Thrombin: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} +, -{{EH}} +, -{{EJ}} +, -{{Editor Help}} +, -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
m (Bot: fix deprecated Citation Style 1 parameters (Task 9)) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | {{Infobox_gene}} | ||
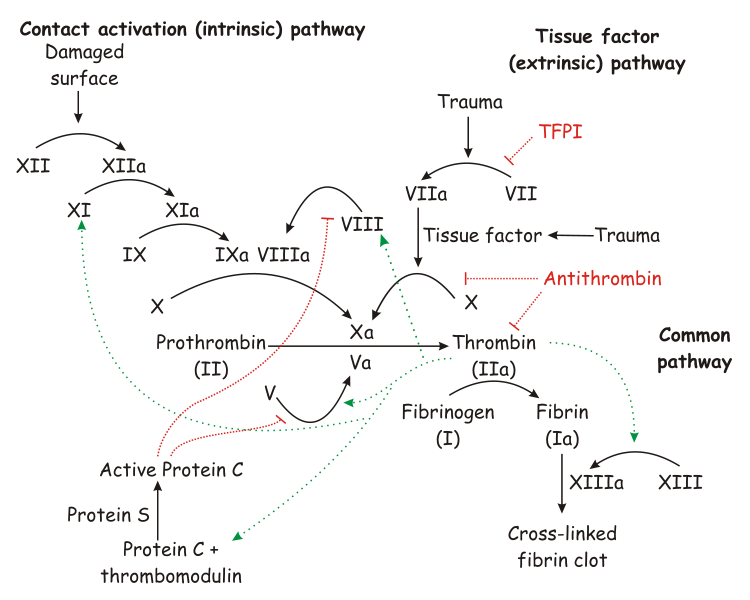
[[File:Coagulation full.svg|thumb|360px|alt=Schematic diagram of the blood coagulation and [[protein C]] pathways. In the blood coagulation pathway, thrombin acts to convert factor XI to XIa, VIII to VIIIa V to Va, fibrinogen to fibrin. In addition, thrombin promotes platelet activation and aggregation via activation of protease-activated receptors on the cell membrane of the platelet. Thrombin also cross over into the protein C pathway by converting protein C into APC. APC in turn converts factor V into Vi, and VIIIa into VIIIi. Finally APC activates PAR-1 and EPCR.|Role of thrombin in the blood coagulation cascade]] | |||
== | '''Thrombin''' ({{EC number|3.4.21.5}}, ''fibrinogenase'', ''thrombase'', ''thrombofort'', ''topical'', ''thrombin-C'', ''tropostasin'', ''activated blood-coagulation factor II'', ''blood-coagulation factor IIa'', ''factor IIa'', ''E thrombin'', ''beta-thrombin'', ''gamma-thrombin'') is a [[serine protease]], an [[enzyme]] that, in humans, is encoded by the ''F2'' [[gene]].<ref name="pmid3474786">{{cite journal | vauthors = Royle NJ, Irwin DM, Koschinsky ML, MacGillivray RT, Hamerton JL | title = Human genes encoding [[prothrombin]] and [[ceruloplasmin]] map to 11p11-q12 and 3q21-24, respectively | journal = Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics | volume = 13 | issue = 3 | pages = 285–92 | date = May 1987 | pmid = 3474786 | doi = 10.1007/BF01535211 }}</ref><ref name="pmid2825773">{{cite journal | vauthors = Degen SJ, Davie EW | title = Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human prothrombin | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 26 | issue = 19 | pages = 6165–77 | date = September 1987 | pmid = 2825773 | doi = 10.1021/bi00393a033 }}</ref> '''Prothrombin''' (coagulation factor II) is [[Proteolysis|proteolytically]] cleaved to form thrombin in the [[Coagulation#Coagulation cascade|clotting process]]. Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble [[fibrinogen]] into insoluble strands of [[fibrin]], as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions. | ||
==History== | |||
After the description of fibrinogen and fibrin, [[Alexander Schmidt (physiologist)|Alexander Schmidt]] hypothesised the existence of an enzyme that converts fibrinogen into fibrin in 1872.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Schmidt A|year=1872|title=Neue Untersuchungen ueber die Fasserstoffesgerinnung|journal=Pflüger's Archiv für die gesamte Physiologie|volume=6|pages=413–538|doi=10.1007/BF01612263}}</ref> | |||
==Physiology== | ==Physiology== | ||
===Synthesis=== | |||
Thrombin is produced by the enzymatic cleavage of two sites on [[prothrombin]] by activated [[Factor X]] (Xa). The activity of factor Xa is greatly enhanced by binding to activated [[Factor V]] (Va), termed the prothrombinase complex. Prothrombin is produced in the liver and is co-translationally modified in a [[vitamin K]]-dependent reaction that converts 10-12 glutamic acids in the N terminus of the molecule to [[gamma-carboxyglutamic acid]] (Gla).<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Knorre|first1=DG|last2=Kudryashova|first2=NV|last3=Godovikova|first3=TS|title=Chemical and Functional Aspects of Posttranslational Modification of Proteins|journal=Acta Nature|date=October 2009|volume=1|issue=3|page=29-51|accessdate=4 August 2017}}</ref> In the presence of calcium, the Gla residues promote the binding of prothrombin to phospholipid bilayers. Deficiency of vitamin K or administration of the anticoagulant [[warfarin]] inhibits the production of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues, slowing the activation of the coagulation cascade. | |||
In human adults, the normal blood level of [[antithrombin]] activity has been measured to be around 1.1 units/mL. Newborn levels of thrombin steadily increase after birth to reach normal adult levels, from a level of around 0.5 units/mL 1 day after birth, to a level of around 0.9 units/mL after 6 months of life.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Andrew M, Paes B, Milner R, Johnston M, Mitchell L, Tollefsen DM, Powers P | title = Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant | journal = Blood | volume = 70 | issue = 1 | pages = 165–72 | date = July 1987 | pmid = 3593964 }}</ref> | |||
=== | ===Mechanism of action=== | ||
In the blood coagulation pathway, thrombin acts to convert [[factor XI]] to XIa, [[factor VIII|VIII]] to VIIIa, [[factor V|V]] to Va, [[fibrinogen]] to [[fibrin]], and [[factor XIII|XIII]] to XIIIa. | |||
[[Factor | [[Factor XIIIa]] is a [[transglutaminase]] that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between lysine and glutamine residues in fibrin. The covalent bonds increase the stability of the fibrin clot. Thrombin [[Protein-protein interaction|interacts]] with [[thrombomodulin]].<ref name="pmid8663147">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bajzar L, Morser J, Nesheim M | title = TAFI, or plasma procarboxypeptidase B, couples the coagulation and fibrinolytic cascades through the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 271 | issue = 28 | pages = 16603–8 | date = July 1996 | pmid = 8663147 | doi = 10.1074/jbc.271.28.16603 }}</ref><ref name="pmid2544585">{{cite journal | vauthors = Jakubowski HV, Owen WG | title = Macromolecular specificity determinants on thrombin for fibrinogen and thrombomodulin | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 264 | issue = 19 | pages = 11117–21 | date = July 1989 | pmid = 2544585 | doi = }}</ref> | ||
As part of its activity in the coagulation cascade, thrombin also promotes [[platelet]] activation and aggregation via activation of [[protease-activated receptor]]s on the cell membrane of the platelet. | |||
===Negative feedback=== | ===Negative feedback=== | ||
Thrombin activates [[protein C]], an inhibitor of the coagulation cascade. | Thrombin bound to thrombomodulin activates [[protein C]], an inhibitor of the coagulation cascade. The activation of protein C is greatly enhanced following the binding of thrombin to [[thrombomodulin]], an integral membrane [[protein]] expressed by [[endothelial]] cells. Activated protein C inactivates factors Va and VIIIa. Binding of activated protein C to [[protein S]] leads to a modest increase in its activity. Thrombin is also inactivated by [[antithrombin]], a [[serpin|serine protease inhibitor]]. | ||
==Structure== | |||
[[Image:1nl2_opm.png|thumb|Anchoring of bovine prothrombin to the membrane through its [[Gla domain]].<ref name="pmid12923575">{{PDB|1nl2}}; {{cite journal | vauthors = Huang M, Rigby AC, Morelli X, Grant MA, Huang G, Furie B, Seaton B, Furie BC | title = Structural basis of membrane binding by Gla domains of vitamin K-dependent proteins | journal = Nature Structural Biology | volume = 10 | issue = 9 | pages = 751–6 | date = September 2003 | pmid = 12923575 | doi = 10.1038/nsb971 }}</ref>]] | |||
The molecular weight of prothrombin is approximately 72,000 [[atomic mass unit|Da]]. The catalytic domain is released from prothrombin fragment 1.2 to create the active enzyme thrombin, which has a molecular weight of 36,000 Da. Structurally, it is a member of the large [[PA clan]] of proteases. | |||
Prothrombin is composed of four domains; an N-terminal [[Gla domain]], two [[kringle domain]]s and a C-terminal [[trypsin]]-like [[serine protease]] domain. | |||
[[Factor Xa]] with [[factor V]] as a cofactor leads to cleavage of the Gla and two Kringle domains (forming together a fragment called fragment 1.2) and leave thrombin, consisting solely of the serine protease domain.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Davie EW, Kulman JD | title = An overview of the structure and function of thrombin | journal = Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis | volume = 32 Suppl 1 | pages = 3–15 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16673262 | doi = 10.1055/s-2006-939550 }}</ref> | |||
As is the case for all [[serine protease]]s, [[prothrombin]] is converted to active thrombin by proteolysis of an internal peptide bond, exposing a new N-terminal Ile-NH3. The historic model of activation of serine proteases involves insertion of this newly formed N-terminus of the heavy chain into the [[Beta barrel|β-barrel]] promoting the correct conformation of the catalytic residues.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Huber|first=Robert|last2=Bode|first2=Wolfram|date=1978-03-01|title=Structural basis of the activation and action of trypsin|url=https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar50123a006|journal=Accounts of Chemical Research|volume=11|issue=3|pages=114–122|doi=10.1021/ar50123a006|issn=0001-4842}}</ref> Contrary to crystal structures of active thrombin, hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry studies indicate that this N-terminal Ile-NH3 does not become inserted into the β-barrel in the apo form of thrombin. However, binding of the active fragment of [[thrombomodulin]] appears to allosterically promote the active conformation of thrombin by inserting this N-terminal region.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Handley LD, Treuheit NA, Venkatesh VJ, Komives EA | title = Thrombomodulin Binding Selects the Catalytically Active Form of Thrombin | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 54 | issue = 43 | pages = 6650–8 | date = November 2015 | pmid = 26468766 | pmc = 4697735 | doi = 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00825 }}</ref> | |||
==Gene== | |||
The thrombin (prothrombin) gene is located on the eleventh [[chromosome]] (11p11-q12).<ref name="pmid3474786"/> | |||
There are an estimated 30 people in the world that have been diagnosed with the congenital form of Factor II deficiency,<ref name="pmid7792730">{{cite journal | vauthors = Degen SJ, McDowell SA, Sparks LM, Scharrer I | title = Prothrombin Frankfurt: a dysfunctional prothrombin characterized by substitution of Glu-466 by Ala | journal = Thrombosis and Haemostasis | volume = 73 | issue = 2 | pages = 203–9 | date = February 1995 | pmid = 7792730 | doi = }}</ref> which should not be confused with the [[prothrombin G20210A]] mutation, which is also called the factor II mutation. Prothrombin G20210A is congenital.<ref name="pmid15262854">{{cite journal | vauthors = Varga EA, Moll S | title = Cardiology patient pages. Prothrombin 20210 mutation (factor II mutation) | journal = Circulation | volume = 110 | issue = 3 | pages = e15-8 | date = July 2004 | pmid = 15262854 | doi = 10.1161/01.CIR.0000135582.53444.87 }}</ref> | |||
Prothrombin G20210A is not usually accompanied by other factor mutations (i.e., the most common is factor V Leiden). The gene may be inherited [[heterozygous]] (1 pair), or much more rarely, [[homozygous]] (2 pairs), and is not related to gender or blood type. Homozygous mutations increase the risk of thrombosis more than heterozygous mutations, but the relative increased risk is not well documented. Other potential risks for [[thrombosis]], such as oral contraceptives may be additive. The previously reported relationship of [[inflammatory bowel disease]] (i.e., [[Crohn's disease]] or [[ulcerative colitis]]) and prothrombin G20210A or [[factor V]] Leiden mutation have been contradicted by research.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bernstein CN, Sargent M, Vos HL, Rosendaal FR | title = Mutations in clotting factors and inflammatory bowel disease | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 102 | issue = 2 | pages = 338–43 | date = February 2007 | pmid = 17156138 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00974.x }}</ref> | |||
==Role in disease== | ==Role in disease== | ||
Activation of prothrombin is crucial in physiological and pathological coagulation. Various rare diseases involving prothrombin have been described (e.g., [[hypoprothrombinemia]]). [[ | Activation of prothrombin is crucial in physiological and pathological coagulation. Various rare diseases involving prothrombin have been described (e.g., [[hypoprothrombinemia]]). Anti-prothrombin [[Antibody|antibodies]] in [[autoimmune disease]] may be a factor in the formation of the [[lupus anticoagulant]] also known as ([[antiphospholipid syndrome]]). [[Hyperprothrombinemia]] can be caused by the G20210A mutation. | ||
Thrombin, a potent [[vasoconstrictor]] and [[mitogen]], is implicated as a major factor in [[vasospasm]] following [[subarachnoid hemorrhage]]. Blood from a ruptured [[cerebral aneurysm]] clots around a cerebral [[artery]], releasing thrombin. This can induce an acute and prolonged narrowing of the blood vessel, potentially resulting in [[cerebral ischemia]] and [[infarction]] ([[stroke]]). | |||
Beyond its key role in the dynamic process of thrombus formation, thrombin has a pronounced pro-inflammatory character, which may influence the onset and progression of atherosclerosis. Acting via its specific cell membrane receptors (protease activated receptors: PAR-1, PAR-3 and PAR-4), which are abundantly expressed in all arterial vessel wall constituents, thrombin has the potential to exert pro-atherogenic actions such as inflammation, leukocyte recruitment into the atherosclerotic plaque, enhanced oxidative stress, migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, apoptosis and angiogenesis.<ref name="pmid19228706">{{cite journal | vauthors = Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, Heeneman S, ten Cate H | title = Is thrombin a key player in the 'coagulation-atherogenesis' maze? | journal = Cardiovascular Research | volume = 82 | issue = 3 | pages = 392–403 | date = June 2009 | pmid = 19228706 | doi = 10.1093/cvr/cvp066 }}</ref><ref name="pmid20697022">{{cite journal | vauthors = Borissoff JI, Heeneman S, Kilinç E, Kassák P, Van Oerle R, Winckers K, Govers-Riemslag JW, Hamulyák K, Hackeng TM, Daemen MJ, ten Cate H, Spronk HM | title = Early atherosclerosis exhibits an enhanced procoagulant state | journal = Circulation | volume = 122 | issue = 8 | pages = 821–30 | date = August 2010 | pmid = 20697022 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.907121 }}</ref><ref name="pmid21542745">{{cite journal | vauthors = Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, ten Cate H | title = The hemostatic system as a modulator of atherosclerosis | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 364 | issue = 18 | pages = 1746–60 | date = May 2011 | pmid = 21542745 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMra1011670 }}</ref> | |||
Thrombin is implicated in the physiology of [[blood clot]]s. Its presence indicates the existence of a clot. In 2013 a system for detecting the presence of thrombin was developed in mice. It combines peptide-coated [[iron oxide]] attached to "reporter chemicals". When a peptide binds to a thrombin molecule, the report is released and appears in the [[urine]] where it can be detected. Human testing has not been conducted.<ref>{{cite web|author=Economist|url=https://www.economist.com/blogs/babbage/2013/11/nanomedicine |title=Nanomedicine: Particle physiology |publisher=The Economist |date=2013-11-05 |accessdate=2013-12-15}}</ref> | |||
==Applications== | |||
== | ===Research tool=== | ||
Due to its high proteolytic specificity, thrombin is a valuable biochemical tool. | Due to its high proteolytic specificity, thrombin is a valuable biochemical tool. The thrombin cleavage site (Leu-Val-Pro-Arg-Gly-Ser) is commonly included in linker regions of [[recombinant fusion protein]] constructs. Following purification of the fusion protein, thrombin can be used to selectively cleave between the Arginine and Glycine residues of the cleavage site, effectively removing the [[purification tag]] from the protein of interest with a high degree of specificity. | ||
== | ===Medicine and surgery=== | ||
[[Prothrombin complex concentrate]] and [[fresh frozen plasma]] are prothrombin-rich coagulation factor preparations that can be used to correct deficiencies (usually due to medication) of prothrombin. Indications include intractable bleeding due to [[warfarin]]. | [[Prothrombin complex concentrate]] and [[fresh frozen plasma]] are prothrombin-rich coagulation factor preparations that can be used to correct deficiencies (usually due to medication) of prothrombin. Indications include intractable bleeding due to [[warfarin]]. | ||
Manipulation of prothrombin is central to the mode of action of most [[anticoagulant]]s. [[Warfarin]] and related drugs inhibit [[vitamin K]]-dependent carboxylation of several coagulation factors, including prothrombin. [[Heparin]] increases the affinity of | Manipulation of prothrombin is central to the mode of action of most [[anticoagulant]]s. [[Warfarin]] and related drugs inhibit [[vitamin K]]-dependent carboxylation of several coagulation factors, including prothrombin. [[Heparin]] increases the affinity of antithrombin to thrombin (as well as [[factor X]]a). The [[direct thrombin inhibitor]]s, a newer class of medication, directly inhibit thrombin by binding to its active site. | ||
Recombinant thrombin is available as a powder for reconstitution into [[aqueous solution]]. It can be applied [[topical]]ly during surgery, as an aid to [[hemostasis]]. It can be useful for controlling minor bleeding from capillaries and small venules, but ineffective and not indicated for massive or brisk arterial bleeding.<ref name="pmid17660072">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chapman WC, Singla N, Genyk Y, McNeil JW, Renkens KL, Reynolds TC, Murphy A, Weaver FA | title = A phase 3, randomized, double-blind comparative study of the efficacy and safety of topical recombinant human thrombin and bovine thrombin in surgical hemostasis | journal = Journal of the American College of Surgeons | volume = 205 | issue = 2 | pages = 256–65 | date = August 2007 | pmid = 17660072 | doi = 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.03.020 }}</ref><ref name="pmid19651065">{{cite journal | vauthors = Singla NK, Ballard JL, Moneta G, Randleman CD, Renkens KL, Alexander WA | title = A phase 3b, open-label, single-group immunogenicity and safety study of topical recombinant thrombin in surgical hemostasis | journal = Journal of the American College of Surgeons | volume = 209 | issue = 1 | pages = 68–74 | date = July 2009 | pmid = 19651065 | doi = 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2009.03.016 }}</ref><ref name="pmid19349898">{{cite journal | vauthors = Greenhalgh DG, Gamelli RL, Collins J, Sood R, Mozingo DW, Gray TE, Alexander WA | title = Recombinant thrombin: safety and immunogenicity in burn wound excision and grafting | journal = Journal of Burn Care & Research | volume = 30 | issue = 3 | pages = 371–9 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19349898 | doi = 10.1097/BCR.0b013e3181a28979 }}</ref> | |||
===Food production=== | |||
Thrombin is sold under the brand name Fibrimex for use as a binding agent for meat. The thrombin in Fibrimex derives from [[porcine]] or [[bovine]] blood.<ref name="dn">{{cite web|url=http://www.dn.se/nyheter/politik/sverige-rostade-ja-till-kottklister-1.1042136|title=Sverige röstade ja till köttklister|trans-title=Sweden voted in favor of the meat paste|language=Swedish|date=2010-02-09|format=|work=|publisher=Dagens Nyheter|accessdate=2010-10-17}}</ref> According to the manufacturer it can be used to produce new kinds of mixed meats (for example combining beef and fish seamlessly). The manufacturer also states that it can be used to combine whole muscle meat, form and portion these thus cutting down on production costs without a loss in quality.<ref name="url_Fibrimex">{{cite web|url=http://www.fibrimex.com|title=Welcome to Fibrimex|work=Fibrimex website|publisher=FX Technology|accessdate=2010-10-17}}</ref> | |||
= | General secretary Jan Bertoft of [[Swedish Consumers' Association]] has stated that "there is danger of misleading the consumers since there is no way to tell this reconstituted meat from real meat"<ref name="dn" /> | ||
== See also == | |||
*[[Cerastocytin]] | |||
*[[Fibrin glue]] | |||
*[[Fibrinogen]] | |||
*[[PA clan]] of proteases | |||
*[[The Proteolysis Map]] | |||
==References== | == References == | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
==Further reading== | == Further reading == | ||
{{refbegin | 2}} | {{refbegin|2}} | ||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Esmon CT | title = Thrombomodulin as a model of molecular mechanisms that modulate protease specificity and function at the vessel surface | journal = FASEB Journal | volume = 9 | issue = 10 | pages = 946–55 | date = July 1995 | pmid = 7615164 | doi = }} | |||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Wu H, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhao R, Li H, Song Y, Qi J, Wang J | title = Time course of upregulation of inflammatory mediators in the hemorrhagic brain in rats: correlation with brain edema | journal = Neurochemistry International | volume = 57 | issue = 3 | pages = 248–53 | date = October 2010 | pmid = 20541575 | doi = 10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.002 | pmc=2910823}} | |||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Lenting PJ, van Mourik JA, Mertens K | title = The life cycle of coagulation factor VIII in view of its structure and function | journal = Blood | volume = 92 | issue = 11 | pages = 3983–96 | date = December 1998 | pmid = 9834200 | doi = }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Plow EF, Cierniewski CS, Xiao Z, Haas TA, Byzova TV | title = AlphaIIbbeta3 and its antagonism at the new millennium | journal = Thrombosis and Haemostasis | volume = 86 | issue = 1 | pages = 34–40 | date = July 2001 | pmid = 11487023 | doi = }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Maragoudakis ME, Tsopanoglou NE, Andriopoulou P | title = Mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis | journal = Biochemical Society Transactions | volume = 30 | issue = 2 | pages = 173–7 | date = April 2002 | pmid = 12023846 | doi = 10.1042/BST0300173 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Han X, Lan X, Li Q, Gao Y, Zhu W, Cheng T, Maruyama T, Wang J | title = Inhibition of prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3 mitigates thrombin-induced brain injury | journal = Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism | volume = 36 | issue = 6 | pages = 1059–74 | date = June 2016 | pmid = 26661165 | doi = 10.1177/0271678X15606462 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Howell DC, Laurent GJ, Chambers RC | title = Role of thrombin and its major cellular receptor, protease-activated receptor-1, in pulmonary fibrosis | journal = Biochemical Society Transactions | volume = 30 | issue = 2 | pages = 211–6 | date = April 2002 | pmid = 12023853 | doi = 10.1042/BST0300211 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Firth SM, Baxter RC | title = Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins | journal = Endocrine Reviews | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 824–54 | date = December 2002 | pmid = 12466191 | doi = 10.1210/er.2001-0033 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Minami T, Sugiyama A, Wu SQ, Abid R, Kodama T, Aird WC | title = Thrombin and phenotypic modulation of the endothelium | journal = Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology | volume = 24 | issue = 1 | pages = 41–53 | date = January 2004 | pmid = 14551154 | doi = 10.1161/01.ATV.0000099880.09014.7D }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = De Cristofaro R, De Candia E | title = Thrombin domains: structure, function and interaction with platelet receptors | journal = Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis | volume = 15 | issue = 3 | pages = 151–63 | date = June 2003 | pmid = 14739624 | doi = 10.1023/B:THRO.0000011370.80989.7b }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Tsopanoglou NE, Maragoudakis ME | title = Role of thrombin in angiogenesis and tumor progression | journal = Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis | volume = 30 | issue = 1 | pages = 63–9 | date = February 2004 | pmid = 15034798 | doi = 10.1055/s-2004-822971 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Bode W | title = Structure and interaction modes of thrombin | journal = Blood Cells, Molecules & Diseases | volume = 36 | issue = 2 | pages = 122–30 | year = 2007 | pmid = 16480903 | doi = 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.027 }} | ||
*{{cite journal | * {{cite journal | vauthors = Wolberg AS | title = Thrombin generation and fibrin clot structure | journal = Blood Reviews | volume = 21 | issue = 3 | pages = 131–42 | date = May 2007 | pmid = 17208341 | doi = 10.1016/j.blre.2006.11.001 }} | ||
}} | |||
* Degen S: Prothrombin. In: High K, Roberts H, eds. Molecular Basis of Thrombosis and Hemostasis. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1995:75. | * Degen S: Prothrombin. In: High K, Roberts H, eds. Molecular Basis of Thrombosis and Hemostasis. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1995:75. | ||
{{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
== External links == | |||
* The [[MEROPS]] online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: [http://merops.sanger.ac.uk/cgi-bin/merops.cgi?id=S01.217 S01.217] | |||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1148/ GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Prothrombin Thrombophilia] | |||
* {{YouTube|H_lVLYgls04|Anti-coagulation & proteases}} by [[The Proteolysis Map]]-animation | |||
* [http://www.proteolysis.org/proteases/m_summarypg/pmap.17563] PMAP: [[The Proteolysis Map]]/Thrombin | |||
* [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/101/motm.do?momID=25 Thrombin: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month] | |||
* [http://sbi.imim.es/web/files/projects/master/2010/Coagulation_serine_proteases/Prothrombin.html Prothrombin Structure] | |||
{{PDB Gallery|geneid=2147}} | |||
{{Coagulation}} | {{Coagulation}} | ||
{{Autoantigens}} | {{Autoantigens}} | ||
{{Antihemorrhagics}} | {{Antihemorrhagics}} | ||
{{Serine endopeptidases}} | |||
{{Enzymes}} | |||
{{Portal bar|Molecular and Cellular Biology|border=no}} | |||
[[Category:Coagulation system]] | [[Category:Coagulation system]] | ||
| Line 76: | Line 116: | ||
[[Category:EC 3.4.21]] | [[Category:EC 3.4.21]] | ||
[[Category:Peripheral membrane proteins]] | [[Category:Peripheral membrane proteins]] | ||
Revision as of 10:00, 12 November 2017
| VALUE_ERROR (nil) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Aliases | |||||||
| External IDs | GeneCards: [1] | ||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||
| Entrez |
|
| |||||
| Ensembl |
|
| |||||
| UniProt |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (protein) |
|
| |||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||
| Wikidata | |||||||
| |||||||
Thrombin (EC 3.4.21.5, fibrinogenase, thrombase, thrombofort, topical, thrombin-C, tropostasin, activated blood-coagulation factor II, blood-coagulation factor IIa, factor IIa, E thrombin, beta-thrombin, gamma-thrombin) is a serine protease, an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the F2 gene.[1][2] Prothrombin (coagulation factor II) is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the clotting process. Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.
History
After the description of fibrinogen and fibrin, Alexander Schmidt hypothesised the existence of an enzyme that converts fibrinogen into fibrin in 1872.[3]
Physiology
Synthesis
Thrombin is produced by the enzymatic cleavage of two sites on prothrombin by activated Factor X (Xa). The activity of factor Xa is greatly enhanced by binding to activated Factor V (Va), termed the prothrombinase complex. Prothrombin is produced in the liver and is co-translationally modified in a vitamin K-dependent reaction that converts 10-12 glutamic acids in the N terminus of the molecule to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla).[4] In the presence of calcium, the Gla residues promote the binding of prothrombin to phospholipid bilayers. Deficiency of vitamin K or administration of the anticoagulant warfarin inhibits the production of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues, slowing the activation of the coagulation cascade.
In human adults, the normal blood level of antithrombin activity has been measured to be around 1.1 units/mL. Newborn levels of thrombin steadily increase after birth to reach normal adult levels, from a level of around 0.5 units/mL 1 day after birth, to a level of around 0.9 units/mL after 6 months of life.[5]
Mechanism of action
In the blood coagulation pathway, thrombin acts to convert factor XI to XIa, VIII to VIIIa, V to Va, fibrinogen to fibrin, and XIII to XIIIa.
Factor XIIIa is a transglutaminase that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between lysine and glutamine residues in fibrin. The covalent bonds increase the stability of the fibrin clot. Thrombin interacts with thrombomodulin.[6][7]
As part of its activity in the coagulation cascade, thrombin also promotes platelet activation and aggregation via activation of protease-activated receptors on the cell membrane of the platelet.
Negative feedback
Thrombin bound to thrombomodulin activates protein C, an inhibitor of the coagulation cascade. The activation of protein C is greatly enhanced following the binding of thrombin to thrombomodulin, an integral membrane protein expressed by endothelial cells. Activated protein C inactivates factors Va and VIIIa. Binding of activated protein C to protein S leads to a modest increase in its activity. Thrombin is also inactivated by antithrombin, a serine protease inhibitor.
Structure
The molecular weight of prothrombin is approximately 72,000 Da. The catalytic domain is released from prothrombin fragment 1.2 to create the active enzyme thrombin, which has a molecular weight of 36,000 Da. Structurally, it is a member of the large PA clan of proteases.
Prothrombin is composed of four domains; an N-terminal Gla domain, two kringle domains and a C-terminal trypsin-like serine protease domain. Factor Xa with factor V as a cofactor leads to cleavage of the Gla and two Kringle domains (forming together a fragment called fragment 1.2) and leave thrombin, consisting solely of the serine protease domain.[9]
As is the case for all serine proteases, prothrombin is converted to active thrombin by proteolysis of an internal peptide bond, exposing a new N-terminal Ile-NH3. The historic model of activation of serine proteases involves insertion of this newly formed N-terminus of the heavy chain into the β-barrel promoting the correct conformation of the catalytic residues.[10] Contrary to crystal structures of active thrombin, hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry studies indicate that this N-terminal Ile-NH3 does not become inserted into the β-barrel in the apo form of thrombin. However, binding of the active fragment of thrombomodulin appears to allosterically promote the active conformation of thrombin by inserting this N-terminal region.[11]
Gene
The thrombin (prothrombin) gene is located on the eleventh chromosome (11p11-q12).[1]
There are an estimated 30 people in the world that have been diagnosed with the congenital form of Factor II deficiency,[12] which should not be confused with the prothrombin G20210A mutation, which is also called the factor II mutation. Prothrombin G20210A is congenital.[13]
Prothrombin G20210A is not usually accompanied by other factor mutations (i.e., the most common is factor V Leiden). The gene may be inherited heterozygous (1 pair), or much more rarely, homozygous (2 pairs), and is not related to gender or blood type. Homozygous mutations increase the risk of thrombosis more than heterozygous mutations, but the relative increased risk is not well documented. Other potential risks for thrombosis, such as oral contraceptives may be additive. The previously reported relationship of inflammatory bowel disease (i.e., Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis) and prothrombin G20210A or factor V Leiden mutation have been contradicted by research.[14]
Role in disease
Activation of prothrombin is crucial in physiological and pathological coagulation. Various rare diseases involving prothrombin have been described (e.g., hypoprothrombinemia). Anti-prothrombin antibodies in autoimmune disease may be a factor in the formation of the lupus anticoagulant also known as (antiphospholipid syndrome). Hyperprothrombinemia can be caused by the G20210A mutation.
Thrombin, a potent vasoconstrictor and mitogen, is implicated as a major factor in vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Blood from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm clots around a cerebral artery, releasing thrombin. This can induce an acute and prolonged narrowing of the blood vessel, potentially resulting in cerebral ischemia and infarction (stroke).
Beyond its key role in the dynamic process of thrombus formation, thrombin has a pronounced pro-inflammatory character, which may influence the onset and progression of atherosclerosis. Acting via its specific cell membrane receptors (protease activated receptors: PAR-1, PAR-3 and PAR-4), which are abundantly expressed in all arterial vessel wall constituents, thrombin has the potential to exert pro-atherogenic actions such as inflammation, leukocyte recruitment into the atherosclerotic plaque, enhanced oxidative stress, migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, apoptosis and angiogenesis.[15][16][17]
Thrombin is implicated in the physiology of blood clots. Its presence indicates the existence of a clot. In 2013 a system for detecting the presence of thrombin was developed in mice. It combines peptide-coated iron oxide attached to "reporter chemicals". When a peptide binds to a thrombin molecule, the report is released and appears in the urine where it can be detected. Human testing has not been conducted.[18]
Applications
Research tool
Due to its high proteolytic specificity, thrombin is a valuable biochemical tool. The thrombin cleavage site (Leu-Val-Pro-Arg-Gly-Ser) is commonly included in linker regions of recombinant fusion protein constructs. Following purification of the fusion protein, thrombin can be used to selectively cleave between the Arginine and Glycine residues of the cleavage site, effectively removing the purification tag from the protein of interest with a high degree of specificity.
Medicine and surgery
Prothrombin complex concentrate and fresh frozen plasma are prothrombin-rich coagulation factor preparations that can be used to correct deficiencies (usually due to medication) of prothrombin. Indications include intractable bleeding due to warfarin.
Manipulation of prothrombin is central to the mode of action of most anticoagulants. Warfarin and related drugs inhibit vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of several coagulation factors, including prothrombin. Heparin increases the affinity of antithrombin to thrombin (as well as factor Xa). The direct thrombin inhibitors, a newer class of medication, directly inhibit thrombin by binding to its active site.
Recombinant thrombin is available as a powder for reconstitution into aqueous solution. It can be applied topically during surgery, as an aid to hemostasis. It can be useful for controlling minor bleeding from capillaries and small venules, but ineffective and not indicated for massive or brisk arterial bleeding.[19][20][21]
Food production
Thrombin is sold under the brand name Fibrimex for use as a binding agent for meat. The thrombin in Fibrimex derives from porcine or bovine blood.[22] According to the manufacturer it can be used to produce new kinds of mixed meats (for example combining beef and fish seamlessly). The manufacturer also states that it can be used to combine whole muscle meat, form and portion these thus cutting down on production costs without a loss in quality.[23]
General secretary Jan Bertoft of Swedish Consumers' Association has stated that "there is danger of misleading the consumers since there is no way to tell this reconstituted meat from real meat"[22]
See also
- Cerastocytin
- Fibrin glue
- Fibrinogen
- PA clan of proteases
- The Proteolysis Map
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Royle NJ, Irwin DM, Koschinsky ML, MacGillivray RT, Hamerton JL (May 1987). "Human genes encoding prothrombin and ceruloplasmin map to 11p11-q12 and 3q21-24, respectively". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 13 (3): 285–92. doi:10.1007/BF01535211. PMID 3474786.
- ↑ Degen SJ, Davie EW (September 1987). "Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human prothrombin". Biochemistry. 26 (19): 6165–77. doi:10.1021/bi00393a033. PMID 2825773.
- ↑ Schmidt A (1872). "Neue Untersuchungen ueber die Fasserstoffesgerinnung". Pflüger's Archiv für die gesamte Physiologie. 6: 413–538. doi:10.1007/BF01612263.
- ↑ Knorre, DG; Kudryashova, NV; Godovikova, TS (October 2009). "Chemical and Functional Aspects of Posttranslational Modification of Proteins". Acta Nature. 1 (3): 29-51.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ Andrew M, Paes B, Milner R, Johnston M, Mitchell L, Tollefsen DM, Powers P (July 1987). "Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant". Blood. 70 (1): 165–72. PMID 3593964.
- ↑ Bajzar L, Morser J, Nesheim M (July 1996). "TAFI, or plasma procarboxypeptidase B, couples the coagulation and fibrinolytic cascades through the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (28): 16603–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.28.16603. PMID 8663147.
- ↑ Jakubowski HV, Owen WG (July 1989). "Macromolecular specificity determinants on thrombin for fibrinogen and thrombomodulin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 264 (19): 11117–21. PMID 2544585.
- ↑ PDB: 1nl2; Huang M, Rigby AC, Morelli X, Grant MA, Huang G, Furie B, Seaton B, Furie BC (September 2003). "Structural basis of membrane binding by Gla domains of vitamin K-dependent proteins". Nature Structural Biology. 10 (9): 751–6. doi:10.1038/nsb971. PMID 12923575.
- ↑ Davie EW, Kulman JD (April 2006). "An overview of the structure and function of thrombin". Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 32 Suppl 1: 3–15. doi:10.1055/s-2006-939550. PMID 16673262.
- ↑ Huber, Robert; Bode, Wolfram (1978-03-01). "Structural basis of the activation and action of trypsin". Accounts of Chemical Research. 11 (3): 114–122. doi:10.1021/ar50123a006. ISSN 0001-4842.
- ↑ Handley LD, Treuheit NA, Venkatesh VJ, Komives EA (November 2015). "Thrombomodulin Binding Selects the Catalytically Active Form of Thrombin". Biochemistry. 54 (43): 6650–8. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00825. PMC 4697735. PMID 26468766.
- ↑ Degen SJ, McDowell SA, Sparks LM, Scharrer I (February 1995). "Prothrombin Frankfurt: a dysfunctional prothrombin characterized by substitution of Glu-466 by Ala". Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 73 (2): 203–9. PMID 7792730.
- ↑ Varga EA, Moll S (July 2004). "Cardiology patient pages. Prothrombin 20210 mutation (factor II mutation)". Circulation. 110 (3): e15–8. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000135582.53444.87. PMID 15262854.
- ↑ Bernstein CN, Sargent M, Vos HL, Rosendaal FR (February 2007). "Mutations in clotting factors and inflammatory bowel disease". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 102 (2): 338–43. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00974.x. PMID 17156138.
- ↑ Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, Heeneman S, ten Cate H (June 2009). "Is thrombin a key player in the 'coagulation-atherogenesis' maze?". Cardiovascular Research. 82 (3): 392–403. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvp066. PMID 19228706.
- ↑ Borissoff JI, Heeneman S, Kilinç E, Kassák P, Van Oerle R, Winckers K, Govers-Riemslag JW, Hamulyák K, Hackeng TM, Daemen MJ, ten Cate H, Spronk HM (August 2010). "Early atherosclerosis exhibits an enhanced procoagulant state". Circulation. 122 (8): 821–30. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.907121. PMID 20697022.
- ↑ Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, ten Cate H (May 2011). "The hemostatic system as a modulator of atherosclerosis". The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (18): 1746–60. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1011670. PMID 21542745.
- ↑ Economist (2013-11-05). "Nanomedicine: Particle physiology". The Economist. Retrieved 2013-12-15.
- ↑ Chapman WC, Singla N, Genyk Y, McNeil JW, Renkens KL, Reynolds TC, Murphy A, Weaver FA (August 2007). "A phase 3, randomized, double-blind comparative study of the efficacy and safety of topical recombinant human thrombin and bovine thrombin in surgical hemostasis". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 205 (2): 256–65. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.03.020. PMID 17660072.
- ↑ Singla NK, Ballard JL, Moneta G, Randleman CD, Renkens KL, Alexander WA (July 2009). "A phase 3b, open-label, single-group immunogenicity and safety study of topical recombinant thrombin in surgical hemostasis". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 209 (1): 68–74. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2009.03.016. PMID 19651065.
- ↑ Greenhalgh DG, Gamelli RL, Collins J, Sood R, Mozingo DW, Gray TE, Alexander WA (2009). "Recombinant thrombin: safety and immunogenicity in burn wound excision and grafting". Journal of Burn Care & Research. 30 (3): 371–9. doi:10.1097/BCR.0b013e3181a28979. PMID 19349898.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "Sverige röstade ja till köttklister" [Sweden voted in favor of the meat paste] (in Swedish). Dagens Nyheter. 2010-02-09. Retrieved 2010-10-17.
- ↑ "Welcome to Fibrimex". Fibrimex website. FX Technology. Retrieved 2010-10-17.
Further reading
- Esmon CT (July 1995). "Thrombomodulin as a model of molecular mechanisms that modulate protease specificity and function at the vessel surface". FASEB Journal. 9 (10): 946–55. PMID 7615164.
- Wu H, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhao R, Li H, Song Y, Qi J, Wang J (October 2010). "Time course of upregulation of inflammatory mediators in the hemorrhagic brain in rats: correlation with brain edema". Neurochemistry International. 57 (3): 248–53. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.002. PMC 2910823. PMID 20541575.
- Lenting PJ, van Mourik JA, Mertens K (December 1998). "The life cycle of coagulation factor VIII in view of its structure and function". Blood. 92 (11): 3983–96. PMID 9834200.
- Plow EF, Cierniewski CS, Xiao Z, Haas TA, Byzova TV (July 2001). "AlphaIIbbeta3 and its antagonism at the new millennium". Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 86 (1): 34–40. PMID 11487023.
- Maragoudakis ME, Tsopanoglou NE, Andriopoulou P (April 2002). "Mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis". Biochemical Society Transactions. 30 (2): 173–7. doi:10.1042/BST0300173. PMID 12023846.
- Han X, Lan X, Li Q, Gao Y, Zhu W, Cheng T, Maruyama T, Wang J (June 2016). "Inhibition of prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3 mitigates thrombin-induced brain injury". Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 36 (6): 1059–74. doi:10.1177/0271678X15606462. PMID 26661165.
- Howell DC, Laurent GJ, Chambers RC (April 2002). "Role of thrombin and its major cellular receptor, protease-activated receptor-1, in pulmonary fibrosis". Biochemical Society Transactions. 30 (2): 211–6. doi:10.1042/BST0300211. PMID 12023853.
- Firth SM, Baxter RC (December 2002). "Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins". Endocrine Reviews. 23 (6): 824–54. doi:10.1210/er.2001-0033. PMID 12466191.
- Minami T, Sugiyama A, Wu SQ, Abid R, Kodama T, Aird WC (January 2004). "Thrombin and phenotypic modulation of the endothelium". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 24 (1): 41–53. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000099880.09014.7D. PMID 14551154.
- De Cristofaro R, De Candia E (June 2003). "Thrombin domains: structure, function and interaction with platelet receptors". Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis. 15 (3): 151–63. doi:10.1023/B:THRO.0000011370.80989.7b. PMID 14739624.
- Tsopanoglou NE, Maragoudakis ME (February 2004). "Role of thrombin in angiogenesis and tumor progression". Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 30 (1): 63–9. doi:10.1055/s-2004-822971. PMID 15034798.
- Bode W (2007). "Structure and interaction modes of thrombin". Blood Cells, Molecules & Diseases. 36 (2): 122–30. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.12.027. PMID 16480903.
- Wolberg AS (May 2007). "Thrombin generation and fibrin clot structure". Blood Reviews. 21 (3): 131–42. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2006.11.001. PMID 17208341.
- Degen S: Prothrombin. In: High K, Roberts H, eds. Molecular Basis of Thrombosis and Hemostasis. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1995:75.
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: S01.217
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Prothrombin Thrombophilia
- Anti-coagulation & proteases on YouTube by The Proteolysis Map-animation
- [2] PMAP: The Proteolysis Map/Thrombin
- Thrombin: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month
- Prothrombin Structure