Simvastatin adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sheng Shi, M.D. [2]
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the pre-marketing controlled clinical studies and their open extensions (2,423 patients with median duration of follow-up of approximately 18 months), 1.4% of patients were discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions that led to treatment discontinuation were: gastrointestinal disorders (0.5%), myalgia (0.1%), and [arthralgia ]](0.1%). The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) in simvastatin controlled clinical trials were: upper respiratory infections (9.0%), headache (7.4%), abdominal pain (7.3%), constipation (6.6%), and nausea (5.4%).
In 4S involving 4,444 (age range 35-71 years, 19% women, 100% Caucasians) treated with 20-40 mg/day of ZOCOR (n=2,221) or placebo (n=2,223) over a median of 5.4 years, adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients and at a rate greater than placebo are shown in Table 2.
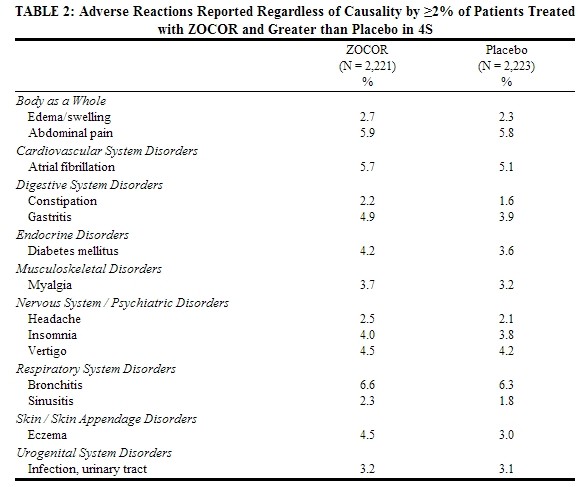 |
Heart Protection Study
In the Heart Protection Study (HPS), involving 20,536 patients (age range 40-80 years, 25% women, 97% Caucasians, 3% other races) treated with ZOCOR 40 mg/day (n=10,269) or placebo (n=10,267) over a mean of 5 years, only serious adverse reactions and discontinuations due to any adverse reactions were recorded. Discontinuation rates due to adverse reactions were 4.8% in patients treated with ZOCOR compared with 5.1% in patients treated with placebo. The incidence of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis was <0.1% in patients treated with ZOCOR.
Other Clinical Studies
In a clinical trial in which 12,064 patients with a history of myocardial infarction were treated with ZOCOR (mean follow-up 6.7 years), the incidence of myopathy (defined as unexplained muscle weakness or pain with a serum creatine kinase [CK] >10 times upper limit of normal [ULN]) in patients on 80 mg/day was approximately 0.9% compared with 0.02% for patients on 20 mg/day. The incidence of rhabdomyolysis (defined as myopathy with a CK >40 times ULN) in patients on 80 mg/day was approximately 0.4% compared with 0% for patients on 20 mg/day. The incidence of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, was highest during the first year and then notably decreased during the subsequent years of treatment. In this trial, patients were carefully monitored and some interacting medicinal products were excluded.
Other adverse reactions reported in clinical trials were: diarrhea, rash, dyspepsia, flatulence, and asthenia.
Laboratory Tests
Marked persistent increases of hepatic transaminases have been noted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Elevated alkaline phosphatase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase have also been reported. About 5% of patients had elevations of CK levels of 3 or more times the normal value on one or more occasions. This was attributable to the noncardiac fraction of CK. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1).]
Adolescent Patients (ages 10-17 years)
In a 48-week, controlled study in adolescent boys and girls who were at least 1 year post-menarche, 10-17 years of age (43.4% female, 97.7% Caucasians, 1.7% Hispanics, 0.6% Multiracial) with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (n=175), treated with placebo or ZOCOR (10-40 mg daily), the most common adverse reactions observed in both groups were upper respiratory infection, headache, abdominal pain, and nausea [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Post-Marketing Experience
Because the below reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of simvastatin: pruritus, alopecia, a variety of skin changes (e.g., nodules, discoloration, dryness of skin/mucous membranes, changes to hair/nails), dizziness, muscle cramps, myalgia, pancreatitis, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, vomiting, anemia, erectile dysfunction, interstitial lung disease, rhabdomyolysis, hepatitis/jaundice, fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure, and depression.
There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy associated with statin use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
An apparent hypersensitivity syndrome has been reported rarely which has included some of the following features: anaphylaxis, angioedema, lupus erythematous-like syndrome, polymyalgia rheumatica, dermatomyositis, vasculitis, purpura, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, positive ANA, ESR increase, eosinophilia, arthritis, arthralgia, urticaria, asthenia, photosensitivity, fever, chills, flushing, malaise, dyspnea, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
There have been rare postmarketing reports of cognitive impairment (e.g., memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion) associated with statin use. These cognitive issues have been reported for all statins. The reports are generally nonserious, and reversible upon statin discontinuation, with variable times to symptom onset (1 day to years) and symptom resolution (median of 3 weeks).[1]
References
- ↑ "ZOCOR (SIMVASTATIN) TABLET, FILM COATED [MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP.]". Retrieved 18 February 2014.