Congestive heart failure laboratory tests: Difference between revisions
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{{Congestive heart failure}} | {{Congestive heart failure}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AOEIC}} {{LG}}; {{MehdiP}}; {{TarekNafee}} | {{CMG}}; {{AOEIC}} {{LG}}; {{MehdiP}}; {{TarekNafee}}; {{EdzelCo}} | ||
== Overview== | == Overview== | ||
Once the diagnosis of heart failure is made, subsequent laboratory studies should be directed toward the identification of an underlying cause of heart failure. | |||
==Laboratory Tests== | ==Laboratory Tests== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Biomarkers== | ==Biomarkers== | ||
Biomarkers are going to play a great role in diagnosis of heart failure. | Biomarkers are going to play a great role in diagnosis of heart failure. | ||
===Natriuretic Peptides: BNP or NT-proBNP=== | ===Natriuretic Peptides: BNP or NT-proBNP=== | ||
*Plasma concentrations of [[NPs]] are recommended as initial diagnostic tests in [[patients]] with [[symptoms]] suggestive of [[HF]] to rule out the diagnosis. | |||
*Elevated concentrations support a diagnosis of [[HF]]. | |||
* Other causes of an elevated [[NP]] include [[atrial fibrillation]], increasing [[age]], and acute or [[chronic kidney disease]]. | |||
* NP concentrations may be low in [[obese]] [[patients]]. | |||
* The upper limits of normal in the non-acute setting are 35 pg/mL for [[BNP]], and 125 pg/mL for [[NT-proBNP]].<ref name="pmid22541282">{{cite journal |vauthors=Verdú JM, Comín-Colet J, Domingo M, Lupón J, Gómez M, Molina L, Casacuberta JM, Muñoz MA, Mena A, Bruguera-Cortada J |title=Rapid point-of-care NT-proBNP optimal cut-off point for heart failure diagnosis in primary care |journal=Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) |volume=65 |issue=7 |pages=613–9 |date=July 2012 |pmid=22541282 |doi=10.1016/j.recesp.2012.01.019 |url=}}</ref> | |||
The CoDE-HF decision support tool may help diagnose heart failure<ref name="pmid35697365">{{cite journal| author=Lee KK, Doudesis D, Anwar M, Astengo F, Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Claessens YE | display-authors=etal| title=Development and validation of a decision support tool for the diagnosis of acute heart failure: systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. | journal=BMJ | year= 2022 | volume= 377 | issue= | pages= e068424 | pmid=35697365 | doi=10.1136/bmj-2021-068424 | pmc=9189738 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=35697365 }} </ref>. The CoDE-HF interprets the N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide ([[NT-proBNP]]) in various settings including obesity. | |||
{| | {| style="cellpadding=0; cellspacing= 0; width: 600px;" | ||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 0 5px; font-size: 100%; background: #4682B4; color: #FFFFFF;" align=center |'''Causes of elevated concentrations of natriuretic peptides''' | |||
|- | |||
|style="font-size: 100; padding: 0 5px; background: #B8B8B8" align=left |''' [[Cardiac]]:''' | |||
|- | |||
|style="padding: 0 5px; font-size: 100%; background: #F5F5F5; width: 70%" align=left| | |||
❑ [[Heart failure]]<br> | |||
❑ [[ACS]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Pulmonary embolism]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Myocarditis]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Left ventricular hypertrophy]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]], [[restrictive cardiomyopathy]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Valvular heart disease]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Congenital heart disease]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Atrial tachyarrhythmia]] , [[ventricular tachyarrhythmias]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Heart]] [[contusion]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Cardioversion]], [[ICD]] [[shock]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Surgical]] procedures involving the [[heart]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Pulmonary hypertension]]<br> | |||
|- | |||
|style="font-size: 100; padding: 0 5px; background: #B8B8B8" align=left |''' Non-Cardiac :''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |style="padding: 0 5px; font-size: 100%; background: #F5F5F5; width: 70%" align=left| | ||
| | ❑ Advanced [[age]]<br> | ||
❑[[Ischaemic stroke]]<br> | |||
❑[[Subarachnoid haemorrhage]]<br> | |||
❑[[Renal]] dysfunction<br> | |||
❑[[Liver]] dysfunction (mainly [[liver cirrhosis]] with [[ascites]])<br> | |||
❑[[Paraneoplastic syndrome]]<br> | |||
❑[[COPD]]<br> | |||
❑Severe [[infections]] (including [[pneumonia]] and [[sepsis]])<br> | |||
❑Severe [[ burns]]<br> | |||
❑[[Anemia]]<br> | |||
❑Severe [[metabolic]] and [[hormone]] abnormalities ([[ thyrotoxicosis]], [[diabetic ketosis]])<br> | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| | |||
! colspan="2" style="background: PapayaWhip;" align="center" + |The above table adopted from 2021 ESC Guideline | |||
|- | |||
|}<ref name="pmid34447992">{{cite journal |vauthors=McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, Burri H, Butler J, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Crespo-Leiro MG, Farmakis D, Gilard M, Heymans S, Hoes AW, Jaarsma T, Jankowska EA, Lainscak M, Lam CSP, Lyon AR, McMurray JJV, Mebazaa A, Mindham R, Muneretto C, Francesco Piepoli M, Price S, Rosano GMC, Ruschitzka F, Kathrine Skibelund A |title=2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure |journal=Eur Heart J |volume=42 |issue=36 |pages=3599–3726 |date=September 2021 |pmid=34447992 |doi=10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[BNP]] or its amino-terminal cleavage equivalent (NT-proBNP) is generated by [[cardiomyocytes]] in the context of numerous triggers, most notably [[myocardial]] stretch. | |||
*[[BNP]] levels may be useful in the initial establishment of the diagnosis of heart failure in the [[patient]] with [[dyspnea]] of unclear etiology. In a [[meta-analysis]], BNP was superior [[N-terminal pro-BNP]] (NTproBNP) and was associated with a [[Sensitivity and specificity#Sensitivity|sensitivity]] of 85% and [[Sensitivity and specificity#Specificity|specificity]] of 84% in the diagnosis of heart failure in the primary care setting.<ref name="pmid18290826">{{cite journal |author=Ewald B, Ewald D, Thakkinstian A, Attia J |title=Meta-analysis of B type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro B natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of clinical heart failure and population screening for left ventricular systolic dysfunction |journal=Intern Med J |volume=38 |issue=2 |pages=101–13 |year=2008 |pmid=18290826 |doi=10.1111/j.1445-5994.2007.01454.x |url=http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1445-5994.2007.01454.x}}</ref> | |||
*These biomarkers have been studied for the detection of elevated [[cardiac pressures]].<ref name="pmid15123522">{{cite journal| author=Dokainish H, Zoghbi WA, Lakkis NM, Al-Bakshy F, Dhir M, Quinones MA et al.| title=Optimal noninvasive assessment of left ventricular filling pressures: a comparison of tissue Doppler echocardiography and B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with pulmonary artery catheters. | journal=Circulation | year= 2004 | volume= 109 | issue= 20 | pages= 2432-9 | pmid=15123522 | doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000127882.58426.7A | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15123522 }} </ref><ref name="pmid21478382">{{cite journal| author=Kelder JC, Cowie MR, McDonagh TA, Hardman SM, Grobbee DE, Cost B et al.| title=Quantifying the added value of BNP in suspected heart failure in general practice: an individual patient data meta-analysis. | journal=Heart | year= 2011 | volume= 97 | issue= 12 | pages= 959-63 | pmid=21478382 | doi=10.1136/hrt.2010.220426 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21478382 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15110205">{{cite journal| author=Dokainish H, Zoghbi WA, Lakkis NM, Quinones MA, Nagueh SF| title=Comparative accuracy of B-type natriuretic peptide and tissue Doppler echocardiography in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure. | journal=Am J Cardiol | year= 2004 | volume= 93 | issue= 9 | pages= 1130-5 | pmid=15110205 | doi=10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.01.042 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15110205 }} </ref>, low ejection fraction<ref name="pmid14966052">{{cite journal| author=Groenning BA, Raymond I, Hildebrandt PR, Nilsson JC, Baumann M, Pedersen F| title=Diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of left ventricular systolic heart failure by plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in a large sample of the general population. | journal=Heart | year= 2004 | volume= 90 | issue= 3 | pages= 297-303 | pmid=14966052 | doi= | pmc=1768111 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14966052 }} </ref>, or both<ref name="pmid12587046">{{cite journal| author=Kuster GM, Tanner H, Printzen G, Suter TM, Mohacsi P, Hess OM| title=B-type natriuretic peptide for diagnosis and treatment of congestive heart failure. | journal=Swiss Med Wkly | year= 2002 | volume= 132 | issue= 43-44 | pages= 623-8 | pmid=12587046 | doi=2002/43/smw-10081 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12587046 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12798574">{{cite journal| author=Maisel AS, McCord J, Nowak RM, Hollander JE, Wu AH, Duc P et al.| title=Bedside B-Type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction. Results from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2003 | volume= 41 | issue= 11 | pages= 2010-7 | pmid=12798574 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12798574 }} </ref>. | |||
*[[Clinical practice guideline]]s suggest their measurement is helpful for diagnosis or ruling out heart failure especially in the acute settings.<ref name="pmid23747642">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL |title=2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines |journal=J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. |volume=62 |issue=16 |pages=e147–239 |year=2013 |pmid=23747642 |doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.019 |url=}}</ref> | |||
===Biomarkers indications for use=== | ===Biomarkers indications for use=== | ||
| Line 69: | Line 99: | ||
=== Carbohydrate Antigen 125 === | === Carbohydrate Antigen 125 === | ||
CA-125 is an emerging, highly sensitive biomarker for heart failure.<ref name="pmid27810078">{{cite journal| author=D'Aloia A, Vizzardi E, Metra M| title=Can Carbohydrate Antigen-125 | CA-125 is an emerging, highly sensitive biomarker for heart failure.<ref name="pmid27810078">{{cite journal| author=D'Aloia A, Vizzardi E, Metra M| title=Can Carbohydrate Antigen-125 Be a New Biomarker to Guide Heart Failure Treatment?: The CHANCE-HF Trial. | journal=JACC Heart Fail | year= 2016 | volume= 4 | issue= 11 | pages= 844-846 | pmid=27810078 | doi=10.1016/j.jchf.2016.09.001 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27810078 }} </ref> Although it is not yet used in clinical practice, the CHANCE-HF trial has demonstrated utility in using CA-125 to guide diuretic therapy and for determining short-term prognosis.<ref name="pmid27522630">{{cite journal| author=Núñez J, Llàcer P, Bertomeu-González V, Bosch MJ, Merlos P, García-Blas S et al.| title=Carbohydrate Antigen-125-Guided Therapy in Acute Heart Failure: CHANCE-HF: A Randomized Study. | journal=JACC Heart Fail | year= 2016 | volume= 4 | issue= 11 | pages= 833-843 | pmid=27522630 | doi=10.1016/j.jchf.2016.06.007 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27522630 }} </ref> CA-125 is a non-specific antigen that is most strongly associated with ovarian cancer. In patients with acute heart failure, ambulatory follow-up care aimed at titrating diuretic use according to CA-125 levels has demonstrated ~50% reduction in rehospitalizations.<ref name="pmid27522630">{{cite journal| author=Núñez J, Llàcer P, Bertomeu-González V, Bosch MJ, Merlos P, García-Blas S et al.| title=Carbohydrate Antigen-125-Guided Therapy in Acute Heart Failure: CHANCE-HF: A Randomized Study. | journal=JACC Heart Fail | year= 2016 | volume= 4 | issue= 11 | pages= 833-843 | pmid=27522630 | doi=10.1016/j.jchf.2016.06.007 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27522630 }} </ref> CA-125 was first associated with heart failure in 1999 by Nagele et al.<ref name="pmid27810078">{{cite journal| author=D'Aloia A, Vizzardi E, Metra M| title=Can Carbohydrate Antigen-125 Be a New Biomarker to Guide Heart Failure Treatment?: The CHANCE-HF Trial. | journal=JACC Heart Fail | year= 2016 | volume= 4 | issue= 11 | pages= 844-846 | pmid=27810078 | doi=10.1016/j.jchf.2016.09.001 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27810078 }} </ref><ref name="pmid10347329">{{cite journal| author=Nägele H, Bahlo M, Klapdor R, Schaeperkoetter D, Rödiger W| title=CA 125 and its relation to cardiac function. | journal=Am Heart J | year= 1999 | volume= 137 | issue= 6 | pages= 1044-9 | pmid=10347329 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10347329 }} </ref> | ||
== | ===Initial lab tests for evaluation of [[HFrEF]]=== | ||
*[[BNP]], [[NT Pro BNP]] | |||
*[[CBC]], [[basic metabolic panel]], [[liver function]], [[Iron]] studies, [[thyroid]] studies, [[Hb A1C]] | |||
== | == 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Heart Failure Guideline (DO NOT EDIT) <ref name="pmid35363500">{{cite journal| author=Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM | display-authors=etal| title=2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=Circulation | year= 2022 | volume= 145 | issue= 18 | pages= e876-e894 | pmid=35363500 | doi=10.1161/CIR.0000000000001062 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=35363500 }} </ref> == | ||
====Initial [[Laboratory]] and [[Electrocardiographic]] Testing (DO NOT EDIT) <ref name="pmid35363500">{{cite journal| author=Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM | display-authors=etal| title=2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=Circulation | year= 2022 | volume= 145 | issue= 18 | pages= e876-e894 | pmid=35363500 | doi=10.1161/CIR.0000000000001062 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=35363500 }} </ref> ==== | |||
{|class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | {|class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGreen"|[[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class I]] | |colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGreen"| [[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class I]] | ||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''1.''' For [[patients]] presenting with [[HF]], the specific cause of [[HF]] should be explored using additional laboratory testing for appropriate [[management]]. <ref name="pmid: 25948538">{{cite journal| author=Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F | display-authors=etal| title=Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. | journal=Circulation | year= 2015 | volume= 131 | issue= 22 | pages= 1981-8 | pmid=: 25948538 | doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013777 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25948538 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15148277">{{cite journal| author=Cardinale D, Sandri MT, Colombo A, Colombo N, Boeri M, Lamantia G | display-authors=etal| title=Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy. | journal=Circulation | year= 2004 | volume= 109 | issue= 22 | pages= 2749-54 | pmid=15148277 | doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000130926.51766.CC | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15148277 }} </ref><ref name="pmid29019612">{{cite journal| author=Castaño A, Narotsky DL, Hamid N, Khalique OK, Morgenstern R, DeLuca A | display-authors=etal| title=Unveiling transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis and its predictors among elderly patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement. | journal=Eur Heart J | year= 2017 | volume= 38 | issue= 38 | pages= 2879-2887 | pmid=29019612 | doi=10.1093/eurheartj/ehx350 | pmc=5837725 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29019612 }} </ref><ref name="pmid27386769">{{cite journal| author=Maurer MS, Hanna M, Grogan M, Dispenzieri A, Witteles R, Drachman B | display-authors=etal| title=Genotype and Phenotype of Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis: THAOS (Transthyretin Amyloid Outcome Survey). | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2016 | volume= 68 | issue= 2 | pages= 161-72 | pmid=27386769 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2016.03.596 | pmc=4940135 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27386769 }} </ref><ref name="pmid27143678">{{cite journal| author=Gillmore JD, Maurer MS, Falk RH, Merlini G, Damy T, Dispenzieri A | display-authors=etal| title=Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. | journal=Circulation | year= 2016 | volume= 133 | issue= 24 | pages= 2404-12 | pmid=27143678 | doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021612 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27143678 }} </ref><ref name="pmid28494620">{{cite journal| author=Brown EE, Lee YZJ, Halushka MK, Steenbergen C, Johnson NM, Almansa J | display-authors=etal| title=Genetic testing improves identification of transthyretin amyloid (ATTR) subtype in cardiac amyloidosis. | journal=Amyloid | year= 2017 | volume= 24 | issue= 2 | pages= 92-95 | pmid=28494620 | doi=10.1080/13506129.2017.1324418 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28494620 }} </ref><ref name="pmid29482029">{{cite journal| author=Crawford TC, Okada DR, Magruder JT, Fraser C, Patel N, Houston BA | display-authors=etal| title=A Contemporary Analysis of Heart Transplantation and Bridge-to-Transplant Mechanical Circulatory Support Outcomes in Cardiac Sarcoidosis. | journal=J Card Fail | year= 2018 | volume= 24 | issue= 6 | pages= 384-391 | pmid=29482029 | doi=10.1016/j.cardfail.2018.02.009 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=29482029 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19864165">{{cite journal| author=Wu RS, Gupta S, Brown RN, Yancy CW, Wald JW, Kaiser P | display-authors=etal| title=Clinical outcomes after cardiac transplantation in muscular dystrophy patients. | journal=J Heart Lung Transplant | year= 2010 | volume= 29 | issue= 4 | pages= 432-8 | pmid=19864165 | doi=10.1016/j.healun.2009.08.030 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19864165 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B-NR]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>''' | | bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''2.''' For [[patients]] who are diagnosed with [[HF]], laboratory evaluation should include [[complete blood count]], [[urinalysis]], [[serum electrolytes]], [[blood urea nitrogen]], [[serum creatinine]], [[glucose]], [[lipid profile]], [[liver function tests]], [[iron studies]], and [[thyroid-stimulating hormone]] to optimize [[management]]. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C-EO]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|bgcolor=" | | bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''3.''' For all [[patients]] presenting with [[HF]], a [[12-lead ECG]] should be performed at the initial encounter to optimize [[management]]. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C-EO]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | ===Use of [[Biomarkers]] for [[Prevention]], Initial [[Diagnosis]], and [[Risk Stratification]] (DO NOT EDIT) <ref name="pmid35363500">{{cite journal| author=Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM | display-authors=etal| title=2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. | journal=Circulation | year= 2022 | volume= 145 | issue= 18 | pages= e876-e894 | pmid=35363500 | doi=10.1161/CIR.0000000000001062 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=35363500 }} </ref> === | ||
{|class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | {|class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background: | |colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGreen"| [[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class I]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|bgcolor=" | | bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''1.''' In [[patients]] presenting with [[dyspnea]], measurement of [[B-type natriuretic peptide]] ([[BNP]]) or [[N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide]] ([[NT-proBNP]]) is useful to support a [[diagnosis]] or exclusion of [[HF]]. <ref name="pmid11401111">{{cite journal| author=Richards AM, Doughty R, Nicholls MG, MacMahon S, Sharpe N, Murphy J | display-authors=etal| title=Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and adrenomedullin: prognostic utility and prediction of benefit from carvedilol in chronic ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. Australia-New Zealand Heart Failure Group. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2001 | volume= 37 | issue= 7 | pages= 1781-7 | pmid=11401111 | doi=10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01269-4 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11401111 }} </ref><ref name="pmid14662703">{{cite journal| author=Tang WH, Girod JP, Lee MJ, Starling RC, Young JB, Van Lente F | display-authors=etal| title=Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in ambulatory patients with established chronic symptomatic systolic heart failure. | journal=Circulation | year= 2003 | volume= 108 | issue= 24 | pages= 2964-6 | pmid=14662703 | doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000106903.98196.B6 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14662703 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15921792">{{cite journal| author=Zaphiriou A, Robb S, Murray-Thomas T, Mendez G, Fox K, McDonagh T | display-authors=etal| title=The diagnostic accuracy of plasma BNP and NTproBNP in patients referred from primary care with suspected heart failure: results of the UK natriuretic peptide study. | journal=Eur J Heart Fail | year= 2005 | volume= 7 | issue= 4 | pages= 537-41 | pmid=15921792 | doi=10.1016/j.ejheart.2005.01.022 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15921792 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22564550">{{cite journal| author=Son CS, Kim YN, Kim HS, Park HS, Kim MS| title=Decision-making model for early diagnosis of congestive heart failure using rough set and decision tree approaches. | journal=J Biomed Inform | year= 2012 | volume= 45 | issue= 5 | pages= 999-1008 | pmid=22564550 | doi=10.1016/j.jbi.2012.04.013 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22564550 }} </ref><ref name="pmid22104551">{{cite journal| author=Kelder JC, Cramer MJ, van Wijngaarden J, van Tooren R, Mosterd A, Moons KG | display-authors=etal| title=The diagnostic value of physical examination and additional testing in primary care patients with suspected heart failure. | journal=Circulation | year= 2011 | volume= 124 | issue= 25 | pages= 2865-73 | pmid=22104551 | doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.019216 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22104551 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24969534">{{cite journal| author=Booth RA, Hill SA, Don-Wauchope A, Santaguida PL, Oremus M, McKelvie R | display-authors=etal| title=Performance of BNP and NT-proBNP for diagnosis of heart failure in primary care patients: a systematic review. | journal=Heart Fail Rev | year= 2014 | volume= 19 | issue= 4 | pages= 439-51 | pmid=24969534 | doi=10.1007/s10741-014-9445-8 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24969534 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11216950">{{cite journal| author=Dao Q, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Harrison A, Amirnovin R, Lenert L | display-authors=etal| title=Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in an urgent-care setting. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2001 | volume= 37 | issue= 2 | pages= 379-85 | pmid=11216950 | doi=10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01156-6 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11216950 }} </ref><ref name="pmid7905953">{{cite journal| author=Davis M, Espiner E, Richards G, Billings J, Town I, Neill A | display-authors=etal| title=Plasma brain natriuretic peptide in assessment of acute dyspnoea. | journal=Lancet | year= 1994 | volume= 343 | issue= 8895 | pages= 440-4 | pmid=7905953 | doi=10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92690-5 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7905953 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12124404">{{cite journal| author=Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P | display-authors=etal| title=Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2002 | volume= 347 | issue= 3 | pages= 161-7 | pmid=12124404 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa020233 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12124404 }} [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=&cmd=prlinks&id=12401145 Review in: J Fam Pract. 2002 Oct;51(10):816] [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=&cmd=prlinks&id=12511135 Review in: ACP J Club. 2003 Jan-Feb;138(1):23] </ref><ref name="pmid18243855">{{cite journal| author=Januzzi JL, Chen-Tournoux AA, Moe G| title=Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing for the diagnosis or exclusion of heart failure in patients with acute symptoms. | journal=Am J Cardiol | year= 2008 | volume= 101 | issue= 3A | pages= 29-38 | pmid=18243855 | doi=10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.017 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18243855 }} </ref><ref name="pmid25052418">{{cite journal| author=Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope AC, Ali U, Oremus M, Brown JA, Bustamam A | display-authors=etal| title=Incremental value of natriuretic peptide measurement in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF): a systematic review. | journal=Heart Fail Rev | year= 2014 | volume= 19 | issue= 4 | pages= 507-19 | pmid=25052418 | doi=10.1007/s10741-014-9444-9 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25052418 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24957908">{{cite journal| author=Hill SA, Booth RA, Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope A, Brown JA, Oremus M | display-authors=etal| title=Use of BNP and NT-proBNP for the diagnosis of heart failure in the emergency department: a systematic review of the evidence. | journal=Heart Fail Rev | year= 2014 | volume= 19 | issue= 4 | pages= 421-38 | pmid=24957908 | doi=10.1007/s10741-014-9447-6 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24957908 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: A]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|- | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|bgcolor=" | | bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''2.'''In [[patients]] with chronic [[HF]], measurements of [[BNP]] or [[NT-proBNP]] levels are recommended for [[risk stratification]]. <ref name="pmid25052418">{{cite journal| author=Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope AC, Ali U, Oremus M, Brown JA, Bustamam A | display-authors=etal| title=Incremental value of natriuretic peptide measurement in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF): a systematic review. | journal=Heart Fail Rev | year= 2014 | volume= 19 | issue= 4 | pages= 507-19 | pmid=25052418 | doi=10.1007/s10741-014-9444-9 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25052418 }} </ref><ref name="pmid16979009">{{cite journal| author=van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL, Ellinor PT, Sharma UC, Bakker JA, Low AF | display-authors=etal| title=Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, galectin-3, and apelin for the evaluation of patients with acute heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2006 | volume= 48 | issue= 6 | pages= 1217-24 | pmid=16979009 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.061 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16979009 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15451800">{{cite journal| author=Bettencourt P, Azevedo A, Pimenta J, Friões F, Ferreira S, Ferreira A| title=N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide predicts outcome after hospital discharge in heart failure patients. | journal=Circulation | year= 2004 | volume= 110 | issue= 15 | pages= 2168-74 | pmid=15451800 | doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000144310.04433.BE | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15451800 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11216951">{{cite journal| author=Cheng V, Kazanagra R, Garcia A, Lenert L, Krishnaswamy P, Gardetto N | display-authors=etal| title=A rapid bedside test for B-type peptide predicts treatment outcomes in patients admitted for decompensated heart failure: a pilot study. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2001 | volume= 37 | issue= 2 | pages= 386-91 | pmid=11216951 | doi=10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01157-8 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11216951 }} </ref><ref name="pmid17498579">{{cite journal| author=Fonarow GC, Peacock WF, Phillips CO, Givertz MM, Lopatin M, ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators| title=Admission B-type natriuretic peptide levels and in-hospital mortality in acute decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2007 | volume= 49 | issue= 19 | pages= 1943-50 | pmid=17498579 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.037 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17498579 }} </ref><ref name="pmid14975475">{{cite journal| author=Logeart D, Thabut G, Jourdain P, Chavelas C, Beyne P, Beauvais F | display-authors=etal| title=Predischarge B-type natriuretic peptide assay for identifying patients at high risk of re-admission after decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2004 | volume= 43 | issue= 4 | pages= 635-41 | pmid=14975475 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.044 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14975475 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15364340">{{cite journal| author=Maisel A, Hollander JE, Guss D, McCullough P, Nowak R, Green G | display-authors=etal| title=Primary results of the Rapid Emergency Department Heart Failure Outpatient Trial (REDHOT). A multicenter study of B-type natriuretic peptide levels, emergency department decision making, and outcomes in patients presenting with shortness of breath. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2004 | volume= 44 | issue= 6 | pages= 1328-33 | pmid=15364340 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2004.06.015 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15364340 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19157603">{{cite journal| author=Zairis MN, Tsiaousis GZ, Georgilas AT, Makrygiannis SS, Adamopoulou EN, Handanis SM | display-authors=etal| title=Multimarker strategy for the prediction of 31 days cardiac death in patients with acutely decompensated chronic heart failure. | journal=Int J Cardiol | year= 2010 | volume= 141 | issue= 3 | pages= 284-90 | pmid=19157603 | doi=10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.12.017 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19157603 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19398076">{{cite journal| author=Dhaliwal AS, Deswal A, Pritchett A, Aguilar D, Kar B, Souchek J | display-authors=etal| title=Reduction in BNP levels with treatment of decompensated heart failure and future clinical events. | journal=J Card Fail | year= 2009 | volume= 15 | issue= 4 | pages= 293-9 | pmid=19398076 | doi=10.1016/j.cardfail.2008.11.007 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19398076 }} </ref><ref name="pmid20185037">{{cite journal| author=O'Connor CM, Hasselblad V, Mehta RH, Tasissa G, Califf RM, Fiuzat M | display-authors=etal| title=Triage after hospitalization with advanced heart failure: the ESCAPE (Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness) risk model and discharge score. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2010 | volume= 55 | issue= 9 | pages= 872-8 | pmid=20185037 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.083 | pmc=3835158 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20185037 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12921811">{{cite journal| author=O'Brien RJ, Squire IB, Demme B, Davies JE, Ng LL| title=Pre-discharge, but not admission, levels of NT-proBNP predict adverse prognosis following acute LVF. | journal=Eur J Heart Fail | year= 2003 | volume= 5 | issue= 4 | pages= 499-506 | pmid=12921811 | doi=10.1016/s1388-9842(03)00098-9 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12921811 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19539144">{{cite journal| author=Cohen-Solal A, Logeart D, Huang B, Cai D, Nieminen MS, Mebazaa A| title=Lowered B-type natriuretic peptide in response to levosimendan or dobutamine treatment is associated with improved survival in patients with severe acutely decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2009 | volume= 53 | issue= 25 | pages= 2343-8 | pmid=19539144 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.058 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19539144 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24179162">{{cite journal| author=Salah K, Kok WE, Eurlings LW, Bettencourt P, Pimenta JM, Metra M | display-authors=etal| title=A novel discharge risk model for patients hospitalised for acute decompensated heart failure incorporating N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels: a European coLlaboration on Acute decompeNsated Heart Failure: ELAN-HF Score. | journal=Heart | year= 2014 | volume= 100 | issue= 2 | pages= 115-25 | pmid=24179162 | doi=10.1136/heartjnl-2013-303632 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24179162 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24922626">{{cite journal| author=Flint KM, Allen LA, Pham M, Heidenreich PA| title=B-type natriuretic peptide predicts 30-day readmission for heart failure but not readmission for other causes. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2014 | volume= 3 | issue= 3 | pages= e000806 | pmid=24922626 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.114.000806 | pmc=4309072 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24922626 }} </ref><ref name="pmid21743005">{{cite journal| author=Kociol RD, Horton JR, Fonarow GC, Reyes EM, Shaw LK, O'Connor CM | display-authors=etal| title=Admission, discharge, or change in B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term outcomes: data from Organized Program to Initiate Lifesaving Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure (OPTIMIZE-HF) linked to Medicare claims. | journal=Circ Heart Fail | year= 2011 | volume= 4 | issue= 5 | pages= 628-36 | pmid=21743005 | doi=10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.962290 | pmc=3465672 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21743005 }} </ref><ref name="pmid23250981">{{cite journal| author=Kociol RD, McNulty SE, Hernandez AF, Lee KL, Redfield MM, Tracy RP | display-authors=etal| title=Markers of decongestion, dyspnea relief, and clinical outcomes among patients hospitalized with acute heart failure. | journal=Circ Heart Fail | year= 2013 | volume= 6 | issue= 2 | pages= 240-5 | pmid=23250981 | doi=10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.969246 | pmc=3865520 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23250981 }} </ref><ref name="pmid18545069">{{cite journal| author=Verdiani V, Ognibene A, Rutili MS, Lombardo C, Bacci F, Terreni A | display-authors=etal| title=NT-ProBNP reduction percentage during hospital stay predicts long-term mortality and readmission in heart failure patients. | journal=J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) | year= 2008 | volume= 9 | issue= 7 | pages= 694-9 | pmid=18545069 | doi=10.2459/JCM.0b013e3282f447ae | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18545069 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15948093">{{cite journal| author=Bayés-Genís A, Lopez L, Zapico E, Cotes C, Santaló M, Ordonez-Llanos J | display-authors=etal| title=NT-ProBNP reduction percentage during admission for acutely decompensated heart failure predicts long-term cardiovascular mortality. | journal=J Card Fail | year= 2005 | volume= 11 | issue= 5 Suppl | pages= S3-8 | pmid=15948093 | doi=10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.04.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15948093 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: A]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''3.''' In [[patients]] [[hospitalized]] for [[HF]], measurement of [[BNP]] or [[NT-proBNP]] levels at admission is recommended to establish [[prognosis]]. <ref name="pmid25052418">{{cite journal| author=Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope AC, Ali U, Oremus M, Brown JA, Bustamam A | display-authors=etal| title=Incremental value of natriuretic peptide measurement in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF): a systematic review. | journal=Heart Fail Rev | year= 2014 | volume= 19 | issue= 4 | pages= 507-19 | pmid=25052418 | doi=10.1007/s10741-014-9444-9 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25052418 }} </ref><ref name="pmid16979009">{{cite journal| author=van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL, Ellinor PT, Sharma UC, Bakker JA, Low AF | display-authors=etal| title=Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, galectin-3, and apelin for the evaluation of patients with acute heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2006 | volume= 48 | issue= 6 | pages= 1217-24 | pmid=16979009 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.061 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16979009 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15451800">{{cite journal| author=Bettencourt P, Azevedo A, Pimenta J, Friões F, Ferreira S, Ferreira A| title=N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide predicts outcome after hospital discharge in heart failure patients. | journal=Circulation | year= 2004 | volume= 110 | issue= 15 | pages= 2168-74 | pmid=15451800 | doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000144310.04433.BE | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15451800 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11216951">{{cite journal| author=Cheng V, Kazanagra R, Garcia A, Lenert L, Krishnaswamy P, Gardetto N | display-authors=etal| title=A rapid bedside test for B-type peptide predicts treatment outcomes in patients admitted for decompensated heart failure: a pilot study. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2001 | volume= 37 | issue= 2 | pages= 386-91 | pmid=11216951 | doi=10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01157-8 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11216951 }} </ref><ref name="pmid17498579">{{cite journal| author=Fonarow GC, Peacock WF, Phillips CO, Givertz MM, Lopatin M, ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators| title=Admission B-type natriuretic peptide levels and in-hospital mortality in acute decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2007 | volume= 49 | issue= 19 | pages= 1943-50 | pmid=17498579 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.037 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17498579 }} </ref><ref name="pmid14975475">{{cite journal| author=Logeart D, Thabut G, Jourdain P, Chavelas C, Beyne P, Beauvais F | display-authors=etal| title=Predischarge B-type natriuretic peptide assay for identifying patients at high risk of re-admission after decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2004 | volume= 43 | issue= 4 | pages= 635-41 | pmid=14975475 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.044 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14975475 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15364340">{{cite journal| author=Maisel A, Hollander JE, Guss D, McCullough P, Nowak R, Green G | display-authors=etal| title=Primary results of the Rapid Emergency Department Heart Failure Outpatient Trial (REDHOT). A multicenter study of B-type natriuretic peptide levels, emergency department decision making, and outcomes in patients presenting with shortness of breath. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2004 | volume= 44 | issue= 6 | pages= 1328-33 | pmid=15364340 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2004.06.015 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15364340 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19157603">{{cite journal| author=Zairis MN, Tsiaousis GZ, Georgilas AT, Makrygiannis SS, Adamopoulou EN, Handanis SM | display-authors=etal| title=Multimarker strategy for the prediction of 31 days cardiac death in patients with acutely decompensated chronic heart failure. | journal=Int J Cardiol | year= 2010 | volume= 141 | issue= 3 | pages= 284-90 | pmid=19157603 | doi=10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.12.017 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19157603 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: A]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|} | |} | ||
{|class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | {|class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background: | |colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LemonChiffon"| [[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class IIa]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| bgcolor=" | | bgcolor="LemonChiffon"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''4.''' In [[patients]] at risk of developing [[HF]], [[BNP]] or [[NT-proBNP]]-based screening followed by [[team-based care]], including a [[cardiovascular]] specialist, can be useful to prevent the development of [[LV dysfunction]] or new-onset [[HF]]. <ref name="pmid23810874">{{cite journal| author=Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, Strunk G, Brath H, Francesconi C | display-authors=etal| title=PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2013 | volume= 62 | issue= 15 | pages= 1365-72 | pmid=23810874 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23810874 }} </ref><ref name="pmid23821090">{{cite journal| author=Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, Tallon E, O'Connell E, Dawkins I | display-authors=etal| title=Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure: the STOP-HF randomized trial. | journal=JAMA | year= 2013 | volume= 310 | issue= 1 | pages= 66-74 | pmid=23821090 | doi=10.1001/jama.2013.7588 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23821090 }} [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=&cmd=prlinks&id=24368334 Review in: Evid Based Med. 2014 Jun;19(3):107] </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B-R]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| bgcolor="LemonChiffon"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''5.'''In [[patients]] [[hospitalized]] for [[HF]], a predischarge [[BNP]] or [[NT-proBNP]] level can be useful to inform the trajectory of the [[patient]] and establish a postdischarge [[prognosis]]. <ref name="pmid15451800">{{cite journal| author=Bettencourt P, Azevedo A, Pimenta J, Friões F, Ferreira S, Ferreira A| title=N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide predicts outcome after hospital discharge in heart failure patients. | journal=Circulation | year= 2004 | volume= 110 | issue= 15 | pages= 2168-74 | pmid=15451800 | doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000144310.04433.BE | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15451800 }} </ref><ref name="pmid14975475">{{cite journal| author=Logeart D, Thabut G, Jourdain P, Chavelas C, Beyne P, Beauvais F | display-authors=etal| title=Predischarge B-type natriuretic peptide assay for identifying patients at high risk of re-admission after decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2004 | volume= 43 | issue= 4 | pages= 635-41 | pmid=14975475 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.044 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14975475 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19398076">{{cite journal| author=Dhaliwal AS, Deswal A, Pritchett A, Aguilar D, Kar B, Souchek J | display-authors=etal| title=Reduction in BNP levels with treatment of decompensated heart failure and future clinical events. | journal=J Card Fail | year= 2009 | volume= 15 | issue= 4 | pages= 293-9 | pmid=19398076 | doi=10.1016/j.cardfail.2008.11.007 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19398076 }} </ref><ref name="pmid20185037">{{cite journal| author=O'Connor CM, Hasselblad V, Mehta RH, Tasissa G, Califf RM, Fiuzat M | display-authors=etal| title=Triage after hospitalization with advanced heart failure: the ESCAPE (Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness) risk model and discharge score. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2010 | volume= 55 | issue= 9 | pages= 872-8 | pmid=20185037 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.083 | pmc=3835158 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20185037 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12921811">{{cite journal| author=O'Brien RJ, Squire IB, Demme B, Davies JE, Ng LL| title=Pre-discharge, but not admission, levels of NT-proBNP predict adverse prognosis following acute LVF. | journal=Eur J Heart Fail | year= 2003 | volume= 5 | issue= 4 | pages= 499-506 | pmid=12921811 | doi=10.1016/s1388-9842(03)00098-9 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12921811 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19539144">{{cite journal| author=Cohen-Solal A, Logeart D, Huang B, Cai D, Nieminen MS, Mebazaa A| title=Lowered B-type natriuretic peptide in response to levosimendan or dobutamine treatment is associated with improved survival in patients with severe acutely decompensated heart failure. | journal=J Am Coll Cardiol | year= 2009 | volume= 53 | issue= 25 | pages= 2343-8 | pmid=19539144 | doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.058 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19539144 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24179162">{{cite journal| author=Salah K, Kok WE, Eurlings LW, Bettencourt P, Pimenta JM, Metra M | display-authors=etal| title=A novel discharge risk model for patients hospitalised for acute decompensated heart failure incorporating N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels: a European coLlaboration on Acute decompeNsated Heart Failure: ELAN-HF Score. | journal=Heart | year= 2014 | volume= 100 | issue= 2 | pages= 115-25 | pmid=24179162 | doi=10.1136/heartjnl-2013-303632 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24179162 }} </ref><ref name="pmid24922626">{{cite journal| author=Flint KM, Allen LA, Pham M, Heidenreich PA| title=B-type natriuretic peptide predicts 30-day readmission for heart failure but not readmission for other causes. | journal=J Am Heart Assoc | year= 2014 | volume= 3 | issue= 3 | pages= e000806 | pmid=24922626 | doi=10.1161/JAHA.114.000806 | pmc=4309072 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24922626 }} </ref><ref name="pmid21743005">{{cite journal| author=Kociol RD, Horton JR, Fonarow GC, Reyes EM, Shaw LK, O'Connor CM | display-authors=etal| title=Admission, discharge, or change in B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term outcomes: data from Organized Program to Initiate Lifesaving Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure (OPTIMIZE-HF) linked to Medicare claims. | journal=Circ Heart Fail | year= 2011 | volume= 4 | issue= 5 | pages= 628-36 | pmid=21743005 | doi=10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.962290 | pmc=3465672 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21743005 }} </ref><ref name="pmid23250981">{{cite journal| author=Kociol RD, McNulty SE, Hernandez AF, Lee KL, Redfield MM, Tracy RP | display-authors=etal| title=Markers of decongestion, dyspnea relief, and clinical outcomes among patients hospitalized with acute heart failure. | journal=Circ Heart Fail | year= 2013 | volume= 6 | issue= 2 | pages= 240-5 | pmid=23250981 | doi=10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.969246 | pmc=3865520 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23250981 }} </ref><ref name="pmid18545069">{{cite journal| author=Verdiani V, Ognibene A, Rutili MS, Lombardo C, Bacci F, Terreni A | display-authors=etal| title=NT-ProBNP reduction percentage during hospital stay predicts long-term mortality and readmission in heart failure patients. | journal=J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) | year= 2008 | volume= 9 | issue= 7 | pages= 694-9 | pmid=18545069 | doi=10.2459/JCM.0b013e3282f447ae | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18545069 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15948093">{{cite journal| author=Bayés-Genís A, Lopez L, Zapico E, Cotes C, Santaló M, Ordonez-Llanos J | display-authors=etal| title=NT-ProBNP reduction percentage during admission for acutely decompensated heart failure predicts long-term cardiovascular mortality. | journal=J Card Fail | year= 2005 | volume= 11 | issue= 5 Suppl | pages= S3-8 | pmid=15948093 | doi=10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.04.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15948093 }} </ref> ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B-NR]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|bgcolor="LemonChiffon"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>''' | |||
|} | |||
== | ==External Links== | ||
*[ | *[https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/epub/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063.full.pdf 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines]<ref name="pmid35363499">{{cite journal |vauthors=Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, Deswal A, Drazner MH, Dunlay SM, Evers LR, Fang JC, Fedson SE, Fonarow GC, Hayek SS, Hernandez AF, Khazanie P, Kittleson MM, Lee CS, Link MS, Milano CA, Nnacheta LC, Sandhu AT, Stevenson LW, Vardeny O, Vest AR, Yancy CW |title=2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines |journal=Circulation |volume=145 |issue=18 |pages=e895–e1032 |date=May 2022 |pmid=35363499 |doi=10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063 |url=}} </ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
| Line 186: | Line 163: | ||
[[Category:Intensive care medicine]] | [[Category:Intensive care medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Medicine]] | [[Category:Medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date cardiology]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date cardiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:49, 8 October 2022
| Resident Survival Guide |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan, M.B.B.S. [2]; Seyedmahdi Pahlavani, M.D. [3]; Tarek Nafee, M.D. [4]; Edzel Lorraine Co, DMD, MD[5]
Overview
Once the diagnosis of heart failure is made, subsequent laboratory studies should be directed toward the identification of an underlying cause of heart failure.
Laboratory Tests
Renal Function
Renal function should be assessed as a rough guide to the patient's intravascular volume status and renal perfusion. A urinalysis is helpful in the assessment of the patient's volume status. Electrolyte assessment and the correction of electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalemia, hyperkalemia and hypomagnesemia is critical in those patients treated with diuretics. Hyponatremia (due to poor stimulation of the baroreceptors and appropriate ADH release and free water retention) is associated with a poor prognosis.
Hematologic Studies
A complete blood count should be obtained to assess for the presence of anemia which may exacerbate heart failure and to assess the patients coagulation status which may be impaired due to hepatic congestion.
Thyroid Studies
The assessment of thyroid function tests is particularly important in the patient who is being treated with concomitant therapy with an agent such as amiodarone.
Biomarkers
Biomarkers are going to play a great role in diagnosis of heart failure.
Natriuretic Peptides: BNP or NT-proBNP
- Plasma concentrations of NPs are recommended as initial diagnostic tests in patients with symptoms suggestive of HF to rule out the diagnosis.
- Elevated concentrations support a diagnosis of HF.
- Other causes of an elevated NP include atrial fibrillation, increasing age, and acute or chronic kidney disease.
- NP concentrations may be low in obese patients.
- The upper limits of normal in the non-acute setting are 35 pg/mL for BNP, and 125 pg/mL for NT-proBNP.[1]
The CoDE-HF decision support tool may help diagnose heart failure[2]. The CoDE-HF interprets the N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in various settings including obesity.
| Causes of elevated concentrations of natriuretic peptides |
| Cardiac: |
|
❑ Heart failure |
| Non-Cardiac : |
|
❑ Advanced age |
| The above table adopted from 2021 ESC Guideline |
|---|
- BNP or its amino-terminal cleavage equivalent (NT-proBNP) is generated by cardiomyocytes in the context of numerous triggers, most notably myocardial stretch.
- BNP levels may be useful in the initial establishment of the diagnosis of heart failure in the patient with dyspnea of unclear etiology. In a meta-analysis, BNP was superior N-terminal pro-BNP (NTproBNP) and was associated with a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 84% in the diagnosis of heart failure in the primary care setting.[4]
- These biomarkers have been studied for the detection of elevated cardiac pressures.[5][6][7], low ejection fraction[8], or both[9][10].
- Clinical practice guidelines suggest their measurement is helpful for diagnosis or ruling out heart failure especially in the acute settings.[11]
Biomarkers indications for use
Abbreviations:
ACC: American College of Cardiology, AHA: American Heart Association, ADHF: acute decompensated
heart failure, BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide, COR: Class of Recommendation, ED: emergency department, HF: heart failure, NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, NYHA: New York Heart Association, pts: patients
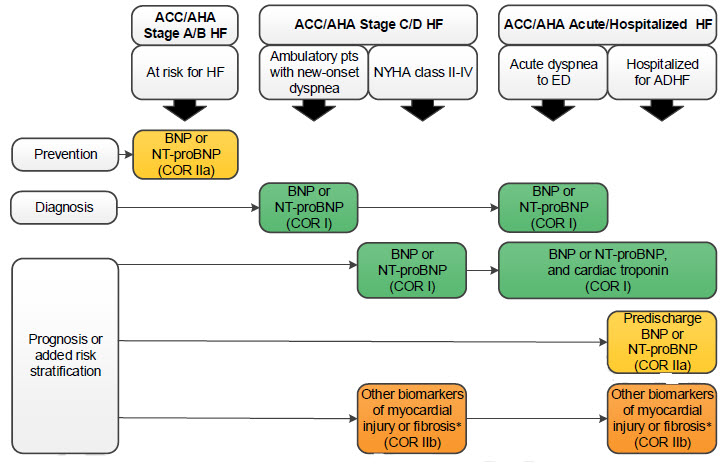
(*)Other biomarkers of injury or fibrosis include soluble ST2 receptor, galectin-3, and high-sensitivity troponin.
Biomarkers of Myocardial Injury: Cardiac Troponin T or I
Even without obvious myocardial ischemic injury, troponin level may be increased in heart failure which means undergoing myocyte injury.[12] Elevated levels of troponin is associated with impaired hemodynamics, progressive LV dysfunction and increased mortality rates.[13]
Carbohydrate Antigen 125
CA-125 is an emerging, highly sensitive biomarker for heart failure.[14] Although it is not yet used in clinical practice, the CHANCE-HF trial has demonstrated utility in using CA-125 to guide diuretic therapy and for determining short-term prognosis.[15] CA-125 is a non-specific antigen that is most strongly associated with ovarian cancer. In patients with acute heart failure, ambulatory follow-up care aimed at titrating diuretic use according to CA-125 levels has demonstrated ~50% reduction in rehospitalizations.[15] CA-125 was first associated with heart failure in 1999 by Nagele et al.[14][16]
Initial lab tests for evaluation of HFrEF
- BNP, NT Pro BNP
- CBC, basic metabolic panel, liver function, Iron studies, thyroid studies, Hb A1C
2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Heart Failure Guideline (DO NOT EDIT) [17]
Initial Laboratory and Electrocardiographic Testing (DO NOT EDIT) [17]
| Class I |
| "1. For patients presenting with HF, the specific cause of HF should be explored using additional laboratory testing for appropriate management. [18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25] (Level of Evidence: B-NR) " |
| "2. For patients who are diagnosed with HF, laboratory evaluation should include complete blood count, urinalysis, serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, glucose, lipid profile, liver function tests, iron studies, and thyroid-stimulating hormone to optimize management. (Level of Evidence: C-EO) " |
| "3. For all patients presenting with HF, a 12-lead ECG should be performed at the initial encounter to optimize management. (Level of Evidence: C-EO) " |
Use of Biomarkers for Prevention, Initial Diagnosis, and Risk Stratification (DO NOT EDIT) [17]
| Class I |
| "1. In patients presenting with dyspnea, measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is useful to support a diagnosis or exclusion of HF. [26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37] (Level of Evidence: A) " |
| "2.In patients with chronic HF, measurements of BNP or NT-proBNP levels are recommended for risk stratification. [36][38][39][40][41][42][43][44][45][46][47][48][49][50][51][52][53][54] (Level of Evidence: A) " |
| "3. In patients hospitalized for HF, measurement of BNP or NT-proBNP levels at admission is recommended to establish prognosis. [36][38][39][40][41][42][43][44] (Level of Evidence: A) " |
| Class IIa |
| "4. In patients at risk of developing HF, BNP or NT-proBNP-based screening followed by team-based care, including a cardiovascular specialist, can be useful to prevent the development of LV dysfunction or new-onset HF. [55][56] (Level of Evidence: B-R) " |
| "5.In patients hospitalized for HF, a predischarge BNP or NT-proBNP level can be useful to inform the trajectory of the patient and establish a postdischarge prognosis. [39][42][45][46][47][48][49][50][51][52][53][54] (Level of Evidence: B-NR) " |
External Links
- 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines[57]
References
- ↑ Verdú JM, Comín-Colet J, Domingo M, Lupón J, Gómez M, Molina L, Casacuberta JM, Muñoz MA, Mena A, Bruguera-Cortada J (July 2012). "Rapid point-of-care NT-proBNP optimal cut-off point for heart failure diagnosis in primary care". Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 65 (7): 613–9. doi:10.1016/j.recesp.2012.01.019. PMID 22541282.
- ↑ Lee KK, Doudesis D, Anwar M, Astengo F, Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Claessens YE; et al. (2022). "Development and validation of a decision support tool for the diagnosis of acute heart failure: systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study". BMJ. 377: e068424. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068424. PMC 9189738 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 35697365 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, Burri H, Butler J, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, Cleland J, Coats A, Crespo-Leiro MG, Farmakis D, Gilard M, Heymans S, Hoes AW, Jaarsma T, Jankowska EA, Lainscak M, Lam C, Lyon AR, McMurray J, Mebazaa A, Mindham R, Muneretto C, Francesco Piepoli M, Price S, Rosano G, Ruschitzka F, Kathrine Skibelund A (September 2021). "2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure". Eur Heart J. 42 (36): 3599–3726. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368. PMID 34447992 Check
|pmid=value (help). Vancouver style error: initials (help) - ↑ Ewald B, Ewald D, Thakkinstian A, Attia J (2008). "Meta-analysis of B type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro B natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of clinical heart failure and population screening for left ventricular systolic dysfunction". Intern Med J. 38 (2): 101–13. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2007.01454.x. PMID 18290826.
- ↑ Dokainish H, Zoghbi WA, Lakkis NM, Al-Bakshy F, Dhir M, Quinones MA; et al. (2004). "Optimal noninvasive assessment of left ventricular filling pressures: a comparison of tissue Doppler echocardiography and B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with pulmonary artery catheters". Circulation. 109 (20): 2432–9. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000127882.58426.7A. PMID 15123522.
- ↑ Kelder JC, Cowie MR, McDonagh TA, Hardman SM, Grobbee DE, Cost B; et al. (2011). "Quantifying the added value of BNP in suspected heart failure in general practice: an individual patient data meta-analysis". Heart. 97 (12): 959–63. doi:10.1136/hrt.2010.220426. PMID 21478382.
- ↑ Dokainish H, Zoghbi WA, Lakkis NM, Quinones MA, Nagueh SF (2004). "Comparative accuracy of B-type natriuretic peptide and tissue Doppler echocardiography in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure". Am J Cardiol. 93 (9): 1130–5. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.01.042. PMID 15110205.
- ↑ Groenning BA, Raymond I, Hildebrandt PR, Nilsson JC, Baumann M, Pedersen F (2004). "Diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of left ventricular systolic heart failure by plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in a large sample of the general population". Heart. 90 (3): 297–303. PMC 1768111. PMID 14966052.
- ↑ Kuster GM, Tanner H, Printzen G, Suter TM, Mohacsi P, Hess OM (2002). "B-type natriuretic peptide for diagnosis and treatment of congestive heart failure". Swiss Med Wkly. 132 (43–44): 623–8. doi:2002/43/smw-10081 Check
|doi=value (help). PMID 12587046. - ↑ Maisel AS, McCord J, Nowak RM, Hollander JE, Wu AH, Duc P; et al. (2003). "Bedside B-Type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction. Results from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study". J Am Coll Cardiol. 41 (11): 2010–7. PMID 12798574.
- ↑ Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL (2013). "2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines". J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 62 (16): e147–239. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.019. PMID 23747642.
- ↑ Hudson MP, O'Connor CM, Gattis WA, Tasissa G, Hasselblad V, Holleman CM, Gaulden LH, Sedor F, Ohman EM (2004). "Implications of elevated cardiac troponin T in ambulatory patients with heart failure: a prospective analysis". Am. Heart J. 147 (3): 546–52. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2003.10.014. PMID 14999208.
- ↑ Horwich TB, Patel J, MacLellan WR, Fonarow GC (2003). "Cardiac troponin I is associated with impaired hemodynamics, progressive left ventricular dysfunction, and increased mortality rates in advanced heart failure". Circulation. 108 (7): 833–8. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000084543.79097.34. PMID 12912820.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 D'Aloia A, Vizzardi E, Metra M (2016). "Can Carbohydrate Antigen-125 Be a New Biomarker to Guide Heart Failure Treatment?: The CHANCE-HF Trial". JACC Heart Fail. 4 (11): 844–846. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2016.09.001. PMID 27810078.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Núñez J, Llàcer P, Bertomeu-González V, Bosch MJ, Merlos P, García-Blas S; et al. (2016). "Carbohydrate Antigen-125-Guided Therapy in Acute Heart Failure: CHANCE-HF: A Randomized Study". JACC Heart Fail. 4 (11): 833–843. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2016.06.007. PMID 27522630.
- ↑ Nägele H, Bahlo M, Klapdor R, Schaeperkoetter D, Rödiger W (1999). "CA 125 and its relation to cardiac function". Am Heart J. 137 (6): 1044–9. PMID 10347329.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM; et al. (2022). "2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines". Circulation. 145 (18): e876–e894. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001062. PMID 35363500 Check
|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F; et al. (2015). "Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy". Circulation. 131 (22): 1981–8. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013777. PMID 25948538 : 25948538 Check
|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Cardinale D, Sandri MT, Colombo A, Colombo N, Boeri M, Lamantia G; et al. (2004). "Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy". Circulation. 109 (22): 2749–54. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000130926.51766.CC. PMID 15148277.
- ↑ Castaño A, Narotsky DL, Hamid N, Khalique OK, Morgenstern R, DeLuca A; et al. (2017). "Unveiling transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis and its predictors among elderly patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement". Eur Heart J. 38 (38): 2879–2887. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehx350. PMC 5837725. PMID 29019612.
- ↑ Maurer MS, Hanna M, Grogan M, Dispenzieri A, Witteles R, Drachman B; et al. (2016). "Genotype and Phenotype of Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis: THAOS (Transthyretin Amyloid Outcome Survey)". J Am Coll Cardiol. 68 (2): 161–72. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.03.596. PMC 4940135. PMID 27386769.
- ↑ Gillmore JD, Maurer MS, Falk RH, Merlini G, Damy T, Dispenzieri A; et al. (2016). "Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis". Circulation. 133 (24): 2404–12. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021612. PMID 27143678.
- ↑ Brown EE, Lee YZJ, Halushka MK, Steenbergen C, Johnson NM, Almansa J; et al. (2017). "Genetic testing improves identification of transthyretin amyloid (ATTR) subtype in cardiac amyloidosis". Amyloid. 24 (2): 92–95. doi:10.1080/13506129.2017.1324418. PMID 28494620.
- ↑ Crawford TC, Okada DR, Magruder JT, Fraser C, Patel N, Houston BA; et al. (2018). "A Contemporary Analysis of Heart Transplantation and Bridge-to-Transplant Mechanical Circulatory Support Outcomes in Cardiac Sarcoidosis". J Card Fail. 24 (6): 384–391. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2018.02.009. PMID 29482029.
- ↑ Wu RS, Gupta S, Brown RN, Yancy CW, Wald JW, Kaiser P; et al. (2010). "Clinical outcomes after cardiac transplantation in muscular dystrophy patients". J Heart Lung Transplant. 29 (4): 432–8. doi:10.1016/j.healun.2009.08.030. PMID 19864165.
- ↑ Richards AM, Doughty R, Nicholls MG, MacMahon S, Sharpe N, Murphy J; et al. (2001). "Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and adrenomedullin: prognostic utility and prediction of benefit from carvedilol in chronic ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. Australia-New Zealand Heart Failure Group". J Am Coll Cardiol. 37 (7): 1781–7. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01269-4. PMID 11401111.
- ↑ Tang WH, Girod JP, Lee MJ, Starling RC, Young JB, Van Lente F; et al. (2003). "Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in ambulatory patients with established chronic symptomatic systolic heart failure". Circulation. 108 (24): 2964–6. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000106903.98196.B6. PMID 14662703.
- ↑ Zaphiriou A, Robb S, Murray-Thomas T, Mendez G, Fox K, McDonagh T; et al. (2005). "The diagnostic accuracy of plasma BNP and NTproBNP in patients referred from primary care with suspected heart failure: results of the UK natriuretic peptide study". Eur J Heart Fail. 7 (4): 537–41. doi:10.1016/j.ejheart.2005.01.022. PMID 15921792.
- ↑ Son CS, Kim YN, Kim HS, Park HS, Kim MS (2012). "Decision-making model for early diagnosis of congestive heart failure using rough set and decision tree approaches". J Biomed Inform. 45 (5): 999–1008. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2012.04.013. PMID 22564550.
- ↑ Kelder JC, Cramer MJ, van Wijngaarden J, van Tooren R, Mosterd A, Moons KG; et al. (2011). "The diagnostic value of physical examination and additional testing in primary care patients with suspected heart failure". Circulation. 124 (25): 2865–73. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.019216. PMID 22104551.
- ↑ Booth RA, Hill SA, Don-Wauchope A, Santaguida PL, Oremus M, McKelvie R; et al. (2014). "Performance of BNP and NT-proBNP for diagnosis of heart failure in primary care patients: a systematic review". Heart Fail Rev. 19 (4): 439–51. doi:10.1007/s10741-014-9445-8. PMID 24969534.
- ↑ Dao Q, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Harrison A, Amirnovin R, Lenert L; et al. (2001). "Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in an urgent-care setting". J Am Coll Cardiol. 37 (2): 379–85. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01156-6. PMID 11216950.
- ↑ Davis M, Espiner E, Richards G, Billings J, Town I, Neill A; et al. (1994). "Plasma brain natriuretic peptide in assessment of acute dyspnoea". Lancet. 343 (8895): 440–4. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92690-5. PMID 7905953.
- ↑ Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P; et al. (2002). "Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure". N Engl J Med. 347 (3): 161–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa020233. PMID 12124404. Review in: J Fam Pract. 2002 Oct;51(10):816 Review in: ACP J Club. 2003 Jan-Feb;138(1):23
- ↑ Januzzi JL, Chen-Tournoux AA, Moe G (2008). "Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing for the diagnosis or exclusion of heart failure in patients with acute symptoms". Am J Cardiol. 101 (3A): 29–38. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.017. PMID 18243855.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope AC, Ali U, Oremus M, Brown JA, Bustamam A; et al. (2014). "Incremental value of natriuretic peptide measurement in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF): a systematic review". Heart Fail Rev. 19 (4): 507–19. doi:10.1007/s10741-014-9444-9. PMID 25052418.
- ↑ Hill SA, Booth RA, Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope A, Brown JA, Oremus M; et al. (2014). "Use of BNP and NT-proBNP for the diagnosis of heart failure in the emergency department: a systematic review of the evidence". Heart Fail Rev. 19 (4): 421–38. doi:10.1007/s10741-014-9447-6. PMID 24957908.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL, Ellinor PT, Sharma UC, Bakker JA, Low AF; et al. (2006). "Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, galectin-3, and apelin for the evaluation of patients with acute heart failure". J Am Coll Cardiol. 48 (6): 1217–24. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.061. PMID 16979009.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 Bettencourt P, Azevedo A, Pimenta J, Friões F, Ferreira S, Ferreira A (2004). "N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide predicts outcome after hospital discharge in heart failure patients". Circulation. 110 (15): 2168–74. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000144310.04433.BE. PMID 15451800.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Cheng V, Kazanagra R, Garcia A, Lenert L, Krishnaswamy P, Gardetto N; et al. (2001). "A rapid bedside test for B-type peptide predicts treatment outcomes in patients admitted for decompensated heart failure: a pilot study". J Am Coll Cardiol. 37 (2): 386–91. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01157-8. PMID 11216951.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Fonarow GC, Peacock WF, Phillips CO, Givertz MM, Lopatin M, ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators (2007). "Admission B-type natriuretic peptide levels and in-hospital mortality in acute decompensated heart failure". J Am Coll Cardiol. 49 (19): 1943–50. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.037. PMID 17498579.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 Logeart D, Thabut G, Jourdain P, Chavelas C, Beyne P, Beauvais F; et al. (2004). "Predischarge B-type natriuretic peptide assay for identifying patients at high risk of re-admission after decompensated heart failure". J Am Coll Cardiol. 43 (4): 635–41. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.044. PMID 14975475.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Maisel A, Hollander JE, Guss D, McCullough P, Nowak R, Green G; et al. (2004). "Primary results of the Rapid Emergency Department Heart Failure Outpatient Trial (REDHOT). A multicenter study of B-type natriuretic peptide levels, emergency department decision making, and outcomes in patients presenting with shortness of breath". J Am Coll Cardiol. 44 (6): 1328–33. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.06.015. PMID 15364340.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Zairis MN, Tsiaousis GZ, Georgilas AT, Makrygiannis SS, Adamopoulou EN, Handanis SM; et al. (2010). "Multimarker strategy for the prediction of 31 days cardiac death in patients with acutely decompensated chronic heart failure". Int J Cardiol. 141 (3): 284–90. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.12.017. PMID 19157603.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Dhaliwal AS, Deswal A, Pritchett A, Aguilar D, Kar B, Souchek J; et al. (2009). "Reduction in BNP levels with treatment of decompensated heart failure and future clinical events". J Card Fail. 15 (4): 293–9. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2008.11.007. PMID 19398076.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 O'Connor CM, Hasselblad V, Mehta RH, Tasissa G, Califf RM, Fiuzat M; et al. (2010). "Triage after hospitalization with advanced heart failure: the ESCAPE (Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness) risk model and discharge score". J Am Coll Cardiol. 55 (9): 872–8. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.083. PMC 3835158. PMID 20185037.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 O'Brien RJ, Squire IB, Demme B, Davies JE, Ng LL (2003). "Pre-discharge, but not admission, levels of NT-proBNP predict adverse prognosis following acute LVF". Eur J Heart Fail. 5 (4): 499–506. doi:10.1016/s1388-9842(03)00098-9. PMID 12921811.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 Cohen-Solal A, Logeart D, Huang B, Cai D, Nieminen MS, Mebazaa A (2009). "Lowered B-type natriuretic peptide in response to levosimendan or dobutamine treatment is associated with improved survival in patients with severe acutely decompensated heart failure". J Am Coll Cardiol. 53 (25): 2343–8. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.058. PMID 19539144.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 Salah K, Kok WE, Eurlings LW, Bettencourt P, Pimenta JM, Metra M; et al. (2014). "A novel discharge risk model for patients hospitalised for acute decompensated heart failure incorporating N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels: a European coLlaboration on Acute decompeNsated Heart Failure: ELAN-HF Score". Heart. 100 (2): 115–25. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2013-303632. PMID 24179162.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Flint KM, Allen LA, Pham M, Heidenreich PA (2014). "B-type natriuretic peptide predicts 30-day readmission for heart failure but not readmission for other causes". J Am Heart Assoc. 3 (3): e000806. doi:10.1161/JAHA.114.000806. PMC 4309072. PMID 24922626.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 Kociol RD, Horton JR, Fonarow GC, Reyes EM, Shaw LK, O'Connor CM; et al. (2011). "Admission, discharge, or change in B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term outcomes: data from Organized Program to Initiate Lifesaving Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure (OPTIMIZE-HF) linked to Medicare claims". Circ Heart Fail. 4 (5): 628–36. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.962290. PMC 3465672. PMID 21743005.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 Kociol RD, McNulty SE, Hernandez AF, Lee KL, Redfield MM, Tracy RP; et al. (2013). "Markers of decongestion, dyspnea relief, and clinical outcomes among patients hospitalized with acute heart failure". Circ Heart Fail. 6 (2): 240–5. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.969246. PMC 3865520. PMID 23250981.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Verdiani V, Ognibene A, Rutili MS, Lombardo C, Bacci F, Terreni A; et al. (2008). "NT-ProBNP reduction percentage during hospital stay predicts long-term mortality and readmission in heart failure patients". J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 9 (7): 694–9. doi:10.2459/JCM.0b013e3282f447ae. PMID 18545069.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Bayés-Genís A, Lopez L, Zapico E, Cotes C, Santaló M, Ordonez-Llanos J; et al. (2005). "NT-ProBNP reduction percentage during admission for acutely decompensated heart failure predicts long-term cardiovascular mortality". J Card Fail. 11 (5 Suppl): S3–8. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.04.006. PMID 15948093.
- ↑ Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, Strunk G, Brath H, Francesconi C; et al. (2013). "PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial". J Am Coll Cardiol. 62 (15): 1365–72. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069. PMID 23810874.
- ↑ Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, Tallon E, O'Connell E, Dawkins I; et al. (2013). "Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure: the STOP-HF randomized trial". JAMA. 310 (1): 66–74. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.7588. PMID 23821090. Review in: Evid Based Med. 2014 Jun;19(3):107
- ↑ Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, Deswal A, Drazner MH, Dunlay SM, Evers LR, Fang JC, Fedson SE, Fonarow GC, Hayek SS, Hernandez AF, Khazanie P, Kittleson MM, Lee CS, Link MS, Milano CA, Nnacheta LC, Sandhu AT, Stevenson LW, Vardeny O, Vest AR, Yancy CW (May 2022). "2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines". Circulation. 145 (18): e895–e1032. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063. PMID 35363499 Check
|pmid=value (help).