Adenocarcinoma of the lung pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
Trushatank (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of [[lung cancer]] found in non-smokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the [[Lung|lungs]]. In past several years many [[Genetics|genetic]] and [[Environmental factor|environmental factors]] has been identified as a [[Causality|causative factor]] for [[lung cancer]]. Individual [[Susceptible individual|susceptibility]], [[smoking|active smoking]], [[radon|radon exposure]], [[Air pollution|exposure to high pollution levels]], [[asbestos|asbestos exposure]], [[Occupational health|occupational]] or [[Environmental factor|environmental exposure]] to particular agents or [[Carcinogen|carcinogens]] contribute to the development of adenocarcinoma of the lung. [[Hydrocarbon|Hydrocarbons]] cause [[DNA damage|damage to the DNA]] and form [[DNA adduct|DNA adducts]]. [[Gene|Genes]] involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of adenocarcinoma of the lung include [[epidermal growth factor receptor|EGFR]], [[HER2]], [[KRAS]], [[anaplastic lymphoma kinase|ALK]], and [[BRAF]]. On [[gross pathology]], peripheral multifocal single or multiple solid firm yellow-white [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] or [[Tumor|mass]] which may invade into the [[pleura]] and cause [[Pleura|pleural]] retraction/puckering. Adenocarcinoma usually does not form a [[Cavity|cavitary lesion]]. It may present as a diffuse [[Pleural cavity|pleural]] thickening resembling [[Mesothelioma|malignant mesothelioma]]. On [[Histopathological|microscopic histopathological analysis]], [[Cell nucleus|nuclear atypia]], eccentrically placed [[Cell nucleus|nuclei]], abundant [[cytoplasm]], and conspicuous [[Nucleolus|nucleoli]] are characteristic findings of adenocarcinoma of the lung. | Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of [[lung cancer]] found in non-smokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the [[Lung|lungs]]. In past several years many [[Genetics|genetic]] and [[Environmental factor|environmental factors]] has been identified as a [[Causality|causative factor]] for [[lung cancer]]. Individual [[Susceptible individual|susceptibility]], [[smoking|active smoking]], [[radon|radon exposure]], [[Air pollution|exposure to high pollution levels]], [[asbestos|asbestos exposure]], [[Occupational health|occupational]] or [[Environmental factor|environmental exposure]] to particular agents or [[Carcinogen|carcinogens]] contribute to the development of adenocarcinoma of the lung. [[Hydrocarbon|Hydrocarbons]] cause [[DNA damage|damage to the DNA]] and form [[DNA adduct|DNA adducts]]. [[Gene|Genes]] involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of adenocarcinoma of the lung include [[epidermal growth factor receptor|EGFR]], [[HER2]], [[KRAS]], [[anaplastic lymphoma kinase|ALK]], and [[BRAF]]. On [[gross pathology]], peripheral multifocal single or multiple solid firm yellow-white [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] or [[Tumor|mass]] which may invade into the [[pleura]] and cause [[Pleura|pleural]] retraction/puckering. Adenocarcinoma usually does not form a [[Cavity|cavitary lesion]]. It may present as a diffuse [[Pleural cavity|pleural]] thickening resembling [[Mesothelioma|malignant mesothelioma]]. On [[Histopathological|microscopic histopathological analysis]], [[Cell nucleus|nuclear atypia]], eccentrically placed [[Cell nucleus|nuclei]], abundant [[cytoplasm]], and conspicuous [[Nucleolus|nucleoli]] are characteristic findings of adenocarcinoma of the lung. | ||
==Pathogenesis== | == Pathophysiology == | ||
===Pathogenesis=== | |||
* Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of [[lung cancer]] found in non-smokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the [[Lung|lungs]], as compared to centrally located [[Tumor|tumors]] such as [[small cell lung cancer]] and [[squamous cell]] lung cancer.<ref name="Travis95">{{cite journal |author=Travis WD, Travis LB, Devesa SS |title=Lung cancer |journal=Cancer |volume=75 |issue=1 Suppl |pages=191–202 |date=January 1995|pmid=8000996 |doi= 10.1002/1097-0142(19950101)75:1+<191::AID-CNCR2820751307>3.0.CO;2-Y|url=}}</ref><ref name="Kumar-adenocarcinoma">{{cite book |chapter=Chapter 13, box on morphology of adenocarcinoma |author=Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson |title=Robbins Basic Pathology|publisher=Saunders |location=Philadelphia |isbn=1-4160-2973-7 |edition=8th}}</ref> | * Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of [[lung cancer]] found in non-smokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the [[Lung|lungs]], as compared to centrally located [[Tumor|tumors]] such as [[small cell lung cancer]] and [[squamous cell]] lung cancer.<ref name="Travis95">{{cite journal |author=Travis WD, Travis LB, Devesa SS |title=Lung cancer |journal=Cancer |volume=75 |issue=1 Suppl |pages=191–202 |date=January 1995|pmid=8000996 |doi= 10.1002/1097-0142(19950101)75:1+<191::AID-CNCR2820751307>3.0.CO;2-Y|url=}}</ref><ref name="Kumar-adenocarcinoma">{{cite book |chapter=Chapter 13, box on morphology of adenocarcinoma |author=Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson |title=Robbins Basic Pathology|publisher=Saunders |location=Philadelphia |isbn=1-4160-2973-7 |edition=8th}}</ref> | ||
* Lung cancer [[pathogenesis]] can be understood with the help of following [[hypothesis]] | * Lung cancer [[pathogenesis]] can be understood with the help of following [[hypothesis]]:<ref name="KanwalDing2017">{{cite journal|last1=Kanwal|first1=Madiha|last2=Ding|first2=Xiao-Ji|last3=Cao|first3=Yi|title=Familial risk for lung cancer|journal=Oncology Letters|volume=13|issue=2|year=2017|pages=535–542|issn=1792-1074|doi=10.3892/ol.2016.5518}}</ref><ref name="KadaraScheet2016">{{cite journal|last1=Kadara|first1=H.|last2=Scheet|first2=P.|last3=Wistuba|first3=I. I.|last4=Spira|first4=A. E.|title=Early Events in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer|journal=Cancer Prevention Research|volume=9|issue=7|year=2016|pages=518–527|issn=1940-6207|doi=10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0400}}</ref><ref name="RasoWistuba2007">{{cite journal|last1=Raso|first1=Maria Gabriela|last2=Wistuba|first2=Ignacio I.|title=Molecular Pathogenesis of Early-Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and a Proposal for Tissue Banking to Facilitate Identification of New Biomarkers|journal=Journal of Thoracic Oncology|volume=2|issue=7|year=2007|pages=S128–S135|issn=15560864|doi=10.1097/JTO.0b013e318074fe42}}</ref> | ||
* '''Familial lung cancer''': | *'''Familial lung cancer''': | ||
** [[Chromosome 6 (human)|6q23–25]] [[Locus (genetics)|locus]] has been identified as a [[Susceptible individual|susceptibility]] [[gene]] for familial [[lung cancer]]. | **[[Chromosome 6 (human)|6q23–25]] [[Locus (genetics)|locus]] has been identified as a [[Susceptible individual|susceptibility]] [[gene]] for familial [[lung cancer]]. | ||
* '''Multistep tumorigenesis''': | *'''Multistep tumorigenesis''': | ||
** [[Tumor|Tumors]] of organs such as [[Skin cancer|skin]], [[lung]] and [[Colorectal cancer|colon]] are developed through a process called [[Tumorigenesis|multistep tumorigenesis]].<ref name="pmid18039118">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wistuba II, Gazdar AF |title=Lung cancer preneoplasia |journal=Annu Rev Pathol |volume=1 |issue= |pages=331–48 |date=2006 |pmid=18039118 |doi=10.1146/annurev.pathol.1.110304.100103 |url=}}</ref> | **[[Tumor|Tumors]] of organs such as [[Skin cancer|skin]], [[lung]] and [[Colorectal cancer|colon]] are developed through a process called [[Tumorigenesis|multistep tumorigenesis]].<ref name="pmid18039118">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wistuba II, Gazdar AF |title=Lung cancer preneoplasia |journal=Annu Rev Pathol |volume=1 |issue= |pages=331–48 |date=2006 |pmid=18039118 |doi=10.1146/annurev.pathol.1.110304.100103 |url=}}</ref> | ||
** As with other [[Epithelial cells|epithelial]] [[Malignancy|malignancies]], [[Lung cancer|lung cancers]] are believed to arise from [[Premalignant condition|preneoplastic or precursor lesions]] in the [[Respiratory epithelium|respiratory mucosa]]. | ** As with other [[Epithelial cells|epithelial]] [[Malignancy|malignancies]], [[Lung cancer|lung cancers]] are believed to arise from [[Premalignant condition|preneoplastic or precursor lesions]] in the [[Respiratory epithelium|respiratory mucosa]]. | ||
** [[Tumorigenesis|Multistep tumorigenesis]] is development of [[tumor]] through a series of progressive [[Pathological|pathologic]] events such as [[Precancerous|preneoplastic]] or [[Precursor|precursor lesions]] with corresponding [[genetic]] and [[Epigenetic|epigenetic aberrations]]. | **[[Tumorigenesis|Multistep tumorigenesis]] is development of [[tumor]] through a series of progressive [[Pathological|pathologic]] events such as [[Precancerous|preneoplastic]] or [[Precursor|precursor lesions]] with corresponding [[genetic]] and [[Epigenetic|epigenetic aberrations]]. | ||
** [[Hyperplasia]], [[squamous metaplasia]], [[Dysplasia|squamous dysplasia]], and [[Carcinoma in situ|carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS)]] comprise changes in the [[Bronchus|large airways]] that precede or accompany [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] [[squamous cell carcinoma of the lung]]. | **[[Hyperplasia]], [[squamous metaplasia]], [[Dysplasia|squamous dysplasia]], and [[Carcinoma in situ|carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS)]] comprise changes in the [[Bronchus|large airways]] that precede or accompany [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] [[squamous cell carcinoma of the lung]]. | ||
** Multistep [[tumorigenesis]] explains pathogenesis of centrally located [[squamous cell carcinoma of the lung]] very well but fails to explain pathogenesis of [[Large cell carcinoma of the lung|large cell lung carcinomas]], [[Adenocarcinoma of the lung|lung adenocarcinomas]], and [[small cell lung cancer]]. | ** Multistep [[tumorigenesis]] explains pathogenesis of centrally located [[squamous cell carcinoma of the lung]] very well but fails to explain pathogenesis of [[Large cell carcinoma of the lung|large cell lung carcinomas]], [[Adenocarcinoma of the lung|lung adenocarcinomas]], and [[small cell lung cancer]]. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
* [[Pathogenesis]] of lung cancer is thought to be result of both due to stepwise, sequence-specific and multistage [[Molecular pathology|molecular pathogenesis]] and due to accumulation and combination of [[Genetics|genetic]] and [[Epigenetics|epigenetic]]<nowiki/>abnormalities. | * [[Pathogenesis]] of lung cancer is thought to be result of both due to stepwise, sequence-specific and multistage [[Molecular pathology|molecular pathogenesis]] and due to accumulation and combination of [[Genetics|genetic]] and [[Epigenetics|epigenetic]]<nowiki/>abnormalities. | ||
=== Field of | === Field of Injury and Field Cancerization === | ||
* [[Premalignant condition|Preneoplastic lung lesions]] frequently extend throughout the [[respiratory epithelium]], indicating a field effect in which much of the [[respiratory epithelium]] has been [[Mutagen|mutagenized]], presumably from [[Tobacco smoking|exposure to tobacco-related carcinogens]].<ref name="DevarakondaMorgensztern2015">{{cite journal|last1=Devarakonda|first1=Siddhartha|last2=Morgensztern|first2=Daniel|last3=Govindan|first3=Ramaswamy|title=Genomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma|journal=The Lancet Oncology|volume=16|issue=7|year=2015|pages=e342–e351|issn=14702045|doi=10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00077-7}}</ref><ref name="pmid27006378">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kadara H, Scheet P, Wistuba II, Spira AE |title=Early Events in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer |journal=Cancer Prev Res (Phila) |volume=9 |issue=7 |pages=518–27 |date=July 2016 |pmid=27006378 |doi=10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0400 |url=}}</ref><ref name="AuerbachStout1961">{{cite journal|last1=Auerbach|first1=Oscar|last2=Stout|first2=A. P.|last3=Hammond|first3=E. Cuyler|last4=Garfinkel|first4=Lawrence|title=Changes in Bronchial Epithelium in Relation to Cigarette Smoking and in Relation to Lung Cancer|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=265|issue=6|year=1961|pages=253–267|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJM196108102650601}}</ref> | * [[Premalignant condition|Preneoplastic lung lesions]] frequently extend throughout the [[respiratory epithelium]], indicating a field effect in which much of the [[respiratory epithelium]] has been [[Mutagen|mutagenized]], presumably from [[Tobacco smoking|exposure to tobacco-related carcinogens]].<ref name="DevarakondaMorgensztern2015">{{cite journal|last1=Devarakonda|first1=Siddhartha|last2=Morgensztern|first2=Daniel|last3=Govindan|first3=Ramaswamy|title=Genomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma|journal=The Lancet Oncology|volume=16|issue=7|year=2015|pages=e342–e351|issn=14702045|doi=10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00077-7}}</ref><ref name="pmid27006378">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kadara H, Scheet P, Wistuba II, Spira AE |title=Early Events in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer |journal=Cancer Prev Res (Phila) |volume=9 |issue=7 |pages=518–27 |date=July 2016 |pmid=27006378 |doi=10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0400 |url=}}</ref><ref name="AuerbachStout1961">{{cite journal|last1=Auerbach|first1=Oscar|last2=Stout|first2=A. P.|last3=Hammond|first3=E. Cuyler|last4=Garfinkel|first4=Lawrence|title=Changes in Bronchial Epithelium in Relation to Cigarette Smoking and in Relation to Lung Cancer|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=265|issue=6|year=1961|pages=253–267|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJM196108102650601}}</ref> | ||
* [[Epithelium|Epithelial cells]] lining the entire [[respiratory tract]] that have been exposed to [[smoking]] show [[Molecular pathology|molecular alterations]] that may signify the onset of lung cancers, a [[paradigm]] known as the "airway field of injury”. | * [[Epithelium|Epithelial cells]] lining the entire [[respiratory tract]] that have been exposed to [[smoking]] show [[Molecular pathology|molecular alterations]] that may signify the onset of lung cancers, a [[paradigm]] known as the "airway field of injury”. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
==== Molecular | ==== Molecular Pathogenesis of Adenocarcinoma of the Lung ==== | ||
* Somatic copy number alterations affect a large fraction of the [[cancer cell]] [[genome]] and are also associated with [[lung cancer]].<ref>{{cite book | last = Stewart | first = Bernard | title = World cancer report 2014 | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization | location = Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland | year = 2014 | isbn = 9283204298 }}</ref><ref name="pmid17625570">{{cite journal| author=Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S et al.| title=Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. | journal=Nature | year= 2007 | volume= 448 | issue= 7153 | pages= 561-6 | pmid=17625570 | doi=10.1038/nature05945 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17625570 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22919003">{{cite journal| author=Davies KD, Le AT, Theodoro MF, Skokan MC, Aisner DL, Berge EM et al.| title=Identifying and targeting ROS1 gene fusions in non-small cell lung cancer. | journal=Clin Cancer Res | year= 2012 | volume= 18 | issue= 17 | pages= 4570-9 | pmid=22919003 | doi=10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0550 | pmc=PMC3703205 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22919003 }} </ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Stewart | first = Bernard | title = World cancer report 2014 | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization | location = Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland | year = 2014 | isbn = 9283204298 }}</ref><ref name="WeirWoo2007">{{cite journal|last1=Weir|first1=Barbara A.|last2=Woo|first2=Michele S.|last3=Getz|first3=Gad|last4=Perner|first4=Sven|last5=Ding|first5=Li|last6=Beroukhim|first6=Rameen|last7=Lin|first7=William M.|last8=Province|first8=Michael A.|last9=Kraja|first9=Aldi|last10=Johnson|first10=Laura A.|last11=Shah|first11=Kinjal|last12=Sato|first12=Mitsuo|last13=Thomas|first13=Roman K.|last14=Barletta|first14=Justine A.|last15=Borecki|first15=Ingrid B.|last16=Broderick|first16=Stephen|last17=Chang|first17=Andrew C.|last18=Chiang|first18=Derek Y.|last19=Chirieac|first19=Lucian R.|last20=Cho|first20=Jeonghee|last21=Fujii|first21=Yoshitaka|last22=Gazdar|first22=Adi F.|last23=Giordano|first23=Thomas|last24=Greulich|first24=Heidi|last25=Hanna|first25=Megan|last26=Johnson|first26=Bruce E.|last27=Kris|first27=Mark G.|last28=Lash|first28=Alex|last29=Lin|first29=Ling|last30=Lindeman|first30=Neal|last31=Mardis|first31=Elaine R.|last32=McPherson|first32=John D.|last33=Minna|first33=John D.|last34=Morgan|first34=Margaret B.|last35=Nadel|first35=Mark|last36=Orringer|first36=Mark B.|last37=Osborne|first37=John R.|last38=Ozenberger|first38=Brad|last39=Ramos|first39=Alex H.|last40=Robinson|first40=James|last41=Roth|first41=Jack A.|last42=Rusch|first42=Valerie|last43=Sasaki|first43=Hidefumi|last44=Shepherd|first44=Frances|last45=Sougnez|first45=Carrie|last46=Spitz|first46=Margaret R.|last47=Tsao|first47=Ming-Sound|last48=Twomey|first48=David|last49=Verhaak|first49=Roel G. W.|last50=Weinstock|first50=George M.|last51=Wheeler|first51=David A.|last52=Winckler|first52=Wendy|last53=Yoshizawa|first53=Akihiko|last54=Yu|first54=Soyoung|last55=Zakowski|first55=Maureen F.|last56=Zhang|first56=Qunyuan|last57=Beer|first57=David G.|last58=Wistuba|first58=Ignacio I.|last59=Watson|first59=Mark A.|last60=Garraway|first60=Levi A.|last61=Ladanyi|first61=Marc|last62=Travis|first62=William D.|last63=Pao|first63=William|last64=Rubin|first64=Mark A.|last65=Gabriel|first65=Stacey B.|last66=Gibbs|first66=Richard A.|last67=Varmus|first67=Harold E.|last68=Wilson|first68=Richard K.|last69=Lander|first69=Eric S.|last70=Meyerson|first70=Matthew|title=Characterizing the cancer genome in lung adenocarcinoma|journal=Nature|volume=450|issue=7171|year=2007|pages=893–898|issn=0028-0836|doi=10.1038/nature06358}}</ref> | * Somatic copy number alterations affect a large fraction of the [[cancer cell]] [[genome]] and are also associated with [[lung cancer]].<ref>{{cite book | last = Stewart | first = Bernard | title = World cancer report 2014 | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization | location = Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland | year = 2014 | isbn = 9283204298 }}</ref><ref name="pmid17625570">{{cite journal| author=Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S et al.| title=Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. | journal=Nature | year= 2007 | volume= 448 | issue= 7153 | pages= 561-6 | pmid=17625570 | doi=10.1038/nature05945 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17625570 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22919003">{{cite journal| author=Davies KD, Le AT, Theodoro MF, Skokan MC, Aisner DL, Berge EM et al.| title=Identifying and targeting ROS1 gene fusions in non-small cell lung cancer. | journal=Clin Cancer Res | year= 2012 | volume= 18 | issue= 17 | pages= 4570-9 | pmid=22919003 | doi=10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0550 | pmc=PMC3703205 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22919003 }} </ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Stewart | first = Bernard | title = World cancer report 2014 | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization | location = Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland | year = 2014 | isbn = 9283204298 }}</ref><ref name="WeirWoo2007">{{cite journal|last1=Weir|first1=Barbara A.|last2=Woo|first2=Michele S.|last3=Getz|first3=Gad|last4=Perner|first4=Sven|last5=Ding|first5=Li|last6=Beroukhim|first6=Rameen|last7=Lin|first7=William M.|last8=Province|first8=Michael A.|last9=Kraja|first9=Aldi|last10=Johnson|first10=Laura A.|last11=Shah|first11=Kinjal|last12=Sato|first12=Mitsuo|last13=Thomas|first13=Roman K.|last14=Barletta|first14=Justine A.|last15=Borecki|first15=Ingrid B.|last16=Broderick|first16=Stephen|last17=Chang|first17=Andrew C.|last18=Chiang|first18=Derek Y.|last19=Chirieac|first19=Lucian R.|last20=Cho|first20=Jeonghee|last21=Fujii|first21=Yoshitaka|last22=Gazdar|first22=Adi F.|last23=Giordano|first23=Thomas|last24=Greulich|first24=Heidi|last25=Hanna|first25=Megan|last26=Johnson|first26=Bruce E.|last27=Kris|first27=Mark G.|last28=Lash|first28=Alex|last29=Lin|first29=Ling|last30=Lindeman|first30=Neal|last31=Mardis|first31=Elaine R.|last32=McPherson|first32=John D.|last33=Minna|first33=John D.|last34=Morgan|first34=Margaret B.|last35=Nadel|first35=Mark|last36=Orringer|first36=Mark B.|last37=Osborne|first37=John R.|last38=Ozenberger|first38=Brad|last39=Ramos|first39=Alex H.|last40=Robinson|first40=James|last41=Roth|first41=Jack A.|last42=Rusch|first42=Valerie|last43=Sasaki|first43=Hidefumi|last44=Shepherd|first44=Frances|last45=Sougnez|first45=Carrie|last46=Spitz|first46=Margaret R.|last47=Tsao|first47=Ming-Sound|last48=Twomey|first48=David|last49=Verhaak|first49=Roel G. W.|last50=Weinstock|first50=George M.|last51=Wheeler|first51=David A.|last52=Winckler|first52=Wendy|last53=Yoshizawa|first53=Akihiko|last54=Yu|first54=Soyoung|last55=Zakowski|first55=Maureen F.|last56=Zhang|first56=Qunyuan|last57=Beer|first57=David G.|last58=Wistuba|first58=Ignacio I.|last59=Watson|first59=Mark A.|last60=Garraway|first60=Levi A.|last61=Ladanyi|first61=Marc|last62=Travis|first62=William D.|last63=Pao|first63=William|last64=Rubin|first64=Mark A.|last65=Gabriel|first65=Stacey B.|last66=Gibbs|first66=Richard A.|last67=Varmus|first67=Harold E.|last68=Wilson|first68=Richard K.|last69=Lander|first69=Eric S.|last70=Meyerson|first70=Matthew|title=Characterizing the cancer genome in lung adenocarcinoma|journal=Nature|volume=450|issue=7171|year=2007|pages=893–898|issn=0028-0836|doi=10.1038/nature06358}}</ref> | ||
**Copy-number [[Mutation|gain]] of [[Chromosome 5|chromosome 5p]] has been identified as the most frequent alteration in lung adenocarcinoma followed by [[Chromosome 3 (human)|chromosome 3q]]. | **Copy-number [[Mutation|gain]] of [[Chromosome 5|chromosome 5p]] has been identified as the most frequent alteration in lung adenocarcinoma followed by [[Chromosome 3 (human)|chromosome 3q]]. | ||
| Line 119: | Line 122: | ||
On [[microscopic]] [[Histopathology|histopathological]] analysis, [[Cell nucleus|nuclear atypia]], eccentrically placed [[Cell nucleus|nuclei]], abundant [[cytoplasm]], and conspicuous [[Nucleolus|nucleoli]] are characteristic findings of adenocarcinoma of the lung. | On [[microscopic]] [[Histopathology|histopathological]] analysis, [[Cell nucleus|nuclear atypia]], eccentrically placed [[Cell nucleus|nuclei]], abundant [[cytoplasm]], and conspicuous [[Nucleolus|nucleoli]] are characteristic findings of adenocarcinoma of the lung. | ||
*Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is the precursor of peripheral adenocarcinomas. It consists of well demarcated [[Columnar epithelia|columnar]] or [[Cuboidal epithelia|cuboidal]] cells with the following features:<ref>{{cite book | last = Kumar | first = Vinay | title = Robbins basic pathology | publisher = Saunders/Elsevier | location = Philadelphia, PA | year = 2007 | isbn = 1416029737 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Stewart | first = Bernard | title = World cancer report 2014 | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization | location = Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland | year = 2014 | isbn = 9283204298 }}</ref> | *Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is the precursor of peripheral adenocarcinomas. It consists of well demarcated [[Columnar epithelia|columnar]] or [[Cuboidal epithelia|cuboidal]] cells with the following features:<ref>{{cite book | last = Kumar | first = Vinay | title = Robbins basic pathology | publisher = Saunders/Elsevier | location = Philadelphia, PA | year = 2007 | isbn = 1416029737 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Stewart | first = Bernard | title = World cancer report 2014 | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization | location = Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland | year = 2014 | isbn = 9283204298 }}</ref> | ||
**Varying degrees of cytologic [[atypia]] | **Varying degrees of cytologic [[atypia]] | ||
**Hyperchromasia | **Hyperchromasia | ||
**[[Pleomorphism]] | **[[Pleomorphism]] | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 15 September 2019
|
Adenocarcinoma of the Lung Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Adenocarcinoma of the Lung from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Adenocarcinoma of the lung pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Adenocarcinoma of the lung pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Adenocarcinoma of the lung pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Trusha Tank, M.D.[2], Shanshan Cen, M.D. [3], Sudarshana Datta, MD [4]
Overview
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer found in non-smokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the lungs. In past several years many genetic and environmental factors has been identified as a causative factor for lung cancer. Individual susceptibility, active smoking, radon exposure, exposure to high pollution levels, asbestos exposure, occupational or environmental exposure to particular agents or carcinogens contribute to the development of adenocarcinoma of the lung. Hydrocarbons cause damage to the DNA and form DNA adducts. Genes involved in the pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma of the lung include EGFR, HER2, KRAS, ALK, and BRAF. On gross pathology, peripheral multifocal single or multiple solid firm yellow-white nodule or mass which may invade into the pleura and cause pleural retraction/puckering. Adenocarcinoma usually does not form a cavitary lesion. It may present as a diffuse pleural thickening resembling malignant mesothelioma. On microscopic histopathological analysis, nuclear atypia, eccentrically placed nuclei, abundant cytoplasm, and conspicuous nucleoli are characteristic findings of adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis
- Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer found in non-smokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the lungs, as compared to centrally located tumors such as small cell lung cancer and squamous cell lung cancer.[1][2]
- Lung cancer pathogenesis can be understood with the help of following hypothesis:[3][4][5]
- Familial lung cancer:
- 6q23–25 locus has been identified as a susceptibility gene for familial lung cancer.
- Multistep tumorigenesis:
- Tumors of organs such as skin, lung and colon are developed through a process called multistep tumorigenesis.[6]
- As with other epithelial malignancies, lung cancers are believed to arise from preneoplastic or precursor lesions in the respiratory mucosa.
- Multistep tumorigenesis is development of tumor through a series of progressive pathologic events such as preneoplastic or precursor lesions with corresponding genetic and epigenetic aberrations.
- Hyperplasia, squamous metaplasia, squamous dysplasia, and carcinoma in situ (CIS) comprise changes in the large airways that precede or accompany invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.
- Multistep tumorigenesis explains pathogenesis of centrally located squamous cell carcinoma of the lung very well but fails to explain pathogenesis of large cell lung carcinomas, lung adenocarcinomas, and small cell lung cancer.
- Accumulation of molecular abnormalities:
- Another theory for pathogenesis of lung cancer is the accumulation of molecular abnormalities beyond a certain threshold point, rather than the sequence of alterations.
- There are no known preneoplastic lesions for the most common type of neuroendocrine lung tumors, small cell carcinoma of the lung,
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is the only sequence of morphologic change identified leading to the development of invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung.
- Pathogenesis of lung cancer is thought to be result of both due to stepwise, sequence-specific and multistage molecular pathogenesis and due to accumulation and combination of genetic and epigeneticabnormalities.
Field of Injury and Field Cancerization
- Preneoplastic lung lesions frequently extend throughout the respiratory epithelium, indicating a field effect in which much of the respiratory epithelium has been mutagenized, presumably from exposure to tobacco-related carcinogens.[7][8][9]
- Epithelial cells lining the entire respiratory tract that have been exposed to smoking show molecular alterations that may signify the onset of lung cancers, a paradigm known as the "airway field of injury”.
- Premalignant airway fields in the molecular pathogenesis of lung cancer:
- Smoking induces widespread molecular alterations, such as gene expression changes in exposed epithelia throughout the respiratory tract.
- The airway field of injury can be seen in smokers with or without lung cancer and is highly relevant for the identification of markers for minimally invasive and early detection of lung cancer.
- The adjacent airway field of carcinoma represents the field in normal appearing airways adjacent to lung tumors.
- It has been suggested that in this adjacent field of tumor, there is closer molecular genealogy between lung cancers and airways that are in closest proximity to the tumors compared with airways that are more distant from the tumors.
- The progression of the molecular airway field of injury to preneoplasia and lung malignancy is still not clear.
- Molecular changes involved in the development of the airway field of injury and changes mediating progression of this field to lung preneoplasia may help the identification of early markers for lung cancer detection and chemoprevention.
- Underlying lung disease such as COPD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and tuberculosis may exacerbate also trigger the process.
Genetics
Molecular Pathogenesis of Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
- Somatic copy number alterations affect a large fraction of the cancer cell genome and are also associated with lung cancer.[10][11][12][13][14]
- Copy-number gain of chromosome 5p has been identified as the most frequent alteration in lung adenocarcinoma followed by chromosome 3q.
- The Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS) pathway is commonly found in smokers.[15]
- Mutation in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), particularly in-frame deletions are associated with never-smoking status, female gender, and East Asian ethnicity.[16]
- Focal amplifications of 14q13·3 are also frequent in adenocarcinoma of the lung, region coding for NKX2–1 (TTF1), a transcription factor crucial for development of the lung, thyroid, and brain.
- RBM10 mutation is more prevalent in men.
- Mutation in MGA, coding for a Max-interacting protein, which functions as a transcriptional repressor capable of blocking MYC-dependent transformation.[17]
- Some of the other recurrent somatic copy number alterations in lung adenocarcinoma include:
| Mutations | TP53, KRAS, EGFR, NF1, BRAF, MET, RIT |
| Fusions | ALK, ROS1, RET |
| SCNAs | Gains: NKX2-1, TERT, EGFR, MET, KRAS, ERBB2, MDM2 |
| Pathway alterations | RTK/RAS/RAF
mTOR, JAK-STAT, DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, epigenetic deregulation |
Environment
- Although genetics play a significant role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer, it is thought that exposure to environmental risk factors plays an equally important role in the development of lung cancer.
- The main causes of lung cancer include carcinogens (such as those present in tobacco smoke), ionizing radiation, and viral infections.
- Chronic exposure results in cumulative alterations to the DNA in the tissue lining the bronchi of the lungs (the bronchial epithelium).
- Irreversible DNA changes following exposure to carcinogens are directly associated with the development of lung cancer.[19]
Smoking
- Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer.[20][21][22]
- Cigarette smoke contains over 60 known carcinogens including radioisotopes from the radon decay sequence, nitrosamine, and benzopyrene.
- Nicotine is thought to reduce the immune response to malignant growths in exposed tissue.
- The length of time an individual smokes, as well as the amount, significantly increases the person's chance of developing lung cancer.
- Among individuals who stopped smoking, the risk of lung cancer steadily decreases as lung tissue repairs itself and as contaminant particles are eliminated from the lungs.
- It is thought that the risk of lung cancer among persons with a history of smoking (even when stopped) is always higher than those who never smoked.
Radon gas
The association of radon gas exposure to lung cancer is described below.[23][24]
- Radon is a colorless and odorless gas generated by the breakdown of radioactive radium (decay product of uranium) found in the Earth's crust. The radiation decay products ionize genetic material, causing mutations that sometimes turn cancerous.
- Radon exposure is the second major cause of lung cancer following smoking.
- The mechanism of lung damage following radon exposure is not thought to be due to the radon gas itself, but due to the short-lived alpha decay products that cause cellular damage and DNA mutations.
Asbestos
- Asbestos exposure is associated with many lung diseases, including lung cancer.[25]
- Tiny asbestos fibers are released into the air are breathed into the lungs. The fibers become lodged in the lungs and are stuck for an indefinite amount of time. They can eventually lead to scarring and inflammation.
Viruses
- Viruses are known to be associated with the development of lung cancer in animals and humans which include:[26][27][28][29][30][31]
- These viruses may affect the cell cycle and inhibit apoptosis, allowing uncontrolled cell division.
- HIV has also been thought to increase the risk of developing lung cancer. Although the mechanism is unknown, HIV is thought to be associated with a state of chronic lung inflammation that may potentiate cellular damage and DNA mutations.
Infection and Inflammation
- There may be a correlation between general inflammation of lung tissue and the development of lung cancers.[31]
- Neutrophils are released in response to bacterial infection and are considered to be the initial responders during inflammation.
- The hypothesis is that neutrophils may activate reactive oxygen or nitrogen species, which can bind to DNA and lead to genomic alterations. Accordingly, inflammation may be thought of as an initiator or promoter of lung cancer development. Also, tissue repair from inflammation is associated with cellular proliferation. During cellular proliferation there may be errors in chromosomal replication that can cause further DNA mutation.
- Angiogenesis, a significant process during tumor growth, may be promoted by chronic states of inflammation, which often require increased blood flow to sites of inflammation.
Gross Pathology
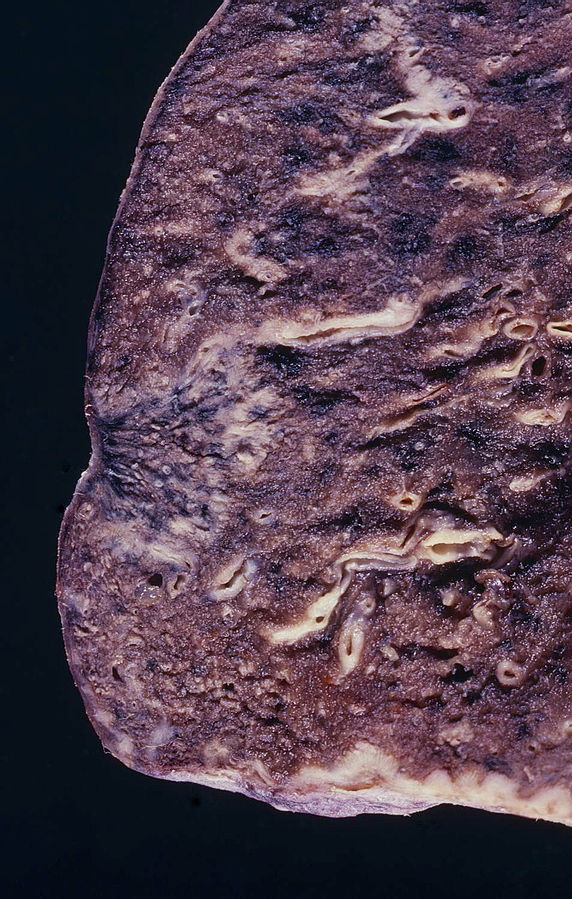
(Source: Libre pathology
- Adenocarcinoma of the lung may be preceded by morphological changes such as atypical adenomatous hypertrophy (AAH) in peripheral airway cells.
- AAH is a parenchymal lesion that arises in the alveoli close to terminal and respiratory bronchioles.
- AAH lesions are small and usually show incidental histological findings.
- They may be detected grossly, especially if they are 0.5 cm or larger.
- AAH is characterized by an alveolar structure lined by rounded, cuboidal, or low columnar cells.
- On gross pathology, peripheral multifocal lesions are characteristic findings in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung.[32]
- Single or multiple solid firm yellow-white nodule or mass which may invade into the pleura and cause pleural retraction/puckering.
- Adenocarcinoma usually does not form a cavitary lesion.
- Adenocarcinoma may present as a diffuse pleural thickening resembling malignant mesothelioma.
Microscopic Pathology
On microscopic histopathological analysis, nuclear atypia, eccentrically placed nuclei, abundant cytoplasm, and conspicuous nucleoli are characteristic findings of adenocarcinoma of the lung.
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is the precursor of peripheral adenocarcinomas. It consists of well demarcated columnar or cuboidal cells with the following features:[33][34]
- Varying degrees of cytologic atypia
- Hyperchromasia
- Pleomorphism
- Prominent nucleoli
- As adenocarcinoma is a derivative of mucus producing glands in the lungs, it tends to stain mucin positive.
- Based on differentiation, the tumor may be:
- Well differentiated (low grade): Normal appearance.
- Poorly differentiated (high grade): Abnormal glandular appearance with a positive mucin stain.
Histological Subtypes
- The IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma histologic classification system was proposed in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology in 2011.[35]
- According to this new classification, tumor size ≤3 cm with pure lepidic pattern, but without lymphatic, vascular, pleural invasion or tumor necrosis was defined as adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS).
- If tumor size ≤3 cm with a lepidic predominant pattern and contained ≤5 mm stromal invasion it was defined as minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA).
- If tumor had >5 mm stromal invasion it was defined as an invasive adenocarcinoma.
- Histologically adenocarcinoma is divided in to following subtypes:[36][37][38][39][40][41]
- Lepidic adenocarcinoma
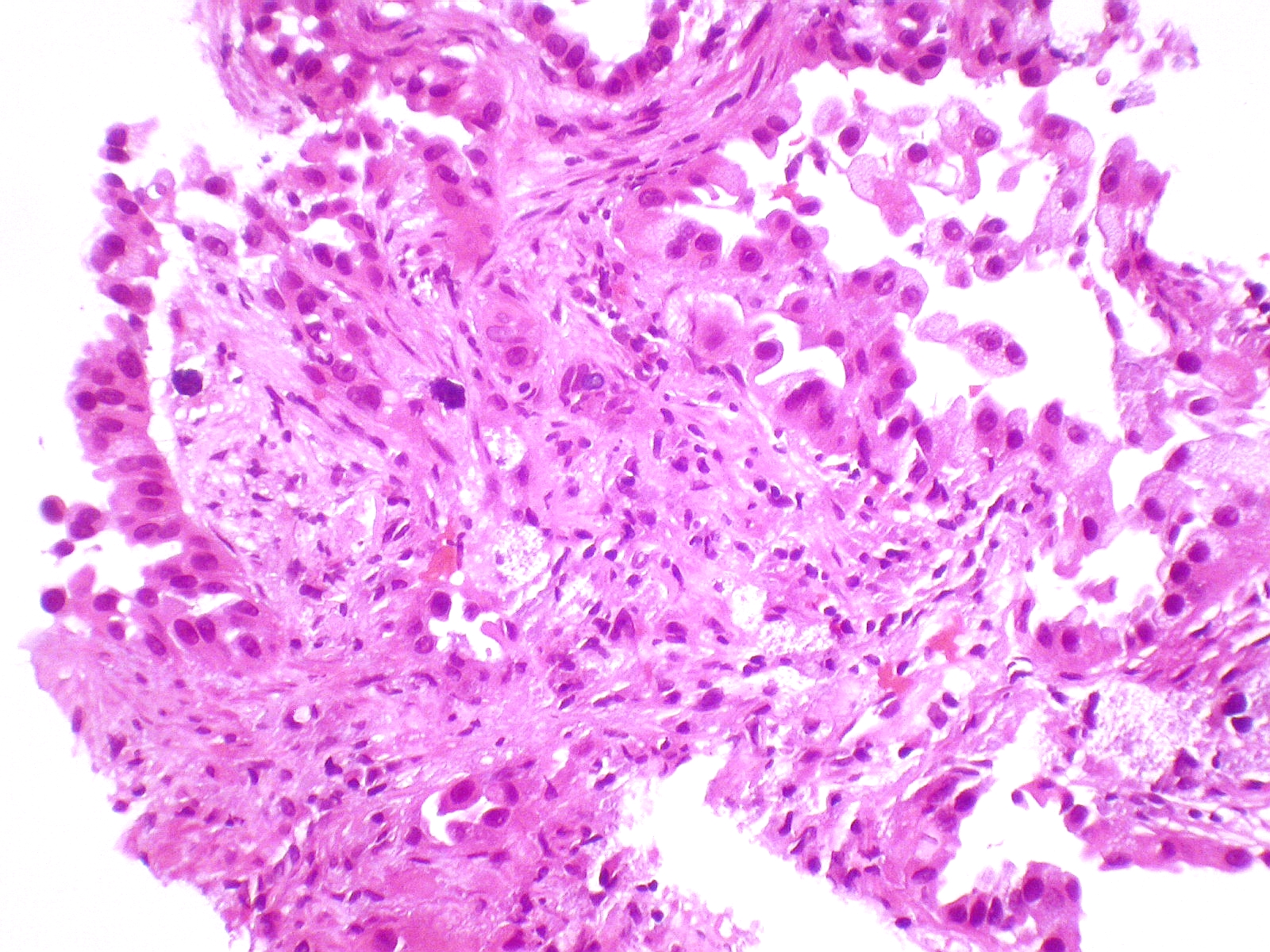
Micrograph showing an invasive carcinoma with a few areas of lepidic growth lining alveoli.
Source: Pathology outlines- Lepidic growth adenocarcinoma is defined as tumor cells proliferating along the surface of intact alveolar walls without stromal or vascular invasion pathologically.
- Solitary adenocarcinomas with pure lepidic growth, termed “AIS” has 100% disease-specific survival, if the lesion is completely resected.
- Acinar adenocarcinoma:
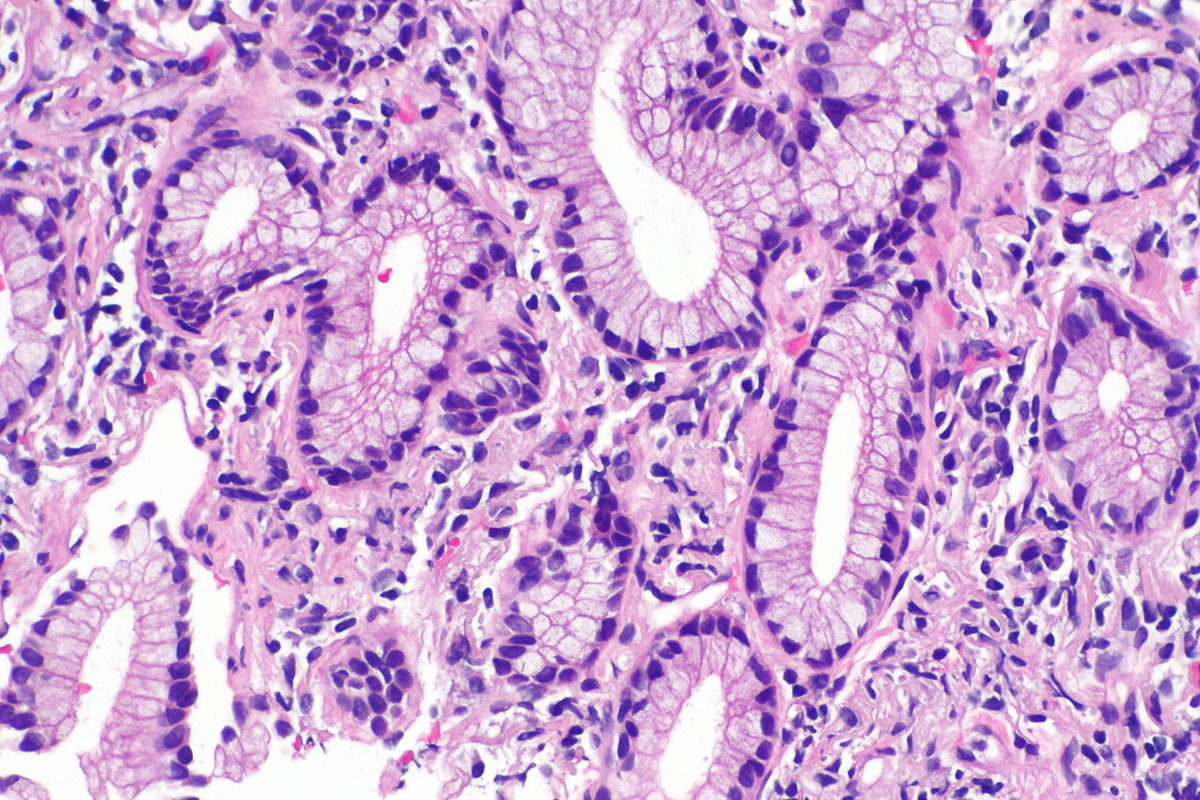
Micrograph showing an adenocarcinoma of the lung (acinar pattern), H&E stain.
Source: Libre pathology- Acinar pattern comprises infiltrating round to oval glands lined by tumor cells.
- Irregular-shaped glands.
- Malignant cells: Hyperchromatic nuclei, fibroblastic stroma.
- Sometimes the glandular cells and lumina may contain mucin.
- Papillary adenocarcinoma
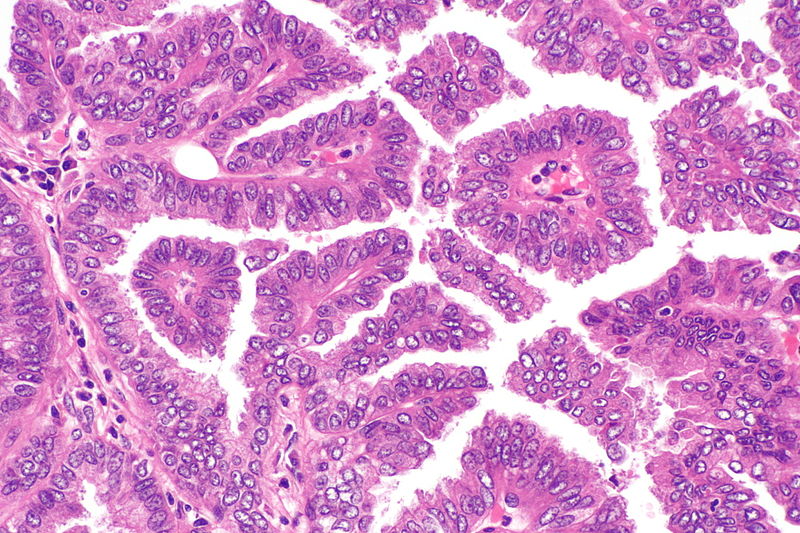
Micrograph showing papillary adenocarcinoma of the lung
Source: Libre pathology- The papillary pattern is composed of glandular tumour cells growing along fibrovascular cores.
- Papillae, necrosis, surrounding invasion, cuboidal to columnar epithelial lining, mucinous or non-mucinous.
- Lung adenocarcinomas with papillary growth show 2 types of papillary architecture:
- True papillary type: Papillae containing a layered glandular epithelium surrounded by fibrovascular core.
- Micropapillary type: The papillary tufts lack a central fibrovascular core and extensively shed within alveolar spaces.
- Micropapillary adenocarcinoma:
- The papillary tufts lack a central fibrovascular core and extensively shed within alveolar spaces.
- Micropapillary growth has been associated with an aggressive clinical course compared with traditional papillary adenocarcinoma.
- Micropapillary adenocarcinoma (MPA) may be often diagnosed at a high stage in nonsmokers, with intralobar satellites.
- Micropapillary adenocarcinoma frequently metastasizes to the contralateral lung, mediastinal lymph nodes, bone, and adrenal glands, with high mortality.
- Solid adenocarcinoma
- Cohesive cell cluster in a nest-like pattern without acinar polarity are the hallmark of the solid growth pattern.
- Solid adenocarcinoma consists of sheets of tumor cells with abundant cytoplasm and mostly vesicular nuclei with several conspicuous nucleoli.
- No acinar, papillary, or lepidic patterns are seen and there was no suggestion of mucin in tumor cell cytoplasm.
- Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma
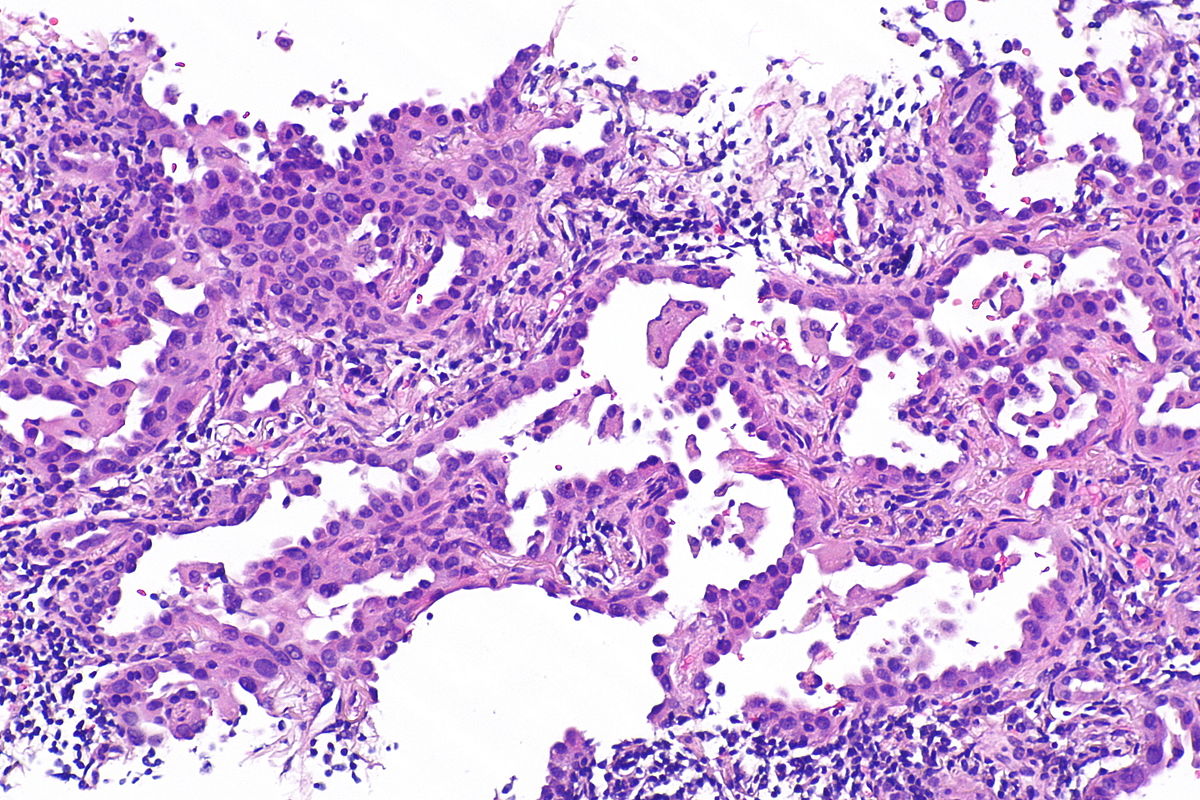
Micrograph of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung, H&E stain.
Source: Libre pathology- Mixed invasive mucinous: Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma demonstrates areas with lepidic, acinar, and papillary patterns.
- Fibrotic focus that contains invasive tumor with a desmoplastic stroma.
- The tumor consists of columnar cells filled with abundant mucin in the apical cytoplasm and shows small, basally oriented nuclei.
- Nonmucinous adenocarcinoma
- Mixed invasive mucinous: Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma demonstrates areas with lepidic, acinar, and papillary patterns.
- Colloid adenocarcinoma:
- This tumor consists of abundant pools of mucin growing within and distending airspaces.
- Well differentiated mucinous glandular epithelium along the surface of fibrous septa and within the pools of mucin.
- Tumor cells may be very inconspicuous.
- The surface of the fibrous wall may be lined by well-differentiated cuboidal or columnar mucinous epithelium.
- Fetal adenocarcinoma:
- Fetal adenocarcinoma consists of malignant glandular cells growing in tubules and papillary structures with endometrioid morphology.
- Some tumor cells have prominent clear cytoplasm, and squamoid morules are present.
- Enteric adenocarcinoma:
- Consists of an adenocarcinoma that morphologically resembles colonic adenocarcinoma with back-to-back angulated acinar structures.
- The tumor cells are cuboidal to columnar with nuclear pseudostratification.
- The tumor stains strongly for CDX-2.
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA)
- Nonmucinous (MIA):
- Mucinous (MIA):
- Mucinous MIA consists of a tumor showing lepidic growth and a small (0.5 cm) area of invasion.
- The tumor cells consist of mucinous columnar cells and pale cytoplasm resembling goblet cells growing mostly in a lepidic pattern along the surface of alveolar walls.
- The tumor invades the areas of stromal fibrosis in an acinar pattern.
- Low grade differentiation.
- Preinvasive lesions
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH): Consists of atypical pneumocytes proliferating along alveolar walls.
- Non invasive.
- The slightly atypical pneumocytes are cuboidal and show gaps between the cells.
- Nuclei are hyperchromatic and may present with nuclear enlargement and multinucleation.
- Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS)
- Nonmucinous (AIS): Tumor grows purely with a lepidic pattern.
- No foci of invasion or scarring is seen.
- It shows atypical pneumocytes proliferating along the thickened, but preserved, alveolar walls.
- Mucinous AIS: Consists of a nodular proliferation of mucinous columnar cells growing in a purely lepidic pattern.
- Although there is a small central scar, no stromal or vascular invasion is seen.
- The tumor cells consist of cuboidal to columnar cells with abundant apical mucin and small, basally oriented nuclei.
- Nonmucinous (AIS): Tumor grows purely with a lepidic pattern.
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH): Consists of atypical pneumocytes proliferating along alveolar walls.
- Lepidic adenocarcinoma
References
- ↑ Travis WD, Travis LB, Devesa SS (January 1995). "Lung cancer". Cancer. 75 (1 Suppl): 191–202. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19950101)75:1+<191::AID-CNCR2820751307>3.0.CO;2-Y. PMID 8000996.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson. "Chapter 13, box on morphology of adenocarcinoma". Robbins Basic Pathology (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 1-4160-2973-7.
- ↑ Kanwal, Madiha; Ding, Xiao-Ji; Cao, Yi (2017). "Familial risk for lung cancer". Oncology Letters. 13 (2): 535–542. doi:10.3892/ol.2016.5518. ISSN 1792-1074.
- ↑ Kadara, H.; Scheet, P.; Wistuba, I. I.; Spira, A. E. (2016). "Early Events in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer". Cancer Prevention Research. 9 (7): 518–527. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0400. ISSN 1940-6207.
- ↑ Raso, Maria Gabriela; Wistuba, Ignacio I. (2007). "Molecular Pathogenesis of Early-Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and a Proposal for Tissue Banking to Facilitate Identification of New Biomarkers". Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 2 (7): S128–S135. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318074fe42. ISSN 1556-0864.
- ↑ Wistuba II, Gazdar AF (2006). "Lung cancer preneoplasia". Annu Rev Pathol. 1: 331–48. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.1.110304.100103. PMID 18039118.
- ↑ Devarakonda, Siddhartha; Morgensztern, Daniel; Govindan, Ramaswamy (2015). "Genomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma". The Lancet Oncology. 16 (7): e342–e351. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00077-7. ISSN 1470-2045.
- ↑ Kadara H, Scheet P, Wistuba II, Spira AE (July 2016). "Early Events in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer". Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 9 (7): 518–27. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0400. PMID 27006378.
- ↑ Auerbach, Oscar; Stout, A. P.; Hammond, E. Cuyler; Garfinkel, Lawrence (1961). "Changes in Bronchial Epithelium in Relation to Cigarette Smoking and in Relation to Lung Cancer". New England Journal of Medicine. 265 (6): 253–267. doi:10.1056/NEJM196108102650601. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ Stewart, Bernard (2014). World cancer report 2014. Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland: International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization. ISBN 9283204298.
- ↑ Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S; et al. (2007). "Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer". Nature. 448 (7153): 561–6. doi:10.1038/nature05945. PMID 17625570.
- ↑ Davies KD, Le AT, Theodoro MF, Skokan MC, Aisner DL, Berge EM; et al. (2012). "Identifying and targeting ROS1 gene fusions in non-small cell lung cancer". Clin Cancer Res. 18 (17): 4570–9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0550. PMC 3703205. PMID 22919003.
- ↑ Stewart, Bernard (2014). World cancer report 2014. Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland: International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization. ISBN 9283204298.
- ↑ Weir, Barbara A.; Woo, Michele S.; Getz, Gad; Perner, Sven; Ding, Li; Beroukhim, Rameen; Lin, William M.; Province, Michael A.; Kraja, Aldi; Johnson, Laura A.; Shah, Kinjal; Sato, Mitsuo; Thomas, Roman K.; Barletta, Justine A.; Borecki, Ingrid B.; Broderick, Stephen; Chang, Andrew C.; Chiang, Derek Y.; Chirieac, Lucian R.; Cho, Jeonghee; Fujii, Yoshitaka; Gazdar, Adi F.; Giordano, Thomas; Greulich, Heidi; Hanna, Megan; Johnson, Bruce E.; Kris, Mark G.; Lash, Alex; Lin, Ling; Lindeman, Neal; Mardis, Elaine R.; McPherson, John D.; Minna, John D.; Morgan, Margaret B.; Nadel, Mark; Orringer, Mark B.; Osborne, John R.; Ozenberger, Brad; Ramos, Alex H.; Robinson, James; Roth, Jack A.; Rusch, Valerie; Sasaki, Hidefumi; Shepherd, Frances; Sougnez, Carrie; Spitz, Margaret R.; Tsao, Ming-Sound; Twomey, David; Verhaak, Roel G. W.; Weinstock, George M.; Wheeler, David A.; Winckler, Wendy; Yoshizawa, Akihiko; Yu, Soyoung; Zakowski, Maureen F.; Zhang, Qunyuan; Beer, David G.; Wistuba, Ignacio I.; Watson, Mark A.; Garraway, Levi A.; Ladanyi, Marc; Travis, William D.; Pao, William; Rubin, Mark A.; Gabriel, Stacey B.; Gibbs, Richard A.; Varmus, Harold E.; Wilson, Richard K.; Lander, Eric S.; Meyerson, Matthew (2007). "Characterizing the cancer genome in lung adenocarcinoma". Nature. 450 (7171): 893–898. doi:10.1038/nature06358. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ↑ Rodenhuis S, Slebos RJ, Boot AJ, Evers SG, Mooi WJ, Wagenaar SS, van Bodegom PC, Bos JL (October 1988). "Incidence and possible clinical significance of K-ras oncogene activation in adenocarcinoma of the human lung". Cancer Res. 48 (20): 5738–41. PMID 3048648.
- ↑ Imielinski M, Berger AH, Hammerman PS, Hernandez B, Pugh TJ, Hodis E, Cho J, Suh J, Capelletti M, Sivachenko A, Sougnez C, Auclair D, Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Cibulskis K, Choi K, de Waal L, Sharifnia T, Brooks A, Greulich H, Banerji S, Zander T, Seidel D, Leenders F, Ansén S, Ludwig C, Engel-Riedel W, Stoelben E, Wolf J, Goparju C, Thompson K, Winckler W, Kwiatkowski D, Johnson BE, Jänne PA, Miller VA, Pao W, Travis WD, Pass HI, Gabriel SB, Lander ES, Thomas RK, Garraway LA, Getz G, Meyerson M (September 2012). "Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing". Cell. 150 (6): 1107–20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.029. PMC 3557932. PMID 22980975.
- ↑ Hurlin, Peter J.; Huang, Jie (2006). "The MAX-interacting transcription factor network". Seminars in Cancer Biology. 16 (4): 265–274. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.07.009. ISSN 1044-579X.
- ↑ Devarakonda S, Morgensztern D, Govindan R (July 2015). "Genomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma". Lancet Oncol. 16 (7): e342–51. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00077-7. PMID 26149886.
- ↑ Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT, Matthay RA (2011). "Lung cancer: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention". Clin. Chest Med. 32 (4): 605–44. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2011.09.001. PMC 3864624. PMID 22054876.
- ↑ Morabia, Alfredo (2012). "Quality, originality, and significance of the 1939 "Tobacco consumption and lung carcinoma" article by Mueller, including translation of a section of the paper". Preventive Medicine. 55 (3): 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2012.05.008. ISSN 0091-7435.
- ↑ Hecht, S (Oct 2003). "Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer". Nature Reviews. Cancer. Nature Publishing Group. 3 (10): 733–744. doi:10.1038/nrc1190. PMID 14570033. Retrieved 2007-08-10.
- ↑ Peto R, R (2006). Mortality from smoking in developed countries 1950–2000: Indirect estimates from National Vital Statistics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-262535-7. Retrieved 2007-08-10. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Catelinois, O (May 2006). "Lung Cancer Attributable to Indoor Radon Exposure in France: Impact of the Risk Models and Uncertainty Analysis". Environmental Health Perspectives. National Institute of Environmental Health Science. 114 (9): 1361–1366. doi:10.1289/ehp.9070. PMID 16966089. Retrieved 2007-08-10. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ University of Minnesota.http://enhs.umn.edu/hazards/hazardssite/radon/radonmolaction.html#Anchor-Molecular-23240/
- ↑ Järvholm, Bengt; Åström, Evelina (2014). "The Risk of Lung Cancer After Cessation of Asbestos Exposure in Construction Workers Using Pleural Malignant Mesothelioma as a Marker of Exposure". Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 56 (12): 1297–1301. doi:10.1097/JOM.0000000000000258. ISSN 1076-2752.
- ↑ Leroux, C (Mar–Apr 2007). "Jaagsiekte Sheep Retrovirus (JSRV): from virus to lung cancer in sheep". Veterinary Research. 38 (2): 211–228. PMID 17257570. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Palmarini, M (November 2001). "Retrovirus-induced ovine pulmonary adenocarcinoma, an animal model for lung cancer". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Oxford University Press. 93 (21): 1603–1614. PMID 11698564. Retrieved 2007-08-11. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Cheng, YW (Apr 2001). "The association of human papillomavirus 16/18 infection with lung cancer among nonsmoking Taiwanese women". Cancer Research. American Association for Cancer Research. 61 (7): 2799–2803. PMID 11306446. Retrieved 2007-08-11. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Zheng, H (May 2007). "Oncogenic role of JC virus in lung cancer". Journal of Pathology. 212 (3): 306–315. PMID 17534844. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Giuliani, L (Sep 2007). "Detection of oncogenic viruses (SV40, BKV, JCV, HCMV, HPV) and p53 codon 72 polymorphism in lung carcinoma". Lung Cancer. 57 (3): 273–281. PMID 17400331. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ 31.0 31.1 Eric A Engels.11/30/11. Inflammation in the development of lung cancer:epidemiological evidence.Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.Apr.2008.p605
- ↑ Adenocarcinoma of the lung. Librepathology 2015. http://librepathology.org/wiki/index.php/File:Adenocarcinoma_%283950819000%29.jpg
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay (2007). Robbins basic pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier. ISBN 1416029737.
- ↑ Stewart, Bernard (2014). World cancer report 2014. Lyon, France Geneva, Switzerland: International Agency for Research on Cancer,Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization. ISBN 9283204298.
- ↑ . doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.09.13. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Travis, William (2004). Pathology and genetics of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus, and heart. Lyon: IARC Press. ISBN 9283224183.
- ↑ "www.jto.org".
- ↑ Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger K, Yatabe Y, Ishikawa Y, Wistuba I, Flieder DB, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Hasleton PS, Henderson DW, Kerr KM, Nakatani Y, Petersen I, Roggli V, Thunnissen E, Tsao M (May 2013). "Diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma in resected specimens: implications of the 2011 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 137 (5): 685–705. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0264-RA. PMID 22913371.
- ↑ Iwata H (September 2016). "Adenocarcinoma containing lepidic growth". J Thorac Dis. 8 (9): E1050–E1052. doi:10.21037/jtd.2016.08.78. PMID 27747060.
- ↑ Jones KD (December 2013). "Whence lepidic?: the history of a Canadian neologism". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 137 (12): 1822–4. doi:10.5858/arpa.2013-0144-HP. PMID 23937575.
- ↑ Lin, Gengpeng; Xie, Canmao (2017). "PUB070 Acinar-Predominant Pattern Correlates with Poorer Outcome in Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung". Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 12 (1): S1489. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2040. ISSN 1556-0864.