Buergers disease
For patient information click here
| Buerger's disease | ||
 | ||
|---|---|---|
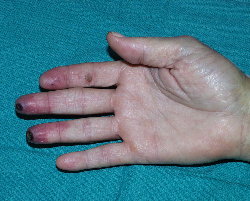
| Buerger's Disease of the Hand | ||
| ICD-10 | I73.1 | |
| ICD-9 | 443.1 | |
| OMIM | 211480 | |
| DiseasesDB | 1762 | |
| MeSH | C14.907.137.870 | |
|
Buerger's disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Buergers disease On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Buergers disease |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Thromboangiitis obliterans
- Not to be confused with Berger's disease (IgA nephropathy)
Overview
Features
There is a recurrent acute and chronic inflammation and thrombosis of arteries and veins of the hands and feet. The main symptom is pain in the affected areas. Ulcerations and gangrene in the extremities are common complications, often resulting in the need for amputation of the involved extremity.
Diagnosis
A concrete diagnosis of thromboangiitis obliterans is often difficult as it relies heavily on exclusion of the conditions. The commonly followed diagnostic criteria are below although the criteria tend to differ slightly from author to author. Olin (2000) proposes the following criteria:[1]
- Age younger than 45 years
- Current (or recent) history of tobacco use
- Presence of distal extremity ischemia (indicated by claudication, pain at rest, ischemic ulcers or gangrene) documented by noninvasive vascular testing such as ultrasound
- Exclusion of autoimmune diseases, hypercoagulable states, and diabetes mellitus by laboratory tests.
- Exclusion of a proximal source of emboli by echocardiography and arteriography
- Consistent arteriographic findings in the clinically involved and noninvolved limbs.
Diagnostic Findings
-
Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's disease): Arterial vascular disease associated with smoking. Note the blackened tips of middle and pinky fingers.
(Image courtesy of Charlie Goldberg, M.D.)
Treatment
Symptoms are treated as there is no treatment for the disease. Cessation of tobacco use may slow any further progression of the disease. Vascular surgery can sometimes be helpful in treating limbs with poor perfusion secondary to this disease. Use of vascular growth factor and stem cell injections have been showing promise in clinical studies.
Prognosis
Amputation is common and more severe in patients who continue to use tobacco. It often leads to vascular insufficiency. Buerger's is rarely immediately fatal, but rather a life shortening disease.
References
- ↑ Olin JW. Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease). N Engl J Med 2000;343:864-9. PMID 10995867.
External Links
de:Endangiitis obliterans
he:מחלת בירגר
nl:Ziekte van Buerger
sv:Morbus Buerger
