Proteinuria
|
WikiDoc Resources for Proteinuria |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Proteinuria Most cited articles on Proteinuria |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Proteinuria |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Proteinuria at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Proteinuria at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Proteinuria
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Proteinuria Discussion groups on Proteinuria Patient Handouts on Proteinuria Directions to Hospitals Treating Proteinuria Risk calculators and risk factors for Proteinuria
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Proteinuria |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Saeedeh Kowsarnia M.D.[2]
Synonyms and keywords: Elevated urinary protein levels; Elevated urine protein
To view a comprehensive algorithm of common findings of urine composition and urine output, click here
Overview
Proteinuria (from protein and urine) means the presence of an excess of serum proteins in the urine.The protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy, although foamy urine may also be caused by bilirubin in the urine (bilirubinuria),retrograde ejaculation, pneumaturia (air bubbles in the urine) due to a fistula,or drugs such as pyridium.
Classification
Proteinuria is classified based upon the site and the amount of protein in the urine.
| Types | Definition | Level of proteinuria |
|---|---|---|
| Glomerular proteinuria | Increased filtration rate of protein due to the damage to the glomerular-capillary barrier | Variable,
usually > 2g/day Dipstick:Positive |
| Tubular proteinuria | Decreased tubular reabsorption of proteins due to tubular cell damage | < 2 g/day
Dipstick:Negative |
| Overflow proteinuria | Increased urinary excretion of proteins due to exceeding reabsorption capacity of renal tubules | Variable up to 20g/day
Dipstick:Negative |
| Post-renal proteinuria | Increased urinary excretion of the small amount of protein especially IgA and IgG | Variable,
usually < 1g/day |
| Isolated proteinuria | Proteinuria with normal urinary sediment with no history of renal disease
Excluding criteria: Proteinuria (≥ 3.5 g/day), edema, hypoalbuminemia, lipiduria, active urine sediment (red blood cells and/or cast), decreased GFR, hypertension |
< 2 g/day |
| Proteinuria | Amount |
|---|---|
| Normal range | Total protein excretion in urine (proteinuria): < 150 mg/day, average 80 mg/day
Albumin excretion: < 20 mg/day (15 mcg/min), 15% of urine total protein (remaining 85% constitutes Tamm-Horsfall proteins, IgA, urokinase) [1] [2] (The rate of proteinuria increases proportionally with age and body weight) |
| Albuminuria
(microalbuminuria) |
30-300 mg/day (20 to 200 mcg/min) |
| Overt proteinuria
(macroalbuminuria) |
Albuminuria > 300 mg/day (200 mcg/min) up to 3500 mg/day, positive dipstick |
| Nephrotic range | Total protein excretion: ≥ 3.5 g/day |
Pathophysiology
The amount of proteins present in the urine is < 150 mg/day with an intact glomerular-capillary barrier and functioning tubules, thus increased levels of proteinuria can demonstrate kidney damage (glomerular or tubular). Overproduction of proteins which exceeds the absorption capacity of the tubules causes proteinuria in spite of relatively normal renal function (overflow). Normally filtration of all plasma proteins like albumin, globulins and other high-molecular-weight proteins through the glomerular-capillary wall is prevented by charge and size of the proteins and glomerular-capillary barrier. The type and quantity of proteins in the urine identifies the cause and site of kidney damage. As injury to the glomerular-capillary barrier causes albuminuria, tubular damage and overflow proteinuria lead to increase loads of low-molecular-weight proteins in the urine. The severity of protein loss in the urine depends on the mechanism of renal injury.
Glomerular-capillary barrier: It consists of endothelial cells of capillary, Glomerular basement membrane and epithelial cells. The endothelial cells of vessels organize a barrier with pores of 100 nm which impede the passing of the proteins from blood to the urinary space. Glomerular basement membrane and epithelial cells (podocytes) prevent the protein passage and trap the proteins especially with the size of > 100 kDa. The slit diaphragm acts as the most selective barrier for protein passage. The endothelial cells, podocytes, and glomerular basement membrane impede traversal of the negative-charge proteins due to the presence of negative charges in their constitution.
Tubular reabsorption: Almost all the proteins which are filtered through glomerulus are reabsorbed by proximal tubular cells by endocytosis. The tubulointerstitial diseases damage the cells cause tubular proteinuria. In circumstances which large amounts of protein is filtered, tubular proteinuria occurs due to exceeding the reabption capacity of the cells. Not all the proteins in the tubules are toxic to the cells but proximal tubule injury, light chain deposition and tubule obstruction (cast nephropathy) due to the large level of light chain may cause further proteinuria by the overwhelming capacity of tubular cells.
Proteins: The size of the protein is one of the determinants of traversal through the glomerular-capillary barrier. Immunoglobulins like IgG and other high-molecular-weight proteins have the higher molecular radius, therefore, there are not able to pass over the barrier. Low-molecular-weight proteins are the ones with < 40kDa and molecular radius < 30 Å are filtered almost completely and reabsorbed by tubular cells.
- In normal physiological condition, HMW proteins do not cross the glomerular barrier. The small percentage of albumin passes the barrier which is reabsorbed completely in the proximal tubules. LMW proteins are filtered and reabsorbed completely.
- Moderate alteration of permeability of glomerular barrier named as selective proteinuria, demonstrates with loss of negative-charged proteins like albumin, LMW proteins and small percetage of HMW proteins in the urine with exceeding the reabsorbtion capacity of tubular cells.
- Severe damage to the barrier, causes loss of the greater percentage of HMW proteins in the urine which is called nonselective proteinuria.
- Profound damage to glomerular barrier causes severe proteinuria of all classes especially LMW and HMW. Increasing loads of protein which exceed the reabsorption capability of tubular cells causes damage to tubular cells and worsens proteinuria.
(an average protein has 250 amino acids which equals molecular weight( MW) of approximately 34 kDa)
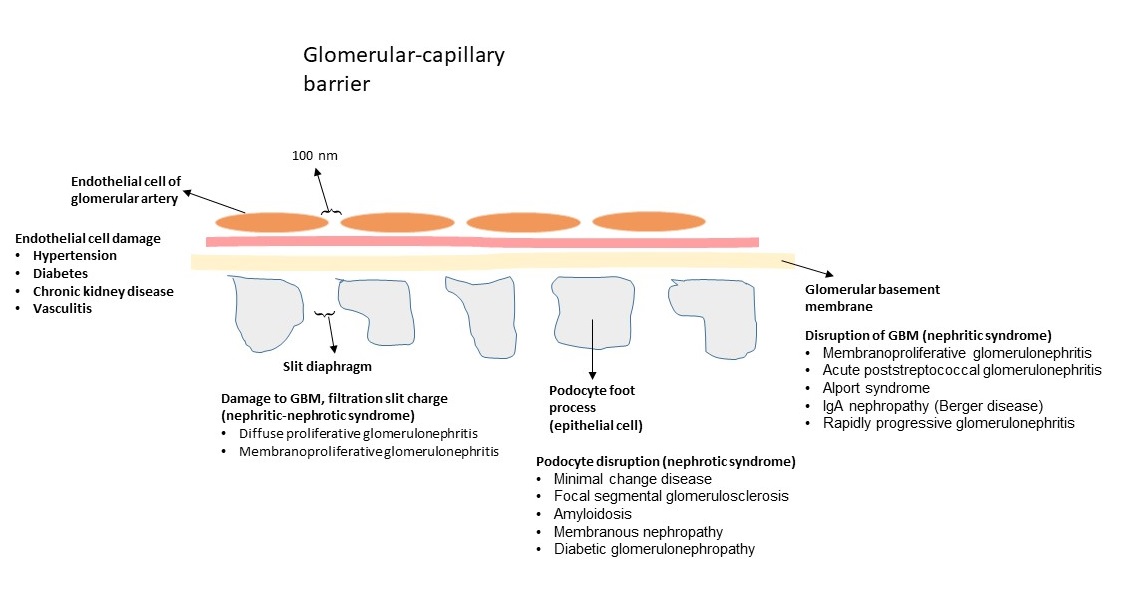
Causes
| Classification | Etiology |
|---|---|
| Glomerular proteinuria | Diabetic nephropathy, orthostatic proteinuria, glomerulonephropathies, hypertensive nephrosclerosis, preeclampsia, collagen vascular disease, infections, cancer, lymphoma, chronic renal transplant rejection, drugs, amyloidosis, post-transplant proteinuria
Transient: Exercise-induced proteinuria, fever, Infection, heart failure, joint inflammation, hyperlipidemia (LDL > 120 mg/dL), hyperglycemia (HbA1c > 8%), hypertension (BP >160/100 mmHg) |
| Tubular proteinuria | Tubulointerstitial diseases, cryoglobulinemia, Sjögren's syndrome, immunosuppressive agents, analgesic use |
| Overflow proteinuria | Light chains of immunoglobulins (multiple myeloma), lysozyme (AML), myoglobin (rhabdomyolysis), free hemoglobin not bound to haptoglobin (intravascular hemolysis), lymphoma, amyloidosis |
| Post-renal proteinuria | Nephrolithiasis, urinary tract tumors or infections |
| Isolated proteinuria | damage to tubular cells or the lower urinary tract, There is a 20% risk for renal insufficiency in the next 10 years, observation with blood pressure measurement, urinalysis and a creatinine clearance every 6 months should be considered. |
| Microalbuminuria |
Essential hypertension, early diabetes, early stages of glomerulonephritis (especially with active sediments; RBCs, RBC casts) |
| Macroalbuminuria |
Fever, exercise, CHF, orthostatic proteinuria, intermittent proteinuria, the kidney disease associated with myeloma, all diseases which are mentioned as the causes of microalbuminuria |
| Nephrotic range proteinuria | Diabetes, minimal change disease, amyloidosis, FSGS, membranous glomerulopathy, IgA nephropathy |
Risk Factors
- Race and ethnicity
- Obesity
- Age
- Medications
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Prevalence of albuminuria is 6100 and 9700 per 100,000 in male and female population, respectively [3].
- The estimated prevalence rate of albuminuria among diabetes population is 28,800 per 100,1000.
- Approximately,16,000 per 100,000 hypertensive cases have albuminuria.
- Isolated albuminuria with normal renal function is estimated 3,300 per 100,000 adult population.
Associated Conditions
Proteinuria may be a sign of renal (kidney) damage. Since serum proteins are readily reabsorbed from urine, the presence of excess protein indicates either an insufficiency of absorption or impaired filtration. Diabetics may suffer from damaged nephrons and develop proteinuria.
With severe proteinuria, general hypoproteinemia can develop which results in diminished oncotic pressure. Symptoms of diminished oncotic pressure may include ascites, edema, and hydrothorax.
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Complications
- Pulmonary edema
- Renal failure
- Increased risk of infections
- Increased risk of thromboembolic events
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
Prognosis
- Proteinuria is associated with left ventricular abnormalities, increased atherosclerosis and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
- Proteinuria is an independent risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease and end stage renal disease [4].
- Higher amounts of albuminuria, even in normal range is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
- Microalbuminuria can be considered as a predictor of morbidity and mortality in patients with no significant renal diseases.
- The presence of proteinuria in renal transplant patients predicts graft and patients survival [5].
- Treatment of proteinuria in patients with chronic renal disease improves outcomes.
- Increases Urinary albumin to creatinine ratio in patients with different medical conditions increases mortality.
- Albuminuria in any measurable levels is associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction in hypertensive patients.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
Qualitative measures
Urine dipstick: The standard urine dipstick is sensitive to urine albumin not to the non-albumin proteins, so the positive result indicates glomerular proteinuria. The dipstick grading is semiquantitative to the amount of protein in the urine and is dependent upon urine concentration. The sensitivity of the urinary dipstick for detection of albumin in the urine ranges from 83% to 98% with a specificity of 59% to 86% [6]. At the lower level of albuminuria, especially microalbuminuria the urine dispstick is specific but not sensitive, therefore microalbuminuria cannot be detected easily by urine dipstick unless the urine is properly concentrated. Few data suggests using specific gravity to estimate the amount of proteinuria, especially with the dipstick result of trace or 1+. Highly concentrated urine overestimates the amount of proteinuria in the urine, similarly, highly diluted urine underestimates the degree of proteinuria detected by dipstick.
- False-positive result: Urine PH > 8, administration of radiocontrast agents (iodinated), gross hematuria
- Newer dipsticks can detect albumin-to-creatinine and total protein-to-creatinine ratios which can help to avoid errors associated with diluted or concentrated urines and non-albumin proteinuria, respectively.
Sulfosalicylic acid test (SSA): Use of SSA is indicated in patients with the possibility of myeloma in the presence of negative or trace dipstick with renal function impairment. Adding SSA to the urine precipitates all proteins, therefore positive dipstick with SSA demonstrates overflow or tubular proteinuria.
- Fals-positive result: Administration of radiocontrast agents (iodinated), gross hematuria, penicillins
| Reference range for proteinuria | Standard dipstick +/- SSA |
|---|---|
| Trace | Slight turbidity (1 to 10 mg/dL) |
| 1+ | Turbidity through which print can be read (15 to 30 mg/dL) |
| 2+ | White cloud without precipitate through which print can be seen (40 to 100 mg/dL) |
| 3+ | White cloud with fine precipitate through which print cannot be seen (150 to 350 mg/dL) |
| 4+ | Fluffy precipitate (>500 mg/dL) |
Quantitative measures
24-hour urine collection: It is the gold standard test to determine the amount of proteinuria in patients who presents with persistent proteinuria (normal value < 150 mg/day).As collecting urine for 24 is cumbersome and erroneous, spot urine of first and second morning samples with protein-creatinine ratio can be used as an estimate of total protein excretion in 24 hour[7].
24-hour protein excretion= Urine protein concentration / Urine creatinine concentration
- Urine creatinine is higher in individuals with higher body muscle mass, therefore urine-protein ratio underestimates proteinuria, similarly in cachectic patients with lower muscle mass, urine-protein ratio overestimates the degree of proteinuria.
Renal biposy:
History and Symptoms
History:
- Fever
- Cardiac disease
- Renal disease
- Infections (HIV, hepatitis)
- Frothy, smoky, red urine
- Edema
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Family history of renal disease
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Chronic inflammatory disease
- Medications
Symptoms:
- Systemic symptoms (fever, night sweats, weight loss, bone pain)
- Heart diseases
- Edema (ankle, periorbital, labial, scrotal)
- High blood pressure
- Hematuria
Physical Examination
- Check blood pressure, orthostatic and supine, JVP
- Weight gain or weight changes
- Edema
- Signs of infectious diseases
- Signs of heart diseases
- Signs of systemic diseases
- Signs for complications (thrombosis, infections)
Laboratory Findings
Laboratory investigations to be considered in proteinuria:
Proteinuria is often diagnosed by a simple dipstick test although it is possible for the test to give a false negative even with nephrotic range proteinuria if the urine is dilute. False negatives may also occur if the protein in the urine is composed mainly globulins or Bence-Jones Proteins because the reagent on the test strips, Bromphenol blue, is highly specific for albumin. [8][9] Traditionally dipstick protein tests would be quantified by measuring the total quantity of protein in a 24-hour urine collection test, and abnormal globulins by specific requests for Protein electrophoresis.[10][11]
Alternatively the concentration of protein in the urine may be compared to the creatinine level in a spot urine sample. This is termed Protein/Creatinine Ratio (PCR). The 2005 UK Chronic Kidney Disease guidelines states that PCR is a better test than 24 hour urinary protein measurement. Proteinuria is defined as a Protein:creatinine ratio >45 mg/mmol (which is equivalent to Albumin:creatinine ratio of >30 mg/mmol) with very high levels of nephrotic syndrome being for PCR > 100 mg/mmol.[12]
Treatment
Specific treatments of proteinuria demands proper diagnosis of the cause.
Non-specific treatments reduce the amount of proteinuaria and the rate of progression or address the complications of proteinuria.
Diuretics: The treatment of fluid overload in patients with moderate to severe proteinuria along with salt restriction is diuretics. For refractory cases two different diuretics with will be used if the increasing doses are not effective. Acute renal failure may happen due to aggressive therapy with diuretics.
ACE inhibitors and ARBs: These agents decrease the progression and the amount of proteinuria by decreasing the intraglomerular pressure. Inhibiting vasoconstriction of efferent arterioles, maintaining the glomerular-capillary wall and decreasing the sclerosis and fibrosis of glomeruls are the action of these drugs aside the anti-hypertensive effects. In normotensive individuals with proteinuria low dose of these drugs have the effect without evident hypotension. Adverse effects are cough, angioedema and hyperkalemia. Adding mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists like eplerenone, spironolactone, help reducing proteinuria further but increase the rate of hyperkalemia. Eplerenone is the new drug in this category which is not associated with hyperkalemia.
Anticoagulants: Urinary loss of proteins in the urine especially anticoagulant proteins like antithrombin III and protein S and C put the patients at the risk of thrombosis and emboli. There is no eveidence supporting the use of anticoagulants as prophylaxis.
Calcium-channel blockers: Diltiazem and verapamil decrease proteinuria by prevent vasoconstriction of both afferent and efferent arterioles. Other CCBs act on afferent arteriols only which worsen proteinuria.
T reating proteinuria mainly needs the proper diagnosis of the cause. The most common cause is diabetic nephropathy; in this case, proper glycemic control may slow the progression. Medical management consists of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which are typically first-line therapy for proteinuria. In patients whose proteinuria is not controlled with ACE inhibitors, the addition of an aldosterone antagonist (i.e., spironolactone)[13] or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)[14] may further reduce protein loss. Caution must be used if these agents are added to ACE inhibitor therapy due to the risk of hyperkalemia. Proteinuria secondary to autoimmune disease should be treated with steroids or steroid-sparing agent plus the use of ACE inhibitors.
Related Chapters
Causes by Organ System
Causes in Alphabetical Order
|
|
|
References
- ↑ Viswanathan, Gautham; Upadhyay, Ashish (2011). "Assessment of Proteinuria". Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease. 18 (4): 243–248. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2011.03.002. ISSN 1548-5595.
- ↑ . doi:10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2011.Jan.10807. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Jones, Camille A.; Francis, Mildred E.; Eberhardt, Mark S.; Chavers, Blanche; Coresh, Josef; Engelgau, Michael; Kusek, John W.; Byrd-Holt, Danita; Narayan, K.M.Venkat; Herman, William H.; Jones, Camara P.; Salive, Marcel; Agodoa, Lawrence Y. (2002). "Microalbuminuria in the US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey". American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 39 (3): 445–459. doi:10.1053/ajkd.2002.31388. ISSN 0272-6386.
- ↑ Astor, Brad C.; Matsushita, Kunihiro; Gansevoort, Ron T.; van der Velde, Marije; Woodward, Mark; Levey, Andrew S.; Jong, Paul E. de; Coresh, Josef (2011). "Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with mortality and end-stage renal disease. A collaborative meta-analysis of kidney disease population cohorts". Kidney International. 79 (12): 1331–1340. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.550. ISSN 0085-2538.
- ↑ Borrego, J.; Mazuecos, A.; Gentil, M.A.; Cabello, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Osuna, A.; Pérez, M.A.; Castro, P.; Alonso, M. (2013). "Proteinuria as a Predictive Factor in the Evolution of Kidney Transplantation". Transplantation Proceedings. 45 (10): 3627–3629. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.10.025. ISSN 0041-1345.
- ↑ Mark J. Siedner, Allan C. Gelber, Brad H. Rovin, Alison M. McKinley, Lisa Christopher-Stine, Brad Astor, Michelle Petri & Derek M. Fine (2008). "Diagnostic accuracy study of urine dipstick in relation to 24-hour measurement as a screening tool for proteinuria in lupus nephritis". The Journal of rheumatology. 35 (1): 84–90. PMID 18085740. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Mark J. Siedner, Allan C. Gelber, Brad H. Rovin, Alison M. McKinley, Lisa Christopher-Stine, Brad Astor, Michelle Petri & Derek M. Fine (2008). "Diagnostic accuracy study of urine dipstick in relation to 24-hour measurement as a screening tool for proteinuria in lupus nephritis". The Journal of rheumatology. 35 (1): 84–90. PMID 18085740. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ http://medlib.med.utah.edu/WebPath/TUTORIAL/URINE/URINE.html Retrieved 2007-01-20
- ↑ Simerville JA, Maxted WC, Pahira JJ (2005). "Urinalysis: a comprehensive review". American family physician. 71 (6): 1153–62. PMID 15791892.
- ↑ http://www.pathguy.com/lectures/urine.htm Retrieved 2007-01-20
- ↑ http://www.answers.com/topic/protein-electrophoresis Retrieved 2007-01-20
- ↑ "Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines" (PDF). UK Renal Association. 27/9/05. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - see Guideline 4 Confirmation of proteinuria, on page 9 - ↑ Mehdi UF, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P; et al. (2009). "Addition of angiotensin receptor blockade or mineralocorticoid antagonism to maximum angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic nephropathy". J Am Soc Nephrol. 20 (12): 2641–50. doi:10.1681/ASN.2009070737. PMC 2794224. PMID 19926893.
- ↑ Burgess E, Muirhead N, Rene de Cotret P; et al. (2009). "Supramaximal dose of candesartan in proteinuric renal disease". J Am Soc Nephrol. 20 (4): 893–900. doi:10.1681/ASN.2008040416. PMC 2663827. PMID 19211712.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Van Vleet TR, Schnellmann RG (2003). "Toxic nephropathy: environmental chemicals". Semin Nephrol. 23 (5): 500–8. PMID 13680539.