberculosis | M. tuberculosis
Traveling or living in endemic regions (Sub-saharan African, Russia, India, Pakistan, China)
The risk of contracting TB increases in:
|
|
+ | - | - | Culture and sensitivity | 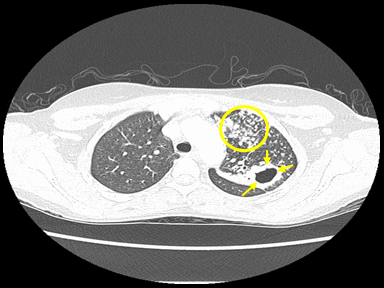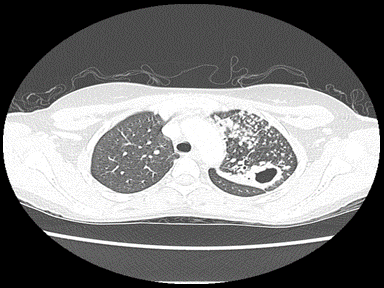 |
Chest X-ray
|
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Cystic mass | ||||||||
| Bronchogenic cyst |
|
|
+ | - | - | CT scan | 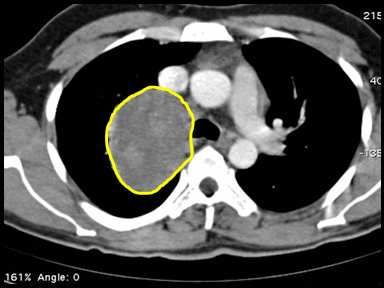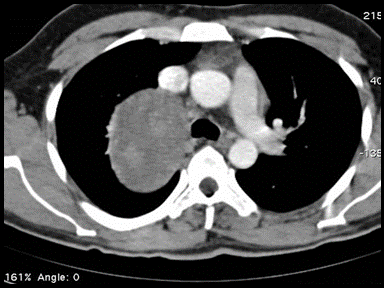 |
CT scan:
|
| Esophageal duplication cysts |
|
|
- | + | - | Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
|
 |
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided FNA
|
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Lymphangioma |
|
|
+ | + | - | Histopathology and cytology | 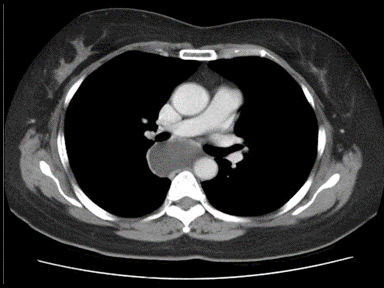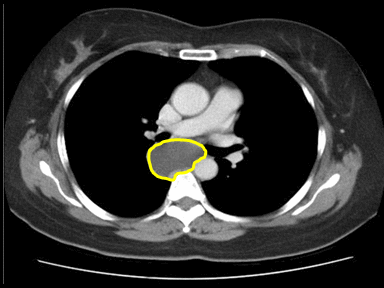 |
|
| Chronic inflammatory disease | ||||||||
| Churg-Strauss syndrome | + | +/- | - | Lung biopsy
4 out of 6 positive :
|
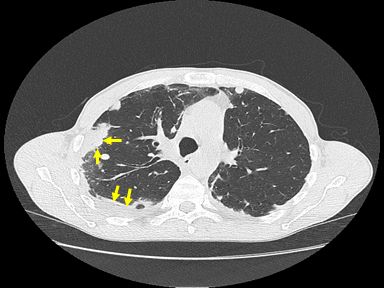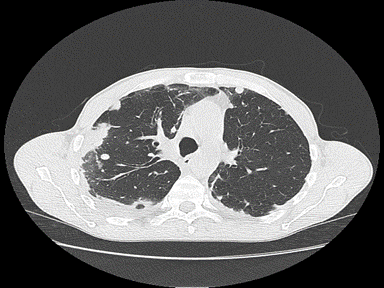 |
High-resolution computerized tomography (HRCT):
| ||
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Posterior mediastinal mass | ||||||||
| Cystic mass | ||||||||
| Mediastinal neurenteric cyst | + | +/- | - | CT scan:
|
 |
Postnatal chest X-ray:
| ||
| Pancreatic pseudocyst |
|
- | - | - | Histopathology and cytology of cyst and fluid content | 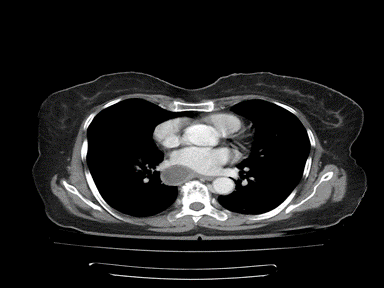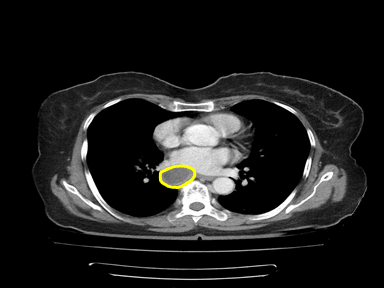 |
CT scan
| |
| Disease | Etiology | Symptoms | Dyspnea/
RI |
Dysphagia | SVCS | Gold standard | Image | Additional findings |
| Central nervous system disease | ||||||||
| Meningocele |
Congenial defect: Maternal nutrition factors:
2. Environmental factors:
|
Symptoms depend on the severity of the defect
Difficulties with executive functions including:
|
- | - | - | Prenatal 2D/3D ultrasound:
|
 |
Laboratory tests:
MRI:
|
| Neurilemmoma |
|
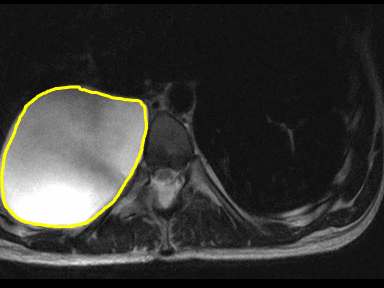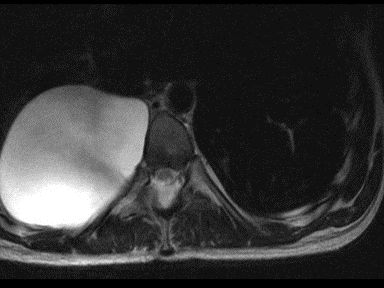
- | - | - | Biopsy with histopathology | 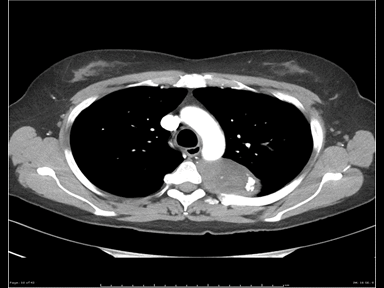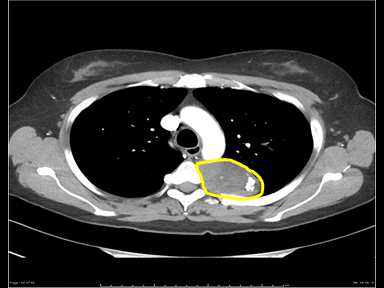 |
MRI | |
| ABBREVIATIONS: N/A: Not available, SOB: Shortness of breath, M/C: Most common, RI: Respiratory insufficiency, NM: Neuromuscular system, SVCS: Superior vena cava syndrome, SLE: Systemic lupus erythematosus disease, T3: Triiodothyronine, T4: Thyroxine, TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone, TFT: Thyroid function test | ||||||||
Causes in Alphabetical Order[80][81]
- Anthrax: This is a classic finding associated with inhaled anthrax. A widened mediastinum was found in 7 of the first 10 victims infected Bacillus anthracis in 2001.[82]
- Aortic dissection
- Bronchogenic cyst
- Churg-Strauss syndrome
- Dermoid cyst
- Esophageal achalasia
- Esophageal cancer
- Esophageal rupture
- Goitre
- Hiatus hernia
- Hilar lymphadenopathy
- Lymphoma
- Mediastinal germ cell tumor
- Mediastinal tumor
- Mediastinitis
- Neurilemmoma
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
- Pericardial effusion
- Pneumomediastinum
- Sarcoidosis
- Superior vena cava obstruction
- Supine AP chest x ray can yield a false positive "widened mediastinum": Among patients who have sustained blunt traum, AP chest radiographs are often obtained in the supine position to maintain spinal precautions. This supine position may result in fluid shifts that are in turn associated with a widening of the mediastinum. After the spine had been "cleared", some authors recommend repeating the chest X ray with the patient in the erect position which results in normalization of the mediastinal size in around 40% of patients.
- Teratoma
- Thymoma
- Thyroid cancer
- Tuberculosis
References
- ↑ Zardi EM, Pipita ME, Afeltra A (October 2016). "Mediastinal syndrome: A report of three cases". Exp Ther Med. 12 (4): 2237–2240. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3596. PMC 5038184. PMID 27698718.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L (February 2013). "A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses". Insights Imaging. 4 (1): 29–52. doi:10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0. PMID 23225215.
- ↑ Molinari F, Bankier AA, Eisenberg RL (November 2011). "Fat-containing lesions in adult thoracic imaging". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 197 (5): W795–813. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.6932. PMID 22021525.
- ↑ Sandlund JT (2015). "Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children". Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 10 (3): 237–43. doi:10.1007/s11899-015-0277-y. PMID 26174528.
- ↑ Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F (2017). "Non-Hodgkin lymphoma". Lancet. 390 (10091): 298–310. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32407-2. PMID 28153383.
- ↑ K. J. Flavell & P. G. Murray (2000). "Hodgkin's disease and the Epstein-Barr virus". Molecular pathology : MP. 53 (5): 262–269. PMID 11091850. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ J. J. Goedert, T. R. Cote, P. Virgo, S. M. Scoppa, D. W. Kingma, M. H. Gail, E. S. Jaffe & R. J. Biggar (1998). "Spectrum of AIDS-associated malignant disorders". Lancet (London, England). 351 (9119): 1833–1839. PMID 9652666. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ M. Tinguely, R. Vonlanthen, E. Muller, C. C. Dommann-Scherrer, J. Schneider, J. A. Laissue & B. Borisch (1998). "Hodgkin's disease-like lymphoproliferative disorders in patients with different underlying immunodeficiency states". Modern pathology : an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. 11 (4): 307–312. PMID 9578079. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Vardhana S, Younes A (2016). "The immune microenvironment in Hodgkin lymphoma: T cells, B cells, and immune checkpoints". Haematologica. 101 (7): 794–802. doi:10.3324/haematol.2015.132761. PMC 5004458. PMID 27365459.
- ↑ Hodgkin-lymphoma. Canadian Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/hodgkin-lymphoma/diagnosis/?region=ab Accessed on September 11, 2015
- ↑ Yalagachin GH (June 2013). "Anterior mediastinal teratoma- a case report with review of literature". Indian J Surg. 75 (Suppl 1): 182–4. doi:10.1007/s12262-012-0569-6. PMID 24426558.
- ↑ No TH, Seol SH, Seo GW, Kim DI, Yang SY, Jeong CH, Hwang YH, Kim JY (September 2015). "Benign Mature Teratoma in Anterior Mediastinum". J Clin Med Res. 7 (9): 726–8. doi:10.14740/jocmr2270w. PMC 4522994. PMID 26251691.
- ↑ Kondov, Goran; Kondov, Borislav; Srceva, Marija Jovanovska; Damjanovski, Goge; Ferati, Imran; Karapetrov, Ivan; Topuzovska, Irena Kondova; Tanevska, Nikolina; Kokareva, Anita (2017). "Giant Mediastinal Thymic Cyst". PRILOZI. 38 (2): 139–145. doi:10.1515/prilozi-2017-0032. ISSN 1857-8985.
- ↑ "Benign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview".
- ↑ Vanneman MW, Fikry K, Quraishi SA, Schoenfeld W (August 2015). "A Young Man with a Mediastinal Mass and Sudden Cardiac Arrest". Ann Am Thorac Soc. 12 (8): 1235–9. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201504-212CC. PMID 26317273.
- ↑ Salem K, Mulji A, Lonn E (November 1999). "Echocardiographically guided pericardiocentesis - the gold standard for the management of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade". Can J Cardiol. 15 (11): 1251–5. PMID 10579740.
- ↑ Weissmann-Brenner A, Schoen R, Divon MY (2004). "Aortic dissection in pregnancy". Obstet Gynecol. 103 (5 Pt 2): 1110–3. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000124984.82336.43. PMID 15121626.
- ↑ Brooke V, Goswami S, Mohanty A, Kasi PM (2012). "Aortic dissection and renal failure in a patient with severe hypothyroidism". Case Rep Med. 2012: 842562. doi:10.1155/2012/842562. PMC 3399550. PMID 22829842.
- ↑ "Classification of diabetic retinopathy from fluorescein angiograms. ETDRS report number 11. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group". Ophthalmology. 98 (5 Suppl): 807–22. 1991. PMID 2062514.
- ↑ Uberoi R (2006). "Quality assurance guidelines for superior vena cava stenting in malignant disease". Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 29 (3): 319–22. doi:10.1007/s00270-005-0284-9. PMID 16502166.
- ↑ Cohen R, Mena D, Carbajal-Mendoza R, Matos N, Karki N (2008). "Superior vena cava syndrome: A medical emergency?". Int. J. Angiol. 17 (1): 43–6. PMID 22477372.
- ↑ Sears EH, Aliotta JM, Klinger JR (2012). "Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return presenting with adult-onset pulmonary hypertension". Pulm Circ. 2 (2): 250–5. doi:10.4103/2045-8932.97637. PMC 3401879. PMID 22837866.
- ↑ Broy C, Bennett S (June 2008). "Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return". Mil Med. 173 (6): 523–4. PMID 18595412.
- ↑ Gockel I, Müller M, Schumacher J (2012). "Achalasia--a disease of unknown cause that is often diagnosed too late". Dtsch Arztebl Int. 109 (12): 209–14. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2012.0209. PMC 3329145. PMID 22532812.
- ↑ Ghoshal UC, Daschakraborty SB, Singh R (2012). "Pathogenesis of achalasia cardia". World J. Gastroenterol. 18 (24): 3050–7. doi:10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3050. PMC 3386318. PMID 22791940.
- ↑ Ates F, Vaezi MF (2015). "The Pathogenesis and Management of Achalasia: Current Status and Future Directions". Gut Liver. 9 (4): 449–63. doi:10.5009/gnl14446. PMC 4477988. PMID 26087861.
- ↑ Boeckxstaens GE, Zaninotto G, Richter JE (2013). "Achalasia". Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60651-0. PMID 23871090.
- ↑ Corley DA, Kerlikowske K, Verma R, Buffler P. Protective association of aspirin/NSAIDs and esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2003;124:47-56. PMID 12512029. See also NCI - "Esophageal Cancer (PDQ®): Prevention".
- ↑ Wong A, Fitzgerald RC. Epidemiologic risk factors for Barrett's esophagus and associated adenocarcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jan;3(1):1-10. PMID 15645398
- ↑ Ye W, Held M, Lagergren J, Engstrand L, Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Nyren O. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric atrophy: risk of adenocarcinoma and squamous-cell carcinoma of the esophagus and adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004 Mar 3;96(5):388-96. PMID 14996860
- ↑ Nakajima S, Hattori T. Oesophageal adenocarcinoma or gastric cancer with or without eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in chronic atrophic gastritis patients: a hypothetical opinion from a systematic review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jul;20 Suppl 1:54-61. PMID 15298606
- ↑ NCI Prevention: Dietary Factors, based on Chainani-Wu N. Diet and oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal cancer. Nutr Cancer 2002;44:104-26. PMID 12734057.
- ↑ McGovern M, Egerton MJ (1991). "Spontaneous perforation of the cervical oesophagus". Med. J. Aust. 154 (4): 277–8. PMID 1994204.
- ↑ Wilson RF, Sarver EJ, Arbulu A, Sukhnandan R (1971). "Spontaneous perforation of the esophagus". Ann. Thorac. Surg. 12 (3): 291–6. PMID 5112482.
- ↑ Bladergroen MR, Lowe JE, Postlethwait RW (1986). "Diagnosis and recommended management of esophageal perforation and rupture". Ann. Thorac. Surg. 42 (3): 235–9. PMID 3753071.
- ↑ Dodds WJ, Stewart ET, Vlymen WJ (1982). "Appropriate contrast media for evaluation of esophageal disruption". Radiology. 144 (2): 439–41. doi:10.1148/radiology.144.2.7089304. PMID 7089304.
- ↑ James AE, Montali RJ, Chaffee V, Strecker EP, Vessal K (1975). "Barium or gastrografin: which contrast media for diagnosis of esophageal tears?". Gastroenterology. 68 (5 Pt 1): 1103–13. PMID 1126592.
- ↑ Schwartz SS (1975). "Letter: Barium or gastrografin: which contrast media for diagnosis of esophageal tears?". Gastroenterology. 69 (6): 1377. PMID 1193339.
- ↑ Vessal K, Montali RJ, Larson SM, Chaffee V, James AE (1975). "Evaluation of barium and gastrografin as contrast media for the diagnosis of esophageal ruptures or perforations". Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 123 (2): 307–19. PMID 1115308.
- ↑ Khajanchee YS, Cassera MA, Swanström LL, Dunst CM (January 2013). "Diagnosis of Type-I hiatal hernia: a comparison of high-resolution manometry and endoscopy". Dis. Esophagus. 26 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01314.x. PMID 22320417.
- ↑ Chang P, Friedenberg F (2014). "Obesity and GERD". Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 43 (1): 161–73. doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2013.11.009. PMC 3920303. PMID 24503366.
- ↑ Jash, Debraj; Maji, Arnab; Patra, Anupam; Sarkar, Supriya (2013). "Approach to unequal hilum on chest X-ray". The Journal of Association of Chest Physicians. 1 (2): 32. doi:10.4103/2320-8775.123204. ISSN 2320-8775.
- ↑ Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A (2014). "Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools". Iran J Med Sci. 39 (2 Suppl): 158–70. PMC 3993046. PMID 24753638.
- ↑ Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A (2014). "Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools". Iran J Med Sci. 39 (2 Suppl): 158–70. PMC 3993046. PMID 24753638.
- ↑ Lymph node enlargment. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymph-node-enlargement Accessed on May 9, 2016
- ↑ Utsumi T, Shiono H, Fukai I, Akashi A (2007). "Artificial pneumomediastinum facilitates thoracoscopic surgery in anterior mediastinum". Interactive cardiovascular and thoracic surgery. 6 (3): 411–2. doi:10.1510/icvts.2006.147355. PMID 17669882.
- ↑ name="pmid18721592">Caceres M, Ali SZ, Braud R, Weiman D, Garrett HE (September 2008). "Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature". Ann. Thorac. Surg. 86 (3): 962–6. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.04.067. PMID 18721592.
- ↑ Kim, Hye Rin; Yoo, Seung Min; Lee, Hwa Yeon; Han, Jin Hee; Frazier, Aletta A; White, Charles S (2016). "Presence of subpleural pulmonary interstitial emphysema as an indication of single or multiple alveolar ruptures on CT in patients with spontaneous pneumomediastinum". Acta Radiologica. 57 (12): 1483–1489. doi:10.1177/0284185116629830. ISSN 0284-1851.
- ↑ . doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.01.11. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Chiu CY, Wong KS, Yao TC, Huang JL (March 2005). "Asthmatic versus non-asthmatic spontaneous pneumomediastinum in children". Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 23 (1): 19–22. PMID 15997870.
- ↑ Iyer VN, Joshi AY, Ryu JH (May 2009). "Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: analysis of 62 consecutive adult patients". Mayo Clin. Proc. 84 (5): 417–21. doi:10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60560-0. PMC 2676124. PMID 19411438.
- ↑ Dionísio, Patrícia; Martins, Luís; Moreira, Susana; Manique, Alda; Macedo, Rita; Caeiro, Fátima; Boal, Luísa; Bárbara, Cristina (2017). "Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: experience in 18 patients during the last 12 years". Jornal Brasileiro de Pneumologia. 43 (2): 101–105. doi:10.1590/s1806-37562016000000052. ISSN 1806-3756.
- ↑ Teirstein AS, Judson MA, Baughman RP, et al: The spectrum of biopsy sites for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 22(2):139 146, 2005.
- ↑ Judson MA, Boan AD, Lackland DT: The clinical course of sarcoidosis: presentation, diagnosis, and treatment in a large white and black cohort in the United States. Sarcoidosis, vasculitis, and diffuse lung diseases : official journal of WASOG 2012, 29(2):119-127.
- ↑ Roberts SD, Mirowski GW, Wilkes D, Kwo PY, Knox KS: Sarcoidosis. Part II: extrapulmonary and systemic manifestations. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2004, 51(4):628-630.
- ↑ Lieberman J, Nosal A, Schlessner A, Sastre-Foken A: Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme for diagnosis and therapeutic evaluation of sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 120(2):329–335, 1979.
- ↑ Martínez Vallina P, Espinosa Jiménez D, Hernández Pérez L, Triviño Ramírez A (2011). "[Mediastinitis]". Arch Bronconeumol. 47 Suppl 8: 32–6. doi:10.1016/S0300-2896(11)70065-5. PMID 23351519.
- ↑ Lewandowski B, Pakla P, Wołek W, Jednakiewicz M, Nicpoń J (2014). "A fatal case of descending necrotizing mediastinitis as a complication of odontogenic infection. A case report". Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 11 (3): 324–8. doi:10.5114/kitp.2014.45685. PMC 4283893. PMID 26336443.
- ↑ Symptoms of mediastinitis. Right Diagnosis (2015). http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/m/mediastinitis/symptoms.htm Accessed on September 28, 2015
- ↑ Mediastinitis: parotid abscess complication. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology (2013). http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S1808-86942014000300268&script=sci_arttext Accessed on September 28, 2015
- ↑ "Symptoms | Anthrax | CDC".
- ↑ "Anthrax in Humans and Animals" (PDF).
- ↑ "Tuberculosis Fact Sheet".
- ↑ Griffith D, Kerr C (1996). "Tuberculosis: disease of the past, disease of the present". J Perianesth Nurs. 11 (4): 240–5. PMID 8964016.
- ↑ Liu R, Adler DG (July 2014). "Duplication cysts: Diagnosis, management, and the role of endoscopic ultrasound". Endosc Ultrasound. 3 (3): 152–60. doi:10.4103/2303-9027.138783. PMC 4145475. PMID 25184121.
- ↑ Carr RF, Ochs RH, Ritter DA, Kenny JD, Fridey JL, Ming PM (June 1986). "Fetal cystic hygroma and Turner's syndrome". Am. J. Dis. Child. 140 (6): 580–3. PMID 3706240.
- ↑ Hellmich B, Ehlers S, Csernok E, Gross WL (2003). "Update on the pathogenesis of Churg-Strauss syndrome". Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 21 (6 Suppl 32): S69–77. PMID 14740430.
- ↑ Safran T, Masckauchan M, Maj J, Green L (December 2017). "Wells syndrome secondary to influenza vaccination: A case report and review of the literature". Hum Vaccin Immunother: 1–3. doi:10.1080/21645515.2017.1417714. PMID 29240526.
- ↑ Szczeklik W, Sokołowska B, Mastalerz L, Grzanka P, Górka J, Pacułt K, Miszalski-Jamka T, Soja J, Musiał J (October 2010). "Pulmonary findings in Churg-Strauss syndrome in chest X-rays and high resolution computed tomography at the time of initial diagnosis". Clin. Rheumatol. 29 (10): 1127–34. doi:10.1007/s10067-010-1530-3. PMID 20623310.
- ↑ Silva CI, Müller NL, Fujimoto K, Johkoh T, Ajzen SA, Churg A (May 2005). "Churg-Strauss syndrome: high resolution CT and pathologic findings". J Thorac Imaging. 20 (2): 74–80. PMID 15818205.
- ↑ Feng RE, Xu WB, Shi JH, Mahmoudi A, Mu WB, Zheng WJ, Zhu YJ, Liu HR (March 2011). "Pathological and high resolution CT findings in Churg-Strauss syndrome". Chin. Med. Sci. J. 26 (1): 1–8. PMID 21496416.
- ↑ Setty, HAN; Hegde, KKS; Narvekar, VN (2005). "Neurenteric cyst of the posterior mediastinum". Australasian Radiology. 49 (2): 151–153. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1673.2005.01360.x. ISSN 0004-8461.
- ↑ Elta, Grace H; Enestvedt, Brintha K; Sauer, Bryan G; Marie Lennon, Anne (2018). "ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 113 (4): 464–479. doi:10.1038/ajg.2018.14. ISSN 0002-9270.
- ↑ "What is Spina Bifida | CDC".
- ↑ Edwards RJ, Witchell C, Pople IK (December 2003). "Chronic headaches in adults with spina bifida and associated hydrocephalus". Eur J Pediatr Surg. 13 Suppl 1: S13–7. doi:10.1055/s-2003-44751. PMID 14758561.
- ↑ Duncan BK (November 1985). "Isolation of insertion, deletion, and nonsense mutations of the uracil-DNA glycosylase (ung) gene of Escherichia coli K-12". J. Bacteriol. 164 (2): 689–95. PMID 2997126.
- ↑ Flenley DC (December 1985). "Disordered breathing during sleep: discussion paper". J R Soc Med. 78 (12): 1031–3. doi:10.1177/014107688507801211. PMID 4067977.
- ↑ Mitchell LE, Adzick NS, Melchionne J, Pasquariello PS, Sutton LN, Whitehead AS (2004). "Spina bifida". Lancet. 364 (9448): 1885–95. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17445-X. PMID 15555669.
- ↑ "Schwannoma | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program".
- ↑ Sailer, Christian, Wasner, Susanne. Differential Diagnosis Pocket. Hermosa Beach, CA: Borm Bruckmeir Publishing LLC, 2002:77 ISBN 1591032016
- ↑ Kahan, Scott, Smith, Ellen G. In A Page: Signs and Symptoms. Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing, 2004:68 ISBN 140510368X
- ↑ Jernigan JA, Stephens DS, Ashford DA; et al. (2001). "Bioterrorism-related inhalational anthrax: the first 10 cases reported in the United States". Emerging Infect. Dis. 7 (6): 933–44. PMID 11747719.