Diabetes mellitus type 1 pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 248: | Line 248: | ||
=== Environment === | === Environment === | ||
Environmental factors were found to influence [[type 1 | *Environmental factors were found to influence [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]] through various pathways. Some were found to confer protection against [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]], while others were associated with the progression and promotion of [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]], including:<ref>Volume 387, Issue 10035, 4–10 June 2016, Pages 2340–2348 | ||
Series | Series | ||
Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes | Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes | ||
| Line 259: | Line 259: | ||
!Protective factors | !Protective factors | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Prenatal triggers | |[[Obstetrics|Prenatal]] triggers | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Congenital rubella|Congenital rubell]]<nowiki/>[[Congenital rubella|a]] | * [[Congenital rubella|Congenital rubell]]<nowiki/>[[Congenital rubella|a]] | ||
* Maternal | * Maternal [[Enterovirus|Enteroviral]] [[infection]] | ||
* [[Caesarean section|Cesarean section]] | * [[Caesarean section|Cesarean section]] | ||
* Higher birth weight | * Higher [[birth weight]] | ||
* Older maternal age | * Older maternal age | ||
* Low maternal intake of vegetables | * Low maternal intake of vegetables | ||
| | | | ||
* Higher maternal [[vitamin D]] intake or concentrations in late pregnancy | * Higher maternal [[vitamin D]] intake or [[vitamin D]] concentrations in late [[pregnancy]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Postnatal triggers | |[[Postnatal]] triggers | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Enterovirus|Enteroviral infection]] | * [[Enterovirus|Enteroviral infection]] | ||
* Frequent respiratory or enteric infections | * Frequent respiratory or enteric infections | ||
* Abnormal microbiome | * Abnormal [[microbiome]] | ||
* Early exposure to cereals, root vegetables, eggs and cow's milk | * Early exposure to cereals, root vegetables, eggs and cow's milk | ||
* Infant weight gain | * Infant [[weight gain]] | ||
* Serious life events | * Serious life events | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 286: | Line 286: | ||
|Promoters of progression | |Promoters of progression | ||
| | | | ||
* Persistent or recurrent | * Persistent or recurrent [[Enterovirus|Enteroviral infections]] | ||
* Overweight or increased height velocity | * [[Overweight]] or increased height velocity | ||
* High glycemic load, [[fructose]] intake | * High glycemic load, [[fructose]] intake | ||
* Dietary [[nitrates]] or [[Nitrosamine|nitrosamines]] | * Dietary [[nitrates]] or [[Nitrosamine|nitrosamines]] | ||
* [[Puberty]] | * [[Puberty]] | ||
*[[Steroid]] treatment | * [[Steroid]] [[treatment]] | ||
* [[Insulin resistance]] | * [[Insulin resistance]] | ||
* Psychological stress | * [[Stress (medicine)|Psychological stress]] | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Immunological === | === Immunological === | ||
Several studies have found that abnormalities in the [[Humoral immunity|humoral]] and cellular arm of the immune system, were identified to be associated with [[ | *Several studies have found that abnormalities in the [[Humoral immunity|humoral]] and [[Cell-mediated immunity|cellular arm]] of the [[immune system]], were identified to be associated with [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]], these include:<ref name="pmid26271890">{{cite journal| author=Jaberi-Douraki M, Pietropaolo M, Khadra A| title=Continuum model of T-cell avidity: Understanding autoreactive and regulatory T-cell responses in type 1 diabetes. | journal=J Theor Biol | year= 2015 | volume= 383 | issue= | pages= 93-105 | pmid=26271890 | doi=10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.07.032 | pmc=4567915 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26271890 }}</ref><ref name="pmid24105410">{{cite journal| author=Rydén A, Ludvigsson J, Fredrikson M, Faresjö M| title=General immune dampening is associated with disturbed metabolism at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. | journal=Pediatr Res | year= 2014 | volume= 75 | issue= 1-1 | pages= 45-50 | pmid=24105410 | doi=10.1038/pr.2013.167 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24105410 }}</ref><ref>Type 1 Diabetes mellitus "Dennis Kasper, Anthony Fauci, Stephen Hauser, Dan Longo, J. Larry Jameson, Joseph Loscalzo"Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e Accessed on December 27th,2016</ref><ref name="PaschouPapadopoulou-Marketou20182">{{cite journal|last1=Paschou|first1=Stavroula A|last2=Papadopoulou-Marketou|first2=Nektaria|last3=Chrousos|first3=George P|last4=Kanaka-Gantenbein|first4=Christina|title=On type 1 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis|journal=Endocrine Connections|volume=7|issue=1|year=2018|pages=R38–R46|issn=2049-3614|doi=10.1530/EC-17-0347}}</ref><ref name="pmid9568688">{{cite journal| author=Ellis TM, Schatz DA, Ottendorfer EW, Lan MS, Wasserfall C, Salisbury PJ | display-authors=etal| title=The relationship between humoral and cellular immunity to IA-2 in IDDM. | journal=Diabetes | year= 1998 | volume= 47 | issue= 4 | pages= 566-9 | pmid=9568688 | doi=10.2337/diabetes.47.4.566 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9568688 }}</ref> | ||
* Islet cell autoantibodies | ** [[Islets of Langerhans|Islet cell]] [[Autoantibody|autoantibodies]] | ||
* Activated [[lymphocytes]] in the islets, peripancreatic lymph nodes, and systemic circulation | ** Activated [[lymphocytes]] in the [[Islets of Langerhans|islets]], peripancreatic [[lymph node|lymph nodes]], and systemic circulation | ||
* [[T lymphocytes]] that proliferate when stimulated with islet proteins | ** [[T lymphocytes]] that proliferate when stimulated with [[Islets of Langerhans|islet]] [[protein|proteins]] | ||
* Release of [[cytokines]] within the insulitis | ** Release of [[cytokines]] within the insulitis | ||
*An [[enzyme]] named [[Glutamate decarboxylase|glutamic acid decarboxylase]] (GAD65) found in [[Beta cell|β cells]] has similar [[amino acid sequence]] with the [[Coxsackie virus|Coxsackie]] B4 P2-C protein, which augments the response of humoral immunity. | ** An [[enzyme]] named [[Glutamate decarboxylase|glutamic acid decarboxylase]] ([[Glutamate decarboxylase|GAD65]]) found in [[Beta cell|β cells]] has similar [[amino acid sequence]] with the [[Coxsackie virus|Coxsackie]] B4 P2-C [[protein]], which augments the response of [[humoral immunity]]. | ||
*[[Autoantibody|Autoantibodies]] against IA-2 and zinc transporter (ZnT8) have been positive in 60% and 60-80% of type 1 | ** [[Autoantibody|Autoantibodies]] against IA-2 and [[zinc]] transporter (ZnT8) have been positive in 60% and 60-80% of [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]] at the time of [[Diagnosis|diagnose]], respectively. | ||
=== Associated conditions === | === Associated conditions === | ||
Conditions associated with type 1 | *Conditions associated with [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]] include:<ref name=":0" /><ref name="pmid22516771">{{cite journal| author=Witek PR, Witek J, Pańkowska E| title=[Type 1 diabetes-associated autoimmune diseases: screening, diagnostic principles and management]. | journal=Med Wieku Rozwoj | year= 2012 | volume= 16 | issue= 1 | pages= 23-34 | pmid=22516771 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22516771 }}</ref> | ||
* Autoimmune thyroid disease (ATD) | ** [[Autoimmunity|Autoimmune]] [[thyroid disease]] (ATD) | ||
* [[Celiac disease|Celiac disease (CD | ** [[Celiac disease|Celiac disease]] ([[Celiac disease|CD]]) | ||
* [[Gastritis|Autoimmune gastritis]] (AIG) | ** [[Gastritis|Autoimmune gastritis]] (AIG) | ||
* [[Pernicious anemia]] (PA) | ** [[Pernicious anemia]] ([[Pernicious anemia|PA]]) | ||
* [[Vitiligo]] | ** [[Vitiligo]] | ||
* [[Addison's disease]] | ** [[Addison's disease]] | ||
==Gross Pathology== | ==Gross Pathology== | ||
On gross pathology, [ | *On [[gross pathology]], [[pancreas]] may demonstrated the following changes:<ref name="pmid23890997">{{cite journal| author=Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS, Michels AW| title=Type 1 diabetes. | journal=Lancet | year= 2014 | volume= 383 | issue= 9911 | pages= 69-82 | pmid=23890997 | doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60591-7 | pmc=4380133 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23890997 }} </ref> | ||
** Decreased overall weight and size | |||
** Dorsal region [[atrophy]] | |||
** Possible [[Hypertrophy (medical)|hypertrophy]] (related to hydrophic changes) | |||
==Microscopic Pathology== | ==Microscopic Pathology== | ||
On microscopic histopathological analysis, [ | *On microscopic [[Histopathology|histopathological]] [[analysis]], the following changes can be detected in [[Islets of Langerhans|Islet cell]]:<ref name="pmid23890997">{{cite journal| author=Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS, Michels AW| title=Type 1 diabetes. | journal=Lancet | year= 2014 | volume= 383 | issue= 9911 | pages= 69-82 | pmid=23890997 | doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60591-7 | pmc=4380133 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23890997 }} </ref> | ||
** Insulitis | |||
** [[Beta cell]] loss due to [[necrosis]] or [[apoptosis]] | |||
** [[Major histocompatibility complex]] class one hyperexpression | |||
** Reduction in [[insulin]] in remnant [[Beta cell|beta cells]] | |||
** [[Interferon type I|Interferon alpha]] [[Gene expression|expression]] in [[Beta cell|beta cells]] | |||
** [[CD3 (immunology)|CD3]]-positive cells in [[Islets of Langerhans|Islet cell]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 26 August 2020
|
Diabetes mellitus type 1 Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Diabetes mellitus type 1 from other Diseases |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management |
|
Case Studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Priyamvada Singh, M.B.B.S. [2]; Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [3]Vishal Devarkonda, M.B.B.S[4]
Overview
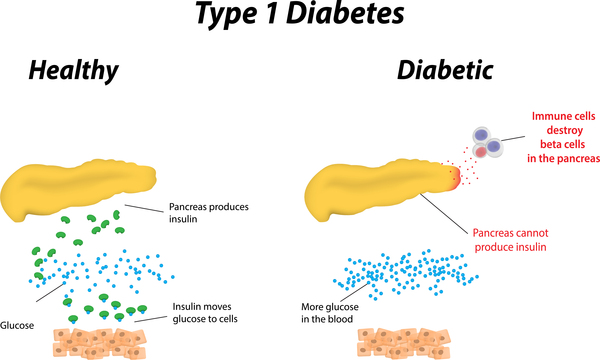
Type 1 diabetes is a disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels. Type 1 DM is the result of interactions of genetic, environmental, and immunologic factors that ultimately lead to the destruction of the pancreatic beta cells and insulin deficiency.
Pathophysiology
- Type 1 diabetes is a disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels.
- In this form of diabetes, specialized cells in the pancreas called beta cells stop producing insulin. Insulin controls how much glucose (a type of sugar) is passed from the blood into cells for conversion to energy. Lack of insulin results in the inability to use glucose for energy or to control the amount of sugar in the blood.
Pathogenesis
- Type 1 DM is the result of interactions of genetic, environmental, and immunologic factors that ultimately lead to the destruction of the pancreatic beta cells and insulin deficiency.
- Concordance of type 1 DM in identical twins ranges between 40 and 60%, indicating the presence of additional modifying factors.
Genetics
- Genes associated with Diabetes mellitus include the following: [1][2][3][4][5][6]
- Currently, 58 genomic regions are known to be associated with Type 1 DM.
- Major susceptibility gene for type 1 diabetes is located on HLA region of chromosome 6. It accounts for 40-50% of the genetic risk for type 1 diabetes. This region encodes for class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules play an important role in presenting antigen to T helper cell and initiating immune response.
- Other major susceptibility genes which were associated with Type 1 DM include polymorphisms in the promoter region of the insulin gene, the CTLA-4 gene, interleukin 2 receptor, Insulin-VNTR, AIRE, FoxP3, STAT3, HIP14 and PTPN22 etc.[7][8]
- Presence of certain genes confer protection against the development of the disease. Haplotype DQA1*0102, DQB1*0602 is extremely rare in individuals with type 1 DM (<1%) and appears to provide protection from type 1 diabetes.
| Genes important to type 1 diabetes pathogenesis | Region | Odds ratio | Gene funtion |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTPN22 | 1p13.2 | 1·89 | Regulation of innate immune response, T cell activation, and natural killer cell proliferation |
| IL10 | 1q32.1 | 0·86 | Cytokines and inflammatory response |
| AFF3 | 2q11.2 | 1·11 | Regulation of transcription |
| IFIH1 | 2q24.2 | 0·85
0·85 0·59 |
Innate immune system NF-κB activation |
| STAT4 | 2q32.3 | 1·10§ | Cytokine-mediated signalling pathway |
| CTLA4 | 2q33.2 | 0·82
0·84 |
T cell activation |
| CCR5 | 3p21.31 | 0·85 | Th1 cell development and chemokine-mediated signalling pathway |
| IL21, IL2 | 4q27 | 1·13
1·12 1·14 1·15 |
Cytokines and inflammatory response and Th1 cell or Th2 cell differentiation |
| IL7R | 5p13.2 | 1·11 | T cell-mediated cytotoxicity, immunoglobulin production, and antigen binding |
| BACH2 | 6q15 | 1·10
0·88 1·20 |
transcription |
| TNFAIP3 | 6q23.3 | 1·12 | Inflammatory response |
| TAGAP | 6q25.3 | 0·92 | Signal transduction |
| IKZF1 | 7p12.2 | 0·89 | Immune-cell regulation |
| GLIS3 | 9p24.2 | 1·12
1·12 0·90 |
Regulation of transcription |
| IL2RA | 10p15.1 | 1·20
0·73 0·52 0·62 0·82 |
Alternative mRNA splicing Th1 or Th2 cell differentiation |
| PRKCQ | 10p15.1 | 0·69 | Apoptotic process, inflammatory response, innate immune response, and T cell-receptor signalling pathway |
| NRP1 | 10p11.22 | 1·11 | Signal transduction |
| INS | 11p15.5 | 0·42
0·63 0·63 |
Insulin signalling pathway |
| BAD | 11q13.1 | 0·92 | Apoptosis |
| CD69 | 12p13.31 | 0·87
1·10 |
Signal transduction |
| ITGB7 | 12q13.13 | 1·19 | Response to virus and regulation of immune response |
| ERBB3 | 12q13.2 | 1·25 | Regulation of transcription, innate immune response, and lipid metabolism |
| CYP27B1 | 12q14.1 | 0·82 | Metabolism of lipids, lipoproteins, steroid hormones, and vitamin D |
| SH2B3 | 12q24.12 | 1·24
0·76 0·76 |
Signal transduction |
| GPR183 | 13q32.3 | 1·12 | Humoral immune response |
| DLK1 | 14q32.2 | 0·88
0·90 |
Regulation of gene expression |
| RASGRP1 | 15q14 | 0·85
1·15 |
Inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus and cytokine production |
| CTSH | 15q25.1 | 0·81
0·78 0·90 |
Immune response-regulating signalling pathway T cell-mediated cytotoxicity adaptive immune response |
| CLEC16A | 16p13.13 | 0·83
0·82 1·14 |
Unknown |
| IL27 | 16p11.2 | 1·19
0·90 1·24 |
Inflammatory response and regulation of defence response to virus |
| ORMDL3 | 17q12 | 0·90 | Protein binding |
| PTPN2 | 18p11.21 | 1·20 | Cytokine signalling and B cell and T cell differentiation |
| CD226 | 18q22.2 | 1·13 | Immunoregulation and adaptive immune system |
| TYK2 | 19p13.2 | 0·82
0·87 0·67 |
Cytokine-mediated signalling pathway, intracellular signal transduction, and type I interferon signalling pathway |
| FUT2 | 19q13.33 | 0·87
0·75 0·87 |
Metabolic pathways |
| UBASH3A | 21q22.3 | 1·16 | Regulation of cytokine production
Regulation of T cell receptor signalling pathway |
| C1QTNF6 | 22q12.3 | 1·11 | B cell receptor signalling pathway, chemokine signalling pathway, and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity |
Environment
- Environmental factors were found to influence Diabetes mellitus type 1 through various pathways. Some were found to confer protection against Diabetes mellitus type 1, while others were associated with the progression and promotion of Diabetes mellitus type 1, including:[9][10]
| Triggers | Protective factors | |
|---|---|---|
| Prenatal triggers |
|
|
| Postnatal triggers |
|
|
| Promoters of progression |
|
Immunological
- Several studies have found that abnormalities in the humoral and cellular arm of the immune system, were identified to be associated with Diabetes mellitus type 1, these include:[11][12][13][14][15]
- Islet cell autoantibodies
- Activated lymphocytes in the islets, peripancreatic lymph nodes, and systemic circulation
- T lymphocytes that proliferate when stimulated with islet proteins
- Release of cytokines within the insulitis
- An enzyme named glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) found in β cells has similar amino acid sequence with the Coxsackie B4 P2-C protein, which augments the response of humoral immunity.
- Autoantibodies against IA-2 and zinc transporter (ZnT8) have been positive in 60% and 60-80% of Diabetes mellitus type 1 at the time of diagnose, respectively.
Associated conditions
- Conditions associated with Diabetes mellitus type 1 include:[6][16]
Gross Pathology
- On gross pathology, pancreas may demonstrated the following changes:[17]
- Decreased overall weight and size
- Dorsal region atrophy
- Possible hypertrophy (related to hydrophic changes)
Microscopic Pathology
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, the following changes can be detected in Islet cell:[17]
- Insulitis
- Beta cell loss due to necrosis or apoptosis
- Major histocompatibility complex class one hyperexpression
- Reduction in insulin in remnant beta cells
- Interferon alpha expression in beta cells
- CD3-positive cells in Islet cell
References
- ↑ Pociot F, Lernmark Å (2016). "Genetic risk factors for type 1 diabetes". Lancet. 387 (10035): 2331–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30582-7. PMID 27302272.
- ↑ Safari-Alighiarloo N, Taghizadeh M, Tabatabaei SM, Shahsavari S, Namaki S, Khodakarim S; et al. (2016). "Identification of new key genes for type 1 diabetes through construction and analysis of protein-protein interaction networks based on blood and pancreatic islet transcriptomes". J Diabetes. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12483. PMID 27625010.
- ↑ Brorsson CA, Pociot F, Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Shared genetic basis for type 1 diabetes, islet autoantibodies, and autoantibodies associated with other immune-mediated diseases in families with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015; 38 (suppl 3): S8–13.
- ↑ Ahlqvist E, van Zuydam NR, Groop LC, McCarthy MI. The genetics of diabetic complications. Nat Rev Nephrol 2015; 11: 277–87.
- ↑ Parkes M, Cortes A, van Heel DA, Brown MA. Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat Rev Genet 2013; 14: 661–73.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Type 1 Diabetes mellitus "Dennis Kasper, Anthony Fauci, Stephen Hauser, Dan Longo, J. Larry Jameson, Joseph Loscalzo"Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e Accessed on December 27th,2016
- ↑ Paschou, Stavroula A; Papadopoulou-Marketou, Nektaria; Chrousos, George P; Kanaka-Gantenbein, Christina (2018). "On type 1 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis". Endocrine Connections. 7 (1): R38–R46. doi:10.1530/EC-17-0347. ISSN 2049-3614.
- ↑ Tuomi, T. (2005). "Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: What Do They Have in Common?". Diabetes. 54 (Supplement 2): S40–S45. doi:10.2337/diabetes.54.suppl_2.S40. ISSN 0012-1797.
- ↑ Volume 387, Issue 10035, 4–10 June 2016, Pages 2340–2348 Series Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes Prof Marian Rewers, MDa, Prof Johnny Ludvigsson, MD
- ↑ Butalia S, Kaplan GG, Khokhar B, Rabi DM (2016). "Environmental Risk Factors and Type 1 Diabetes: Past, Present, and Future". Can J Diabetes. 40 (6): 586–593. doi:10.1016/j.jcjd.2016.05.002. PMID 27545597.
- ↑ Jaberi-Douraki M, Pietropaolo M, Khadra A (2015). "Continuum model of T-cell avidity: Understanding autoreactive and regulatory T-cell responses in type 1 diabetes". J Theor Biol. 383: 93–105. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.07.032. PMC 4567915. PMID 26271890.
- ↑ Rydén A, Ludvigsson J, Fredrikson M, Faresjö M (2014). "General immune dampening is associated with disturbed metabolism at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes". Pediatr Res. 75 (1–1): 45–50. doi:10.1038/pr.2013.167. PMID 24105410.
- ↑ Type 1 Diabetes mellitus "Dennis Kasper, Anthony Fauci, Stephen Hauser, Dan Longo, J. Larry Jameson, Joseph Loscalzo"Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e Accessed on December 27th,2016
- ↑ Paschou, Stavroula A; Papadopoulou-Marketou, Nektaria; Chrousos, George P; Kanaka-Gantenbein, Christina (2018). "On type 1 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis". Endocrine Connections. 7 (1): R38–R46. doi:10.1530/EC-17-0347. ISSN 2049-3614.
- ↑ Ellis TM, Schatz DA, Ottendorfer EW, Lan MS, Wasserfall C, Salisbury PJ; et al. (1998). "The relationship between humoral and cellular immunity to IA-2 in IDDM". Diabetes. 47 (4): 566–9. doi:10.2337/diabetes.47.4.566. PMID 9568688.
- ↑ Witek PR, Witek J, Pańkowska E (2012). "[Type 1 diabetes-associated autoimmune diseases: screening, diagnostic principles and management]". Med Wieku Rozwoj. 16 (1): 23–34. PMID 22516771.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS, Michels AW (2014). "Type 1 diabetes". Lancet. 383 (9911): 69–82. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60591-7. PMC 4380133. PMID 23890997.
Template:WH Template:WS Template:WH Template:WS