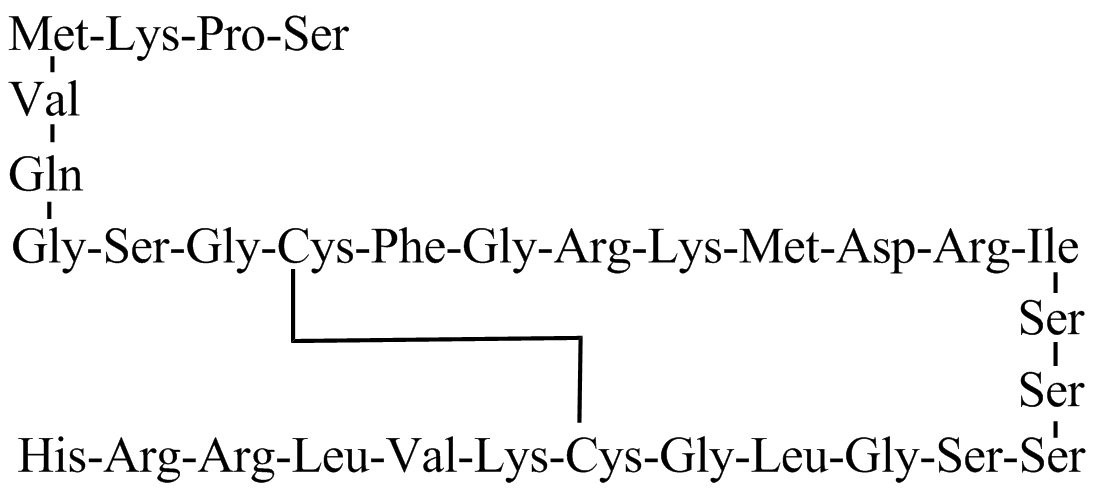Nesiritide
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Nesiritide is a natriuretic peptide that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of patients with acutely decompensated heart failure who have dyspnea at rest or with minimal activity. Common adverse reactions include hypotension, nausea, dizziness, headache, and elevated serum creatinine.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
- Natrecor® (nesiritide) is for intravenous (IV) use only. There is limited experience with administering Natrecor® for longer than 96 hours. Monitor blood pressure closely during Natrecor® administration.
- Dosing Information
- Recommended Dosage: IV bolus of 2 μg/kg followed by a continuous infusion of 0.01 μg/kg/min. Do not initiate Natrecor® at a dose that is above the recommended dose.
- The loading dose may not be appropriate for those with low systolic blood pressure (SBP) <110 mm Hg or for patients recently treated with afterload reducers.
- The administration of the recommended dose of Natrecor® is a two step process:
- Step 1. Administration of the IV Bolus
- After preparation of the infusion bag, withdraw the bolus volume (see Table 1) from the Natrecor® infusion bag, and administer it over approximately 60 seconds through an IV port in the tubing.
- Bolus Volume (mL) = Patient Weight (kg) / 3
- Step 2. Administration of the Continuous Infusion
- Immediately following the administration of the bolus, infuse Natrecor® at a flow rate of 0.1 mL/kg/hr. This will deliver a Natrecor® infusion dose of 0.01 μg/kg/min.
- To calculate the infusion flow rate to deliver a 0.01 μg/kg/min dose, use the following formula (see Table 2):
- Infusion Flow Rate (mL/hr) = Patient Weight (kg) × 0.1


Dose Adjustments
- The dose-limiting side effect of Natrecor® is hypotension. If hypotension occurs during the administration of Natrecor®, reduce the dose of or discontinue Natrecor® and initiate other measures to support blood pressure (IV fluids, changes in body position). When symptomatic hypotension occurs, discontinue Natrecor®. Because hypotension caused by Natrecor® may be prolonged (up to hours), a period of observation may be necessary before restarting the drug. Natrecor® may be subsequently restarted at a dose that is reduced by 30% (with no bolus administration) once the patient has stabilized.
- Do not up-titrate Natrecor® more frequently than every 3 hours. Use central hemodynamic monitoring and do not exceed 0.03 μg/kg/min.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Nesiritide in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Nesiritide in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- The safety and effectiveness of Natrecor® in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Nesiritide in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Nesiritide in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Persistent systolic blood pressure <100 mm Hg prior to therapy because of an increased risk of symptomatic hypotension
- Hypersensitivity to any of its components
- Cardiogenic shock
Warnings
Hypotension
- Natrecor® may cause hypotension . In the ASCEND-HF trial, the incidence of symptomatic hypotension was 7.1% in Natrecor®-treated patients compared to 4.0% in placebo-treated patients on a background of standard care. The risk of hypotension may be increased by the concomitant use of Natrecor® with drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system (i.e., angiotensin receptor blockers and/or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) or other afterload reducers. In the VMAC trial, in patients given the recommended dose (2 μg/kg bolus followed by a 0.01 μg/kg/min infusion) or the adjustable dose, the incidence of symptomatic hypotension in the first 24 hours was similar for Natrecor® (4%) and IV nitroglycerin (5%). When hypotension occurred, however, the duration of symptomatic hypotension was longer with Natrecor® (mean duration was 2.2 hours) than with nitroglycerin (mean duration was 0.7 hours).
- Administer Natrecor® only in settings where blood pressure can be monitored closely and hypotension aggressively treated. Reduce the dose of or discontinue Natrecor® in patients who develop hypotension.
- Avoid administration of Natrecor® in patients suspected of having, or known to have, low cardiac filling pressures.
- Natrecor® is not recommended for patients for whom vasodilating agents are not appropriate, such as patients with significant valvular stenosis, restrictive or obstructive cardiomyopathy, constrictive pericarditis, pericardial tamponade, or other conditions in which cardiac output is dependent upon venous return, or for patients suspected to have low cardiac filling pressures.
Worsening of Renal Function
- Natrecor® may decrease renal function as judged by increases in serum creatinine. Monitor serum creatinine both during and after therapy has been completed. Monitor serum creatinine until values have stabilized. In patients with severe heart failure whose renal function may depend on the activity of the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system, treatment with Natrecor® may be associated with azotemia. When Natrecor® was initiated at doses higher than 0.01 μg/kg/min (0.015 and 0.03 μg/kg/min), there was an increased rate of elevated serum creatinine over baseline compared with standard therapies, although the rate of acute renal failure and need for dialysis was not increased.
Hypersensitivity
- Serious hypersensitivity/allergic reactions following administration of Natrecor® have been reported.
- These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to recombinant peptides. Before therapy with Natrecor® is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had a previous hypersensitivity reaction to other recombinant peptides. If an allergic reaction to Natrecor® occurs, discontinue the drug. Some serious hypersensitivity/allergic reactions may require treatment with epinephrine, oxygen, IV fluids, antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines and airway management, as clinically indicated.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice. A causal relationship for Natrecor® cannot be reliably established in individual cases.
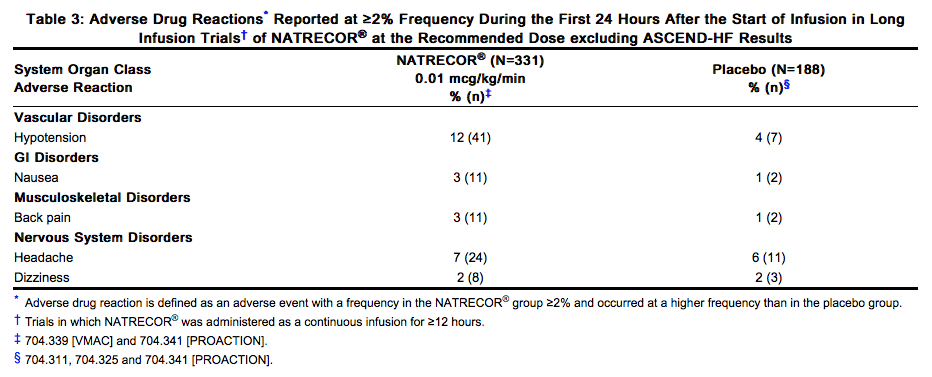
- Adverse drug reactions that occurred at least ≥2% more frequently on Natrecor® than on placebo during the first 24 hours of infusion (excluding the ASCEND-HF study) are shown in Table 3.
- Laboratory adverse drug reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients and collected during the first 14 days after the start of Natrecor® infusion included: hypoglycemia.
Worsening Renal Function
- In the ASCEND-HF trial, through Day 30, the incidence of renal impairment as measured by a >25% decrease in glomerular filtration rate (calculated based on serum creatinine) was observed in 31.4% and 29.5% in the Natrecor® and placebo groups, respectively. Other metrics of decompensated renal function such as an increase in creatinine of > 0.5 mg/dl, a 50% increase in creatinine or a value of ≥ 2 or 100% increase in creatinine were more frequent in the Natrecor® group. At 30 days post enrollment, more subjects in the Natrecor® group had elevated levels of creatinine of 50% greater than baseline compared to placebo 4.6% versus 3.3%. In the ASCEND-HF study there were relatively few subjects requiring either hemofiltration or dialysis.
- In the PRECEDENT trial, the incidence of elevations in serum creatinine to >0.5 mg/dL above baseline through Day 14 was higher in the Natrecor® 0.015 μg/kg/min group (17%) and the Natrecor® 0.03 μg/kg/min group (19%) than with standard therapy (11%). In the VMAC trial, through Day 30, the incidence of elevations in creatinine to >0.5 mg/dL above baseline was 28% and 21% in the Natrecor® (2 μg/kg bolus followed by 0.01 μg/kg/min) and nitroglycerin groups, respectively.
Neutral Effect on Mortality
- A meta-analysis performed of seven clinical trials demonstrated Natrecor® did not increase mortality in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) at Day 30 or Day 180 (see Figures 1 and 2). Data from seven studies in which 30-day data were collected are presented in Figure 1. The data depict hazard ratios (HR) and confidence intervals (CI) of mortality data for randomized and treated patients with Natrecor® relative to active or placebo controls through Day 30 for each of the seven individual studies along with the overall combined estimate (Studies 311, 325, 326, 329 [PRECEDENT], 339 [VMAC], 341 [PROACTION], and A093 [ASCEND-HF]).
- Figure 1 (on logarithmic scale) also contains an estimate for the seven studies combined (n=8514). The results indicate that there is no increased mortality risk for Natrecor® at Day 30 (seven studies pooled: HR=0.99; 95% CI: 0.80, 1.22). The percentages are the Kaplan-Meier estimates.

- Figure 2 presents 180-day mortality hazard ratios from all six individual studies where 180-day data were collected (Studies 325, 326, 329, 339, 341 and A093 [ASCEND-HF]). The results indicate that with the addition of the ASCEND-HF data, there is no increased mortality risk for Natrecor® at Day 180 (six studies pooled: HR=0.98; 95% CI: 0.88, 1.10).

Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Natrecor®. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Infusion site extravasation
- Pruritus
- Rash
Drug Interactions
- No trials specifically examining potential drug interactions with Natrecor® were conducted, although many concomitant drugs (including IV nitroglycerin) were used in clinical trials. No drug interactions were detected except for an increase in symptomatic hypotension in patients receiving afterload reducers or affecting the renin-angiotensin system (i.e., ARBs and/or ACE inhibitors).
- The co-administration of Natrecor® with nitroprusside, milrinone, or IV ACE inhibitors has not been evaluated.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- It is not known whether Natrecor® can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women or if it can affect reproductive capacity. A developmental reproductive toxicology study was conducted in pregnant rabbits using doses up to 1440 μg/kg/day given by constant infusion for 13 days. At this level of exposure (based on AUC, approximately 70 × human exposure at the recommended dose) no adverse effects on live births or fetal development were observed. Natrecor® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies any possible risk to the fetus.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Nesiritide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Nesiritide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of Natrecor® in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Of the total number of patients in clinical trials treated with Natrecor® (n=4505), 52% were 65 years or older and 27% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Some older individuals may be more sensitive to the effect of Natrecor® than younger individuals.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nesiritide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nesiritide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nesiritide in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nesiritide in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nesiritide in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Nesiritide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Preparation and Administration Instructions
- The Natrecor® bolus must be drawn from the prepared infusion bag. Prime the IV tubing with 5 mL of the solution for infusion prior to connecting to the patient's vascular access port and prior to administering the bolus or starting the infusion.
- Reconstitute one 1.5 mg vial of Natrecor® by adding 5 mL of diluent removed from a pre-filled 250 mL plastic IV bag containing the diluent of choice. After reconstitution of the vial, each mL contains 0.32 mg of nesiritide. The following preservative-free diluents are recommended for reconstitution: 5% Dextrose Injection (D5W), USP; 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP; 5% Dextrose and 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose and 0.2% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Do not shake the vial. Rock the vial gently so that all surfaces, including the stopper, are in contact with the diluent to ensure complete reconstitution. Use only a clear, essentially colorless solution.
- Withdraw the entire contents of the reconstituted Natrecor® vial and add to the 250 mL plastic IV bag. This will yield a solution with a concentration of Natrecor® of approximately 6 μg/mL. Invert the IV bag several times to ensure complete mixing of the solution.
- Use the reconstituted solution within 24 hours, as Natrecor® contains no antimicrobial preservative. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Reconstituted vials of Natrecor® may be stored at 2 to 25°C (36 to 77°F) for up to 24 hours.
Monitoring
Blood Pressure
- Monitor blood pressure closely during Natrecor® administration.
Renal Function
- Natrecor® may decrease renal function as judged by increases in serum creatinine. Monitor serum creatinine both during and after therapy has been completed. Monitor serum creatinine until values have stabilized.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Nesiritide in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Overdose with Natrecor® therapy has been reported and is primarily the result of either a miscalculated Natrecor® dose or a mechanical error such as an infusion-pump malfunction or an infusion-pump programming error. The most frequently reported adverse event reported with Natrecor® overdose is hypotension , which may be symptomatic and may persist for several hours.
- Asymptomatic hypotensive events may resolve with drug stoppage.
- In some cases hypotension may persist for several hours beyond discontinuation.
Management
- In the event of an overdose, discontinue Natrecor® and support blood pressure.
Chronic Overdose
- There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Nesiritide in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Human BNP (hBNP) is secreted by the ventricular myocardium in response to stretch and exists in several isoforms in the human body. Elevated levels of BNP have been associated with advanced heart failure and are considered to be a compensatory mechanism in this disease. Human BNP binds to the particulate guanylate cyclase receptor of vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells, leading to increased intracellular concentrations of guanosine 3'5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) and smooth muscle cell relaxation. Cyclic GMP serves as a second messenger to dilate veins and arteries. Nesiritide has been shown to relax isolated human arterial and venous tissue preparations that were precontracted with either endothelin-1 or the alpha-adrenergic agonist, phenylephrine.
- In animals, nesiritide had no effects on cardiac contractility or on measures of cardiac electrophysiology such as atrial and ventricular effective refractory times or atrioventricular node conduction.
Structure
- Natrecor® (nesiritide) is a sterile, purified preparation of human B-type natriuretic peptide (hBNP), and is manufactured from E. coli using recombinant DNA technology. Nesiritide has a molecular weight of 3464 g/mol and an empirical formula of C143H244N50O42S4. Nesiritide has the same 32 amino acid sequence as the endogenous peptide, which is produced by the ventricular myocardium.
- Natrecor® is formulated as the citrate salt of rhBNP, and is provided in a sterile, single-use vial. Each 1.5 mg vial contains a white- to off-white lyophilized powder for intravenous (IV) administration after reconstitution. The quantitative composition of the lyophilized drug per vial is: nesiritide 1.58 mg, citric acid monohydrate 2.1 mg, mannitol 20.0 mg, and sodium citrate dihydrate 2.94 mg.

Pharmacodynamics
- With a dosing regimen of Natrecor® of 2 μg/kg IV bolus followed by an intravenous infusion dose of 0.01 μg/kg/min, Table 4 and Figure 3 summarize the changes in the VMAC trial in PCWP and other measures during the first 3 hours.


- With this dosing regimen, 60% of the 3-hour effect on PCWP reduction is achieved within 15 minutes after the bolus, reaching 95% of the 3-hour effect within 1 hour. Approximately 70% of the 3-hour effect on SBP reduction is reached within 15 minutes. The pharmacodynamic (PD) half-life of the onset and offset of the hemodynamic effect of Natrecor® is longer than what the PK half-life of 18 minutes would predict. Longer infusions may exaggerate the discrepancy from onset and offset effects. For example, in patients who developed symptomatic hypotension in the VMAC (Vasodilation in the Management of Acute Congestive Heart Failure) trial, half of the recovery of SBP toward the baseline value after discontinuation or reduction of the dose of Natrecor® was observed in about 60 minutes. When higher doses of Natrecor® were infused, the duration of hypotension was sometimes several hours.
- No rebound increase to levels above baseline state was observed. There was also no evidence of tachyphylaxis to the hemodynamic effects of Natrecor® in the clinical trials.
- In the VMAC trial, in which the use of diuretics was not restricted, the mean change in volume status (output minus input) during the first 24 hours in the nitroglycerin and Natrecor® groups was similar: 1279 ± 1455 mL and 1257 ± 1657 mL, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
- In patients with heart failure (HF), Natrecor® administered intravenously by infusion or bolus exhibits biphasic disposition from the plasma. The mean terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of nesiritide is approximately 18 minutes and was associated with approximately 2/3 of the area-under-the-curve (AUC). The mean initial elimination phase was estimated to be approximately 2 minutes.
- In these patients, the mean volume of distribution of the central compartment (Vc) of nesiritide was estimated to be 0.073 L/kg, the mean steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) was 0.19 L/kg, and the mean clearance (CL) was approximately 9.2 mL/min/kg. At steady state, plasma BNP levels increase from baseline endogenous levels by approximately 3-fold to 6-fold with Natrecor® infusion doses ranging from 0.01 to 0.03 μg/kg/min.
Metabolism and Excretion
- The mechanism of elimination of nesiritide has not been studied specifically in humans.
Special Populations
Renal Impairment
- Clinical data suggest that dose adjustment is not required in patients with renal impairment. The effects of nesiritide on PCWP, cardiac index (CI), and systolic blood pressure (SBP) were not significantly different in patients with chronic renal impairment (baseline serum creatinine ranging from 2 mg/dL to 4.3 mg/dL), and patients with normal renal function.
Body Weight
- The population pharmacokinetic (PK) analyses carried out to determine the effects of demographics and clinical variables on PK parameters showed that clearance of nesiritide is proportional to body weight, supporting the administration of weight-adjusted dosing of nesiritide (i.e., administration on a μg/kg/min basis).
Age, Gender, Race/Ethnicity
- Nesiritide clearance was not influenced significantly by age, gender, or race/ethnicity.
Severity of HF
- Nesiritide clearance was not influenced significantly by baseline endogenous hBNP concentration, severity of HF (as indicated by baseline PCWP, baseline CI, or New York Heart Association [NYHA] classification).
Effects of Concomitant Medications
- The co-administration of Natrecor® with enalapril did not have significant effects on the PK of Natrecor®. The PK effect of co-administration of Natrecor® with other IV vasodilators such as nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, milrinone, or IV ACE inhibitors has not been evaluated. During clinical studies, Natrecor® was administered concomitantly with other medications, including: diuretics, digoxin, oral ACE inhibitors, anticoagulants, oral nitrates, statins, class III antiarrhythmic agents, beta-blockers, dobutamine, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and dopamine. Although no PK interactions were specifically assessed, there did not appear to be evidence suggesting any clinically significant PK interaction.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of nesiritide. Nesiritide did not increase the frequency of mutations when used in an in vitro bacterial cell assay (Ames test). No other genotoxicity studies were performed.
Clinical Studies
- Natrecor® has been studied in 11 clinical trials including 4505 patients with HF (NYHA class II–III 56%, NYHA class IV 27%; mean age 64 years, women 32%). There were six randomized, multi-center, placebo- or active-controlled studies (comparative agents included nitroglycerin, dobutamine, milrinone, nitroprusside, or dopamine) in which 4269 patients with decompensated HF received continuous infusions of Natrecor® at doses ranging from 0.01 to 0.03 μg/kg/min. Of these patients, the majority (n=3358, 79%) received the Natrecor® infusion for at least 24 hours; 2182 (51%) received Natrecor® for 24 to 48 hours, and 1176 (28%) received Natrecor® for greater than 48 hours.
- In the initial five of these six controlled trials, Natrecor® was used alone or in conjunction with other standard therapies, including diuretics (79%), digoxin (62%), oral ACE inhibitors (55%), anticoagulants (38%), oral nitrates (32%), statins (18%), class III antiarrhythmic agents (16%), beta-blockers (15%), dobutamine (15%), calcium channel blockers (11%), angiotensin II receptor antagonists (6%), and dopamine (4%).
- In the ASCEND-HF trial (Acute Study of Clinical Effectiveness of Nesiritide in patients with Decompensated Heart Failure), Natrecor® was used alone or in conjunction with other standard therapies. Most patients (99.4%) received diuretic medications in conjunction with Natrecor®, with the most commonly used diuretic being furosemide (55%). The following standard therapies were used in ≥2% of patients: beta-blockers (72%), aspirin (64%); oral ACE inhibitors (60%), statins (50%), aldosterone antagonists (48%), digoxin/digitalis glycoside (39%), oral or topical nitrates (30%), oral anticoagulants (29%), clopidogrel/thienopyridine (21%), angiotensin receptor antagonists (19%), antiarrhythmic agents (16%), IV nitroglycerin (16%); calcium channel blockers (13%), hydralazine (11%), dobutamine (8%), dopamine (5%), alpha blockers (4%), IV opiates (5%), and NSAIDs (4%). The following standard therapies were used in <2% of patients: COX2 inhibitors, milrinone, epinephrine, levosimendan, nitroprusside, norepinephrine, phenylephrine, and vasopressin.
- Natrecor® has been studied in a broad range of patients, including the elderly (53% >65 years of age), women (33%), minorities (17% black), and patients with a history of significant morbidities such as hypertension (71%), previous myocardial infarction (38%), diabetes (43%), atrial fibrillation flutter (37%), ventricular tachycardia fibrillation (10%), and preserved systolic function (20%). In trials other than the ASCEND-HF trial, Natrecor® was also studied in patients with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia (25%) and patients with acute coronary syndromes less than 7 days before the start of Natrecor® (4%).
- The VMAC (Vasodilation in the Management of Acute Congestive Heart Failure) trial was a randomized, double-blind study of 489 patients (246 patients requiring a right heart catheter, 243 patients without a right heart catheter) who required hospitalization for management of shortness of breath at rest due to acutely decompensated HF. The study compared the effects of Natrecor®, placebo, and IV nitroglycerin when added to background therapy (IV and oral diuretics, non-IV cardiac medications, dobutamine and dopamine). Patients with acute coronary syndrome preserved systolic function, arrhythmia and renal impairment were not excluded. The primary endpoints of the study were the change from baseline in PCWP and the change from baseline in patients' dyspnea, evaluated after three hours. Close attention was also paid to the occurrence and persistence of hypotension , given nesiritide's relatively long (compared to nitroglycerin) PK and PD half-life.
- Natrecor® was administered as a 2 μg/kg bolus over approximately 60 seconds, followed by a continuous fixed dose infusion of 0.01 μg/kg/min. After the 3-hour placebo-controlled period, patients receiving placebo crossed over to double-blinded active therapy with either Natrecor® or nitroglycerin The nitroglycerin dose was titrated at the physician's discretion. A subset of patients in the VMAC trial with central hemodynamic monitoring who were treated with Natrecor® (62 of 124 patients) were allowed dose increases of Natrecor® after the first 3 hours of treatment if the PCWP was ≥20 mm Hg and the SBP was ≥100 mm Hg. Dose increases of a 1 μg/kg bolus followed by an increase of the infusion dose by 0.005 μg/kg/min were allowed every 3 hours, up to a maximum dose of 0.03 μg/kg/min. Overall, 23 patients in this subset had the dose of Natrecor® increased in the VMAC trial.
- In the VMAC study, patients receiving Natrecor® reported greater improvement in their dyspnea at 3 hours than patients receiving placebo (p=0.034).
- In the dose-response study, patients receiving both doses of Natrecor® reported greater improvement in dyspnea at 6 hours than patients receiving placebo.
- Natrecor® was also studied in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Natrecor® compared with placebo the ASCEND-HF Study, which was a trial where both arms were administered in addition to standard care, in patients with ADHF. The study was divided into a screening phase, a double-blind treatment phase, and a follow-up phase, including a Day 30 visit and a telephone contact at Day 180. Patients who qualified for the study were ≥18 years of age, hospitalized for the management of ADHF or diagnosed with ADHF within 48 hours after being hospitalized for another reason. They were randomized to receive either Natrecor® as a continuous IV infusion at 0.010 μg/kg/min with or without an initial 2 μg/kg bolus (at the discretion of the physician) or a matching placebo bolus and infusion.
- The primary objective of ASCEND-HF was to evaluate whether treatment with Natrecor® compared to placebo improved patient outcomes (as measured by a reduction in the composite of HF rehospitalization and all-cause mortality from randomization through Day 30) or HF symptoms (as measured by patient self-assessed Likert dyspnea scale which included Markedly Better, Moderately Better, Minimally Better, No Change, Minimally Worse, Moderately Worse and Markedly Worse at 6 hours and 24 hours after Natrecor® initiation).
- A total of 7141 patients were randomized of which 7007 patients took at least one dose of study medication (modified intent-to-treat population) and received treatment for 24 to 168 hours (7 days), if the patient's clinical condition warranted continued treatment for dyspnea or pulmonary congestion at the physician's discretion. The median treatment duration was 42.9 hours for the placebo group and 40.8 hours for the Natrecor® group. The patients' mean age was 65.5 years. The patient population was 65.8% male, 55.9% Caucasian, 24.7% Asian and 15.1% Black or African American.
- The incidence rate for the composite of HF rehospitalization and all-cause mortality from randomization through Day 30 was 9.4% in the Natrecor® group compared with 10.1% in the placebo group. The difference was not statistically significant (p=0.313). The self-assessed dyspnea results did not meet the pre-specified criteria for statistical significance (p ≤0.005 for both or p ≤0.0025 for either) at either time point.
- A total of 273 deaths were reported during the first 30 days after therapy and 876 (12.5%) deaths were reported from randomization through Day 180, 429 (12.3%) patients in the Natrecor® group and 447 (12.7%) patients in the placebo group. Approximately 65% of the deaths at 180 days were cardiovascular (mostly worsening heart failure . There was no statistically significant difference between treatment groups (p=0.5).
How Supplied
- Natrecor® (nesiritide) is provided as a sterile lyophilized powder in 1.5 mg, single-use vials. Each carton contains one vial and is available in the following package:
- 1 vial/carton (NDC 65847-205-25)
Storage
- Store below 25°C. Do not freeze. Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Nesiritide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Nesiritide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Nesiritide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Advise patients of the potential benefits and risks of Natrecor®. Advise patients to notify their physician or healthcare professional if they have symptoms of hypotension .
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Nesiritide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Natrecor®
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Natrecor® — Norcuron®[1]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Nesiritide |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name=Nesiritide injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |Pill Ingred=Nesiritide|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage=1.5 mg |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author=Hospira, Inc. |NDC=65847-205
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Nesiritide |Label Name=Nesiritide09.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Nesiritide |Label Name=Nesiritide10.png
}}