Adrenal atrophy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy overview|Overview]]== | |||
== | ==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
== | ==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy classification|Classification]]== | ||
==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | |||
==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy causes|Causes]]== | |||
==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy differential diagnosis|Differentiating Adiposogenital dystrophy from other Diseases]]== | |||
== | ==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ||
==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | |||
==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy screening|Screening]]== | |||
== | ==[[Adiposogenital dystrophy natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ||
==Diagnosis== | |||
[[Adiposogenital dystrophy history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy head x ray|Head X Ray]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy CT|CT]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy MRI|MRI]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy vision_test|Vision Test]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
[[ | ==Treatment== | ||
[[Adiposogenital dystrophy medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Adiposogenital dystrophy future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | |||
== | ==Case Studies== | ||
[[Adiposogenital dystrophy case study one|Case #1]] | |||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
{{Endocrine pathology}} | |||
[[Category:Growth disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Endocrinology]] | |||
==Pathological Findings== | ==Pathological Findings== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 15:57, 20 September 2012
For patient information, click here
|
Adrenal atrophy Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Adrenal atrophy On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Adrenal atrophy |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Adiposogenital dystrophy from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Electrocardiogram | Head X Ray | CT | MRI | Vision Test | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies
Case Studies
Pathological Findings
-
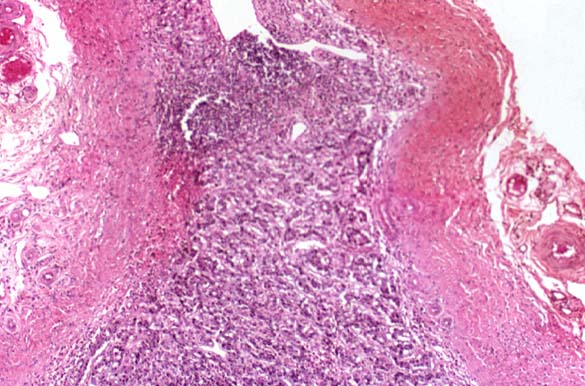
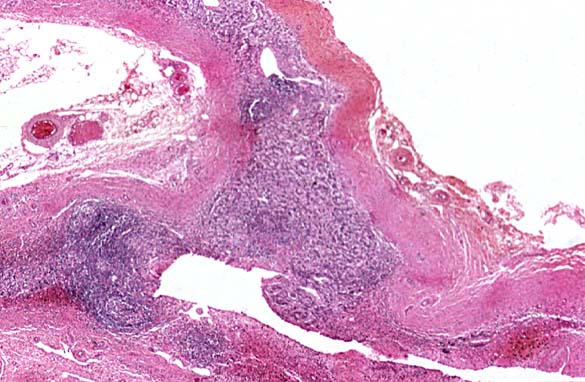
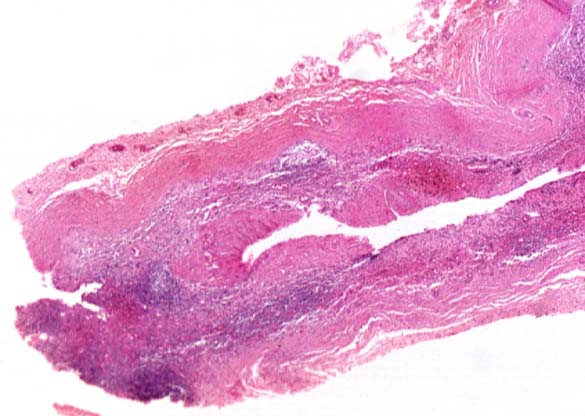
SCHILDER'S DISEASE, ADRENAL ATROPHY Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD © PEIR University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
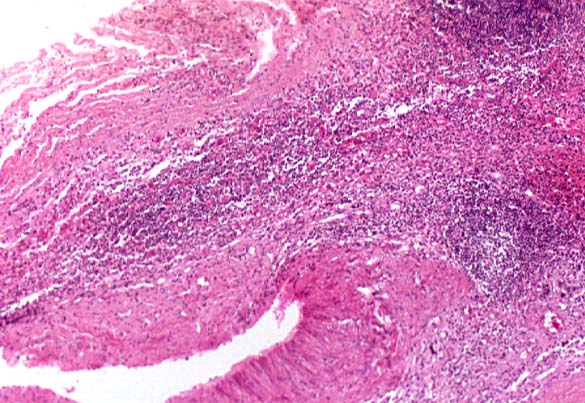
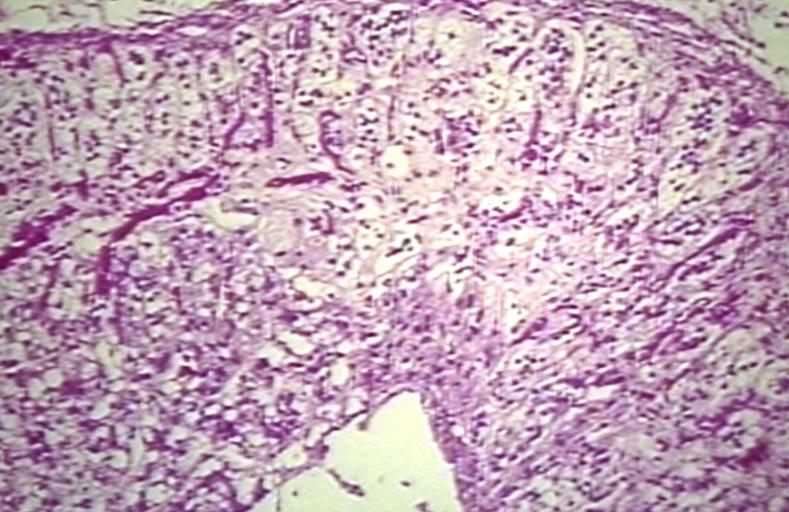
SCHILDER'S DISEASE, ADRENAL ATROPHY, KIDNEY AND AORTA Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
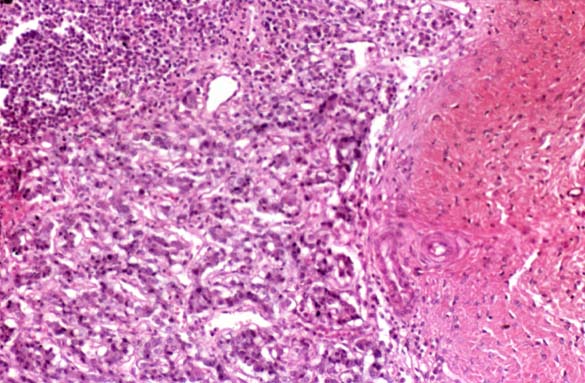
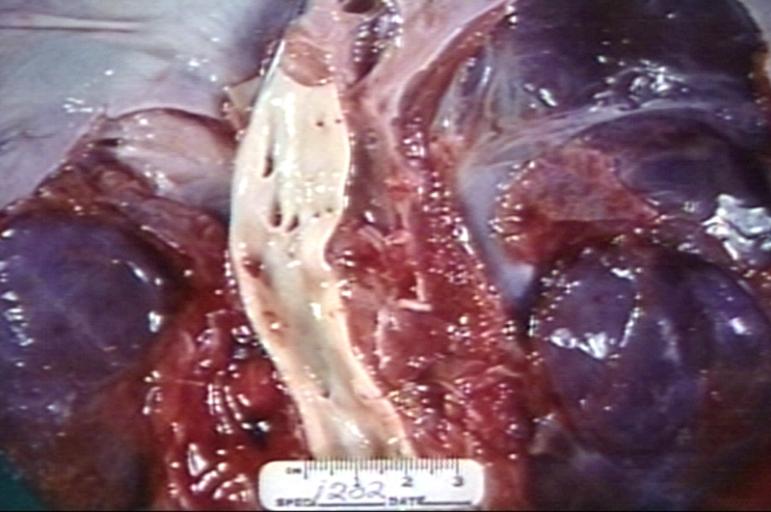
ADDISON'S DISEASE, ADRENAL ATROPHY Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology