Bowen's disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Sara Mohsin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (212 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{ | {{Bowen's disease}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{S.M.}}, {{JH}} | |||
}} | |||
{{ | |||
{{SK}} Bowen's carcinoma; [[squamous cell carcinoma]] in situ of skin; intraepidermal carcinoma skin, Intraepithelial neoplasia | |||
{{SK}} Bowen's carcinoma; squamous cell carcinoma in situ of skin; intraepidermal carcinoma skin | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
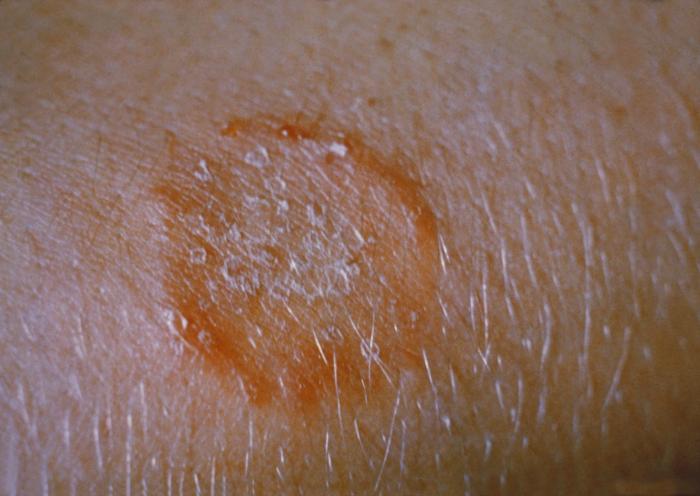
In [[medicine]] ([[dermatology]]), '''Bowen's disease''' (BD) is a [[sunlight]]-induced skin disease, | In [[medicine]] ([[dermatology]]), '''Bowen's [[disease]]''' (BD) is a [[sunlight]]-[[Induced activity|induced]] [[skin disease]], [[Classification|classified]] either as an early noninvasive stage or intraepidermal form of [[squamous cell carcinoma]] which if left undiagnosed, untreated, or neglected has <10% [[chance]] of [[malignant transformation]] into [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] [[squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]]. It usually [[Appearance|appears]] as a [[erythematous]], [[Scaling skin|scaly]] or [[Crustacea|crusty]] [[Patched|patch]] or [[plaque]] anywhere on the [[Human body|body]] but most commonly involves [[Lower leg|lower legs]], with other [[Possibility theory|possible]] sites of involvement to be [[head]], [[neck]], [[genitals]], and [[Skin fold|skin folds]]. It is easily [[Cure|curable]] by various [[Treatments|treatment]] options such as [[cryotherapy]], [[curettage]], [[cautery]], [[photodynamic therapy]], [[topical]] [[chemotherapy]], [[radiotherapy]], or [[excision]] of the [[lesion]]. | ||
==Historical Perspective== | ==Historical Perspective== | ||
*In 1912, Dr John T. Bowen was the first one to describe this [[disease]], hence, it is [[Name reaction|named]] after him | |||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 17: | ||
===Microscopic Pathology=== | ===Microscopic Pathology=== | ||
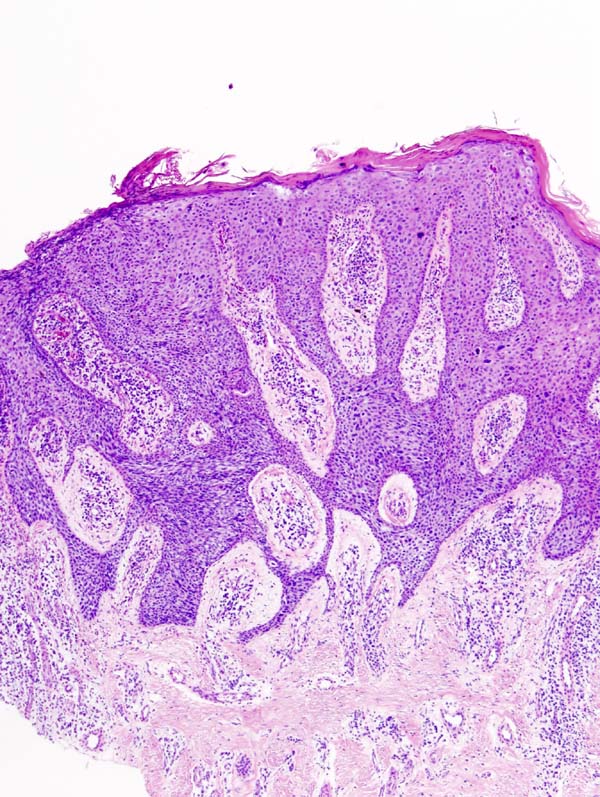
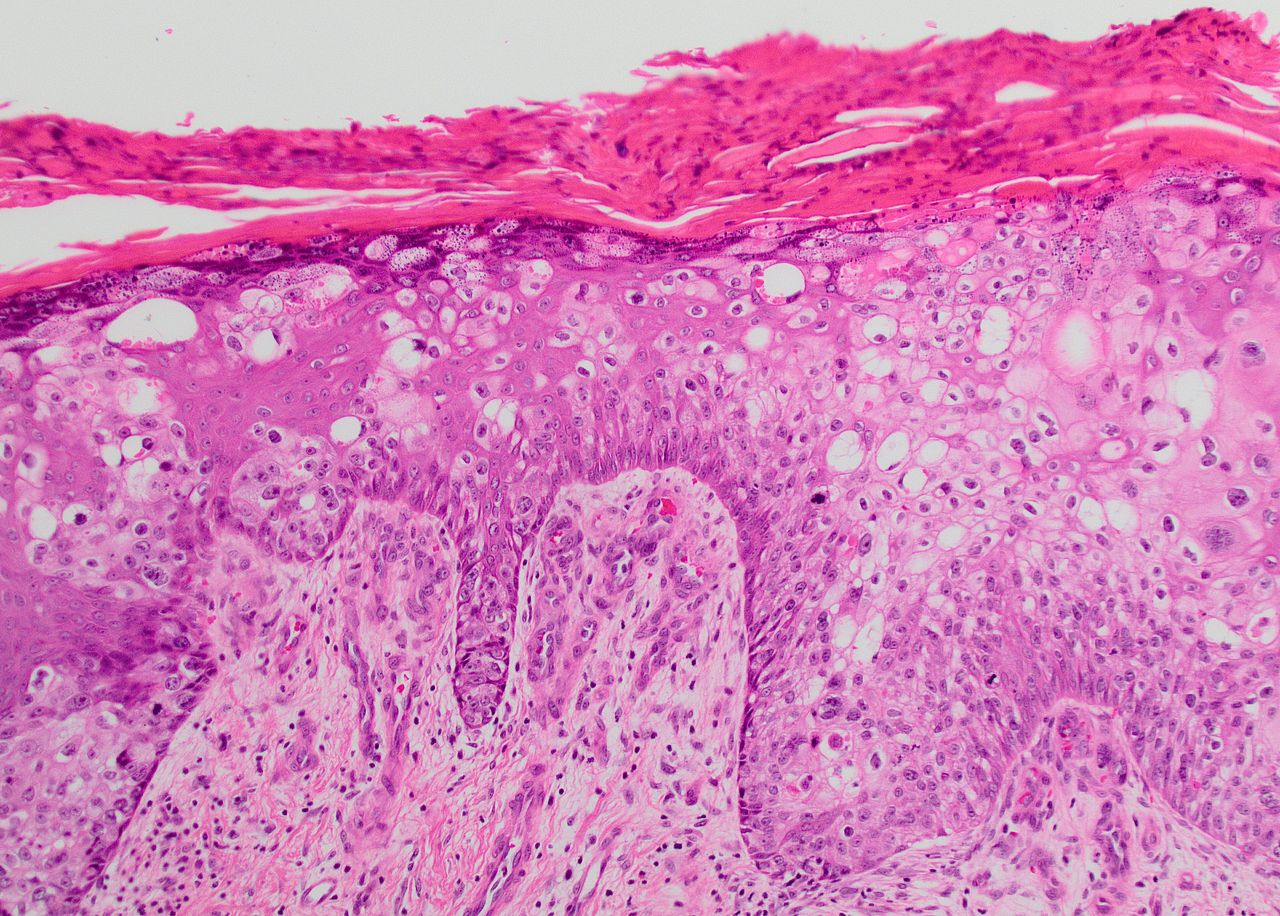
*[[Cells (biology)|Cells]] in Bowen's [[disease]] are [[Extreme value|extremely]] unusual or atypical under the [[light microscopy|microscope]]<ref name="pmid28523295">{{cite journal |vauthors=Neagu TP, Tiglis M, Botezatu D, Enache V, Cobilinschi CO, Vâlcea-Precup MS, GrinTescu IM |title=Clinical, histological and therapeutic features of Bowen's disease |journal=Rom J Morphol Embryol |volume=58 |issue=1 |pages=33–40 |year=2017 |pmid=28523295 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
< | *In many [[Case-based reasoning|cases]], [[Cells (biology)|cells]] [[Lookahead|look]] worse under the [[microscope]] than the [[Cells (biology)|cells]] of many outright and [[Invasive (medical)|invading]] [[squamous cell carcinomas]] | ||
< | *[[Degree (angle)|Degree]] of [[atypia]] ([[Strange matter|strangeness]], unusualness) seen under the [[microscope]] [[Best practice|best]] tells how [[Cells (biology)|cells]] may [[Behavior|behave]] (should they [[Invasive (medical)|invade]] another portion of the [[Human body|body]])<ref name="pmid3195216">{{cite journal| author=Nemkaeva RM, Kurmashov NA, Oslopova S| title=[Bowen's disease]. | journal=Vestn Dermatol Venerol | year= 1988 | volume= | issue= 8 | pages= 71-2 | pmid=3195216 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3195216 }} </ref><ref name="pmid7138058">{{cite journal| author=Scarborough DA, Bisaccia EP, Yoder FW| title=Solitary pigmented Bowen's disease. | journal=Arch Dermatol | year= 1982 | volume= 118 | issue= 11 | pages= 954-5 | pmid=7138058 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7138058 }} </ref> | ||
</ | ===Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon=== | ||
== | *Bowen's [[disease]] can also occur as a part of '''Borst-Jadassohn [[Phenomenology|phenomenon]]''' (previously known as '''intraepidermal epithelioma)''' which is a [[Heterogeneous mixture|heterogeneous]] [[Group (sociology)|group]] of following intraepithelial [[lesions]]:<ref name="pmid31145080">{{cite journal| author=Yanagihara S, Oiso N, Hirota N, Kato M, Miyake S, Kawada A| title=Acantholytic Bowen's disease histopathologically showing the Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon. | journal=Eur J Dermatol | year= 2019 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=31145080 | doi=10.1684/ejd.2019.3545 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=31145080 }} </ref><ref name="pmid26373350">{{cite journal| author=Baykal C, Buyukbabani N, Babuna G, Polat Ekinci A, Kurul S| title=Giant Bowen's disease histologically showing Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon and complicated with squamous cell carcinoma development. | journal=J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol | year= 2016 | volume= 30 | issue= 10 | pages= e88-e89 | pmid=26373350 | doi=10.1111/jdv.13335 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26373350 }} </ref><ref name="urlBorst-Jadassohn phenomenon | definition of Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon by Medical dictionary">{{cite web |url=https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Borst-Jadassohn+phenomenon |title=Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon | definition of Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon by Medical dictionary |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="urlPathology Outlines - Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon">{{cite web |url=https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticborstjadassohn.html |title=Pathology Outlines - Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="urlPayPerView: Jadassohn’s Intraepidermal Epithelioma - Karger Publishers">{{cite web |url=https://www.karger.com/Article/PDF/249658 |title=PayPerView: Jadassohn’s Intraepidermal Epithelioma - Karger Publishers |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21587033">{{cite journal| author=Lora V, Chouvet B, Kanitakis J| title=The "intraepidermal epithelioma" revisited: immunohistochemical study of the borst-jadassohn phenomenon. | journal=Am J Dermatopathol | year= 2011 | volume= 33 | issue= 5 | pages= 492-7 | pmid=21587033 | doi=10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181fe6f90 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21587033 }} </ref> | ||
**[[Irritation|Irritated]] [[seborrheic keratosis]] | |||
**[[Clonal colony|Clonal]] [[seborrheic keratosis]] | |||
**[[Eccrine sweat glands|Eccrine]] poroma | |||
**[[Malignant]] [[Eccrine sweat glands|eccrine]] poroma | |||
**Intraepithelial [[neoplasia]] (Bowen's [[disease]]) | |||
**Other intraepidermal [[sweat gland]] [[tumors]] | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
[[File:Bowen disease (2).jpg|thumb|200px|none|H & E stain of'''Bowen's disease''' as seen under a microscope [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Histopathology_of_Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Bowen_disease_(2).jpg Source: Wikimedia Commons]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Bowen disease (3).jpg|thumb|200px|none|Histopathology of squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the skin (Bowen disease). H & E stain [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Histopathology_of_Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Bowen_disease_(3).jpg Source: Wikimedia Commons]] | |||
| | |||
[[image:Bowen disease (1).jpg|thumb|200px|none|'''Bowen's disease''' as seen under a microscope]] | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
[[File:Bowen disease (4).jpg|thumb|200px|none|Histopathology of squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the skin (Bowen disease). H & E stain [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Histopathology_of_Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Bowen_disease_(4).jpg Source: Wikimedia Commons]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Skin SCCIS PagetoidandConventional 15BR30103.jpg|thumb|200px|none|SCCIS from sundamaged skin. Pagetoid SCCIS on the left, conventional SCCIS on the right. [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Histopathology_of_Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Skin_SCCIS_PagetoidandConventional_15BR30103.jpg Source: Wikimedia Commons]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:1280px-SkinTumors-P5280074.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Squamous cell carcinoma in situ or Bowen disease[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Histopathology_of_Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:SkinTumors-P5280074.JPG Source: Wikimedia Commons]] | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
==Causes== | |||
Bowen's [[disease]] is a non-[[infectious]], non-[[familial]] [[disease]] with common [[causes]] as mentioned below: | |||
*[[ | *'''[[Solar nebula|Solar]] damage''' due to [[Long-term potentiation|long-term]] [[sun exposure]] or [[Usage analysis|use]] of sunbeds, especially in [[People's Solidarity|people]] with [[Fair use|fair]] [[skin]] | ||
* | *'''[[Aging]]''' | ||
*[[ | *'''[[Carcinogens]] such as [[arsenic]]''': | ||
*[[ | **[[Usage analysis|Used]] in manufacturing industry and for other commercial [[Usage analysis|uses]] | ||
** | **10 [[Year|years]] or so [[Aftereffect|after]] the initial [[Exposure assessment|exposure]] to [[arsenic]] are required before it [[causes]] Bowen's [[disease]] | ||
*[[ | **[[WellPoint|Well]] [[water]] once [[Usage analysis|used]] in various [[medical]] [[Preparation (dental)|preparations]] was [[Knowledge|known]] to have been [[Contamination|contaminated]] with [[arsenic]] in [[Past life regression|past]] | ||
*[[Viral infection]] | *'''[[Weak force|Weak]] [[immune system]]''' due to: | ||
**[[HPV]]/[[human papillomavirus]] | **[[Immunosuppressants]] after [[Organ transplantation|organ transplant]] | ||
**[[AIDS]] | |||
*[[Viral infection|'''Viral infection''']] such as: | |||
**Different types '''[[HPV]]/[[human papillomavirus]]''':<ref name="pmid10421264">{{cite journal| author=Clavel CE, Huu VP, Durlach AP, Birembaut PL, Bernard PM, Derancourt CG| title=Mucosal oncogenic human papillomaviruses and extragenital Bowen disease. | journal=Cancer | year= 1999 | volume= 86 | issue= 2 | pages= 282-7 | pmid=10421264 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10421264 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15948988">{{cite journal| author=Zheng S, Adachi A, Shimizu M, Shibata SI, Yasue S, Sakakibara A et al.| title=Human papillomaviruses of the mucosal type are present in some cases of extragenital Bowen's disease. | journal=Br J Dermatol | year= 2005 | volume= 152 | issue= 6 | pages= 1243-7 | pmid=15948988 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06643.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15948988 }} </ref><ref name="pmid10717561">{{cite journal| author=Lampert A, Pauwels C, Duboucher C, Morel G, Poveda JD, Périé G| title=[Detection of human papillomavirus in cutaneous extragenital Bowen's disease in immunocompetent patients]. | journal=Ann Dermatol Venereol | year= 2000 | volume= 127 | issue= 1 | pages= 40-5 | pmid=10717561 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10717561 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8599431">{{cite journal| author=Collina G, Rossi E, Bettelli S, Cook MG, Cesinaro AM, Trentini GP| title=Detection of human papillomavirus in extragenital Bowen's disease using in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction. | journal=Am J Dermatopathol | year= 1995 | volume= 17 | issue= 3 | pages= 236-41 | pmid=8599431 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8599431 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11460032">{{cite journal| author=Derancourt C, Mougin C, Chopard Lallier M, Coumes-Marquet S, Drobacheff C, Laurent R| title=[Oncogenic human papillomaviruses in extra-genital Bowen disease revealed by in situ hybridization]. | journal=Ann Dermatol Venereol | year= 2001 | volume= 128 | issue= 6-7 | pages= 715-8 | pmid=11460032 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11460032 }} </ref><ref name="pmid10612858">{{cite journal| author=Pham-Huu V, Derancourt C, Clavel C, Durlach A, Birembaut P, Bernard P| title=[Oncogenic mucosal human papillomaviruses in Bowen's disease of the hands]. | journal=Ann Dermatol Venereol | year= 1999 | volume= 126 | issue= 11 | pages= 808-12 | pmid=10612858 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10612858 }} </ref><ref name="pmid25201325">{{cite journal |vauthors=Murao K, Yoshioka R, Kubo Y |title=Human papillomavirus infection in Bowen disease: negative p53 expression, not p16(INK4a) overexpression, is correlated with human papillomavirus-associated Bowen disease |journal=J. Dermatol. |volume=41 |issue=10 |pages=878–84 |year=2014 |pmid=25201325 |doi=10.1111/1346-8138.12613 |url=}}</ref> | |||
***[[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] 16, 18, 34, and 48 are [[Association (statistics)|associated]] with Bowen's [[disease]] of perianal & [[Genital area|genital region]] especially [[bowenoid papulosis]] and [[Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia|VIN]] are [[Causes|caused]] by [[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] 16 | |||
***[[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] 2, 16, 34, and 35 are [[Association (statistics)|associated]] with Bowen's [[disease]] in other [[Area|areas]] of [[Human body|body]] (excluding [[genitals]]) | |||
***47% of acral and 24% of nonacral extragenital Bowen's [[disease]] [[lesion]] contains [[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] [[genome]] | |||
**[[Merkel cell]] [[polyomavirus]] | |||
*'''Previous irradiation''' such as: | |||
**[[Ultraviolet radiation|Ultraviolet irradiation]] | |||
**[[Radiotherapy]] [[Treatments|treatment]] | |||
**Photochemotherapy | |||
*'''[[Chronic (medicine)|Chronic]] [[wound|skin injury]]''' | |||
*'''[[Dermatoses]]''' | |||
*[[Sjögren's syndrome|'''Sjögren's syndrome''']] | |||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
===Age=== | |||
*Bowen's [[disease]] can [[affect]] [[Adult|adults]] of any [[age]], most commonly involves [[Old age|older]] [[patients]] in their 60s or 70s | |||
Bowen's disease | *It is [[rare]] before the [[age]] of 30 [[Year|years]] | ||
===Gender=== | ===Gender=== | ||
Bowen's disease occurs predominantly in women (70-85% of cases). | |||
*Bowen's [[disease]] occurs more [[Predominance diagram|predominantly]] in [[men]] than in [[Womens Pack|women]] (70-85% of [[Case-based reasoning|cases]]) | |||
===Race=== | |||
*[[Caucasian honey bee|Caucasians]] are the ones most commonly [[Affect|affected]] by Bowen's [[disease]] | |||
==Natural History, Complications and Prognosis== | |||
*Bowen's [[disease]] [[Growth|grows]] very [[Slow|slowly]] over the [[period]] of months or even [[Year|years]]<ref name="urlBowens disease - NHS">{{cite web |url=https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bowens-disease/ |title=Bowen's disease - NHS |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
*It is easily [[Treatments|treatable]] if [[Diagnose|diagnosed]] in [[Time constant|time]] | |||
*If left undiagnosed, untreated or [[Neglected Diseases|neglected]], Bowen's [[disease]] can ultimately [[Progressively measurable process|progressively]] [[Development|develop]] into '''[[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] [[squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]]''' in 1 in 20-30 [[People's Solidarity|people]] (i.e. 3-5% [[RiskMetrics|risk]]) | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin|SCC]] is a [[Treatments|treatable]] [[condition]], but if it's deeper or [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]], it means it's very serious | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
===Common symptoms=== | |||
*It usually [[Appearance|appears]] as one or more [[skin]] [[Patching|patches]] with following [[Characteristic function (probability theory)|characteristics]]:<ref name="urlBowens disease - NHS">{{cite web |url=https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bowens-disease/ |title=Bowen's disease - NHS |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
**Persistent | |||
**Progressive | |||
**Non-elevated | |||
**Non-[[healing]] | |||
**[[Irregular lesion|Irregular]] clear [[Edge detection|edges]] | |||
**[[Scaling skin|Scaly]] | |||
**[[Crustacean|Crusty]] | |||
**[[Red-Al|Red]] or [[Pinks|pink]] | |||
**[[Wart|Warty]] ([[Verrucous carcinoma|verrucous]]) | |||
**Upto a [[Fewmets|few]] [[Centimetre|centimetres]] across (larger than half-[[inch]] [[Wide and fast|wide]]) | |||
**[[Flats|Flat]] or raised | |||
**Oozing of [[pus]] | |||
**[[Itchy]] (but not all the [[Time constant|time]]) | |||
**[[SplitsTree|Splits]] open ([[fissured]]) | |||
**[[Dark matter|Darkly]] [[Color|colored]] ([[Pigmented lesions|pigmented]]) | |||
===Signs and symptoms of malignant transformation=== | |||
*Following [[Change detection|changes]] in the [[skin]] [[Patched|patch]] are the [[signs]] that bowen's [[disease]] has [[Turn (biochemistry)|turned]] into [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] [[squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]]: | |||
**Easy [[bleeding]] | |||
**[[Tenderness]] | |||
**[[Turn (biochemistry)|Turns]] into an open [[sore]] i.e. [[Ulcerated lesion|ulcerates]] | |||
**[[Hard science|Hardening]] ([[induration]]) | |||
**[[Development|Develops]] into a [[lump]]/[[Fleshy beams|fleshy]] [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] | |||
=== | ===Common sites of involvement=== | ||
< | *Common sites involved are:<ref name="pmid3760318">{{cite journal| author=Wagner RF, Grande DJ| title=Solitary pigmented Bowen's disease of the scrotum. | journal=J Dermatol Surg Oncol | year= 1986 | volume= 12 | issue= 10 | pages= 1114-5 | pmid=3760318 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3760318 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24746300">{{cite journal| author=Al-Dawsari NA, Raslan W, Dawamneh MF| title=Pigmented Bowen's disease of the penis and scrotum in a patient with AIDS. | journal=Dermatol Online J | year= 2014 | volume= 20 | issue= 4 | pages= 22337 | pmid=24746300 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24746300 }} </ref><ref name="pmid31141219">{{cite journal| author=Narahira A, Yanagi T, Kitamura S, Hata H, Shimizu H| title=Dermoscopic features of genital pigmented Bowen's disease: Report of a case and review of the published work. | journal=J Dermatol | year= 2019 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=31141219 | doi=10.1111/1346-8138.14938 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=31141219 }} </ref> | ||
< | |||
</ | |||
====Skin==== | ====Skin==== | ||
*[[Lesions]] can occur anywhere on the [[skin]] [[Surface area|surface]] or on [[mucosal]] [[Surface area|surfaces]], although the involvement of [[Palms of the hands|palms]] or [[Sole of the foot|soles]] is uncommon | |||
*A persistent progressive non-elevated [[Red-Al|red]] [[Scale (social sciences)|scaly]] or [[Crustacean|crusted]] [[plaque]] which is due to an [[intradermal]] [[carcinoma]] and is [[Potential|potentially]] [[malignant]] | |||
*Atypical [[squamous]] (resembling [[Fish scale disease|fish scales]]) [[Cells (biology)|cells]] [[proliferate]] through the whole [[Thickener|thickness]] of the [[epidermis]] | |||
Image:Bowen_disease_01.jpg|Bowen disease. | {| | ||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen_disease_01.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease.[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=59 Source: Dermatology Atlas]]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen_disease_02.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease.[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=59 Source: Dermatology Atlas]]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen_disease_03.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease.[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=59 Source: Dermatology Atlas]]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Bowen disease.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease.[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Bowen_disease.JPG Source: Wikimedia Commons]]] | |||
|} | |||
====Extremities==== | |||
*About three-quarters of the [[patients]] have [[lesions]] on the [[lower leg]] (60-85%), usually in previously or [[Presenting symptom|presently]] [[Sun exposure|sun-exposed]] [[Area|areas]] of [[skin]] | |||
====Head and neck area==== | |||
*Being [[prone]] to the [[sun exposure]], [[head]] and [[neck]] [[area]] is also one of the common sites to be [[Affect (philosophy)|affected]] by Bowen's [[disease]] | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
[[File:Bowen's disease plaque.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease. [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bowen%27s_disease_plaque.jpg Source: Wikimedia Commons]]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:1280px-Bowen03.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease. [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Bowen03.JPG Source: Wikimedia Commons]]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:1280px-Bowen10.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease. [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Bowen%27s_disease#/media/File:Bowen10.jpg Source: Wikimedia Commons]]] | |||
|} | |||
====Subungal, periungal region==== | |||
*Bowen's [[disease]] also commonly involves [[Subungal exostosis|subungal]] or [[Periungual warts|periungal]] [[Area|areas]] (i.e. either under or around [[fingernails]] or [[toenails]]) | |||
====Skinfolds==== | ====Skinfolds==== | ||
< | {| | ||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen_disease_04.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease. [http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=59 Source: Dermatology Atlas]]] | |||
|} | |||
====Genitourinary system==== | |||
*Bowen's [[disease]] can also involve [[Genital area|genital]] and perianal [[Area|areas]] | |||
*It [[Appearance|appears]] in following 3 forms in [[genital area]]:<ref name="urlBowen’s Disease: Skin Cancer Linked to HPV Infection">{{cite web |url=https://www.webmd.com/cancer/what-is-bowens-disease#1 |title=Bowen’s Disease: Skin Cancer Linked to HPV Infection |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
Image: | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+Multiple forms of Bowen's disease involving genital region | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Bowen's disease form}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 400px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Characteristic features}} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Bowenoid papulosis]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Affect|Affects]] both [[men]] and [[Womens Pack|women]] | |||
*[[Lesions]] can last from 2 weeks to several [[Year|years]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Erythroplasia of Queyrat]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Affect|Affects]] tip of the [[penis]] ([[glans penis]]-[[Outer coat|outer]] [[keratinized]] [[Surface area|surface]] of the [[penis]]) | |||
*Occurs in [[Middle age|middle-aged]] uncircumscribed [[men]] due to unknown [[Reasoning|reasons]] | |||
*May [[Causes|cause]] any of the following: | |||
**[[Red-Al|Reddish]], [[Velvet (fish disease)|velvety]] or [[Smooth pursuit|smooth]] [[plaque]] | |||
**[[Ulcers]] | |||
**[[Discharge]] | |||
**[[Bleeding]] | |||
**[[Itching]] | |||
**[[Scaling skin|Scaling]] | |||
**[[Crustacea|Crusting]] | |||
**[[Difficulty passing urine|Difficulty urinating]] | |||
**[[Dysuria]] | |||
*Also known as Bowen's [[disease]] of the [[glans penis]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia]] ([[Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia|VIN]]) | |||
| | |||
*[[Affect|Affects]] [[vulva]] in [[Womens Pack|women]] | |||
*[[Causes]] bright [[Red-Al|red]], [[Velvet (fish disease)|velvety]], [[Patching|patches]] that severely [[itch]] or [[burn]] in [[Womens Pack|women]] | |||
*[[Association (statistics)|Associated]] with [[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] 16 | |||
|} | |||
<br /> | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen_disease_05.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease.[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=59 Source: Dermatology Atlas]]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen_disease_06.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Bowen disease.[http://www.atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=59 Source: Dermatology Atlas]]] | |||
|} | |||
===Physical Examination=== | |||
==== | *Bowen's [[disease]] [[Typical set|typically]] [[Presenting symptom|presents]] as a gradually enlarging, well [[Demarcation problem|demarcated]] [[erythematous]] [[plaque]] with an [[Irregular lesion|irregular]] border and [[Surface area|surface]] [[Crustacea|crusting]] or [[Scaling skin|scaling]]<ref name="pmid20811602">{{cite journal| author=Inoue T, Kobayashi K, Sawada M, Ishizaki S, Ito H, Fujibayashi M et al.| title=Dermoscopic Features of Pigmented Bowen's Disease in a Japanese Female Mimicking Malignant Melanoma. | journal=Dermatol Res Pract | year= 2010 | volume= 2010 | issue= | pages= | pmid=20811602 | doi=10.1155/2010/543091 | pmc=2929512 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20811602 }} </ref><ref name="pmid20652107">{{cite journal| author=Hayashi Y, Tanaka M, Suzaki R, Mori N, Konohana I| title=Dermoscopy of Pigmented Bowen's Disease Mimicking Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma. | journal=Case Rep Dermatol | year= 2009 | volume= 1 | issue= 1 | pages= 11-15 | pmid=20652107 | doi=10.1159/000227284 | pmc=2895203 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20652107 }} </ref><ref name="pmid28832993">{{cite journal| author=Yang Y, Lin J, Fang S, Han S, Song Z| title=What's new in dermoscopy of Bowen's disease: two new dermoscopic signs and its differential diagnosis. | journal=Int J Dermatol | year= 2017 | volume= 56 | issue= 10 | pages= 1022-1025 | pmid=28832993 | doi=10.1111/ijd.13734 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28832993 }} </ref> | ||
*[[Lesion]] might [[Feeling|feel]] [[Tenderness (medicine)|tender]] [[Representative agent|representing]] its [[malignant transformation]] | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen.jpg|thumb|200px|none| Bowen's disease [https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6839115Source: Klaus D. Peter, Gummersbach, Germany, CC BY 3.0 de]]] | |||
| | |||
[[image:Bowens.jpg|thumb|200px|none|'''Bowen's disease''']] | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
===Dermoscopy=== | |||
*[[Dermoscopy]] is the [[skin]] [[examination]] via [[skin]] [[Surface area|surface]] [[microscopy]] | |||
*Also known as: | |||
**'Epiluminoscopy' | |||
**'Epiluminescent [[microscopy]]' | |||
*It is usually [[Usage analysis|used]] for [[examination]] of [[Pigmented lesions|pigmented]] [[skin lesions]] | |||
*Benefits of [[dermoscopy]] include: | |||
**Improvement of [[diagnostic]] [[accuracy]] of [[Pigmented lesions|pigmented]] [[skin lesions]] | |||
**Evaluation of nonpigmented [[skin]] [[tumors]] ([[Recognition sequence|recognizes]] [[vascular]] [[Structure determination|structures]] not [[Visible light|visible]] to naked [[eye]]) | |||
**Helpful in [[diagnosis]] of Bowen's [[disease]] and shows:<ref name="pmid15214896">{{cite journal| author=Zalaudek I, Argenziano G, Leinweber B, Citarella L, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, Malvehy J et al.| title=Dermoscopy of Bowen's disease. | journal=Br J Dermatol | year= 2004 | volume= 150 | issue= 6 | pages= 1112-6 | pmid=15214896 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05924.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15214896 }} </ref> | |||
***[[Repeatability|Repetitive]] [[Morphological computation|morphological]] findings such as [[Glomerular capillaries|glomerular vessels]] and [[Scalar (mathematics)|scaly]] [[Surface anatomy|surface]] | |||
***Small [[brown]] globules and/or [[homogeneous]] [[pigmentation]] in [[Case-based reasoning|case]] of [[Pigmented lesions|pigmented]] Bowen's [[disease]]<ref name="pmid20079953">{{cite journal| author=Cameron A, Rosendahl C, Tschandl P, Riedl E, Kittler H| title=Dermatoscopy of pigmented Bowen's disease. | journal=J Am Acad Dermatol | year= 2010 | volume= 62 | issue= 4 | pages= 597-604 | pmid=20079953 | doi=10.1016/j.jaad.2009.06.008 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20079953 }} </ref> | |||
===Skin biopsy=== | |||
*[[Skin biopsy]] must be [[done]] to: | |||
**Confirm the [[diagnosis]] Bowen's [[disease]] | |||
**[[Differentiate]] from other [[skin lesions]] | |||
**Rule out [[Invasive (medical)|invasive]] [[squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]] | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
===Surgery and | *[[Specific activity|Specific]] [[Treatments|treatment]] for an [[Individual growth|individual]] [[Case-based reasoning|case]] [[Dependent variable|depends]] upon various factors, such as:<ref name="urlBowen Disease - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders)">{{cite web |url=https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/bowen-disease/ |title=Bowen Disease - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders) |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | ||
**[[Affect|Affected]] [[Human body|body]] site | |||
**[[Size consistency|Size]] | |||
**[[Thickener|Thickness]] of the [[Lesions|lesion(s)]] | |||
**[[Number]] of the [[Lesions|lesion(s)]] | |||
**[[Presenting symptom|Presence]] or absence of [[Certain safety factor|certain]] [[symptoms]] | |||
**[[Patient|Patient’s]] [[age]] | |||
**[[Patient|Patient's]] [[Generalization|general]] [[health]] | |||
**[[Possibility theory|Possible]] [[side effects]] of the [[Treatments|treatment]] | |||
**[[Possibility theory|Possible]] long [[Term logic|term]] [[Effect size|effects]] of the [[Treatments|treatment]] | |||
**[[Patient|Patient's]] [[Preferences|preference]] | |||
*Different [[Treatments|treatment]] options for Bowen's [[disease]] include the following: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+Different treatment options for Bowen's disease | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Treatment option}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 400px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Details}} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Watch and wait]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Patient]] with a [[slow]]-[[Growth|growing]] [[disease]] is followed up without any [[Treatments|treatment]] given until the [[disease]] progression occurs | |||
*[[Done]] in elderly [[patients]] having a [[Slow|slowly]] [[Growth|growing]] [[lesion]] in poor [[healing]] [[area]] such as [[lower leg]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Cryosurgery]]/[[Freezing]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Cells (biology)|Cells]] of the [[lesion]] are destroyed by [[freezing]] them with either [[liquid nitrogen]] or [[argon]] [[gas]] | |||
*Later on, the [[Dead space|dead]] [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] sloughs off on thawing within [[Fewmets|few]] weeks | |||
*Favored by some [[clinicians]] over [[excision]] | |||
*Mostly [[Effective method|effective]] for single or small [[lesions]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Topical application|Topical]] [[Cream (pharmaceutical)|cream]]''' | |||
| | |||
*Includes following 2 options: | |||
**5% [[Imiquimod]] [[Cream (pharmaceutical)|cream]] | |||
**[[Chemotherapy]] [[Cream (pharmaceutical)|cream]] ([[5-fluorouracil]]) | |||
*Favored by some [[clinicians]] over [[excision]] | |||
*[[Cream (pharmaceutical)|Cream]] needs to be [[Applied probability|applied]] once or twice for atleast two weeks if not longer | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Curettage]] & electrodesiccation or [[cryotherapy]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Affect|Affected]] [[skin]] [[area]] is [[Scrapie|scraped]] away under [[local anaesthetic]] (which [[Numbed|numbs]] the [[skin]]) [[Usage analysis|using]] a device having a [[Circular folds|circular]] blade ([[Curette|curet]]) | |||
*Then an [[electric current]] is [[Passing (disability)|passed]] through the remaining of the [[lesion]] via an [[Electric current|electric]] [[needle]] which destroys any of the remaining [[Cancer cells|cells]] | |||
*[[Liquid nitrogen]] can be [[Usage analysis|used]] in order to [[Freezing|freeze]] the [[base]] and [[Edge detection|edges]] of the [[Treatments|treated]] [[area]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Cauterization]] or [[diathermy]] [[coagulation]]'''<ref name="pmid19209288">{{cite journal| author=Neubert T, Lehmann P| title=Bowen's disease - a review of newer treatment options. | journal=Ther Clin Risk Manag | year= 2008 | volume= 4 | issue= 5 | pages= 1085-95 | pmid=19209288 | doi= | pmc=2621408 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19209288 }} </ref> | |||
| | |||
*After [[Scrapie|scraping]] the [[Affect|affected]] [[area]], [[cautery]] is [[Applied probability|applied]] to the remaining of [[lesion]] and to [[Stop signs|stop]] any [[bleeding]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Photodynamic therapy]] (PDT)'''<ref name="pmid11359493">{{cite journal| author=Wong TW, Sheu HM, Lee JY, Fletcher RJ| title=Photodynamic therapy for Bowen's disease (squamous cell carcinoma in situ) of the digit. | journal=Dermatol Surg | year= 2001 | volume= 27 | issue= 5 | pages= 452-6 | pmid=11359493 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11359493 }} </ref><ref name="pmid16181460">{{cite journal| author=Britton JE, Goulden V, Stables G, Stringer M, Sheehan-Dare R| title=Investigation of the use of the pulsed dye laser in the treatment of Bowen's disease using 5-aminolaevulinic acid phototherapy. | journal=Br J Dermatol | year= 2005 | volume= 153 | issue= 4 | pages= 780-4 | pmid=16181460 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06830.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16181460 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24882981">{{cite journal| author=Kang HK, Yun JH, Son YM, Roh JY, Lee JR| title=Photodynamic Therapy for Bowen's Disease of the Vulva Area. | journal=Ann Dermatol | year= 2014 | volume= 26 | issue= 2 | pages= 241-5 | pmid=24882981 | doi=10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.241 | pmc=4037679 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24882981 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11843215">{{cite journal| author=Dijkstra AT, Majoie IM, van Dongen JW, van Weelden H, van Vloten WA| title=Photodynamic therapy with violet light and topical 6-aminolaevulinic acid in the treatment of actinic keratosis, Bowen's disease and basal cell carcinoma. | journal=J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol | year= 2001 | volume= 15 | issue= 6 | pages= 550-4 | pmid=11843215 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11843215 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9693665">{{cite journal| author=Harth Y, Hirshowitz B, Kaplan B| title=Modified topical photodynamic therapy of superficial skin tumors, utilizing aminolevulinic acid, penetration enhancers, red light, and hyperthermia. | journal=Dermatol Surg | year= 1998 | volume= 24 | issue= 7 | pages= 723-6 | pmid=9693665 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9693665 }} </ref><ref name="pmid18031503">{{cite journal| author=de Haas ER, de Vijlder HC, Sterenborg HJ, Neumann HA, Robinson DJ| title=Fractionated aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy provides additional evidence for the use of PDT for non-melanoma skin cancer. | journal=J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol | year= 2008 | volume= 22 | issue= 4 | pages= 426-30 | pmid=18031503 | doi=10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02445.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18031503 }} </ref> | |||
| | |||
*[[Usage analysis|Uses]] [[Combination therapy|combination]] of [[laser]] [[light]] and [[drugs]] [[MakeBot|making]] [[Affect|affected]] [[Cells (biology)|cells]] [[Sensitive Skin|sensitive]] to [[light]] to destroy [[Affect|affected]] [[skin]] [[Cells (biology)|cells]] | |||
*One [[Treatments|treatment]] session lasts for 20-45 [[Minute|minutes]] | |||
*More than one sessions might be required | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Radiation therapy|'''Radiation therapy''']]<ref name="pmid21864250">{{cite journal| author=Anna Z, John K, Maria T, George K, Ivelina B, Ioanna K et al.| title=The potential role of radiation therapy in Bowen's disease: a review of the current literature. | journal=Rev Recent Clin Trials | year= 2012 | volume= 7 | issue= 1 | pages= 42-6 | pmid=21864250 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21864250 }} </ref><ref name="pmid16168842">{{cite journal| author=Lukas VanderSpek LA, Pond GR, Wells W, Tsang RW| title=Radiation therapy for Bowen's disease of the skin. | journal=Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys | year= 2005 | volume= 63 | issue= 2 | pages= 505-10 | pmid=16168842 | doi=10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.02.024 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16168842 }} </ref><ref name="pmid18571754">{{cite journal| author=Herman JM, Pierce LJ, Sandler HM, Griffith KA, Jabbari S, Hiniker SM et al.| title=Radiotherapy using a water bath in the treatment of Bowen's disease of the digit. | journal=Radiother Oncol | year= 2008 | volume= 88 | issue= 3 | pages= 398-402 | pmid=18571754 | doi=10.1016/j.radonc.2008.05.025 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18571754 }} </ref><ref name="pmid28356127">{{cite journal| author=Goodman CR, DeNittis A| title=Photon irradiation using a water bath technique for treatment of confluent carcinoma in situ of the hand, digits, and nail bed: a case report. | journal=J Med Case Rep | year= 2017 | volume= 11 | issue= 1 | pages= 86 | pmid=28356127 | doi=10.1186/s13256-017-1233-3 | pmc=5372342 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28356127 }} </ref><ref name="pmid23937119">{{cite journal| author=Hunt WT, Cameron A, Craig P, de Berker DA| title=Multiple-digit periungual Bowen's disease: a novel treatment approach with radiotherapy. | journal=Clin Exp Dermatol | year= 2013 | volume= 38 | issue= 8 | pages= 857-61 | pmid=23937119 | doi=10.1111/ced.12149 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23937119 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11511838">{{cite journal| author=Dupree MT, Kiteley RA, Weismantle K, Panos R, Johnstone PA| title=Radiation therapy for Bowen's disease: lessons for lesions of the lower extremity. | journal=J Am Acad Dermatol | year= 2001 | volume= 45 | issue= 3 | pages= 401-4 | pmid=11511838 | doi=10.1067/mjd.2001.116581 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11511838 }} </ref> | |||
| | |||
*High-[[Power (communication)|powered]] [[Energy (biology)|energy]] [[Beamline|beams]] such as [[X-rays]] are [[Usage analysis|used]] to [[Killer cell|kill]] [[Affect|affected]] [[Cells (biology)|cells]] | |||
*Two types of [[radiation therapy]] can be [[Usage analysis|used]]: | |||
**[[External beam radiation therapy|External radiation therapy]] (a [[Machine perception|machine]] outside the [[Human body|body]] is [[Usage analysis|used]] to send [[radiation]] towards the [[diseased]] [[Cells (biology)|cells]]) | |||
**[[Internal]] [[radiation therapy]] ([[radioactive]] [[substance]] is [[Usage analysis|used]] which is [[Sealed source radiotherapy|sealed]] in [[Needle|needles]], [[Seed|seeds]], [[Wire|wires]], or [[catheters]] which are [[Place cell|placed]] [[Directly observed treatment|directly]] into or near the [[lesion]]) | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Excision]]''' | |||
| | |||
*It includes [[Cut|cutting]] off the [[Affect|affected]] [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] with a surrounding [[Marginal distribution|margin]] of [[healthy]] [[skin]] under [[local anesthetic]] and might require [[Stitch|stitches]] afterwards | |||
*Highly successful | |||
*[[Complications]] include [[Surgery|surgical]] [[scar]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Mohs micrographic surgery]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Usage analysis|Uses]] [[Special function|special]] [[training]] & technique involving the [[skin]] removal, layer by layer with subsequent [[examination]] of each layer under [[microscope]], until no [[abnormal]] [[Cells (biology)|cells]] are remaining | |||
*[[Least squares|Least]] [[Amount of substance|amount]] of the surrounding [[healthy]] [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] is removed | |||
*[[Edge detection|Edges]] are immediately [[Check|checked]] to [[See Clearly Method|see]] if [[tumor]] is found | |||
*Provides [[Best practice|best]] [[Cosmetics|cosmetically]] favorable [[Result|results]] especially on the [[skin]] [[Area|areas]] with: | |||
*[[Recurrence plot|Recurrent]] [[lesions]] of [[head]] and [[neck]] region with [[Limiting factor|limited]] [[Excess risk|excess]] [[skin]] such as [[face]] | |||
*Larger [[lesions]] | |||
*[[Lesions]] involving the [[Area|areas]] requiring as much [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] [[Preservative|preservation]] as [[Possibility theory|possible]] such as around the [[Nail (anatomy)|nail]] | |||
*Highest [[cure]] [[Rates|rate]] among all the available [[Treatments|treatment]] options | |||
|} | |||
==Prevention== | |||
Following are the [[Fewmets|few]] [[Preventive care|preventive]] [[Measure (mathematics)|measures]] to lower the [[RiskMetrics|risk]] for [[Development|developing]] Bowen's [[disease]]: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+Primary preventive measures for Bowen's disease | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Preventive method}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 400px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Details}} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Avoidance reaction|Avoiding]] [[Sunburn|sunburns]] and [[Suntanning|suntans]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Avoidance response|Avoid]] [[sun exposure]]: | |||
**During the middle of the [[Day spa|day]], usually from 10 AM to 4 PM, especially in North America | |||
**Even during [[Cloud|cloudy]] [[Day spa|days]] or winters | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Wear red day|Wearing]] [[Protective group|protective]] clothing | |||
|[[Wear red day|Wear]] the following while being in the outdoor [[Environment (biophysical)|environment]]: | |||
*Tightly woven, [[Dark matter|dark]] clothing | |||
*Shirts with long sleeves | |||
*[[Broad Institute|Broad]]-brimmed hats | |||
*Pants that [[Full service|fully]] [[Cover test|cover]] the [[legs]] ([[Avoidance response|avoid]] shorts) | |||
*Photoprotective clothing | |||
*[[Sunglasses]] (the ones which [[Block design|block]] both types of [[UV radiation]] i.e. [[UVA radiation|UVA]] & [[UVB radiation|UVB]]) | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Wear red day|Wearing]] [[SPF]] [[sunscreen]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Wear red day|Wear]] a [[sunscreen]] generously [[year]]-round, even during winters & cloudy days | |||
*It should be at least [[SPF]] 30 | |||
*It should be [[broad-spectrum]] [[Blocking (statistics)|blocking]] both [[UVA radiation|UVA]] and [[UVB radiation|UVB rays]] | |||
*[[Cover test|Cover]] all the [[Exposure effect|exposed]] [[Area|areas]] including the [[back]] of [[hands]], [[neck]], [[lips]], tip of [[ears]] | |||
*Reapply it every 2 hours & more often after [[swimming]] or if [[Perspiration|perspiring]] a lot | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Avoidance response|Avoiding]] [[Tanning booths|tanning beds]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Tanning booths|Tanning beds]] [[Usage analysis|use]] the [[Light|lights]] that emit [[Ultraviolet|UV]] [[Ray (optics)|rays]] which can increase the [[RiskMetrics|risk]] for [[Development|developing]] Bowen's [[disease]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''Being aware of [[Sun exposure|sun]]-[[Sensitization|sensitizing]] [[medications]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Over-the-counter drugs]] and common [[prescriptions]] including [[antibiotics]] may have tendency to increase the [[sensitivity]] of [[skin]] | |||
*Always [[Ask a question|ask]] the [[Doctor of Medicine|doctor]] or [[pharmacist]] about the [[Possibility theory|possible]] [[side effects]] of any [[medications]] before taking them | |||
*Take extra [[Precautionary principle|precautions]] to [[Protecting group|protect]] the [[skin]] by staying away from the [[Sun exposure|sun]],in case if the [[medications]] being [[Usage analysis|used]] have tendency to increase the [[skin]] [[Sensitivity (human)|sensitivity]] to [[sunlight]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Check|Checking]] [[skin]] regularly and [[Reporting disease cases|reporting]] any [[new]] or unusual [[skin changes]] to the [[Doctor of Medicine|doctor]]''' | |||
| | |||
*[[Examination|Examine]] the [[skin]] often for any [[new]] [[skin]] [[Growth|growths]] or [[Change detection|changes]] in [[Existential therapy|existing]] [[Bumps on skin|bumps]],[[Patching|patches]] or [[plaques]] | |||
*[[Check]] [[face]], [[ears]], [[neck]], and [[scalp]] by [[Usage analysis|using]] the [[mirror]] | |||
*[[Examination|Examine]] the [[chest]], [[trunk]], [[Top7|top]] & [[Arm pit|underside of arms]] and [[hands]] | |||
*[[Examination|Examine]] both the [[Frontal|front]] and [[back]] of [[legs]], and [[feet]], including [[soles]] and spaces between the [[toes]] | |||
*Also [[check]] the [[genital area]] and [[area]] between the [[buttocks]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Reducing equivalent|Reducing]] the [[Exposure effect|exposure]] to [[Ultraviolet radiation|ultraviolet (UV) radiation]], especially during the early [[Year|years]] of [[life]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Prior probability|Prior]] [[History and Physical examination|history]] of [[radiation exposure]] (both [[Ultraviolet|UV]] or artifical [[radiation therapy]] for [[acne]] or [[eczema]]) [[Lead|leads]] to increased [[chance]] for [[development]] of Bowen's [[disease]] | |||
|} | |||
==Differentiating Bowen's disease from other Diseases== | |||
*Bowen's [[disease]] must be [[Differentiate|differentiated]] from the following: | |||
**[[Psoriasis]] | |||
**[[Eczema]] | |||
**[[Superficial]] [[basal cell carcinoma]] | |||
**[[Actinic keratosis]] | |||
**[[Seborrheic keratosis]] | |||
**[[Lichen planus]] | |||
**[[Tinea corporis]] | |||
**[[Extramammary Paget's disease|Extramammary Paget’s disease]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+Differentiating Bowen's disease from other diseases | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Disease entity}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 400px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Etiology}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Pathophysiology}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 400px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Common sites of involvement}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Clinical manifestations}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 400px;" |{{fontcolor|#FFF|Images}} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''Bowen's [[disease]]''' | |||
|Common [[causes]] include: | |||
*[[Solar nebula|Solar]] damage | |||
*[[Aging]] | |||
*[[Arsenic]] | |||
*[[Immunosuppression]] (after [[organ transplant]], [[AIDS]]) | |||
*[[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] | |||
*[[Merkel cell]] [[polyomavirus]] | |||
*[[Irradiation]] ([[UV radiation|UV irradiation,]] photochemotherapy, [[radiotherapy]]) | |||
*[[Chronic (medical)|Chronic]] [[skin]] [[injury]] | |||
*[[Dermatosis|Dermatoses]] | |||
*[[Sjögren's syndrome|Sjogren's syndrome]] | |||
|[[Histopathology]] shows: | |||
*Unusual or atypical [[Cells (biology)|cells]] | |||
*Borst-Jadassohn [[Phenomenology|phenomenon]] | |||
<br /> | |||
|Most commonly involves: | |||
*[[Lower leg|Lower legs]] | |||
*[[Head]] and [[neck]] [[area]] | |||
*[[Skin fold|Skin folds]] | |||
*Perianal and [[genital area]] | |||
*[[Subungal exostosis|Subungal]] and periungal [[area]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Appearance|Appears]] as one or more persistent, non-[[healing]], non-elevated, [[Scaling skin|scaly]] or [[Crustacea|crusty]], [[itchy]], [[erythematous]] [[Patching|patches]] or [[plaques]] | |||
*[[Signs]] of [[malignant transformation]] of the [[lesion]] include [[bleeding]], [[ulceration]], [[induration]], [[tenderness]], [[Fleshy beams|fleshy]] [[Bumps on skin|bump]] | |||
| | |||
[[image:Bowens.jpg|thumb|200px|none|'''Bowen's disease''']] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Psoriasis]]''' | |||
| | |||
*PSORS-1 (part of the [[major histocompatibility complex]]) on [[chromosome]] 6p2, is the major [[genetic]] determinant of [[psoriasis]] | |||
*[[Environmental factor|Environmental factors]] implicated in the [[Development (biology)|development]] or aggravation of [[psoriasis]] are: | |||
**[[Stress]] (physical and [[mental]]) | |||
**[[Smoking]] | |||
**[[Alcohol consumption|Excessive alcohol consumption]] | |||
**[[Infection]] ([[Streptococcal Infection|Streptococcal]], [[HIV]]) | |||
**[[Seasonal allergy|Seasonal]] variation | |||
**[[Medications]] ([[lithium]], [[beta blockers]], [[Pegylated interferon-alpha-2b|pegylated interferon alpha-2b]], [[siltuximab]]) | |||
**[[Obesity]] | |||
**[[Skin]] injury | |||
**[[Skin dryness]] | |||
|[[Histopathology]] shows: | |||
*[[Hyperkeratosis]] | |||
*Parakeratosis | |||
*Munro's microabscess | |||
*Kogoj [[pustules]] | |||
*[[Dermal]] [[Infiltration (medical)|infiltration]] with [[mononuclear cells]] mainly [[myeloid]] and [[T cells]] | |||
*[[Capillary]] loop [[dilation]] ([[causes]] [[Red-Al|red]] [[appearance]] of [[psoriatic]] [[lesions]]) | |||
|Involves: | |||
*[[Dorsal|Extensor]] [[Surface area|surfaces]] like [[elbows]] and [[knees]] | |||
*[[Scalp]] | |||
*[[Lumbosacral trunk|Lumbosacral area]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Red-Al|Red]] or [[salmon]]-[[Color|colored]] well-defined [[Plaque|plaques]]<nowiki/> with [[Silver|silvery]]-[[White (mutation)|white]] dry [[Scaling skin|scaling]] | |||
*[[Pain]] described as unpleasant, [[Burn|burning]], [[itchy]], [[Hot aches|hot]] | |||
*[[Pruritis]] | |||
*[[High fever]] | |||
*[[Dystrophy|Dystrophic]] [[nails]] | |||
*[[Arthralgia]] | |||
*[[Conjunctivitis]] or [[blepharitis]] | |||
*[[Enthesitis]] | |||
*[[Depression]] | |||
*[[Dactylitis]] | |||
*[[Geographic tongue]] | |||
| | |||
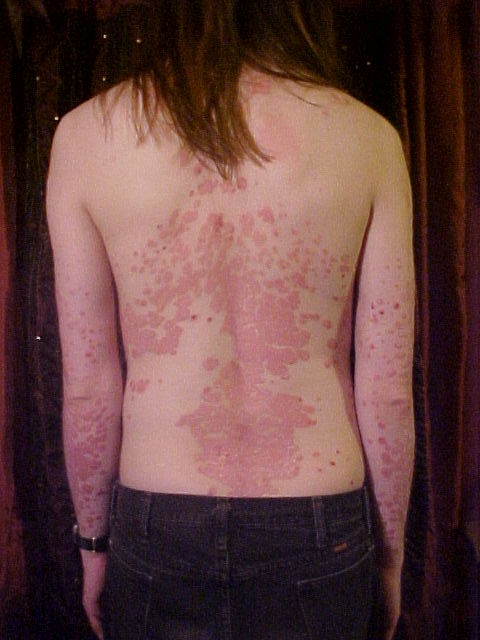
[[File:Psoriasis on back.jpg|thumb|200px|none|A young man whose back and arms are affected by psoriasis, source: wikipedia.org]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Eczema]]''' | |||
|Common [[causes]] include: | |||
*'''Netherton’s [[syndrome]]/ [[Congenital]] [[erythroderma]]''' [[Characterization (mathematics)|characterized]] by [[mutations]] in '''[[SPINK5]]''' [[gene]] which [[Product (biology)|produces]] [[LEKTI]], a '''[[protease inhibitor]]''' providing [[Protecting group|protection]] against damage [[Causes|caused]] by [[allergens]] | |||
*[[Mutations]] in [[gene]] [[Product (biology)|producing]] [[filaggrin]] [[protein]] ([[Prevention (medical)|prevents]] [[skin]] dryness and provides physcial [[Barrier (pharmaceutical)|barrier]] of [[skin]]) | |||
*[[Association (statistics)|Associated]] with other [[atopic diseases]] such as: | |||
**[[Asthma]] | |||
**[[Allergic rhinitis]] | |||
**[[Hay fever]] | |||
**[[Food allergy]] | |||
**[[Urticaria]] | |||
*[[Allergens]] such as: | |||
**[[Pollen|Pollens]] | |||
**[[Animal dander]] | |||
**[[Mold allergy|Mold]] | |||
**[[Cigarette smoke]] | |||
**[[Dust mite|Dust mites]] | |||
*[[Weather Data Mining|Weather]] [[Change detection|changes]] | |||
*[[Stress (medicine)|Stress]] ([[Physical culture|physical]], [[mental]], [[emotional]]) | |||
*[[Hyper IgE syndrome]] ([[Job syndrome]]) | |||
*[[Phenylketonuria]] | |||
*[[Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Autoimmune]] mediated type 1 [[hypersensitivity reaction]] [[Causes|caused]] by [[allergens]] such as [[Pollen|pollens]], [[animal dander]], [[mold]], [[cigarette smoke]], [[Dust mite|dust mites]] etc [[Lead|leading]] to [[skin]] [[inflammation]] | |||
|Involves: | |||
[[ | *[[Flexor]] [[Surface area|surfaces]] such as insides of [[elbows]], [[wrist]] creases, [[back]] of [[knees]] | ||
*[[Exposure (photography)|Exposed]] [[skin]] [[Surface area|surfaces]] such as [[face]], [[hands]], [[feet]] | |||
*[[Infants]] have [[rash]] on [[face]] and [[Scalp rash|scalp]] | |||
| | |||
*Dry, [[Scaling skin|scaly]], [[Erythematous rash|erythematous]] [[skin rash]] | |||
*[[Itching]] (worst at night) | |||
*[[Blister|Blistering]] | |||
*Peeling of [[skin]] | |||
*[[Lichenification]] of [[skin]] (leather like) | |||
*[[Depression (clinical)|Depression]] | |||
*[[Social anxiety]] | |||
| | |||
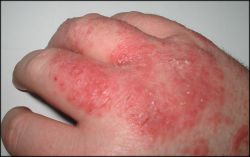
[[File:Dermatitis.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Typical, mild dermatitis]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |'''[[Superficial]] [[basal cell carcinoma]]''' | |||
|Common [[causes]] include: | |||
*[[Radiation exposure]][[Sunlight|(sunlight]] ([[UV light]]), [[Tanning booths|tanning beds]], and [[x-rays]]) | |||
*[[TP53 (gene)|TP53 gene]] [[mutations]] | |||
*Inappropriate [[Activation energy|activation]] of the [[hedgehog signaling pathway]] ([[Loss function|loss-of-function]] [[mutations]] in [[Tumor-suppressor gene|tumor-suppressor]][[protein]] [[patched]] [[Homolog|homologue]] 1 ([[PTCH1]]) | |||
*[[Gain-of-function mutation|Gain-of-function mutations]] in [[sonic hedgehog]] (SHH), [[smoothened]] (SMO) | |||
*[[Xeroderma pigmentosum]] | |||
*Epidermodysplastic verruciformis | |||
*[[Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome]] | |||
*[[Bazex syndrome|Bazex Syndrome]] | |||
*Rombo [[syndrome]] | |||
* | |||
| | |||
*Multiple [[lobular]] foci of basaloid palisading [[keratinocyte]] [[tumors]] | |||
*These are usually [[Attachment (psychology)|attached]] [[Superficial|superficially]] to the [[epidermis]] with a myxoid [[stroma]] and band-like [[Lichen|lichenoid]] [[Infiltration (medical)|infiltrate]] | |||
| | |||
*Most commonly involves the [[trunk]] | |||
*Can also involve [[Head (anatomy)|head]], [[neck]], and [[face]] | |||
| | |||
*Well-circumscribed,[[erythematous]], thin [[plaque]] or [[Patched|patch]] with [[Scaling skin|scaling]] | |||
*[[Central]] clearing and thin rolled borders | |||
| | |||
[[File:Basal cell carcinoma, superficial.jpg|thumb|center|200px|Kelly Nelson (Photographer) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons,https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/32/Basal_cell_carcinoma%2C_superficial.jpg]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Actinic keratosis|'''Actinic keratosis''']] | |||
| | |||
*Solar damage [[Causes|caused]] by [[constant]] [[Repeatability|repeated]] [[sun exposure]] in [[Fair use|fair]]-[[Skin|skinned]] [[Individual growth|individuals]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Constant]] [[Repeatability|repeated]] [[sun exposure]] [[causes]] dry, thick, [[Scaling skin|scaly]], or [[Crustacea|crusty]] [[Bumps on skin|bumps]] | |||
*[[Growth|Growths]] start out as [[Flat affect|flat]] [[Scaling skin|scaly]] [[Area|areas]], and later [[Growth|grow]] into a tough, [[wart]]-like [[area]] | |||
|Can involve any [[Sun exposure|sun-exposed]] [[area]] such as: | |||
*[[Face]] | |||
*[[Ear|Ears]] | |||
*[[Neck]] | |||
*[[Scalp]] | |||
*[[Chest]] | |||
*[[Back]] of [[hands]] | |||
*[[Forearm|Forearms]] | |||
*[[Lip|Lips]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Scaling skin|Scaly]], [[Crustacea|crusty]], dry, thick [[Growth|growths]] or [[Bumps on skin|bumps]] which are [[Dark matter|dark]] or [[light]], [[Tanning oil|tan]], [[Pinks|pink]], [[Red-Al|red]], a [[Combination reaction|combination]] of all of these | |||
| | |||
[[File:Actinic keratosis 1.jpg|thumb|200px|none| Actinic keratosis [http://peir.path.uab.edu/wiki/Main_Page Source: Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD]]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Seborrheic keratosis|'''Seborrheic keratosis''']] | |||
| | |||
*[[Association (statistics)|Associated]] with [[Activating group|activating]] [[mutation|mutations]] of a [[gene]] [[Coding sequence|coding]] for a [[growth factor receptor]] ([[FGFR3]]) | |||
| | |||
*Increased [[Cell (biology)|cell]] [[replication]] and [[proliferation]] | |||
|Involves: | |||
*[[Face]] | |||
*[[Chest]] | |||
*[[Shoulders]] | |||
*[[Back]] | |||
| | |||
*Round or [[oval]] [[Waxy flexibility|waxy]] [[Growth|growths]] resembling[[Flat affect|flattened]] or raised [[Wart|warts]], giving the [[appearance]] as if they were [[Dripping|dripped]] onto the [[skin]] by a [[Candlelighters|candle]] | |||
*Exhibit a variety of [[Color|colors]], from [[Pinks|pink]] or [[Yellow 2G|yellow]] through [[light]] tan, [[brown]] and [[black]] | |||
*"[[Paste (rheology)|Pasted]]-on" [[appearance]] | |||
*[[Local|Localized]] [[infection]] | |||
*[[Excess risk|Excessive]] [[itching]] due to [[irritation]] [[Causes|caused]] by jewelry or clothing | |||
*[[Size consistency|Size]] [[Variable|varies]] from very small to more than 1 [[inch]] (2.5 [[Centimeter|centimeters]]) | |||
| | |||
[[File:Seborrheic keratosis.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Gross natural color photo of face with multiple typical lesions [http://www.peir.net Source: Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology]]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Lichen planus|'''Lichen planus''']] | |||
|[[Causes]] include: | |||
*[[Allergic reaction]] to[[medications]] for [[high blood pressure]], [[heart disease]] and [[arthritis]] such as [[bendrofluazide]], [[chloroquine]], [[gold salts]], [[hydrochlorothiazide]], [[mepacrine]], [[methyldopa]], [[methyldopate]], [[penicillamine]] | |||
*[[Chronic (medical)|Chronic]] [[hepatitis C]] [[Virus (biology)|virus]] [[infection]] | |||
*[[Chronic (medical)|Chronic]] [[graft-versus-host disease]] of the [[skin]] | |||
*[[Stress (medicine)|Stress]] | |||
*[[Heart disease]] | |||
*[[Lichen planopilaris]] | |||
*[[Lichen ruber moniliformis]] | |||
| | |||
*Hyperparakeratosis with [[Thickener|thickening]] of the [[Granular cell|granular cel]]<nowiki/>l layer | |||
*[[Development (biology)|Development]] of a "saw-tooth" [[appearance]] of the [[rete pegs]] | |||
*[[Degeneration (medical)|Degeneration]] of the [[basal cell layer]] | |||
*[[Infiltration (medical)|Infiltration]] of [[inflammatory cells]] into the subepithelial layer of [[connective tissue]] | |||
|Involves: | |||
*Sites are near [[wrist]] and [[ankle]] | |||
*[[Scalp]] ([[Lichen planopilaris|'''lichen Planopilaris''']]''')''' | |||
*[[Oral mucosa|Oral]] [[Mucous membranes|mucous membrane]] | |||
| | |||
*Well-defined [[rash]] well-described by the "5 P's": | |||
*[[Pruritis|Pruritic]] | |||
*[[Planar chirality|Planar]] | |||
*[[Purple haze|Purple]] | |||
*Polygonal | |||
*[[Papules]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Lichen planus 1.jpg|thumb|200px|none|Lichen planus]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Tinea corporis|'''Tinea corporis''']] | |||
| | |||
*[[Causes|Caused]] by a tiny [[fungus]] known as [[dermatophyte]] | |||
*[[Risk factors]] for [[Acquired|acquiring]] this [[fungal infection]] include: | |||
**Petting or grooming [[animals]] such as [[Dog odor|dogs]], cats, horses, pigs, [[ferrets]] and cows | |||
**[[Touch|Touching]] inanimate [[Objectivity (science)|objects]] such as personal care [[Product (biology)|products]], bed linen, combs, athletic gear, or [[hair]] [[Brushing|brushes]] [[Contamination|contaminated]] by an [[Affect|affected]] [[person]] | |||
**Living in crowded, [[Humidity|humid]] [[conditions]] | |||
**Excessively [[sweating]] | |||
**Participating in close contact [[Sports medicine|sports]] like soccer, rugby, or wrestling | |||
**[[Wear red day|Wearing]] tight, constrictive clothing with poor [[Aerated lagoon|aeration]] | |||
**[[Immunodeficiency|Weakened immune system]] ([[HIV]] [[infection]] or taking [[Immunosuppressive drug|immunosuppressive drugs]]) | |||
| | |||
*[[Fungal]] [[skin infection]] [[Causes|caused]] by [[ringworm]]/[[dermatophytes]] | |||
*[[Fungi]] inhabit the nonliving, cornified layers of the [[skin]], [[Hair|hair,]] and [[nail]] (attractive and [[Conduct|conducive]] for [[fungal]] [[proliferation]] due to [[Moist skin|moist]], warm [[Environment (biophysical)|environment]]) | |||
*After 1-3 weeks of [[incubation period]], [[dermatophytes]] [[Invasive (medical)|invade]] peripherally in a [[Centrifuge|centrifugal]] [[pattern]] | |||
*Increased [[epidermal]] [[cell proliferation]] occurs in active border with [[Result|resultant]] [[Scaling skin|scaling]] in [[Response element|response]] to [[infection]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Arm|Arms]] especially [[armpits]] in [[People's Solidarity|people]] who [[sweat]] excessively | |||
*[[Legs]] | |||
*[[Groin]] creases | |||
*[[Skin fold|Skin folds]] of [[Human abdomen|abdomen]] | |||
*[[Hair]] | |||
*[[Nails]] | |||
| | |||
*Enlarging, raised [[Red-Al|red]] rings with a [[central]] [[area]] of clearing ([[ringworm]]) | |||
*[[Scaling skin|Scaly,]] elevated [[Edge detection|edges]] of [[rash]] | |||
*Dry, flaky surrounding [[skin]] | |||
*[[Hair loss]] ([[alopecia]]) in the [[Infection|infective]] [[area]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Ringworm on the arm, or tinea corporis due to Trichophyton mentagrophytes PHIL 2938 lores.jpg|thumb|200px|none|This patient presented with ringworm on the arm, or tinea corporis due to Trichophyton mentagrophytes.]] | |||
{| | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Extramammary Paget's disease|'''Extramammary Paget’s disease''']]<ref name="urlExtramammary Paget Disease - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf">{{cite web |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493224/ |title=Extramammary Paget Disease - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid29636019">{{cite journal| author=Yao H, Xie M, Fu S, Guo J, Peng Y, Cai Z et al.| title=Survival analysis of patients with invasive extramammary Paget disease: implications of anatomic sites. | journal=BMC Cancer | year= 2018 | volume= 18 | issue= 1 | pages= 403 | pmid=29636019 | doi=10.1186/s12885-018-4257-1 | pmc=5894213 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29636019 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24617434">{{cite journal| author=Karam A, Dorigo O| title=Increased risk and pattern of secondary malignancies in patients with invasive extramammary Paget disease. | journal=Br J Dermatol | year= 2014 | volume= 170 | issue= 3 | pages= 661-71 | pmid=24617434 | doi=10.1111/bjd.12635 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24617434 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22244907">{{cite journal| author=van der Zwan JM, Siesling S, Blokx WA, Pierie JP, Capocaccia R| title=Invasive extramammary Paget's disease and the risk for secondary tumours in Europe. | journal=Eur J Surg Oncol | year= 2012 | volume= 38 | issue= 3 | pages= 214-21 | pmid=22244907 | doi=10.1016/j.ejso.2011.12.008 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22244907 }} </ref><ref name="pmid30497678">{{cite journal| author=Asel M, LeBoeuf NR| title=Extramammary Paget's Disease. | journal=Hematol Oncol Clin North Am | year= 2019 | volume= 33 | issue= 1 | pages= 73-85 | pmid=30497678 | doi=10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.003 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30497678 }} </ref><ref name="pmid28058078">{{cite journal| author=Chumbalkar V, Jennings TA, Ainechi S, Lee EC, Lee H| title=Extramammary Paget's Disease of Anal Canal Associated With Rectal Adenoma Without Invasive Carcinoma. | journal=Gastroenterology Res | year= 2016 | volume= 9 | issue= 6 | pages= 99-102 | pmid=28058078 | doi=10.14740/gr727e | pmc=5191897 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28058078 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24072832">{{cite journal| author=Jabir S, Khatib M, Ali S, Niranjan N| title=Perianal Paget's disease: a diagnostic dilemma. | journal=BMJ Case Rep | year= 2013 | volume= 2013 | issue= | pages= | pmid=24072832 | doi=10.1136/bcr-2013-200504 | pmc=3794179 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24072832 }} </ref><ref name="pmid2178040">{{cite journal| author=Tarng SJ, Fan HA, Lin SE, Lai CR, Tang RP, You YD et al.| title=Perianal Paget's disease--report of 4 cases. | journal=Changgeng Yi Xue Za Zhi | year= 1990 | volume= 13 | issue= 4 | pages= 314-21 | pmid=2178040 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2178040 }} </ref><ref name="pmid20556842">{{cite journal| author=Lian P, Gu WL, Zhang Z, Cai GX, Wang MH, Xu Y et al.| title=Retrospective analysis of perianal Paget's disease with underlying anorectal carcinoma. | journal=World J Gastroenterol | year= 2010 | volume= 16 | issue= 23 | pages= 2943-8 | pmid=20556842 | doi=10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2943 | pmc=2887592 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20556842 }} </ref><ref name="pmid25113623">{{cite journal| author=Rajendran S, Koh CE, Solomon MJ| title=Extramammary Paget's disease of the perianal region: a 20-year experience. | journal=ANZ J Surg | year= 2017 | volume= 87 | issue= 3 | pages= 132-137 | pmid=25113623 | doi=10.1111/ans.12814 | pmc= | <nowiki><ref name="pmid27746643"></nowiki>{{cite journal| author=Nagai Y, Kazama S, Yamada D, Miyagawa T, Murono K, Yasuda K et al.| title=Perianal and Vulvar Extramammary Paget Disease: A Report of Six Cases and Mapping Biopsy of the Anal Canal. | journal=Ann Dermatol | year= 2016 | volume= 28 | issue= 5 | pages= 624-628 | pmid=27746643 | doi=10.5021/ad.2016.28.5.624 | pmc=5064193 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27746643 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24363864">{{cite journal| author=Jung JH, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH| title=Extramammary Paget Disease of External Genitalia: Surgical Excision and Follow-up Experiences With 19 Patients. | journal=Korean J Urol | year= 2013 | volume= 54 | issue= 12 | pages= 834-9 | pmid=24363864 | doi=10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.834 | pmc=3866286 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24363864 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15882734">{{cite journal| author=Yang WJ, Kim DS, Im YJ, Cho KS, Rha KH, Cho NH et al.| title=Extramammary Paget's disease of penis and scrotum. | journal=Urology | year= 2005 | volume= 65 | issue= 5 | pages= 972-5 | pmid=15882734 | doi=10.1016/j.urology.2004.12.010 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15882734 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11829881">{{cite journal| author=Fu M, Gao S, Wang P| title=[19 cases of Paget's disease]. | journal=Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi | year= 1999 | volume= 37 | issue= 7 | pages= 429-31 | pmid=11829881 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11829881 }} </ref><ref name="urlExtramammary Pagets disease of the perianal region: a 20‐year experience - Rajendran - 2017 - ANZ Journal of Surgery - Wiley Online Library">{{cite web |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/ans.12814 |title=Extramammary Paget's disease of the perianal region: a 20‐year experience - Rajendran - 2017 - ANZ Journal of Surgery - Wiley Online Library |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
|Most common [[Causes|cause]] is the [[Underlying representation|underlying]] [[malignancy]] such as: | |||
*[[Underlying representation|Underlying]] [[cutaneous]] [[adnexal]] [[carcinoma]] (mainly [[Apocrine gland|apocrine]] type) | |||
*Sometimes arises from [[Periurethral phlegmon|periurethral]], [[Eccrine sweat glands|eccrine]], perianal, or [[Bartholin's glands]] | |||
*[[Internal]] [[carcinoma]] of [[Urinary bladder|bladder]], [[rectum]], [[cervix]], [[Prostate Gland|prostate]], or [[urethra]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Paget's disease|Paget's]] [[Cells (biology)|cells]] (large [[Cells (biology)|cells]] with abundant amphophilic or [[basophilic]], finely [[Granular cell|granular]] [[cytoplasm]], large centrally-[[Location parameter|located]] [[Cell nucleus|nucleus]] with prominent [[nucleolus]]) and [[Signet cell|signet ring cells]] | |||
*Arises from [[Keratinocyte|keratinocytic]] [[Stem cell|stem cells]] or from [[apocrine gland]] [[ducts]] | |||
|[[Frequentism|Frequently]] occurs in [[Area|areas]] of [[Abundance (chemistry)|abundance]] of [[apocrine sweat glands]] such as: | |||
*[[Vulva]] | |||
*[[Perineum]] | |||
*[[Scrotum]] | |||
*Perianal [[skin]] | |||
*[[Penis]] | |||
| | |||
*Irregular, or ring-[[Shape parameter|shaped]], [[erythematous]], or [[White (mutation)|white]], [[Eczematous Scaling|eczematous]] [[skin]] [[plaque]] | |||
*'''“[[Strawberry|Strawberries]] and [[Cream (pharmaceutical)|cream]]” [[appearance]]''' due to scattered [[Area|areas]] of [[Erosion (dental)|erosion]] and [[White (mutation)|white]] [[Scale (social sciences)|scale]] | |||
*Weeping, crusting[[Erosion (dental)|erosions]] | |||
*[[Ulceration]] | |||
*'''‘Underpants-[[pattern]] [[erythema]]’''' in the [[groin area]] which [[Spread of the cancer|spreads]] peripherally to the [[Area|areas]] [[Cover test|covered]] by underwear (due to [[lymphatic system]] [[invasion]]) | |||
* | |||
| | |||
[[File:Extramammary Paget's Disease.png|thumb|200px|none|Extramammary paget's disease [[https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Extramammary_Paget%27s_Disease.png Source: Wikimedia Commons]]] | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Dermatology]] | [[Category:Dermatology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:47, 22 January 2021
|
Bowen's disease Microchapters |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mohsin, M.D.[2], Jesus Rosario Hernandez, M.D. [3]
Synonyms and keywords: Bowen's carcinoma; squamous cell carcinoma in situ of skin; intraepidermal carcinoma skin, Intraepithelial neoplasia
Overview
In medicine (dermatology), Bowen's disease (BD) is a sunlight-induced skin disease, classified either as an early noninvasive stage or intraepidermal form of squamous cell carcinoma which if left undiagnosed, untreated, or neglected has <10% chance of malignant transformation into invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. It usually appears as a erythematous, scaly or crusty patch or plaque anywhere on the body but most commonly involves lower legs, with other possible sites of involvement to be head, neck, genitals, and skin folds. It is easily curable by various treatment options such as cryotherapy, curettage, cautery, photodynamic therapy, topical chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or excision of the lesion.
Historical Perspective
Pathophysiology
Microscopic Pathology
- Cells in Bowen's disease are extremely unusual or atypical under the microscope[1]
- In many cases, cells look worse under the microscope than the cells of many outright and invading squamous cell carcinomas
- Degree of atypia (strangeness, unusualness) seen under the microscope best tells how cells may behave (should they invade another portion of the body)[2][3]
Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon
- Bowen's disease can also occur as a part of Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon (previously known as intraepidermal epithelioma) which is a heterogeneous group of following intraepithelial lesions:[4][5][6][7][8][9]
- Irritated seborrheic keratosis
- Clonal seborrheic keratosis
- Eccrine poroma
- Malignant eccrine poroma
- Intraepithelial neoplasia (Bowen's disease)
- Other intraepidermal sweat gland tumors
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Causes
Bowen's disease is a non-infectious, non-familial disease with common causes as mentioned below:
- Solar damage due to long-term sun exposure or use of sunbeds, especially in people with fair skin
- Aging
- Carcinogens such as arsenic:
- Weak immune system due to:
- Viral infection such as:
- Different types HPV/human papillomavirus:[10][11][12][13][14][15][16]
- HPV 16, 18, 34, and 48 are associated with Bowen's disease of perianal & genital region especially bowenoid papulosis and VIN are caused by HPV 16
- HPV 2, 16, 34, and 35 are associated with Bowen's disease in other areas of body (excluding genitals)
- 47% of acral and 24% of nonacral extragenital Bowen's disease lesion contains HPV genome
- Merkel cell polyomavirus
- Different types HPV/human papillomavirus:[10][11][12][13][14][15][16]
- Previous irradiation such as:
- Ultraviolet irradiation
- Radiotherapy treatment
- Photochemotherapy
- Chronic skin injury
- Dermatoses
- Sjögren's syndrome
Epidemiology and Demographics
Age
- Bowen's disease can affect adults of any age, most commonly involves older patients in their 60s or 70s
- It is rare before the age of 30 years
Gender
- Bowen's disease occurs more predominantly in men than in women (70-85% of cases)
Race
- Caucasians are the ones most commonly affected by Bowen's disease
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- Bowen's disease grows very slowly over the period of months or even years[17]
- It is easily treatable if diagnosed in time
- If left undiagnosed, untreated or neglected, Bowen's disease can ultimately progressively develop into invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in 1 in 20-30 people (i.e. 3-5% risk)
- SCC is a treatable condition, but if it's deeper or invasive, it means it's very serious
Diagnosis
Common symptoms
- It usually appears as one or more skin patches with following characteristics:[17]
Signs and symptoms of malignant transformation
- Following changes in the skin patch are the signs that bowen's disease has turned into invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin:
Common sites of involvement
Skin
- Lesions can occur anywhere on the skin surface or on mucosal surfaces, although the involvement of palms or soles is uncommon
- A persistent progressive non-elevated red scaly or crusted plaque which is due to an intradermal carcinoma and is potentially malignant
- Atypical squamous (resembling fish scales) cells proliferate through the whole thickness of the epidermis
 |
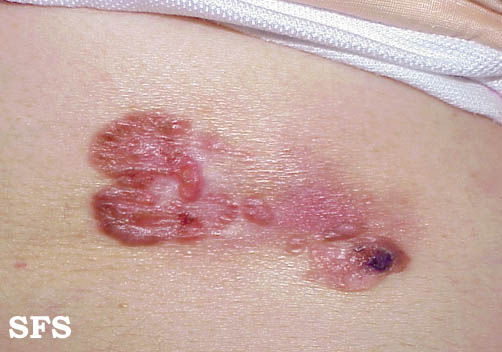 |
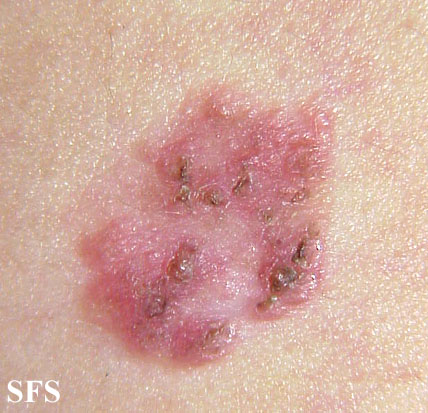 |
 |
Extremities
- About three-quarters of the patients have lesions on the lower leg (60-85%), usually in previously or presently sun-exposed areas of skin
Head and neck area
- Being prone to the sun exposure, head and neck area is also one of the common sites to be affected by Bowen's disease
 |
 |
 |
Subungal, periungal region
- Bowen's disease also commonly involves subungal or periungal areas (i.e. either under or around fingernails or toenails)
Skinfolds
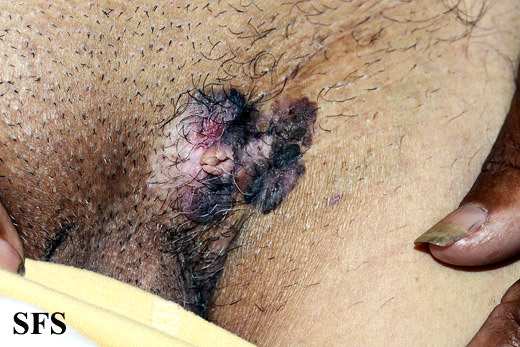 |
Genitourinary system
- Bowen's disease can also involve genital and perianal areas
- It appears in following 3 forms in genital area:[21]
| Bowen's disease form | Characteristic features |
|---|---|
| Bowenoid papulosis | |
| Erythroplasia of Queyrat |
|
| Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) |
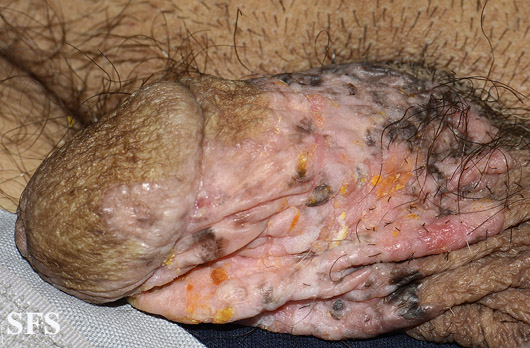 |
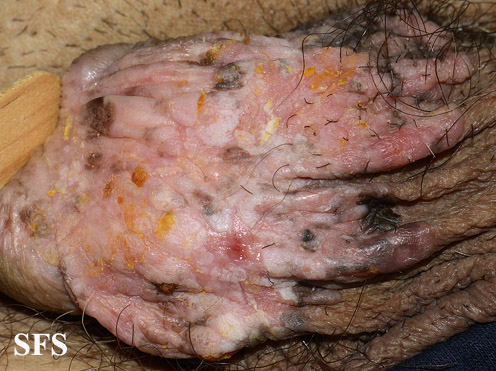 |
Physical Examination
- Bowen's disease typically presents as a gradually enlarging, well demarcated erythematous plaque with an irregular border and surface crusting or scaling[22][23][24]
- Lesion might feel tender representing its malignant transformation
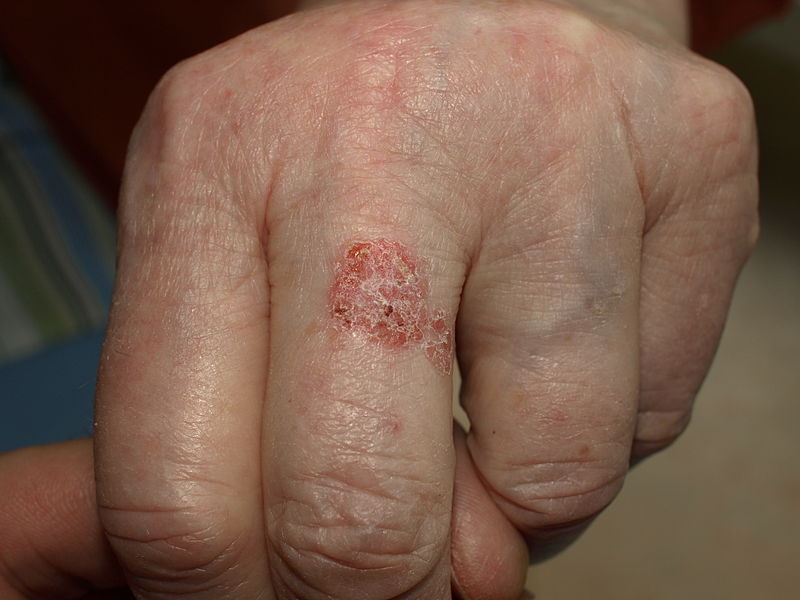 |
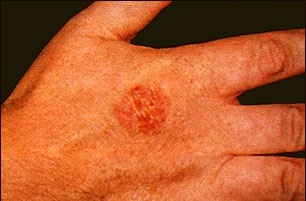 |
Dermoscopy
- Dermoscopy is the skin examination via skin surface microscopy
- Also known as:
- 'Epiluminoscopy'
- 'Epiluminescent microscopy'
- It is usually used for examination of pigmented skin lesions
- Benefits of dermoscopy include:
- Improvement of diagnostic accuracy of pigmented skin lesions
- Evaluation of nonpigmented skin tumors (recognizes vascular structures not visible to naked eye)
- Helpful in diagnosis of Bowen's disease and shows:[25]
- Repetitive morphological findings such as glomerular vessels and scaly surface
- Small brown globules and/or homogeneous pigmentation in case of pigmented Bowen's disease[26]
Skin biopsy
- Skin biopsy must be done to:
- Confirm the diagnosis Bowen's disease
- Differentiate from other skin lesions
- Rule out invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
Treatment
- Specific treatment for an individual case depends upon various factors, such as:[27]
- Different treatment options for Bowen's disease include the following:
| Treatment option | Details |
|---|---|
| Watch and wait | |
| Cryosurgery/Freezing | |
| Topical cream |
|
| Curettage & electrodesiccation or cryotherapy |
|
| Cauterization or diathermy coagulation[28] | |
| Photodynamic therapy (PDT)[29][30][31][32][33][34] | |
| Radiation therapy[35][36][37][38][39][40] | |
| Excision | |
| Mohs micrographic surgery |
|
Prevention
Following are the few preventive measures to lower the risk for developing Bowen's disease:
| Preventive method | Details |
|---|---|
| Avoiding sunburns and suntans | |
| Wearing protective clothing | Wear the following while being in the outdoor environment: |
| Wearing SPF sunscreen | |
| Avoiding tanning beds |
|
| Being aware of sun-sensitizing medications |
|
| Checking skin regularly and reporting any new or unusual skin changes to the doctor |
|
| Reducing the exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, especially during the early years of life |
|
Differentiating Bowen's disease from other Diseases
- Bowen's disease must be differentiated from the following:
References
- ↑ Neagu TP, Tiglis M, Botezatu D, Enache V, Cobilinschi CO, Vâlcea-Precup MS, GrinTescu IM (2017). "Clinical, histological and therapeutic features of Bowen's disease". Rom J Morphol Embryol. 58 (1): 33–40. PMID 28523295.
- ↑ Nemkaeva RM, Kurmashov NA, Oslopova S (1988). "[Bowen's disease]". Vestn Dermatol Venerol (8): 71–2. PMID 3195216.
- ↑ Scarborough DA, Bisaccia EP, Yoder FW (1982). "Solitary pigmented Bowen's disease". Arch Dermatol. 118 (11): 954–5. PMID 7138058.
- ↑ Yanagihara S, Oiso N, Hirota N, Kato M, Miyake S, Kawada A (2019). "Acantholytic Bowen's disease histopathologically showing the Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon". Eur J Dermatol. doi:10.1684/ejd.2019.3545. PMID 31145080.
- ↑ Baykal C, Buyukbabani N, Babuna G, Polat Ekinci A, Kurul S (2016). "Giant Bowen's disease histologically showing Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon and complicated with squamous cell carcinoma development". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 30 (10): e88–e89. doi:10.1111/jdv.13335. PMID 26373350.
- ↑ "Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon | definition of Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon by Medical dictionary".
- ↑ "Pathology Outlines - Borst-Jadassohn phenomenon".
- ↑ "PayPerView: Jadassohn's Intraepidermal Epithelioma - Karger Publishers".
- ↑ Lora V, Chouvet B, Kanitakis J (2011). "The "intraepidermal epithelioma" revisited: immunohistochemical study of the borst-jadassohn phenomenon". Am J Dermatopathol. 33 (5): 492–7. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181fe6f90. PMID 21587033.
- ↑ Clavel CE, Huu VP, Durlach AP, Birembaut PL, Bernard PM, Derancourt CG (1999). "Mucosal oncogenic human papillomaviruses and extragenital Bowen disease". Cancer. 86 (2): 282–7. PMID 10421264.
- ↑ Zheng S, Adachi A, Shimizu M, Shibata SI, Yasue S, Sakakibara A; et al. (2005). "Human papillomaviruses of the mucosal type are present in some cases of extragenital Bowen's disease". Br J Dermatol. 152 (6): 1243–7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06643.x. PMID 15948988.
- ↑ Lampert A, Pauwels C, Duboucher C, Morel G, Poveda JD, Périé G (2000). "[Detection of human papillomavirus in cutaneous extragenital Bowen's disease in immunocompetent patients]". Ann Dermatol Venereol. 127 (1): 40–5. PMID 10717561.
- ↑ Collina G, Rossi E, Bettelli S, Cook MG, Cesinaro AM, Trentini GP (1995). "Detection of human papillomavirus in extragenital Bowen's disease using in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction". Am J Dermatopathol. 17 (3): 236–41. PMID 8599431.
- ↑ Derancourt C, Mougin C, Chopard Lallier M, Coumes-Marquet S, Drobacheff C, Laurent R (2001). "[Oncogenic human papillomaviruses in extra-genital Bowen disease revealed by in situ hybridization]". Ann Dermatol Venereol. 128 (6–7): 715–8. PMID 11460032.
- ↑ Pham-Huu V, Derancourt C, Clavel C, Durlach A, Birembaut P, Bernard P (1999). "[Oncogenic mucosal human papillomaviruses in Bowen's disease of the hands]". Ann Dermatol Venereol. 126 (11): 808–12. PMID 10612858.
- ↑ Murao K, Yoshioka R, Kubo Y (2014). "Human papillomavirus infection in Bowen disease: negative p53 expression, not p16(INK4a) overexpression, is correlated with human papillomavirus-associated Bowen disease". J. Dermatol. 41 (10): 878–84. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12613. PMID 25201325.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Bowen's disease - NHS".
- ↑ Wagner RF, Grande DJ (1986). "Solitary pigmented Bowen's disease of the scrotum". J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 12 (10): 1114–5. PMID 3760318.
- ↑ Al-Dawsari NA, Raslan W, Dawamneh MF (2014). "Pigmented Bowen's disease of the penis and scrotum in a patient with AIDS". Dermatol Online J. 20 (4): 22337. PMID 24746300.
- ↑ Narahira A, Yanagi T, Kitamura S, Hata H, Shimizu H (2019). "Dermoscopic features of genital pigmented Bowen's disease: Report of a case and review of the published work". J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14938. PMID 31141219.
- ↑ "Bowen's Disease: Skin Cancer Linked to HPV Infection".
- ↑ Inoue T, Kobayashi K, Sawada M, Ishizaki S, Ito H, Fujibayashi M; et al. (2010). "Dermoscopic Features of Pigmented Bowen's Disease in a Japanese Female Mimicking Malignant Melanoma". Dermatol Res Pract. 2010. doi:10.1155/2010/543091. PMC 2929512. PMID 20811602.
- ↑ Hayashi Y, Tanaka M, Suzaki R, Mori N, Konohana I (2009). "Dermoscopy of Pigmented Bowen's Disease Mimicking Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma". Case Rep Dermatol. 1 (1): 11–15. doi:10.1159/000227284. PMC 2895203. PMID 20652107.
- ↑ Yang Y, Lin J, Fang S, Han S, Song Z (2017). "What's new in dermoscopy of Bowen's disease: two new dermoscopic signs and its differential diagnosis". Int J Dermatol. 56 (10): 1022–1025. doi:10.1111/ijd.13734. PMID 28832993.
- ↑ Zalaudek I, Argenziano G, Leinweber B, Citarella L, Hofmann-Wellenhof R, Malvehy J; et al. (2004). "Dermoscopy of Bowen's disease". Br J Dermatol. 150 (6): 1112–6. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05924.x. PMID 15214896.
- ↑ Cameron A, Rosendahl C, Tschandl P, Riedl E, Kittler H (2010). "Dermatoscopy of pigmented Bowen's disease". J Am Acad Dermatol. 62 (4): 597–604. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.06.008. PMID 20079953.
- ↑ "Bowen Disease - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders)".
- ↑ Neubert T, Lehmann P (2008). "Bowen's disease - a review of newer treatment options". Ther Clin Risk Manag. 4 (5): 1085–95. PMC 2621408. PMID 19209288.
- ↑ Wong TW, Sheu HM, Lee JY, Fletcher RJ (2001). "Photodynamic therapy for Bowen's disease (squamous cell carcinoma in situ) of the digit". Dermatol Surg. 27 (5): 452–6. PMID 11359493.
- ↑ Britton JE, Goulden V, Stables G, Stringer M, Sheehan-Dare R (2005). "Investigation of the use of the pulsed dye laser in the treatment of Bowen's disease using 5-aminolaevulinic acid phototherapy". Br J Dermatol. 153 (4): 780–4. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06830.x. PMID 16181460.
- ↑ Kang HK, Yun JH, Son YM, Roh JY, Lee JR (2014). "Photodynamic Therapy for Bowen's Disease of the Vulva Area". Ann Dermatol. 26 (2): 241–5. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.241. PMC 4037679. PMID 24882981.
- ↑ Dijkstra AT, Majoie IM, van Dongen JW, van Weelden H, van Vloten WA (2001). "Photodynamic therapy with violet light and topical 6-aminolaevulinic acid in the treatment of actinic keratosis, Bowen's disease and basal cell carcinoma". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 15 (6): 550–4. PMID 11843215.
- ↑ Harth Y, Hirshowitz B, Kaplan B (1998). "Modified topical photodynamic therapy of superficial skin tumors, utilizing aminolevulinic acid, penetration enhancers, red light, and hyperthermia". Dermatol Surg. 24 (7): 723–6. PMID 9693665.
- ↑ de Haas ER, de Vijlder HC, Sterenborg HJ, Neumann HA, Robinson DJ (2008). "Fractionated aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy provides additional evidence for the use of PDT for non-melanoma skin cancer". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 22 (4): 426–30. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02445.x. PMID 18031503.
- ↑ Anna Z, John K, Maria T, George K, Ivelina B, Ioanna K; et al. (2012). "The potential role of radiation therapy in Bowen's disease: a review of the current literature". Rev Recent Clin Trials. 7 (1): 42–6. PMID 21864250.
- ↑ Lukas VanderSpek LA, Pond GR, Wells W, Tsang RW (2005). "Radiation therapy for Bowen's disease of the skin". Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 63 (2): 505–10. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.02.024. PMID 16168842.
- ↑ Herman JM, Pierce LJ, Sandler HM, Griffith KA, Jabbari S, Hiniker SM; et al. (2008). "Radiotherapy using a water bath in the treatment of Bowen's disease of the digit". Radiother Oncol. 88 (3): 398–402. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2008.05.025. PMID 18571754.
- ↑ Goodman CR, DeNittis A (2017). "Photon irradiation using a water bath technique for treatment of confluent carcinoma in situ of the hand, digits, and nail bed: a case report". J Med Case Rep. 11 (1): 86. doi:10.1186/s13256-017-1233-3. PMC 5372342. PMID 28356127.
- ↑ Hunt WT, Cameron A, Craig P, de Berker DA (2013). "Multiple-digit periungual Bowen's disease: a novel treatment approach with radiotherapy". Clin Exp Dermatol. 38 (8): 857–61. doi:10.1111/ced.12149. PMID 23937119.
- ↑ Dupree MT, Kiteley RA, Weismantle K, Panos R, Johnstone PA (2001). "Radiation therapy for Bowen's disease: lessons for lesions of the lower extremity". J Am Acad Dermatol. 45 (3): 401–4. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.116581. PMID 11511838.
- ↑ "Extramammary Paget Disease - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf".
- ↑ Yao H, Xie M, Fu S, Guo J, Peng Y, Cai Z; et al. (2018). "Survival analysis of patients with invasive extramammary Paget disease: implications of anatomic sites". BMC Cancer. 18 (1): 403. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4257-1. PMC 5894213. PMID 29636019.
- ↑ Karam A, Dorigo O (2014). "Increased risk and pattern of secondary malignancies in patients with invasive extramammary Paget disease". Br J Dermatol. 170 (3): 661–71. doi:10.1111/bjd.12635. PMID 24617434.
- ↑ van der Zwan JM, Siesling S, Blokx WA, Pierie JP, Capocaccia R (2012). "Invasive extramammary Paget's disease and the risk for secondary tumours in Europe". Eur J Surg Oncol. 38 (3): 214–21. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2011.12.008. PMID 22244907.
- ↑ Asel M, LeBoeuf NR (2019). "Extramammary Paget's Disease". Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 33 (1): 73–85. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.003. PMID 30497678.
- ↑ Chumbalkar V, Jennings TA, Ainechi S, Lee EC, Lee H (2016). "Extramammary Paget's Disease of Anal Canal Associated With Rectal Adenoma Without Invasive Carcinoma". Gastroenterology Res. 9 (6): 99–102. doi:10.14740/gr727e. PMC 5191897. PMID 28058078.
- ↑ Jabir S, Khatib M, Ali S, Niranjan N (2013). "Perianal Paget's disease: a diagnostic dilemma". BMJ Case Rep. 2013. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-200504. PMC 3794179. PMID 24072832.
- ↑ Tarng SJ, Fan HA, Lin SE, Lai CR, Tang RP, You YD; et al. (1990). "Perianal Paget's disease--report of 4 cases". Changgeng Yi Xue Za Zhi. 13 (4): 314–21. PMID 2178040.
- ↑ Lian P, Gu WL, Zhang Z, Cai GX, Wang MH, Xu Y; et al. (2010). "Retrospective analysis of perianal Paget's disease with underlying anorectal carcinoma". World J Gastroenterol. 16 (23): 2943–8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2943. PMC 2887592. PMID 20556842.
- ↑ {{cite journal| author=Rajendran S, Koh CE, Solomon MJ| title=Extramammary Paget's disease of the perianal region: a 20-year experience. | journal=ANZ J Surg | year= 2017 | volume= 87 | issue= 3 | pages= 132-137 | pmid=25113623 | doi=10.1111/ans.12814 | pmc= | <ref name="pmid27746643">Nagai Y, Kazama S, Yamada D, Miyagawa T, Murono K, Yasuda K; et al. (2016). "Perianal and Vulvar Extramammary Paget Disease: A Report of Six Cases and Mapping Biopsy of the Anal Canal". Ann Dermatol. 28 (5): 624–628. doi:10.5021/ad.2016.28.5.624. PMC 5064193. PMID 27746643.
- ↑ Jung JH, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH (2013). "Extramammary Paget Disease of External Genitalia: Surgical Excision and Follow-up Experiences With 19 Patients". Korean J Urol. 54 (12): 834–9. doi:10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.834. PMC 3866286. PMID 24363864.
- ↑ Yang WJ, Kim DS, Im YJ, Cho KS, Rha KH, Cho NH; et al. (2005). "Extramammary Paget's disease of penis and scrotum". Urology. 65 (5): 972–5. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2004.12.010. PMID 15882734.
- ↑ Fu M, Gao S, Wang P (1999). "[19 cases of Paget's disease]". Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 37 (7): 429–31. PMID 11829881.
- ↑ "Extramammary Paget's disease of the perianal region: a 20‐year experience - Rajendran - 2017 - ANZ Journal of Surgery - Wiley Online Library".