IKZF1
| IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (Ikaros) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | IKZF1 ; IK1; Hs.54452; IKAROS; LYF1; PRO0758; ZNFN1A1; hIk-1 | ||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 55948 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
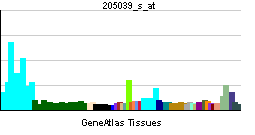 | |||||||||||
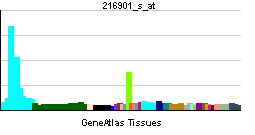 | |||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (Ikaros), also known as IKZF1, is a human gene.[1]
References
Further reading
- Tonnelle C, Calmels B, Maroc C; et al. (2003). "Ikaros gene expression and leukemia". Leuk. Lymphoma. 43 (1): 29–35. PMID 11908734.
- Westman BJ, Mackay JP, Gell D (2002). "Ikaros: a key regulator of haematopoiesis". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34 (10): 1304–7. PMID 12127581.
- Georgopoulos K, Moore DD, Derfler B (1992). "Ikaros, an early lymphoid-specific transcription factor and a putative mediator for T cell commitment". Science. 258 (5083): 808–12. PMID 1439790.
- Hahm K, Ernst P, Lo K; et al. (1994). "The lymphoid transcription factor LyF-1 is encoded by specific, alternatively spliced mRNAs derived from the Ikaros gene". Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 (11): 7111–23. PMID 7935426.
- Molnár A, Wu P, Largespada DA; et al. (1996). "The Ikaros gene encodes a family of lymphocyte-restricted zinc finger DNA binding proteins, highly conserved in human and mouse". J. Immunol. 156 (2): 585–92. PMID 8543809.
- Nietfeld W, Meyerhans A (1996). "Cloning and sequencing of hIk-1, a cDNA encoding a human homologue of mouse Ikaros/LyF-1". Immunol. Lett. 49 (1–2): 139–41. PMID 8964602.
- Morgan B, Sun L, Avitahl N; et al. (1997). "Aiolos, a lymphoid restricted transcription factor that interacts with Ikaros to regulate lymphocyte differentiation". EMBO J. 16 (8): 2004–13. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.8.2004. PMID 9155026.
- Kelley CM, Ikeda T, Koipally J; et al. (1998). "Helios, a novel dimerization partner of Ikaros expressed in the earliest hematopoietic progenitors". Curr. Biol. 8 (9): 508–15. PMID 9560339.
- Sun L, Heerema N, Crotty L; et al. (1999). "Expression of dominant-negative and mutant isoforms of the antileukemic transcription factor Ikaros in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (2): 680–5. PMID 9892693.
- Kim J, Sif S, Jones B; et al. (1999). "Ikaros DNA-binding proteins direct formation of chromatin remodeling complexes in lymphocytes". Immunity. 10 (3): 345–55. PMID 10204490.
- Honma Y, Kiyosawa H, Mori T; et al. (1999). "Eos: a novel member of the Ikaros gene family expressed predominantly in the developing nervous system". FEBS Lett. 447 (1): 76–80. PMID 10218586.
- Koipally J, Renold A, Kim J, Georgopoulos K (1999). "Repression by Ikaros and Aiolos is mediated through histone deacetylase complexes". EMBO J. 18 (11): 3090–100. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.11.3090. PMID 10357820.
- Sun L, Goodman PA, Wood CM; et al. (2000). "Expression of aberrantly spliced oncogenic ikaros isoforms in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia". J. Clin. Oncol. 17 (12): 3753–66. PMID 10577847.
- Hosokawa Y, Maeda Y, Ichinohasama R; et al. (2000). "The Ikaros gene, a central regulator of lymphoid differentiation, fuses to the BCL6 gene as a result of t(3;7)(q27;p12) translocation in a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma". Blood. 95 (8): 2719–21. PMID 10753856.
- Koipally J, Georgopoulos K (2000). "Ikaros interactions with CtBP reveal a repression mechanism that is independent of histone deacetylase activity". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (26): 19594–602. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000254200. PMID 10766745.
- Perdomo J, Holmes M, Chong B, Crossley M (2001). "Eos and pegasus, two members of the Ikaros family of proteins with distinct DNA binding activities". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (49): 38347–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005457200. PMID 10978333.
- Payne KJ, Nicolas JH, Zhu JY; et al. (2001). "Cutting edge: predominant expression of a novel Ikaros isoform in normal human hemopoiesis". J. Immunol. 167 (4): 1867–70. PMID 11489963.
- Koipally J, Heller EJ, Seavitt JR, Georgopoulos K (2002). "Unconventional potentiation of gene expression by Ikaros". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (15): 13007–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111371200. PMID 11799125.
- Dorsam G, Goetzl EJ (2002). "Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) is a novel gene target of the hemolymphopoietic transcription factor Ikaros". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (16): 13488–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107922200. PMID 11812772.
External links
- IKZF1+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |