Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==[[Squamous cell carcinoma physical examination|Physical Examination]]== | ==[[Squamous cell carcinoma physical examination|Physical Examination]]== | ||
===Esophagus=== | ===Esophagus=== | ||
Revision as of 20:04, 16 June 2012
For patient information click here
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Govindavarjhulla, M.B.B.S. [2], Raviteja Guddeti, M.B.B.S. [3]
Overview
Historical Aspects
Pathophysiology
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Causes of Squamous cell carcinoma
Differential Diagnosis
Natural History Complications and Prognosis
History & Symptoms
Physical Examination
Esophagus
Esophageal cancer may be due to either squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) or adenocarcinoma (EAC). SCCs tend to occur closer to the mouth, while adenocarcinomas occur closer to the stomach. Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing, solids worse than liquids) and odynophagia are common initial symptoms. If the disease is localized, esophagectomy may offer the possibility of a cure. If the disease has spread, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are commonly used.
Penis
When squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen's disease) is found on the penis, it is called erythroplasia of Queyrat[1]. This type of cancer respond very well to an experimental agent called Aldara.
Prostate
When associated with the prostate, squamous cell carcinoma is very aggressive in nature. It is difficult to detect as there is no increase in prostate specific antigen levels seen; meaning that the cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Lung
When associated with the lung, it often causes ectopic production of parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), resulting in hypercalcemia.
-
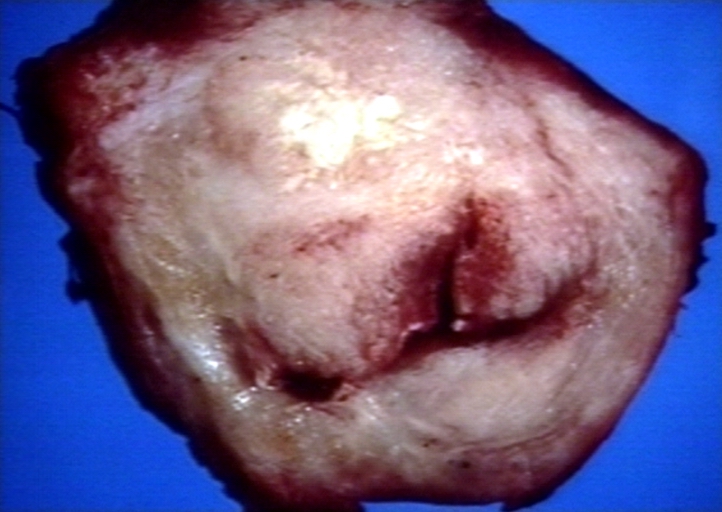
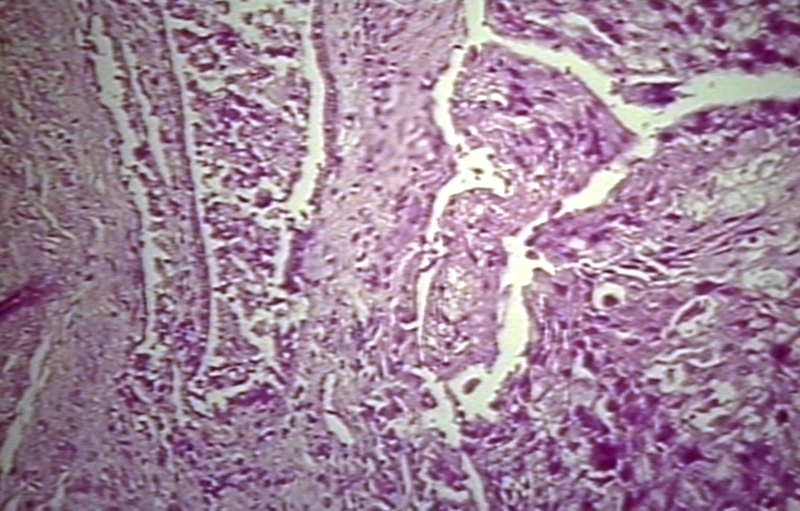
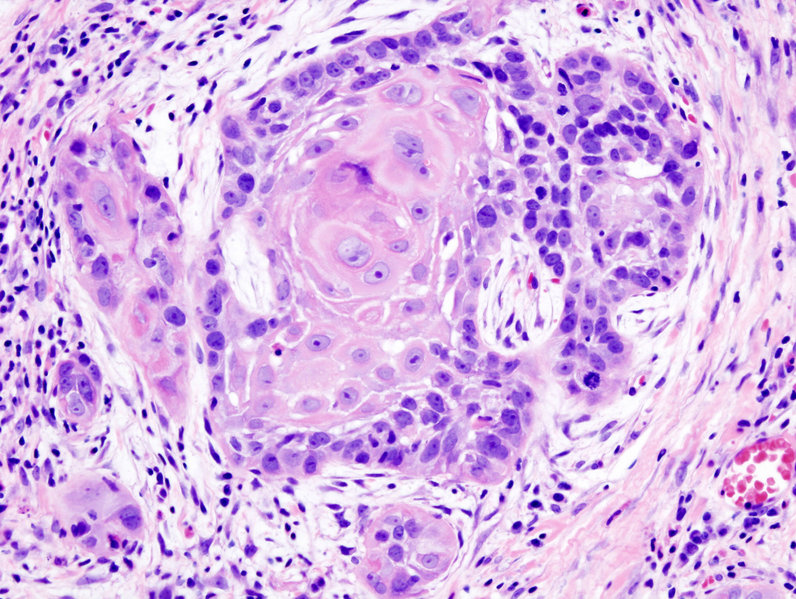
Biopsy of a highly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the mouth. Haematoxylin & eosin stain.
-
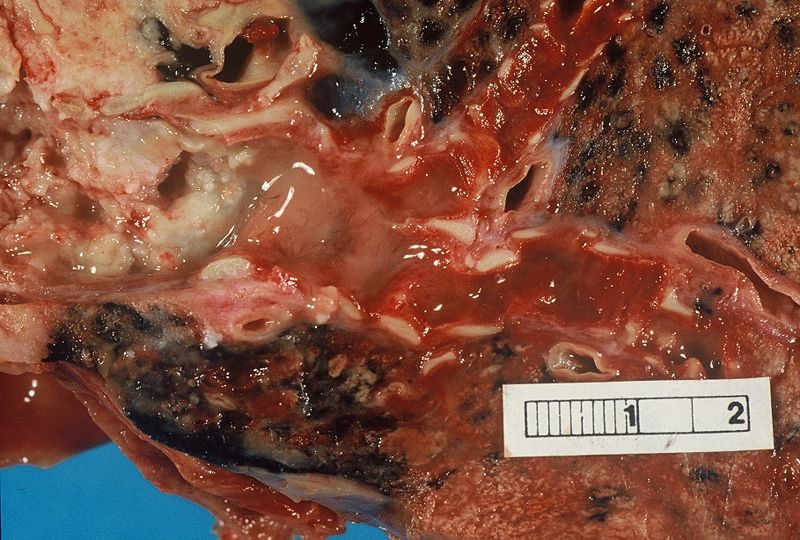
Photograph of a squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour is on the left, obstructing the bronchus (lung). Beyond the tumour the bronchus is inflammed and contains mucus
Vagina and cervix
Vaginal squamous cell carcinoma spreads slowly and usually stays near the vagina, but may spread to the lungs and liver. This is the most common type of vaginal cancer.
Cervix: Squamous cell carcinoma
<youtube v=zB47nE-i8dQ/>
<youtube v=J3kULzKGzws/>
Staging
Treatment
Future and Investigational treatment strategies
In 2007, Australian biopharmaceutical company Clinuvel Pharmaceuticals Limited began clinical trials with a melanocyte-stimulating hormone called melanotan (known by the International Nonproprietary Name afamelanotide, formerly CUV1647)[2] to provide photoprotection for organ transplant patients against squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and actinic keratosis.[3][4]
Cetuximab a monoclonal antibody that targets the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), has antitumor activity in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, as initially suggested by case reports.
References
External links
- Information on Squamous Cell Carcinoma from The Skin Cancer Foundation
- Article by Stephen D Hess, MD, PhD
- DermNet NZ: Squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma in transplant recipients
Template:Tumors of bone, cartilage, skin, connective, and soft tissue Template:Respiratory and intrathoracic neoplasia Template:Genital neoplasia Template:Epithelial neoplasms
de:Plattenepithelkarzinom he:קרצינומת תאי קשקש nl:Plaveiselcelcarcinoom