Sandbox:Sahar: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Differentiating diagnosis of Lymphoma | ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Differentiating diagnosis of Lymphoma | ||
! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Symptoms | ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Symptoms | ||
! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Signs | ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Signs | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Arthritis | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Arthritis | ||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Lab Findings | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Lab Findings | ||
|- | |||
|Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Lymphoma]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Lymphoma]] | ||
| Line 133: | Line 145: | ||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Differentiating tests | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Differentiating tests | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Lymphoma|CNS lymphoma]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Lymphoma|CNS lymphoma]] | ||
| | | | ||
* Patient is [[immunocompetent]] | *Patient is [[immunocompetent]] | ||
* Focal symptoms indicative of a mass [[lesion]] | *Focal symptoms indicative of a mass [[lesion]] | ||
* [[Seizure]] | *[[Seizure]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Single solitary ring enhancing [[lesion]] on [[CT]] or [[MRI]] | *Single solitary ring enhancing [[lesion]] on [[CT]] or [[MRI]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Disseminated tuberculosis]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Disseminated tuberculosis]] | ||
| | | | ||
* Prior history of residence in an [[Endemic (epidemiology)|endemic]] area | *Prior history of residence in an [[Endemic (epidemiology)|endemic]] area | ||
* Chronic [[cough]], [[weight loss]], [[hemoptysis]] | *Chronic [[cough]], [[weight loss]], [[hemoptysis]] | ||
| | | | ||
* [[PCR]] of [[CSF]] for [[tuberculosis]] | *[[PCR]] of [[CSF]] for [[tuberculosis]] | ||
* Mycobacterial culture of [[CSF]] | *Mycobacterial culture of [[CSF]] | ||
* [[Brain]] biopsy for [[acid-fast bacilli]] staining | *[[Brain]] biopsy for [[acid-fast bacilli]] staining | ||
* Culture and acid stain positive for [[acid-fast bacilli]] | *Culture and acid stain positive for [[acid-fast bacilli]] | ||
* CXR shows [[Cavitation|cavitations]] | *CXR shows [[Cavitation|cavitations]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Aspergillosis]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Aspergillosis]] | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Pulmonary]] [[lesions]] in addition to [[CNS]] [[lesions]] | *[[Pulmonary]] [[lesions]] in addition to [[CNS]] [[lesions]] | ||
* Symptoms may include [[cough]], [[chest pain]], and [[hemoptysis]] | *Symptoms may include [[cough]], [[chest pain]], and [[hemoptysis]] | ||
| | | | ||
*[[CSF]] fungal culture, [[galactomannan]] | *[[CSF]] fungal culture, [[galactomannan]] | ||
| Line 166: | Line 178: | ||
*[[CSF]] fungal culture | *[[CSF]] fungal culture | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Chagas disease]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Chagas disease]] | ||
| | | | ||
*History of residence in Central or South America | *History of residence in Central or South America | ||
| Line 176: | Line 188: | ||
*[[Trypanosoma cruzi]] in [[blood]], [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]], or [[CSF]], [[PCR]] of [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] or [[body fluids]], and [[Serological testing|serologic tests]] | *[[Trypanosoma cruzi]] in [[blood]], [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]], or [[CSF]], [[PCR]] of [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] or [[body fluids]], and [[Serological testing|serologic tests]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Cytomegalovirus infection|CMV infection]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Cytomegalovirus infection|CMV infection]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Most common [[CNS]] [[opportunistic infection]] in [[AIDS]] patients | *Most common [[CNS]] [[opportunistic infection]] in [[AIDS]] patients | ||
| Line 186: | Line 198: | ||
*[[Brain biopsy]] with + [[staining]] for [[CMV]] or evidence of owl's eyes is also diagnostic, but it is rarely performed because of the location of [[brain]] lesions | *[[Brain biopsy]] with + [[staining]] for [[CMV]] or evidence of owl's eyes is also diagnostic, but it is rarely performed because of the location of [[brain]] lesions | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[HSV|HSV infection]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[HSV|HSV infection]] | ||
| | | | ||
*[[Seizures]], [[headache]], [[confusion]] and/or [[urinary retention]] can be seen in [[disseminated disease]], which usually affects only the [[immunocompromised]] or acute [[infections]] | *[[Seizures]], [[headache]], [[confusion]] and/or [[urinary retention]] can be seen in [[disseminated disease]], which usually affects only the [[immunocompromised]] or acute [[infections]] | ||
| Line 195: | Line 207: | ||
*[[PCR]] of [[CSF]] with detectable [[virus]] is diagnostic | *[[PCR]] of [[CSF]] with detectable [[virus]] is diagnostic | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Chickenpox|Varicella Zoster infection]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Chickenpox|Varicella Zoster infection]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Multifocal involvement has subacute course, usually only in [[immunosuppressed]], with [[headache]], [[fever]], focal deficits, and [[seizures]]. | *Multifocal involvement has subacute course, usually only in [[immunosuppressed]], with [[headache]], [[fever]], focal deficits, and [[seizures]]. | ||
*Unifocal involvement is more typically seen in [[immunocompetent]] hosts, occurring after [[contralateral]] [[cranial nerve]] [[herpes zoster]], with [[Altered mental status|mental status changes]], [[TIA|TIAs]], and [[stroke]] | *Unifocal involvement is more typically seen in [[immunocompetent]] hosts, occurring after [[contralateral]] [[cranial nerve]] [[herpes zoster]], with [[Altered mental status|mental status changes]], [[TIA|TIAs]], and [[stroke]] | ||
*[[Disseminated disease|Disseminated]] [[varicella zoster virus]] can occur in adults during primary [[infection]], presenting with [[pneumonitis]] and/or [[hepatitis]] | *[[Disseminated disease|Disseminated]] [[varicella zoster virus]] can occur in adults during primary [[infection]], presenting with [[pneumonitis]] and/or [[hepatitis]] | ||
| Line 204: | Line 216: | ||
*[[PCR]] of [[CSF]] with detectable [[virus]] is diagnostic | *[[PCR]] of [[CSF]] with detectable [[virus]] is diagnostic | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Brain abscess]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Brain abscess]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Associated with [[sinusitis]] (abutting the sinuses) or with [[bacteremia]] | *Associated with [[sinusitis]] (abutting the sinuses) or with [[bacteremia]] | ||
| Line 211: | Line 223: | ||
*[[CSF]] culture or culture of [[brain abscess]] | *[[CSF]] culture or culture of [[brain abscess]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy]] | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |[[Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy]] | ||
| | | | ||
*Symptoms are often more insidious in onset and progress over months. Symptoms include progressive [[weakness]], poor [[coordination]], with gradual slowing of [[mental]] function. Only seen in the [[immunosuppressed]]. Rarely associated with [[fever]] or other systemic symptoms | *Symptoms are often more insidious in onset and progress over months. Symptoms include progressive [[weakness]], poor [[coordination]], with gradual slowing of [[mental]] function. Only seen in the [[immunosuppressed]]. Rarely associated with [[fever]] or other systemic symptoms | ||
| Line 299: | Line 311: | ||
[[File:Fl000816-300x300.jpg|center|200px|thumb|wikimedia commons]] | [[File:Fl000816-300x300.jpg|center|200px|thumb|wikimedia commons|link=Special:FilePath/Fl000816-300x300.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 14:02, 1 July 2021
| Differentiating diagnosis of Lymphoma | Symptoms | Signs | Diagnosis | Additional Findings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Rash | Diarrhea | Abdominal pain | Weight loss | Painful lymphadenopathy | Hepatosplenomegaly | Arthritis | Lab Findings | ||
| Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome | ||||||||||
| Lymphoma | + | – | – | + | + | – | + | – | Increase ESR, increased LDH | Night sweats, constant fatigue |
| Brucellosis | + | + | – | + | + | + | + | + | Relative lymphocytosis | Night sweats, often with characteristic smell, likened to wet hay |
| Typhoid fever | + | + | – | + | – | – | + | + | Decreased hemoglobin | Incremental increase in temperature initially and than sustained fever as high as 40°C (104°F) |
| Malaria | + | – | + | + | – | – | + | + | Microcytosis,
elevated LDH |
"Tertian" fever: paroxysms occur every second day |
| Tuberculosis | + | + | – | + | + | + | – | + | Mild normocytic anemia, hyponatremia, and | Night sweats, constant fatigue |
| Mumps | + | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | Relative lymphocytosis, serum amylaseelevated | Parotidswelling/tenderness |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | + | ESR and CRP elevated, positive rheumatoid factor | Morning stiffness |
| SLE | – | + | – | + | + | – | – | + | ESR and CRP elevated, positive ANA | Fatigue |
| HIV | – | – | – | + | + | + | – | + | Leukopenia | Constant fatigue |
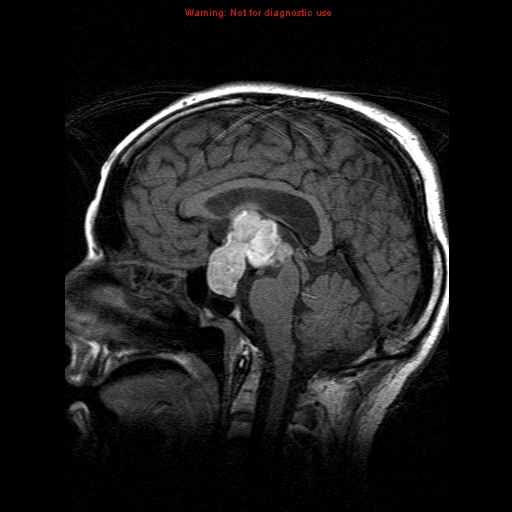
CNS lymphoma must be differentiated from other causes of seizures, headache, and fever in immunocompromised patients such as disseminated tuberculosis and disseminated aspergillosis.
| Disease | Differentiating signs and symptoms | Differentiating tests |
|---|---|---|
| CNS lymphoma |
|
|
| Disseminated tuberculosis |
|
|
| Aspergillosis |
|
|
| Cryptococcosis |
|
|
| Chagas disease |
|
|
| CMV infection |
|
|
| HSV infection |
|
|
| Varicella Zoster infection |
|
|
| Brain abscess |
|
|
| Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
|

Classification
Syncope is classified into three components:
| Classification of Syncope | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Pathophysiology | Treatment | Additional information |
| syncope | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| cardiac | neurogenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D01 | D02 | D03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E01 | E02 | E03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| F01 | F02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| disease | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Syncope is classified into three types.
| Syncope classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardia | |||
Syncope
Syncope is classified to three types:
Syncope is classified into three types:
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sahar Memar Montazerin, M.D.[2]
| Syncope | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C01 | C03 | C02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D01' D01 | D02' D02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E01 | E02 | E03 | E04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| F01 | F02 | F03 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Syncope classifications:
- Orthostatic:
- Cardiac
- Neurolgoic
| Syncope ddx | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical manifestations | ||||