Estrogen-related receptor alpha
| Estrogen-related receptor alpha | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1lo1. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | ESRRA ; ERR1; ERRa; ERRalpha; ESRL1; NR3B1 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 20941 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
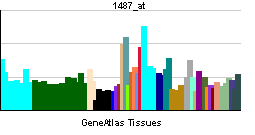 | |||||||||||||
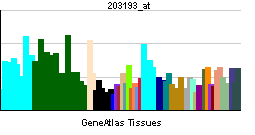 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERR-alpha), also known as NR3B1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group B, member 1), is a nuclear receptor which is encoded by the gene ESRRA (EStrogen Related Receptor Alpha).[1]
The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear receptor that is closely related to the estrogen receptor. This protein acts as a site-specific transcription regulator and has been also shown to interact with estrogen and the transcription factor TFIIB by direct protein-protein contact. The binding and regulatory activities of this protein have been demonstrated in the regulation of a variety of genes including lactoferrin, osteopontin, medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase (MCAD) and thyroid hormone receptor genes. A processed pseudogene of ESRRA is located on chromosome 13q12.1.[1]
See also
References
Further reading
- Giguère V, Yang N, Segui P, Evans RM (1988). "Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors". Nature. 331 (6151): 91–4. doi:10.1038/331091a0. PMID 3267207.
- Wiley SR, Kraus RJ, Zuo F; et al. (1993). "SV40 early-to-late switch involves titration of cellular transcriptional repressors". Genes Dev. 7 (11): 2206–19. PMID 8224847.
- Yang N, Shigeta H, Shi H, Teng CT (1996). "Estrogen-related receptor, hERR1, modulates estrogen receptor-mediated response of human lactoferrin gene promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (10): 5795–804. PMID 8621448.
- Johnston SD, Liu X, Zuo F; et al. (1997). "Estrogen-related receptor alpha 1 functionally binds as a monomer to extended half-site sequences including ones contained within estrogen-response elements". Mol. Endocrinol. 11 (3): 342–52. PMID 9058380.
- Sladek R, Bader JA, Giguère V (1997). "The orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor alpha is a transcriptional regulator of the human medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (9): 5400–9. PMID 9271417.
- Shi H, Shigeta H, Yang N; et al. (1997). "Human estrogen receptor-like 1 (ESRL1) gene: genomic organization, chromosomal localization, and promoter characterization". Genomics. 44 (1): 52–60. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4850. PMID 9286700.
- Sladek R, Beatty B, Squire J; et al. (1998). "Chromosomal mapping of the human and murine orphan receptors ERRalpha (ESRRA) and ERRbeta (ESRRB) and identification of a novel human ERRalpha-related pseudogene". Genomics. 45 (2): 320–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4939. PMID 9344655.
- Vanacker JM, Bonnelye E, Delmarre C, Laudet V (1998). "Activation of the thyroid hormone receptor alpha gene promoter by the orphan nuclear receptor ERR alpha". Oncogene. 17 (19): 2429–35. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202167. PMID 9824153.
- Zhang Z, Teng CT (2001). "Estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha1 compete for binding and coactivator". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 172 (1–2): 223–33. PMID 11165056.
- Eiler S, Gangloff M, Duclaud S; et al. (2001). "Overexpression, purification, and crystal structure of native ER alpha LBD". Protein Expr. Purif. 22 (2): 165–73. doi:10.1006/prep.2001.1409. PMID 11437591.
- Zhou D, Chen S (2001). "PNRC2 is a 16 kDa coactivator that interacts with nuclear receptors through an SH3-binding motif". Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (19): 3939–48. PMID 11574675.
- Tchernev VT, Mansfield TA, Giot L; et al. (2002). "The Chediak-Higashi protein interacts with SNARE complex and signal transduction proteins". Mol. Med. 8 (1): 56–64. PMID 11984006.
- Kraus RJ, Ariazi EA, Farrell ML, Mertz JE (2002). "Estrogen-related receptor alpha 1 actively antagonizes estrogen receptor-regulated transcription in MCF-7 mammary cells". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (27): 24826–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202952200. PMID 11986328.
- Ichida M, Nemoto S, Finkel T (2003). "Identification of a specific molecular repressor of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma Coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1alpha)". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (52): 50991–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210262200. PMID 12397057.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Schreiber SN, Knutti D, Brogli K; et al. (2003). "The transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 regulates the expression and activity of the orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha)". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (11): 9013–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212923200. PMID 12522104.
- Igarashi M, Kawaguchi Y, Hirai K, Mizuno F (2003). "Physical interaction of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen leader protein (EBNA-LP) with human oestrogen-related receptor 1 (hERR1): hERR1 interacts with a conserved domain of EBNA-LP that is critical for EBV-induced B-cell immortalization". J. Gen. Virol. 84 (Pt 2): 319–27. PMID 12560563.
- Sengupta K, Banerjee S, Saxena N, Banerjee SK (2003). "Estradiol-induced vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression in breast tumor cells is biphasic and regulated by estrogen receptor-alpha dependent pathway". Int. J. Oncol. 22 (3): 609–14. PMID 12579315.
- Sumi D, Ignarro LJ (2004). "Estrogen-related receptor alpha 1 up-regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (24): 14451–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.2235590100. PMID 14610283.
- Laganière J, Tremblay GB, Dufour CR; et al. (2004). "A polymorphic autoregulatory hormone response element in the human estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) promoter dictates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha control of ERRalpha expression". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 18504–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313543200. PMID 14978033.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |