Ondansetron (oral)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Ondansetron (oral) is an antiemetic that is FDA approved for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, highly emetogenic chemotherapy; prophylaxis, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, moderately emetogenic chemotherapy; prophylaxis, postoperative nausea and vomiting; prophylaxis, radiation-induced nausea and vomiting; prophylaxis. Common adverse reactions include constipation, diarrhea, increased liver enzymes, headache, fatigue, malaise.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated With Highly Emetogenic Cancer Chemotherapy
- The recommended adult oral dosage of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets is 24 mg given as three 8-mg tablets administered 30 minutes before the start of single-day highly emetogenic chemotherapy, including cisplatin ≥50 mg/m2. Multiday, single-dose administration of a 24 mg dosage has not been studied.
Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Moderately Emetogenic Cancer Chemotherapy
- The recommended adult oral dosage is one 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet given twice a day. The first dose should be administered 30 minutes before the start of emetogenic chemotherapy, with a subsequent dose 8 hours after the first dose. One 8 mg ondansetron tablet should be administered twice a day (every 12 hours) for 1 to 2 days after completion of chemotherapy.
Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Radiotherapy, Either Total Body Irradiation, or Single High-Dose Fraction or Daily Fractions to the Abdomen
- The recommended oral dosage is one 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet given 3 times a day.
- For total body irradiation, one 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet should be administered 1 to 2 hours before each fraction of radiotherapy administered each day.
- For single high-dose fraction radiotherapy to the abdomen, one 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet should be administered 1 to 2 hours before radiotherapy, with subsequent doses every 8 hours after the first dose for 1 to 2 days after completion of radiotherapy.
- For daily fractionated radiotherapy to the abdomen, one 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet should be administered 1 to 2 hours before radiotherapy, with subsequent doses every 8 hours after the first dose for each day radiotherapy is given.
Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
- The recommended dosage is 16 mg given as two 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 1 hour before induction of anesthesia.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ondansetron in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ondansetron in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Moderately Emetogenic Cancer Chemotherapy
- For pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, the dosage is the same as for adults. For pediatric patients 4 through 11 years of age, the dosage is one 4 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet given three times a day. The first dose should be administered 30 minutes before the start of emetogenic chemotherapy, with subsequent doses 4 and 8 hours after the first dose. One 4 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet should be administered 3 times a day (every 8 hours) for 1 to 2 days after completion of chemotherapy.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ondansetron in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Gastroenteritis - Vomiting
- Dosing Information
- Ondansetron (2 milligrams (mg) for children weighing 8 to 15 kilograms (kg), 4 mg for children weighing greater than 15 kg up to 30 kg, and 8 mg for children weighing more than 30 kg).
Contraindications
- The concomitant use of apomorphine with ondansetron is contraindicated based on reports of profound hypotension and loss of consciousness when apomorphine was administered with ondansetron.
- Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets are contraindicated for patients known to have hypersensitivity to the drug.
Warnings
- Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients who have exhibited hypersensitivity to other selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonists.
Precautions
- Ondansetron is not a drug that stimulates gastric or intestinal peristalsis. It should not be used instead of nasogastric suction. The use of ondansetron in patients following abdominal surgery or in patients with chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting may mask a progressive ileus and/or gastric distension.
- Rarely and predominantly with intravenous ondansetron, transient ECG changes including QT interval prolongation have been reported.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following have been reported as adverse events in clinical trials of patients treated with ondansetron, the active ingredient of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets. A causal relationship to therapy with Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets has been unclear in many cases.
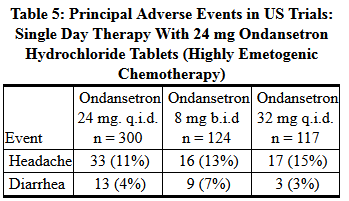
- The adverse events in Table 5 have been reported in ≥5% of adult patients receiving a single 24-mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet in 2 trials. These patients were receiving concurrent highly emetogenic cisplatin-based chemotherapy regimens (cisplatin dose ≥50 mg/m2).
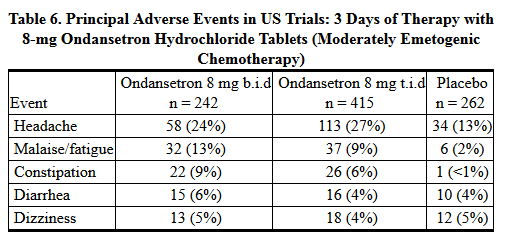
- The adverse events in Table 6 have been reported in ≥5% of adults receiving either 8 mg of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 2 or 3 times a day for 3 days or placebo in 4 trials. These patients were receiving concurrent moderately emetogenic chemotherapy, primarily cyclophosphamide-based regimens.
- Central Nervous System
- There have been rare reports consistent with, but not diagnostic of, extrapyramidal reactions in patients receiving ondansetron.
- Hepatic
- In 723 patients receiving cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy in US clinical trials, AST and/or ALT values have been reported to exceed twice the upper limit of normal in approximately 1% to 2% of patients receiving Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets. The increases were transient and did not appear to be related to dose or duration of therapy. On repeat exposure, similar transient elevations in transaminase values occurred in some courses, but symptomatic hepatic disease did not occur. The role of cancer chemotherapy in these biochemical changes cannot be clearly determined.
- There have been reports of liver failure and death in patients with cancer receiving concurrent medications including potentially hepatotoxic cytotoxic chemotherapy and antibiotics. The etiology of the liver failure is unclear.
- Integumentary
- Rash has occurred in approximately 1% of patients receiving ondansetron.
- Other
- Rare cases of anaphylaxis, bronchospasm, tachycardia, angina (chest pain), hypokalemia, electrocardiographic alterations, vascular occlusive events, and grand mal seizures have been reported. Except for bronchospasm and anaphylaxis, the relationship to Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets was unclear.
- The adverse events reported in patients receiving Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets and concurrent radiotherapy were similar to those reported in patients receiving Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets and concurrent chemotherapy. The most frequently reported adverse events were headache, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
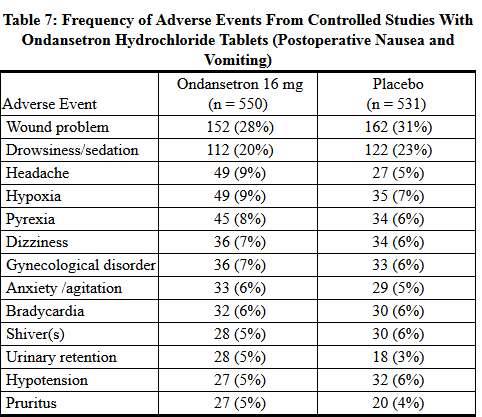
- The adverse events in Table 7 have been reported in ≥5% of patients receiving Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets at a dosage of 16 mg orally in clinical trials. With the exception of headache, rates of these events were not significantly different in the ondansetron and placebo groups. These patients were receiving multiple concomitant perioperative and postoperative medications.
Postmarketing Experience
- In addition to adverse events reported from clinical trials, the following events have been identified during post-approval use of oral formulations of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The events have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets.
Cardiovascular
Rarely and predominantly with intravenous ondansetron, transient ECG changes including QT interval prolongation have been reported.
General
Flushing. Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions, sometimes severe (e.g., anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reactions, angioedema, bronchospasm, shortness of breath, hypotension, laryngeal edema, stridor) have also been reported. Laryngospasm, shock, and cardiopulmonary arrest have occurred during allergic reactions in patients receiving injectable ondansetron.
Hepatobiliary
Liver enzyme abnormalities
Lower Respiratory
Neurology
Oculogyric crisis, appearing alone, as well as with other dystonic reactions
Skin
Special Senses
Eye Disorders: Cases of transient blindness, predominantly during intravenous administration, have been reported. These cases of transient blindness were reported to resolve within a few minutes up to 48 hours.
Drug Interactions
- Ondansetron does not itself appear to induce or inhibit the cytochrome P-450 drug-metabolizing enzyme system of the liver. Because ondansetron is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P-450 drug-metabolizing enzymes (CYP3A4, CYP2D6, CYP1A2), inducers or inhibitors of these enzymes may change the clearance and, hence, the half-life of ondansetron. On the basis of available data, no dosage adjustment is recommended for patients on these drugs.
- Based on reports of profound hypotension and loss of consciousness when apomorphine was administered with ondansetron, concomitant use of apomorphine with ondansetron is contraindicated.
- Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, and Rifampicin
- In patients treated with potent inducers of CYP3A4 (i.e., phenytoin, carbamazepine, and rifampicin), the clearance of ondansetron was significantly increased and ondansetron blood concentrations were decreased. However, on the basis of available data, no dosage adjustment for ondansetron is recommended for patients on these drugs.
- Tramadol
- Chemotherapy
- Tumor response to chemotherapy in the P-388 mouse leukemia model is not affected by ondansetron. In humans, carmustine, etoposide, and cisplatin do not affect the pharmacokinetics of ondansetron.
- In a crossover study in 76 pediatric patients, I.V. ondansetron did not increase blood levels of high-dose methotrexate.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category B
- Reproduction studies have been performed in pregnant rats and rabbits at daily oral doses up to 15 and 30 mg/kg/day, respectively, and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ondansetron. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ondansetron in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Ondansetron during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Ondansetron is excreted in the breast milk of rats. It is not known whether ondansetron is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ondansetron is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Little information is available about dosage in pediatric patients 4 years of age or younger.
Geriatic Use
- Of the total number of subjects enrolled in cancer chemotherapy-induced and postoperative nausea and vomiting in US- and foreign-controlled clinical trials, for which there were subgroup analyses, 938 were 65 years of age and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. Dosage adjustment is not needed in patients over the age of 65.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ondansetron with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ondansetron with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ondansetron in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ondansetron in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ondansetron in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ondansetron in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Ondansetron in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Ondansetron in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- In addition to the adverse events listed above, the following events have been described in the setting of ondansetron overdose: "Sudden blindness" (amaurosis) of 2 to 3 minutes' duration plus severe constipation occurred in 1 patient that was administered 72 mg of ondansetron intravenously as a single dose. Hypotension (and faintness) occurred in a patient that took 48 mg of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets. Following infusion of 32 mg over only a 4-minute period, a vasovagal episode with transient second-degree heart block was observed. In all instances, the events resolved completely.
Management
- There is no specific antidote for ondansetron overdose. Patients should be managed with appropriate supportive therapy. Individual intravenous doses as large as 150 mg and total daily intravenous doses as large as 252 mg have been inadvertently administered without significant adverse events. These doses are more than 10 times the recommended daily dose.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Ondansetron in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- *Ondansetron is a selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. While its mechanism of action has not been fully characterized, ondansetron is not a dopamine-receptor antagonist. Serotonin receptors of the 5-HT3 type are present both peripherally on vagal nerve terminals and centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the area postrema. It is not certain whether ondansetron's antiemetic action is mediated centrally, peripherally, or in both sites. However, cytotoxic chemotherapy appears to be associated with release of serotonin from the enterochromaffin cells of the small intestine. In humans, urinary 5-HIAA (5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid) excretion increases after cisplatin administration in parallel with the onset of emesis. The released serotonin may stimulate the vagal afferents through the 5-HT3 receptors and initiate the vomiting reflex.
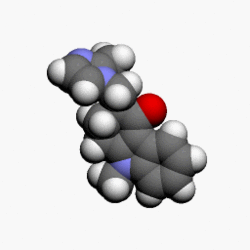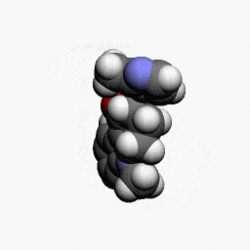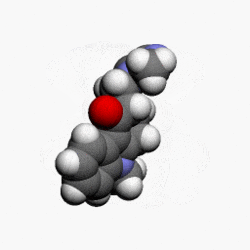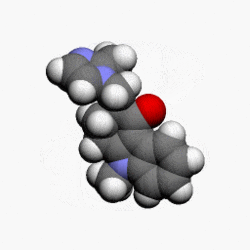
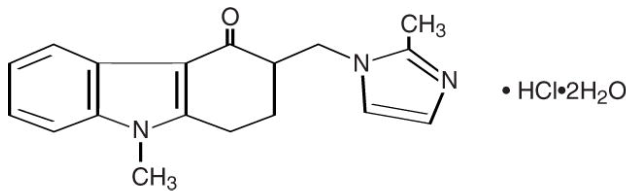
Structure
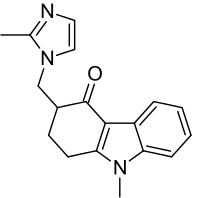
- The active ingredient in Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets is ondansetron hydrochloride (HCl) as the dihydrate, the racemic form of ondansetron and a selective blocking agent of the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor type. Chemically it is (±) 1, 2, 3, 9-tetrahydro-9-methyl-3-[(2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-4H-carbazol-4-one, monohydrochloride, dihydrate. It has the following structural formula:
- The empirical formula is C18H19N3O•HCl•2H2O, representing a molecular weight of 365.9. Ondansetron HCl dihydrate is a white to off-white powder that is soluble in water and normal saline.
- Each 4 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet for oral administration contains 5 mg of ondansetron HCl dihydrate equivalent to 4 mg of ondansetron. :*Each 8 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet for oral administration contains 10 mg of ondansetron HCl dihydrate equivalent to 8 mg of ondansetron. :*Each 24 mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet for oral administration contains 30 mg of ondansetron HCl dihydrate equivalent to 24 mg of ondansetron.
- Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized starch. Polishing solution contains hypromellose and polyethylene glycol. Film coating solution contains the following:
- 4 mg: opadry white YS-1-7003, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80 and titanium dioxide.
- 8 mg: opadry clear YS-1-7006, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide.
- 24 mg: opadry clear, YS-1-7006, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, polyethylene glycol, red iron oxide, and titanium dioxide.
Pharmacodynamics
- In animals, the emetic response to cisplatin can be prevented by pretreatment with an inhibitor of serotonin synthesis, bilateral abdominal vagotomy and greater splanchnic nerve section, or pretreatment with a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist.
- In normal volunteers, single intravenous doses of 0.15 mg/kg of ondansetron had no effect on esophageal motility, gastric motility, lower esophageal sphincter pressure, or small intestinal transit time. Multiday administration of ondansetron has been shown to slow colonic transit in normal volunteers. Ondansetron has no effect on plasma prolactin concentrations.
- Ondansetron does not alter the respiratory depressant effects produced by alfentanil or the degree of neuromuscular blockade produced by atracurium. Interactions with general or local anesthetics have not been studied.
Pharmacokinetics
- Ondansetron is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes some first-pass metabolism. Mean bioavailability in healthy subjects, following administration of a single 8-mg tablet, is approximately 56%.
- Ondansetron systemic exposure does not increase proportionately to dose. AUC from a 16-mg tablet was 24% greater than predicted from an 8-mg tablet dose. This may reflect some reduction of first-pass metabolism at higher oral doses. Bioavailability is also slightly enhanced by the presence of food but unaffected by antacids.
- Ondansetron is extensively metabolized in humans, with approximately 5% of a radiolabeled dose recovered as the parent compound from the urine. The primary metabolic pathway is hydroxylation on the indole ring followed by subsequent glucuronide or sulfate conjugation. Although some nonconjugated metabolites have pharmacologic activity, these are not found in plasma at concentrations likely to significantly contribute to the biological activity of ondansetron.
- In vitro metabolism studies have shown that ondansetron is a substrate for human hepatic cytochrome P-450 enzymes, including CYP1A2, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. In terms of overall ondansetron turnover, CYP3A4 played the predominant role. Because of the multiplicity of metabolic enzymes capable of metabolizing ondansetron, it is likely that inhibition or loss of one enzyme (e.g., CYP2D6 genetic deficiency) will be compensated by others and may result in little change in overall rates of ondansetron elimination. Ondansetron elimination may be affected by cytochrome P-450 inducers. In a pharmacokinetic study of 16 epileptic patients maintained chronically on CYP3A4 inducers, carbamazepine, or phenytoin, reduction in AUC, Cmax, and T1/2 of ondansetron was observed.1 This resulted in a significant increase in clearance. However, on the basis of available data, no dosage adjustment for ondansetron is recommended.
- In humans, carmustine, etoposide, and cisplatin do not affect the pharmacokinetics of ondansetron.
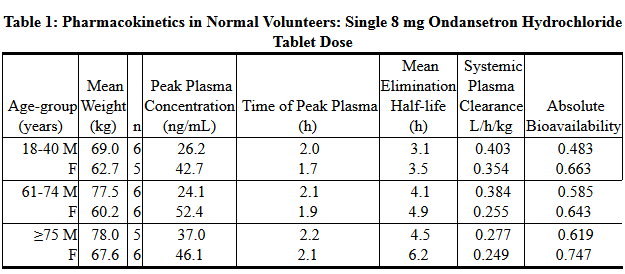
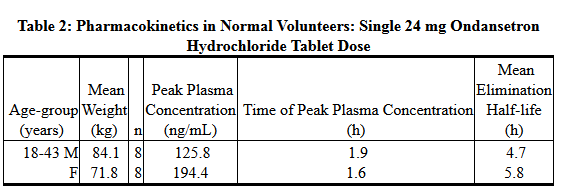
- Gender differences were shown in the disposition of ondansetron given as a single dose. The extent and rate of ondansetron's absorption is greater in women than men. Slower clearance in women, a smaller apparent volume of distribution (adjusted for weight), and higher absolute bioavailability resulted in higher plasma ondansetron levels. These higher plasma levels may in part be explained by differences in body weight between men and women. It is not known whether these gender-related differences were clinically important. More detailed pharmacokinetic information is contained in Tables 1 and 2 taken from 2 studies.
- A reduction in clearance and increase in elimination half-life are seen in patients over 75 years of age. In clinical trials with cancer patients, safety and efficacy was similar in patients over 65 years of age and those under 65 years of age; there was an insufficient number of patients over 75 years of age to permit conclusions in that age-group. No dosage adjustment is recommended in the elderly.
- In patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment, clearance is reduced 2-fold and mean half-life is increased to 11.6 hours compared to 5.7 hours in normals. In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh2 score of 10 or greater), clearance is reduced 2-fold to 3-fold and apparent volume of distribution is increased with a resultant increase in half-life to 20 hours. In patients with severe hepatic impairment, a total daily dose of 8 mg should not be exceeded.
- Due to the very small contribution (5%) of renal clearance to the overall clearance, renal impairment was not expected to significantly influence the total clearance of ondansetron. However, ondansetron oral mean plasma clearance was reduced by about 50% in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min). This reduction in clearance is variable and was not consistent with an increase in half-life. No reduction in dose or dosing frequency in these patients is warranted.
- Plasma protein binding of ondansetron as measured in vitro was 70% to 76% over the concentration range of 10 to 500 mg/mL. Circulating drug also distributes into erythrocytes.
- Four and 8 mg doses of either Ondansetron Oral Solution or Ondansetron Orally Disintegrating Tablets are bioequivalent to corresponding doses of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets and may be used interchangeably. One 24-mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet is bioequivalent to and interchangeable with three 8-mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Carcinogenic effects were not seen in 2-year studies in rats and mice with oral ondansetron doses up to 10 and 30 mg/kg/day, respectively. Ondansetron was not mutagenic in standard tests for mutagenicity. Oral administration of ondansetron up to 15 mg/kg/day did not affect fertility or general reproductive performance of male and female rats.
Clinical Studies
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy
- In 2 randomized, double-blind, monotherapy trials, a single 24-mg Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablet was superior to a relevant historical placebo control in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including cisplatin ≥50 mg/m2. Steroid administration was excluded from these clinical trials. More than 90% of patients receiving a cisplatin dose ≥50 mg/m2 in the historical placebo comparator experienced vomiting in the absence of antiemetic therapy.
- The first trial compared oral doses of ondansetron 24 mg once-a-day, 8 mg twice-a-day, and 32 mg once-a-day in 357 adult cancer patients receiving chemotherapy regimens containing cisplatin ≥50 mg/m2. A total of 66% of patients in the ondansetron 24-mg once-a-day group, 55% in the ondansetron 8-mg twice-a-day group, and 55% in the ondansetron 32-mg once-a-day group completed the 24-hour study period with 0 emetic episodes and no rescue antiemetic medications, the primary endpoint of efficacy. Each of the 3 treatment groups was shown to be statistically significantly superior to a historical placebo control.
- In the same trial, 56% of patients receiving oral ondansetron 24 mg once-a-day experienced no nausea during the 24-hour study period, compared with 36% of patients in the oral ondansetron 8-mg twice-a-day group (p = 0.001) and 50% in the oral ondansetron 32-mg once-a-day group.
- In a second trial, efficacy of the oral ondansetron 24-mg once-a-day regimen in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including cisplatin ≥50 mg/m2, was confirmed.
Moderately Emetogenic Chemotherapy
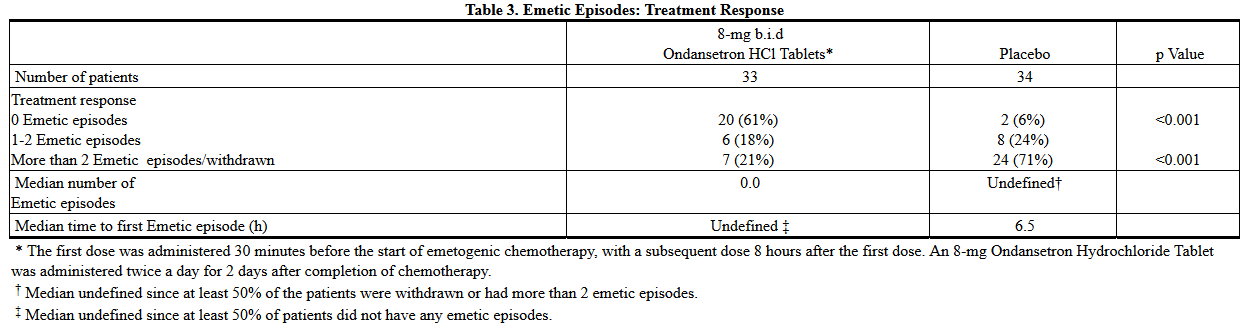
- In 1 double-blind US study in 67 patients, Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 8 mg administered twice-a-day were significantly more effective than placebo in preventing vomiting induced by cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy containing doxorubicin. Treatment response is based on the total number of emetic episodes over the 3-day study period. The results of this study are summarized in Table 3:
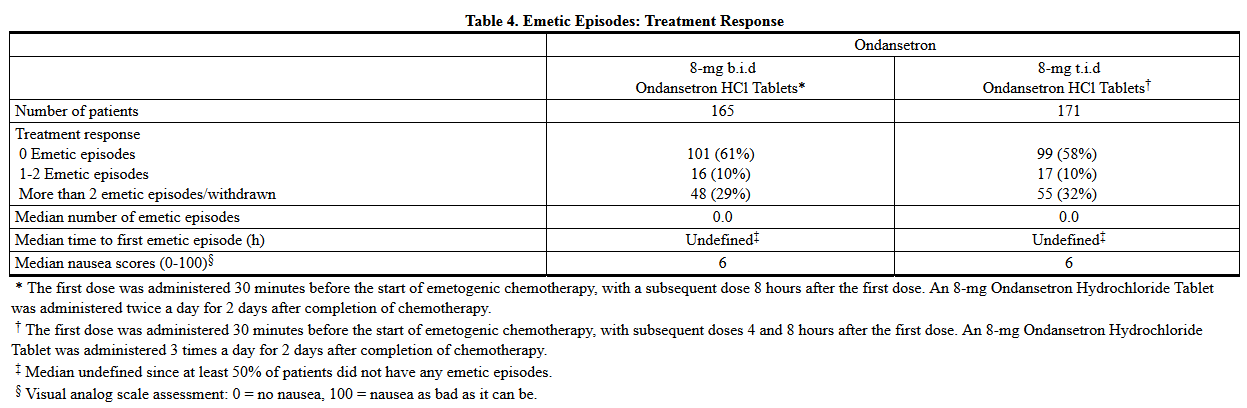
- In 1 double-blind US study in 336 patients, Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 8 mg administered twice a day were as effective as Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 8 mg administered 3 times a day in preventing nausea and vomiting induced by cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy containing either methotrexate or doxorubicin.
- Treatment response is based on the total number of emetic episodes over the 3-day study period. The results of this study are summarized in Table 4:
- Re-treatment
- In uncontrolled trials, 148 patients receiving cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy were re-treated with Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 8 mg 3 times daily during subsequent chemotherapy for a total of 396 re-treatment courses. No emetic episodes occurred in 314 (79%) of the re-treatment courses, and only 1 to 2 emetic episodes occurred in 43 (11%) of the re-treatment courses.
- Pediatric Studies
- Three open-label, uncontrolled, foreign trials have been performed with 182 pediatric patients 4 to 18 years old with cancer who were given a variety of cisplatin or noncisplatin regimens. In these foreign trials, the initial dose of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Injection ranged from 0.04 to 0.87 mg/kg for a total dose of 2.16 to 12 mg. This was followed by the administration of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets ranging from 4 to 24 mg daily for 3 days. In these studies, 58% of the 170 evaluable patients had a complete response (no emetic episodes) on day 1. Two studies showed the response rates for patients less than 12 years of age who received Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 4 mg 3 times a day to be similar to those in patients 12 to 18 years of age who received Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 8 mg 3 times daily. Thus, prevention of emesis in these pediatric patients was essentially the same as for patients older than 18 years of age. Overall, Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets were well tolerated in these pediatric patients.
- Radiation-Induced Nausea and Vomiting:Total Body Irradiation
- In a randomized, double-blind study in 20 patients, Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets (8 mg given 1.5 hours before each fraction of radiotherapy for 4 days) were significantly more effective than placebo in preventing vomiting induced by total body irradiation. Total body irradiation consisted of 11 fractions (120 cGy per fraction) over 4 days for a total of 1,320 cGy. Patients received 3 fractions for 3 days, then 2 fractions on day 4.
- Single High-Dose Fraction Radiotherapy
- Ondansetron was significantly more effective than metoclopramide with respect to complete control of emesis (0 emetic episodes) in a double-blind trial in 105 patients receiving single high-dose radiotherapy (800 to 1,000 cGy) over an anterior or posterior field size of ≥80 cm2 to the abdomen. Patients received the first dose of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets (8 mg) or metoclopramide (10 mg) 1 to 2 hours before radiotherapy. If radiotherapy was given in the morning, 2 additional doses of study treatment were given (1 tablet late afternoon and 1 tablet before bedtime). If radiotherapy was given in the afternoon, patients took only 1 further tablet that day before bedtime. Patients continued the oral medication on a 3 times a day basis for 3 days.
- Daily Fractionated Radiotherapy
- Ondansetron was significantly more effective than prochlorperazine with respect to complete control of emesis (0 emetic episodes) in a double-blind trial in 135 patients receiving a 1- to 4-week course of fractionated radiotherapy (180 cGy doses) over a field size of ≥100 cm2 to the abdomen. Patients received the first dose of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets (8 mg) or prochlorperazine (10 mg) 1 to 2 hours before the patient received the first daily radiotherapy fraction, with 2 subsequent doses on a 3 times a day basis. Patients continued the oral medication on a 3 times a day basis on each day of radiotherapy.
- Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
- Surgical patients who received ondansetron 1 hour before the induction of general balanced anesthesia (barbiturate: thiopental, methohexital, or thiamylal; opioid: alfentanil, sufentanil, morphine, or fentanyl; nitrous oxide; neuromuscular blockage: succinylcholine/curare or gallamine and/or vecuronium, pancuronium, or atracurium; and supplemental isoflurane or enflurane) were evaluated in 2 double-blind studies (1 US study, 1 foreign) involving 865 patients. Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets (16 mg) were significantly more effective than placebo in preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting.
- The study populations in all trials thus far consisted of women undergoing inpatient surgical procedures. No studies have been performed in males. No controlled clinical study comparing Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets to Ondansetron Hydrochloride Injection has been performed.
How Supplied
- Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 4 mg (5 mg ondansetron HCl dihydrate equivalent to 4 mg of ondansetron), are Round, White Coated Tablet; Unscored and Debossed “W 04” on one side and are available in:
- Bottles of 30 tablets
- Bottles of 100 tablets
- Unit Dose Packs of 3 tablets
- Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets 8 mg (10 mg ondansetron HCl dihydrate equivalent to 8 mg of ondansetron), are Oblong, Unscored, Yellow Coated Tablet; Debossed “WW” on one side and “12” on the other side and are available in:
- Bottles of 30 tablets
- Bottles of 100 tablets
- Unit Dose Packs of 3 tablets
- Ondansetron HCl Tablets 24 mg (30 mg of ondansetron HCl dihydrate equivalent to 24 mg of ondansetron), are Capsule Shaped, Unscored, Light Pink Coated Tablets; Debossed "WW" on one side and "24" on the other side and are available in:
- Daily Unit Dose Packs of 1 Tablet
- Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F).
- Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Ondansetron (oral) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Ondansetron (oral) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Ondansetron (oral) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Ondansetron in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Ondansetron interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ONDANSETRON®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Ondansetron (oral) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Ondansetron (oral)
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ondansetron (oral) |Label Name=Ondansetron08.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ondansetron (oral) |Label Name=Ondansetron09.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ondansetron (oral) |Label Name=Ondansetron10.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ondansetron (oral) |Label Name=Ondansetron11.png
}}