Psoriatic arthritis physical examination
|
Xyz Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Psoriatic arthritis physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Psoriatic arthritis physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Psoriatic arthritis physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance]. Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
Common physical examination findings of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is diagnostic of [disease name].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Physical Examination
- Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for:[finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
- The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is diagnostic of [disease name].
- The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with psoriatic arthritis usually appear normal.
Vital Signs
- Vital signs of patients with psoriatic arthritis are usually with in normal limits.
Skin
- Psoriatic arthritis may occur after the onset of psoriasis in most of the patients. However, in some cases, arthritis precede psoriasis. The phenotypes of skin psoriasis that are associated with an increased risk of psoriatic arthritis are the lesions in the scalp, nail, intergluteal, and perianal regions.[3]
-
Description (Adapted from Dermatology Atlas)
-
Description (Adapted from Dermatology Atlas)
HEENT
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Jugular venous distension
- Carotid bruits may be auscultated unilaterally/bilaterally using the bell/diaphragm of the otoscope
- Lymphadenopathy (describe location, size, tenderness, mobility, and symmetry)
- Thyromegaly / thyroid nodules
- Hepatojugular reflux
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Asymmetric chest expansion / Decreased chest expansion
- Lungs are hypo/hyperresonant
- Fine/coarse crackles upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally
- Rhonchi
- Vesicular breath sounds / Distant breath sounds
- Expiratory/inspiratory wheezing with normal / delayed expiratory phase
- Wheezing may be present
- Egophony present/absent
- Bronchophony present/absent
- Normal/reduced tactile fremitus
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Chest tenderness upon palpation
- PMI within 2 cm of the sternum (PMI) / Displaced point of maximal impulse (PMI) suggestive of ____
- Heave / thrill
- Friction rub
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
- Gallops
- A high/low grade early/late systolic murmur / diastolic murmur best heard at the base/apex/(specific valve region) may be heard using the bell/diaphgram of the otoscope
Abdomen
Abdominal examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Abdominal distention
- Abdominal tenderness in the right/left upper/lower abdominal quadrant
- Rebound tenderness (positive Blumberg sign)
- A palpable abdominal mass in the right/left upper/lower abdominal quadrant
- Guarding may be present
- Hepatomegaly / splenomegaly / hepatosplenomegaly
- Additional findings, such as obturator test, psoas test, McBurney point test, Murphy test
Back
- Back examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Point tenderness over __ vertebrae (e.g. L3-L4)
- Sacral edema
- Costovertebral angle tenderness bilaterally/unilaterally
- Buffalo hump
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- A pelvic/adnexal mass may be palpated
- Inflamed mucosa
- Clear/(color), foul-smelling/odorless penile/vaginal discharge
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Patient is usually oriented to persons, place, and time
- Altered mental status
- Glasgow coma scale is ___ / 15
- Clonus may be present
- Hyperreflexia / hyporeflexia / areflexia
- Positive (abnormal) Babinski / plantar reflex unilaterally/bilaterally
- Muscle rigidity
- Proximal/distal muscle weakness unilaterally/bilaterally
- ____ (finding) suggestive of cranial nerve ___ (roman numerical) deficit (e.g. Dilated pupils suggestive of CN III deficit)
- Unilateral/bilateral upper/lower extremity weakness
- Unilateral/bilateral sensory loss in the upper/lower extremity
- Positive straight leg raise test
- Abnormal gait (describe gait: e.g. ataxic (cerebellar) gait / steppage gait / waddling gait / choeiform gait / Parkinsonian gait / sensory gait)
- Positive/negative Trendelenburg sign
- Unilateral/bilateral tremor (describe tremor, e.g. at rest, pill-rolling)
- Normal finger-to-nose test / Dysmetria
- Absent/present dysdiadochokinesia (palm tapping test)
Extremities
- Extremities examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Clubbing
- Cyanosis
- Pitting/non-pitting edema of the upper/lower extremities
- Muscle atrophy
- Fasciculations in the upper/lower extremity
|
Psoriatic arthritis Microchapters | |
|
Diagnosis | |
|---|---|
|
Treatment | |
|
Case Studies | |
|
Psoriatic arthritis physical examination On the Web | |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Psoriatic arthritis physical examination | |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Psoriatic arthritis physical examination | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Chandrakala Yannam, MD [3]
Overview
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with psoriatic arthritis usually appear normal.
Vital signs
- Vital signs are within normal limits in patients with psoriatic arthritis.
- Physical examination of a patient with psoriatic arthritis may include:
- Joint involvement:[6][7]
- Joint tenderness
- Joint swelling may or may not be present
- Redness and warmth
- Patterns of joint involvement in psoriatic arthritis may include according to moll and wright :
- Distal arthritis: Involving mostly DIP joints, may be symmetric or asymmetric. It may involve multiple joints or only few joints.
- Asymmetric oligoarthritis: Most common pattern can be seen in psoriatic arthritis. It is characterized by asymmetric involvement of less than 5 small or large joints.
- Symmetric polyarthritis
- Arthritis mutilans: Resorption of phalanges, metatarsals and, metacarpals.
- Spondylitis
- Sacroiliitis
- Joint effusion
- Achilles tendinitis[8]
- Dactylitis: sausage digit due to swelling of the whole finger or toe.[9]
- Skin:[1][2]
- Psoriatic arthritis may occur after the onset of psoriasis in most of the patients. However, in some cases, arthritis precede psoriasis. The phenotypes of skin psoriasis that are associated with an increased risk of psoriatic arthritis are the lesions in the scalp, nail, intergluteal, and perianal regions.[3]
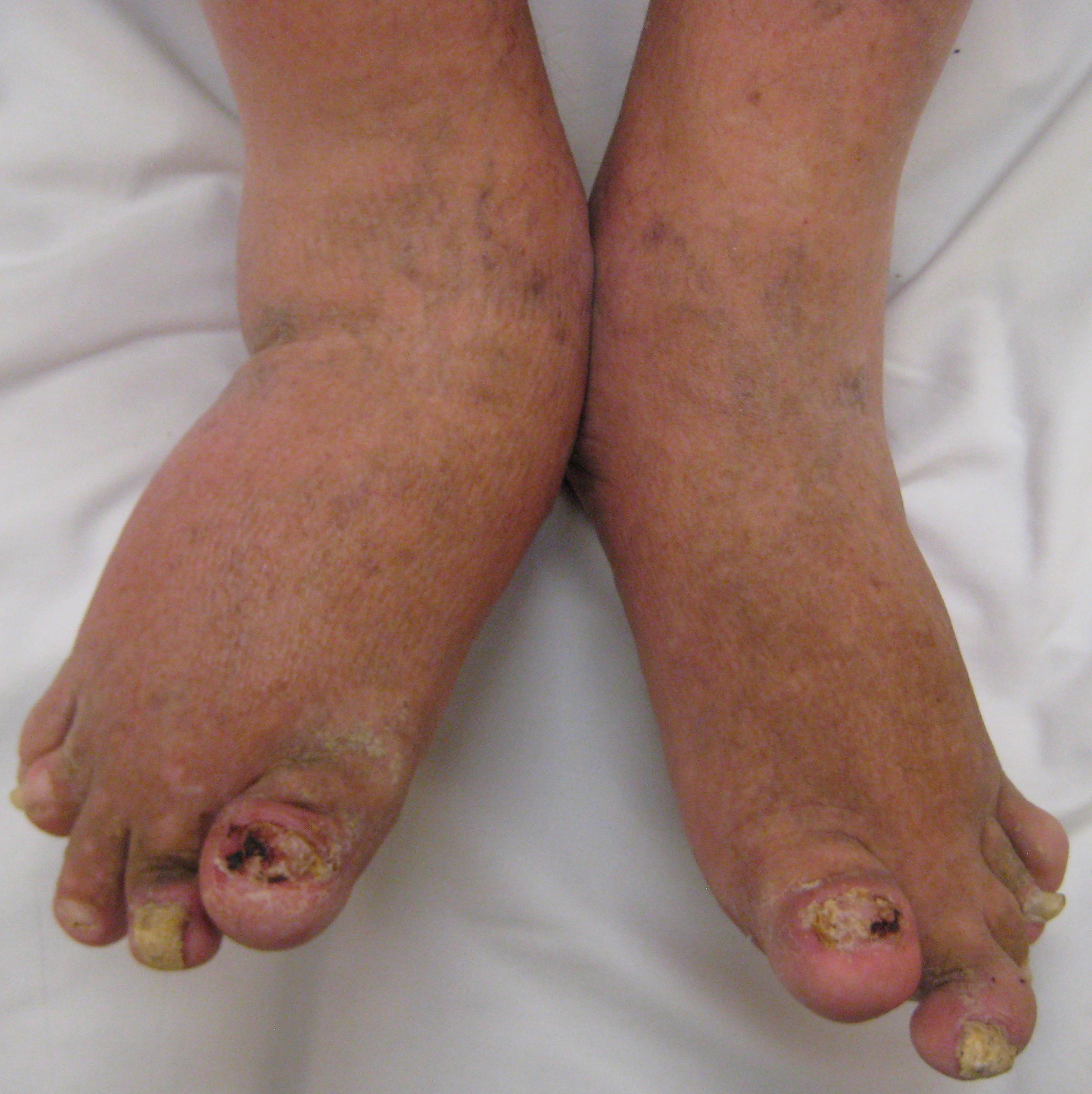
- Nails:[10][11]
- Nail pits
- Onycholysis
- Subungual hyperkeratosis
- Splinter hemorrhages
- Beau lines
- Leukonychia
- Oil drop patches
- Nail crumbling
- Nail destruction
- Involvement of eyes:[4][5]
- Edema of hands or feet: Swelling of hands and feet which is asymmetrical with pitting edema may be found in some cases.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Elkayam O, Ophir J, Yaron M, Caspi D (2000). "Psoriatic arthritis: interrelationships between skin and joint manifestations related to onset, course and distribution". Clin. Rheumatol. 19 (4): 301–5. PMID 10941813.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wright V, Roberts MC, Hill AG (1979). "Dermatological manifestations in psoriatic arthritis: a follow-up study". Acta Derm. Venereol. 59 (3): 235–40. PMID 87081.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wilson FC, Icen M, Crowson CS, McEvoy MT, Gabriel SE, Kremers HM (February 2009). "Incidence and clinical predictors of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: a population-based study". Arthritis Rheum. 61 (2): 233–9. doi:10.1002/art.24172. PMC 3061343. PMID 19177544.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lambert JR, Wright V (August 1976). "Eye inflammation in psoriatic arthritis". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 35 (4): 354–6. PMC 1007395. PMID 970993.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Abbouda A, Abicca I, Fabiani C, Scappatura N, Peña-García P, Scrivo R, Priori R, Paroli MP (2017). "Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis-Related Uveitis: Different Ophthalmological Manifestations and Ocular Inflammation Features". Semin Ophthalmol. 32 (6): 715–720. doi:10.3109/08820538.2016.1170161. PMID 27419848.
- ↑ Moll JM, Wright V (1973). "Psoriatic arthritis". Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 3 (1): 55–78. PMID 4581554.
- ↑ Scarpa R, Peluso R, Atteno M (2007). "Clinical presentation of psoriatic arthritis". Reumatismo. 59 Suppl 1: 49–51. PMID 17828344.
- ↑ De Simone C, Guerriero C, Giampetruzzi AR, Costantini M, Di Gregorio F, Amerio P, Giampietruzzi AR (August 2003). "Achilles tendinitis in psoriasis: clinical and sonographic findings". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 49 (2): 217–22. PMID 12894068.
- ↑ Brockbank JE, Stein M, Schentag CT, Gladman DD (February 2005). "Dactylitis in psoriatic arthritis: a marker for disease severity?". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64 (2): 188–90. doi:10.1136/ard.2003.018184. PMC 1755375. PMID 15271771.
- ↑ Sobolewski P, Walecka I, Dopytalska K (2017). "Nail involvement in psoriatic arthritis". Reumatologia. 55 (3): 131–135. doi:10.5114/reum.2017.68912. PMC 5534507. PMID 28769136.
- ↑ Lai TL, Pang HT, Cheuk YY, Yip ML (August 2016). "Psoriatic nail involvement and its relationship with distal interphalangeal joint disease". Clin. Rheumatol. 35 (8): 2031–2037. doi:10.1007/s10067-016-3319-5. PMID 27251673.
- ↑ Cantini F, Salvarani C, Olivieri I, Macchioni L, Niccoli L, Padula A, Falcone C, Boiardi L, Bozza A, Barozzi L, Pavlica P (2001). "Distal extremity swelling with pitting edema in psoriatic arthritis: a case-control study". Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 19 (3): 291–6. PMID 11407082.