CYP3A4
| Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, polypeptide 4 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | CYP3A4 ; CYP3A; CP33; CP34; CYP3A3; HLP; MGC126680; NF-25; P450C3; P450PCN1 | ||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 HomoloGene: 88816 | ||||||||||
| EC number | 1.14.13.97 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
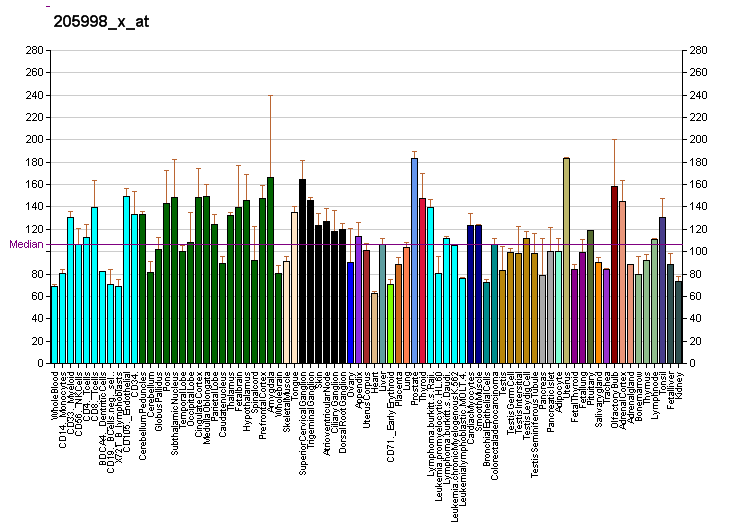
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
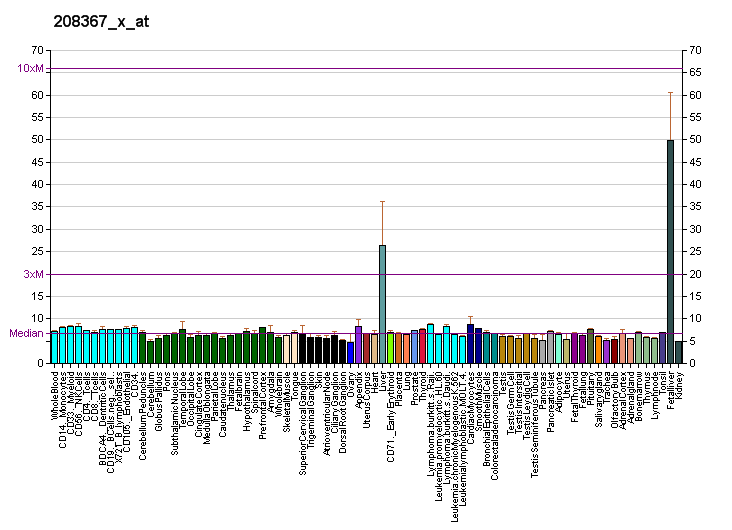 | |||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
|
WikiDoc Resources for CYP3A4 |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on CYP3A4 at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on CYP3A4 at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on CYP3A4
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating CYP3A4 Risk calculators and risk factors for CYP3A4
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) (EC 1.14.13.97), a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is one of the most important enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP3A4 is involved in the oxidation of the largest range of substrates of all the CYPs. CYP3A4 is also, correspondingly, present in the largest quantity of all the CYPs in the liver.
Fetuses do not express CYP3A4 in their liver/tissues; but rather CYP3A7, which acts on a similar range of substrates. CYP3A7 is gradually replaced by CYP3A4 in the developing neonate.
Distribution
Although CYP3A4 is predominantly found in the liver, it is also present in other organs and tissues of the body where it may play an important role in metabolism. CYP3A4 in the intestine plays an important role in the metabolism of certain drugs. Often this allows prodrugs to be activated and absorbed - as in the case of the histamine H1-receptor antagonist terfenadine.
Recently CYP3A4 has also been identified in the brain, however its role in the CNS is still unknown.[1]
Variability
While over 28 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been identified in the CYP3A4 gene, it has been found that this does not translate into significant interindividual variability in vivo. It can be supposed that this may be due to the induction of CYP3A4 on exposure to substrates.
Variability in CYP3A4 function can be determined noninvasively by the erythromycin breath test (ERMBT). The ERMBT estimates in vivo CYP3A4 activity by measuring the radiolabelled carbon dioxide exhaled after an intravenous dose of (14C-N-methyl)-erythromycin.[2]
Induction
CYP3A4 is induced by a wide variety of ligands. These ligands bind to the Pregnane X Receptor (PXR). The activated PXR complex forms a heterodimer with the Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) which binds to the XREM region of the CYP3A4 gene. XREM is a regulatory region of the CYP3A4 gene, and binding causes a cooperative interaction with proximal promoter regions of the gene, resulting in increased transcription and expression of CYP3A4.
CYP3A4 ligands
References
- ↑ Robertson G, Field J, Goodwin B, Bierach S, Tran M, Lehnert A, Liddle C (2003). "Transgenic mouse models of human CYP3A4 gene regulation". Mol Pharmacol. 64 (1): 42–50. doi:10.1124/mol.64.1.42. PMID 12815159.
- ↑ Watkins P (1994). "Noninvasive tests of CYP3A enzymes". Pharmacogenetics. 4 (4): 171–84. doi:10.1097/00008571-199408000-00001. PMID 7987401.
- ↑ Where classes of agents are listed, there may be exceptions within the class
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mentioned both in the reference named FASS and were previously mentioned in Wikipedia. Further contributions may follow other systems
- ↑ [http://www.fass.se/LIF/produktfakta/fakta_lakare_artikel.jsp?articleID=18352 Swedish environmental classification of pharmaceuticals] Facts for prescribers (Fakta för förskrivare)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors have been shown to both induce and inhibit CYP3A4.