Glycogen storage disease type III pathophysiology
|
Glycogen storage disease type III Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Glycogen storage disease type III from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Glycogen storage disease type III pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Glycogen storage disease type III pathophysiology |
|
Glycogen storage disease type III pathophysiology in the news |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Glycogen storage disease type III pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Anmol Pitliya, M.B.B.S. M.D.[2]
Overview
Glycogen storage disease type 3 (GSD 3) results due to deficiency of glycogen debrancher enzyme. Glycogen debrancher enzyme is present in the liver and muscle. Glycogen debrancher enzyme catalyzes the conversion of phosphorylase limit dextrin into glucose-6-phosphate during glycogenolysis. This defect hinders this conversion. The inability of glucose to leave cells leads to fasting hypoglycemia. Impairment of glycogenolysis leads to the accumulation of fat and glycogen deposition resulting in characteristic hepatomegaly. Hepatomegaly is more pronounced when the child is young and decreases as the age progresses. The hepatomegaly leads to protrusion of the abdomen. Myopathy is usually present and becomes more pronounced as age progress. AGL gene mutation is responsible for glycogen debrancher enzyme deficiency in GSD type 3 and is located on chromosome locus 1p21. GSD type 3 follows an autosomal recessive pattern.
Pathophysiology
- Glycogen storage disease type 3 (GSD 3) results due to deficiency of glycogen debrancher enzyme.
- GSD type 3a is due to the deficiency of enzyme glycogen debrancher enzyme in both liver and muscle.
- GSD type 3b is due to the deficiency of enzyme glycogen debrancher enzyme in liver only.
Mechanism of hypoglycemia
- Glycogen debrancher enzyme is present in the liver and muscle.[1][2]
- Glycogen debrancher enzyme catalyzes the conversion of phosphorylase limit dextrin into glucose-6-phosphate during glycogenolysis.
- Absence of glycogen debrancher enzyme hinders glycogenolysis.
- This leads to accumulation of limit dextrin in organs including liver and muscle.
- The inability of glucose to leave cells leads to fasting hypoglycemia.
- This also results in the development of various secondary metabolic and biochemical abnormalities.
Metabolic Pathway
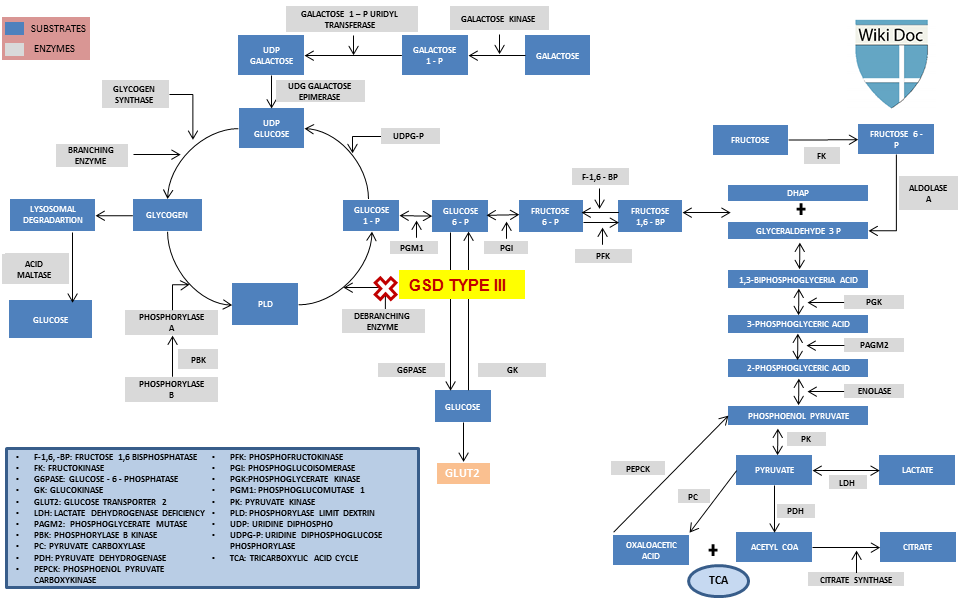
Hepatomegaly and liver disorders
- Impairment of glycogenolysis leads to the accumulation of fat and glycogen deposition, resulting in characteristic hepatomegaly.
- Hepatomegaly is more pronounced when the child is young and decreases as the age progresses. The hepatomegaly leads to protrusion of the abdomen.
- Patients with GSD type 2 may develop hepatic lesions including:[3][4][5][6][7]
Myopathy
- The following different phenotypes of myopathy are described in glycogen storage disease type 3:[8]
- Adult onset distal myopathy
- Subacute myopathy of the respiratory muscles
- Severe generalized myopathy
- Minimal variant myopathy
- Exercise intolerance is usually not present.
Genetics
- GSD type 3 follows an autosomal recessive pattern.
- AGL gene mutation is responsible for glycogen debrancher enzyme deficiency in GSD type 3 and is located on chromosome locus 1p21.[9][10]
Associated Conditions
- Conditions associated with glycogen storage disease type 3 include:[11]
Gross Pathology
- On gross pathology analysis, the features of glycogen storage disease type 1 include hepatomegaly. Hepatomegaly decreases as age increases.[12]
Microscopic Pathology
On microscopic histopathological analysis, the features of glycogen storage disease type 1 include:
- Liver[12]
- Early disease
- Distension of hepatocytes by glycogen
- Periportal septal fibrosis
- Late disease
- Steatosis
- Hepatocyte ballooning
- Eventually centrilobular and portal-based fibrosis
- Early disease
- Muscles
- Accumulation of glycogen between intact myofibrils and in subsarcolemmal position[13]
- Heart
- Endomyocardial biopsy specimen shows:[14]
References
- ↑ Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP (2002). "Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis, management, clinical course and outcome. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I)". Eur J Pediatr. 161 Suppl 1: S20–34. doi:10.1007/s00431-002-0999-4. PMID 12373567.
- ↑ Wolfsdorf JI, Weinstein DA (2003). "Glycogen storage diseases". Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 4 (1): 95–102. PMID 12618563.
- ↑ Demo E, Frush D, Gottfried M, Koepke J, Boney A, Bali D; et al. (2007). "Glycogen storage disease type III-hepatocellular carcinoma a long-term complication?". J Hepatol. 46 (3): 492–8. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2006.09.022. PMC 2683272. PMID 17196294.
- ↑ Labrune P, Trioche P, Duvaltier I, Chevalier P, Odièvre M (1997). "Hepatocellular adenomas in glycogen storage disease type I and III: a series of 43 patients and review of the literature". J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 24 (3): 276–9. PMID 9138172.
- ↑ Matern D, Starzl TE, Arnaout W, Barnard J, Bynon JS, Dhawan A; et al. (1999). "Liver transplantation for glycogen storage disease types I, III, and IV". Eur J Pediatr. 158 Suppl 2: S43–8. PMC 3006437. PMID 10603098.
- ↑ Siciliano M, De Candia E, Ballarin S, Vecchio FM, Servidei S, Annese R; et al. (2000). "Hepatocellular carcinoma complicating liver cirrhosis in type IIIa glycogen storage disease". J Clin Gastroenterol. 31 (1): 80–2. PMID 10914784.
- ↑ Cosme A, Montalvo I, Sánchez J, Ojeda E, Torrado J, Zapata E; et al. (2005). "[Type III glycogen storage disease associated with hepatocellular carcinoma]". Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28 (10): 622–5. PMID 16373012.
- ↑ Kiechl S, Kohlendorfer U, Thaler C, Skladal D, Jaksch M, Obermaier-Kusser B; et al. (1999). "Different clinical aspects of debrancher deficiency myopathy". J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 67 (3): 364–8. PMC 1736538. PMID 10449560.
- ↑ Shen J, Bao Y, Liu HM, Lee P, Leonard JV, Chen YT (1996). "Mutations in exon 3 of the glycogen debranching enzyme gene are associated with glycogen storage disease type III that is differentially expressed in liver and muscle". J Clin Invest. 98 (2): 352–7. doi:10.1172/JCI118799. PMC 507437. PMID 8755644.
- ↑ Aoyama Y, Ozer I, Demirkol M, Ebara T, Murase T, Podskarbi T; et al. (2009). "Molecular features of 23 patients with glycogen storage disease type III in Turkey: a novel mutation p.R1147G associated with isolated glucosidase deficiency, along with 9 AGL mutations". J Hum Genet. 54 (11): 681–6. doi:10.1038/jhg.2009.100. PMID 19834502.
- ↑ Dagli A, Sentner CP, Weinstein DA. Glycogen Storage Disease Type III. 2010 Mar 9 [Updated 2016 Dec 29]. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2017. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26372/
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Kishnani, Priya S; Austin, Stephanie L; Arn, Pamela; Bali, Deeksha S; Boney, Anne; Case, Laura E; Chung, Wendy K; Desai, Dev M; El-Gharbawy, Areeg; Haller, Ronald; Smit, G Peter A; Smith, Alastair D; Hobson-Webb, Lisa D; Wechsler, Stephanie Burns; Weinstein, David A; Watson, Michael S (2010). "Glycogen Storage Disease Type III diagnosis and management guidelines". Genetics in Medicine. 12 (7): 446–463. doi:10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181e655b6. ISSN 1098-3600.
- ↑ McAdams AJ, Hug G, Bove KE (1974). "Glycogen storage disease, types I to X: criteria for morphologic diagnosis". Hum Pathol. 5 (4): 463–87. PMID 4525190.
- ↑ Olson LJ, Reeder GS, Noller KL, Edwards WD, Howell RR, Michels VV (1984). "Cardiac involvement in glycogen storage disease III: morphologic and biochemical characterization with endomyocardial biopsy". Am J Cardiol. 53 (7): 980–1. PMID 6584026.