Portal hypertension pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The exact [[pathogenesis]] in portal hypertension is disturbance in normal physiology of [[Portocaval anastomoses|portocaval circulation]]. The main factors that affect the [[pressure gradient]] in [[blood vessels]] are [[Blood flow|blood flow (Q)]] and [[Blood vessel|vessel]] radius (r) in a direct and inverse way, respectively. Portal hypertension is related to elevation of [[Portal venous system|portal vasculature]] resistance. Peripheral [[vasodilatation]] is the basis for decreased systemic [[vascular resistance]] and [[mean arterial pressure]], plasma volume expansion, elevated [[splanchnic]] [[blood flow]], and elevated [[cardiac index]]. Fourteen different [[genes]] are involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of portal hypertension. [[Homozygous]] [[missense mutation]] in [[DGUOK]] gene found to be related with [[non-cirrhotic portal hypertension]]. On [[gross pathology]], [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]], [[splenomegaly]], and [[esophageal varices]] are characteristic findings in portal hypertension. The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in portal hypertension are related to [[Cirrhosis (patient information)|cirrhosis]], [[esophageal varices]], [[Hepatic amyloidosis with intrahepatic cholestasis|hepatic amyloidosis]], and congestive [[hepatopathy]] due to [[heart failure]] or [[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]. | The exact [[pathogenesis]] in portal hypertension is disturbance in normal physiology of [[Portocaval anastomoses|portocaval circulation]]. The main factors that affect the [[pressure gradient]] in [[blood vessels]] are [[Blood flow|blood flow (Q)]] and [[Blood vessel|vessel]] radius (r) in a direct and inverse way, respectively. Portal hypertension is related to elevation of [[Portal venous system|portal vasculature]] resistance. Peripheral [[vasodilatation]] is the basis for decreased systemic [[vascular resistance]] and [[mean arterial pressure]], plasma volume expansion, elevated [[splanchnic]] [[blood flow]], and elevated [[cardiac index]]. Fourteen different [[genes]] are involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of portal hypertension. [[Homozygous]] [[missense mutation]] in [[DGUOK]] gene is found to be related with [[non-cirrhotic portal hypertension]]. On [[gross pathology]], [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]], [[splenomegaly]], and [[esophageal varices]] are characteristic findings in portal hypertension. The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in portal hypertension are related to [[Cirrhosis (patient information)|cirrhosis]], [[esophageal varices]], [[Hepatic amyloidosis with intrahepatic cholestasis|hepatic amyloidosis]], and congestive [[hepatopathy]] due to [[heart failure]] or [[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
=== Physiology === | === Physiology === | ||
* [[Ohm's law]] in vascular system defines the [[pressure gradient]] (ΔP) in [[blood vessels]] as equal to product of [[Blood flow|blood flow (Q)]] and [[Vascular resistance|vascular resistance (R)]]: | * [[Ohm's law]] in vascular system defines the [[pressure gradient]] (ΔP) in [[blood vessels]] as equal to product of [[Blood flow|blood flow (Q)]] and [[Vascular resistance|vascular resistance (R)]]: | ||
[[image:1111.jpg|center]] | |||
* Vascular resistance (R) has to be measured through Pouseuille’s law formula: | * Vascular resistance (R) has to be measured through Pouseuille’s law formula: | ||
[[image:1dffhdfg.jpg|center]] | |||
η= [[Viscosity index|Viscosity]]; L= Length of [[vessel]]; r= Radius of [[vessel]]; π=22/7</small> | η= [[Viscosity index|Viscosity]]; L= Length of [[vessel]]; r= Radius of [[vessel]]; π=22/7</small> | ||
* When the (R) measurement formula is integrated in [[Ohm's law]] it becomes as the following: | * When the (R) measurement formula is integrated in [[Ohm's law]] it becomes as the following: | ||
[[image:1svsdfv.jpg|center]] | |||
* Length of [[blood vessels]] (L) never differs in normal [[physiologic]] condition. | * Length of [[blood vessels]] (L) never differs in normal [[physiologic]] condition. | ||
* Blood [[viscosity]] (η) does not change, unless dramatic changes in [[hematocrit]] happen. | * Blood [[viscosity]] (η) does not change, unless dramatic changes in [[hematocrit]] happen. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 32: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{Family tree/start}} | {{Family tree/start}} | ||
{{Family tree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | | | A01 | | | | | | A02 | | A03 | | |A01=• [[Anatomical]] (irreversible component)<br>• Functional/ | {{Family tree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | | | A01 | | | | | | A02 | | A03 | | |A01=• [[Anatomical]] (irreversible component)<br>• Functional/vascular tone (reversible component)|A02=• Opening of pre-existing vascular channels<br>• Formation of new vascular channels|A03=• Systemic [[vasodilation]] ('''r''')<br>• Increasing plasma volume ('''Q''')}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | |}} | {{Family tree | | | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | |}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | B01 | | | | | | B02 | | |!| | | |B01=lntra-[[hepatic]] resistance ('''r''')|B02= Portosystemic collaterals ('''Q''')}} | {{Family tree | | | B01 | | | | | | B02 | | |!| | | |B01=lntra-[[hepatic]] resistance ('''r''')|B02= Portosystemic collaterals ('''Q''')}} | ||
| Line 47: | Line 41: | ||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | |}} | {{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | |}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | E01 | | | | | | |E01='''Portal hypertension'''}} | {{Family tree | | | | | | | | | | | E01 | | | | | | |E01='''Portal hypertension'''}} | ||
{{Family tree/end}} | {{Family tree/end}} | ||
| Line 59: | Line 52: | ||
*** Portal hypertension occurs when [[compliance]] is decreased and [[blood flow]] is increased in [[liver]].<ref name="pmid5543903">{{cite journal |vauthors=Greenway CV, Stark RD |title=Hepatic vascular bed |journal=Physiol. Rev. |volume=51 |issue=1 |pages=23–65 |year=1971 |pmid=5543903 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** Portal hypertension occurs when [[compliance]] is decreased and [[blood flow]] is increased in [[liver]].<ref name="pmid5543903">{{cite journal |vauthors=Greenway CV, Stark RD |title=Hepatic vascular bed |journal=Physiol. Rev. |volume=51 |issue=1 |pages=23–65 |year=1971 |pmid=5543903 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*** Pre-[[hepatic]] and post-[[hepatic]] portal hypertension are due to some secondary obstruction before or after [[liver]] [[vasculature]], respectively.<ref>{{cite book | last = Schiff | first = Eugene | title = Schiff's diseases of the liver | publisher = John Wiley & Sons | location = Chichester, West Sussex, UK | year = 2012 | isbn = 9780470654682 }}</ref> | *** Pre-[[hepatic]] and post-[[hepatic]] portal hypertension are due to some secondary obstruction before or after [[liver]] [[vasculature]], respectively.<ref>{{cite book | last = Schiff | first = Eugene | title = Schiff's diseases of the liver | publisher = John Wiley & Sons | location = Chichester, West Sussex, UK | year = 2012 | isbn = 9780470654682 }}</ref> | ||
*** [[Schistosomiasis]] causes both pre-[[sinusoidal]] and [[sinusoidal]] pathologies. The [[granulomas]] compress the pre-[[sinusoidal]] [[veins]]. In late stages [[sinusoidal]] resistance also increased.<ref name="BekerValencia-Parparcén1968">{{cite journal|last1=Beker|first1=Simón G.|last2=Valencia-Parparcén|first2=Joel|title=Portal hypertension syndrome|journal=The American Journal of Digestive Diseases|volume=13|issue=12|year=1968|pages=1047–1054|issn=0002-9211|doi=10.1007/BF02233549}}</ref> | *** [[Schistosomiasis]] causes both pre-[[sinusoidal]] and [[sinusoidal]] pathologies. The [[granulomas]] compress the pre-[[sinusoidal]] [[veins]]. In late stages [[sinusoidal]] resistance is also increased.<ref name="BekerValencia-Parparcén1968">{{cite journal|last1=Beker|first1=Simón G.|last2=Valencia-Parparcén|first2=Joel|title=Portal hypertension syndrome|journal=The American Journal of Digestive Diseases|volume=13|issue=12|year=1968|pages=1047–1054|issn=0002-9211|doi=10.1007/BF02233549}}</ref> | ||
*** [[Alcoholic hepatitis]] causes both [[sinusoidal]] and post-[[sinusoidal]] pathologies.<ref name="pmid13976646">{{cite journal |vauthors=SCHAFFNER F, POPER H |title=Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=44 |issue= |pages=239–42 |year=1963 |pmid=13976646 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid5775031">{{cite journal |vauthors=Reynolds TB, Hidemura R, Michel H, Peters R |title=Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=70 |issue=3 |pages=497–506 |year=1969 |pmid=5775031 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** [[Alcoholic hepatitis]] causes both [[sinusoidal]] and post-[[sinusoidal]] pathologies.<ref name="pmid13976646">{{cite journal |vauthors=SCHAFFNER F, POPER H |title=Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=44 |issue= |pages=239–42 |year=1963 |pmid=13976646 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid5775031">{{cite journal |vauthors=Reynolds TB, Hidemura R, Michel H, Peters R |title=Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=70 |issue=3 |pages=497–506 |year=1969 |pmid=5775031 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*** [[Hepatic]] vascular [[endothelium]] synthesizes and secretes both [[vasodilator]] (e.g., [[nitric oxide]], [[Prostacyclin|prostacyclins]]) and [[vasoconstrictor]] (e.g., [[endothelin]] and [[Prostanoid|prostanoids]]) [[chemicals]].<ref name="pmid1874796">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rubanyi GM |title=Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors |journal=J. Cell. Biochem. |volume=46 |issue=1 |pages=27–36 |year=1991 |pmid=1874796 |doi=10.1002/jcb.240460106 |url=}}</ref><ref name="EpsteinVane1990">{{cite journal|last1=Epstein|first1=Franklin H.|last2=Vane|first2=John R.|last3=Änggård|first3=Erik E.|last4=Botting|first4=Regina M.|title=Regulatory Functions of the Vascular Endothelium|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=323|issue=1|year=1990|pages=27–36|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJM199007053230106}}</ref> | *** [[Hepatic]] vascular [[endothelium]] synthesizes and secretes both [[vasodilator]] (e.g., [[nitric oxide]], [[Prostacyclin|prostacyclins]]) and [[vasoconstrictor]] (e.g., [[endothelin]] and [[Prostanoid|prostanoids]]) [[chemicals]].<ref name="pmid1874796">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rubanyi GM |title=Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors |journal=J. Cell. Biochem. |volume=46 |issue=1 |pages=27–36 |year=1991 |pmid=1874796 |doi=10.1002/jcb.240460106 |url=}}</ref><ref name="EpsteinVane1990">{{cite journal|last1=Epstein|first1=Franklin H.|last2=Vane|first2=John R.|last3=Änggård|first3=Erik E.|last4=Botting|first4=Regina M.|title=Regulatory Functions of the Vascular Endothelium|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=323|issue=1|year=1990|pages=27–36|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJM199007053230106}}</ref> | ||
*** Increased resistance due to the elevation of vascular tone | *** Increased resistance due to the elevation of vascular tone may be caused by excess of [[vasoconstrictors]] or lack of [[vasodilators]]. | ||
*** It is postulated that in [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]] the [[nitric oxide]] level is lower and the response to [[endothelin]] response in [[myofibrils]] is higher than normal [[liver]].<ref name="pmid8707268">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rockey DC, Weisiger RA |title=Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance |journal=Hepatology |volume=24 |issue=1 |pages=233–40 |year=1996 |pmid=8707268 |doi=10.1002/hep.510240137 |url=}}</ref> | *** It is postulated that in [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]] the [[nitric oxide]] level is lower and the response to [[endothelin]] response in [[myofibrils]] is higher than normal [[liver]].<ref name="pmid8707268">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rockey DC, Weisiger RA |title=Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance |journal=Hepatology |volume=24 |issue=1 |pages=233–40 |year=1996 |pmid=8707268 |doi=10.1002/hep.510240137 |url=}}</ref> | ||
** '''Portosystemic collateral resistance''' | ** '''Portosystemic collateral resistance''' | ||
*** [[Collateral]] formation is the consequence of portal hypertension | *** [[Collateral]] formation is the consequence of portal hypertension which is also the main contributor to [[esophageal varices]]. | ||
*** The main purpose of the [[collaterals]] is to decompress and bypass the [[portal]] blood flow. | *** The main purpose of the [[collaterals]] is to decompress and bypass the [[portal]] blood flow. | ||
*** However, the resistance in [[collaterals]] is less than the normal liver. | *** However, the resistance in [[collaterals]] is less than the normal liver. | ||
*** Thus, [[Portocaval anastomoses|portosystemic collaterals]] can not lead to a complete decompression. | *** Thus, [[Portocaval anastomoses|portosystemic collaterals]] can not lead to a complete decompression. | ||
*** [[Portocaval anastomoses|Portosystemic collateraling]] occurs between the [[short gastric]], [[coronary]] veins, and the [[esophageal]] [[azygos]] and the [[intercostal veins]]; superior | *** [[Portocaval anastomoses|Portosystemic collateraling]] occurs between the [[short gastric]], [[coronary]] veins, and the [[esophageal]] [[azygos]] and the [[intercostal veins]]; the superior, the middle, and the inferior [[Hemorrhoidal plexus|hemorrhoidal veins]]; the [[Paraumbilical veins|paraumbilical venous plexus]] and the venous system of abdominal organs juxtaposed with the retroperitoneum and abdominal wall; the left renal vein, the splanchnic, the adrenal, and the spermatic veins.<ref name="pmid1415713">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mosca P, Lee FY, Kaumann AJ, Groszmann RJ |title=Pharmacology of portal-systemic collaterals in portal hypertensive rats: role of endothelium |journal=Am. J. Physiol. |volume=263 |issue=4 Pt 1 |pages=G544–50 |year=1992 |pmid=1415713 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
==== Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertension ==== | ==== Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertension ==== | ||
| Line 85: | Line 78: | ||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
*[[Genes]] are involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of portal hypertension include the following: | *[[Genes]] are involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of portal hypertension include the following: | ||
{| | {| | ||
! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Gene | |||
!OMIM number | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |OMIM number | ||
!Chromosome | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Chromosome | ||
!Function | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Function | ||
!Gene expression in portal hypertension | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Gene expression in portal hypertension | ||
!Notes | ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" + |Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[DGUOK|Deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[DGUOK|Deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK)]]''' | ||
|601465 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |601465 | ||
|2p13.1 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |2p13.1 | ||
|[[DNA replication]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |[[DNA replication]] | ||
|[[Point mutation]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |[[Point mutation]] | ||
|[[Mutation]] leads to:<ref name="pmid11687800">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mandel H, Szargel R, Labay V, Elpeleg O, Saada A, Shalata A, Anbinder Y, Berkowitz D, Hartman C, Barak M, Eriksson S, Cohen N |title=The deoxyguanosine kinase gene is mutated in individuals with depleted hepatocerebral mitochondrial DNA |journal=Nat. Genet. |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=337–41 |year=2001 |pmid=11687800 |doi=10.1038/ng746 |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |[[Mutation]] leads to:<ref name="pmid11687800">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mandel H, Szargel R, Labay V, Elpeleg O, Saada A, Shalata A, Anbinder Y, Berkowitz D, Hartman C, Barak M, Eriksson S, Cohen N |title=The deoxyguanosine kinase gene is mutated in individuals with depleted hepatocerebral mitochondrial DNA |journal=Nat. Genet. |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=337–41 |year=2001 |pmid=11687800 |doi=10.1038/ng746 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* [[Liver failure]] | * [[Liver failure]] | ||
* [[Neurologic]] abnormalities | * [[Neurologic]] abnormalities | ||
| Line 106: | Line 99: | ||
* [[Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension]] | * [[Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Adenosine deaminase|Adenosine deaminase (ADA)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Adenosine deaminase|Adenosine deaminase (ADA)]]''' | ||
|608958 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |608958 | ||
|20q13.12 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |20q13.12 | ||
|Irreversible [[deamination]] of [[adenosine]] and [[deoxyadenosine]] in the [[Purine metabolism|purine catabolic pathway]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Irreversible [[deamination]] of [[adenosine]] and [[deoxyadenosine]] in the [[Purine metabolism|purine catabolic pathway]] | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015">{{cite journal|last1=Kotani|first1=Kohei|last2=Kawabe|first2=Joji|last3=Morikawa|first3=Hiroyasu|last4=Akahoshi|first4=Tomohiko|last5=Hashizume|first5=Makoto|last6=Shiomi|first6=Susumu|title=Comprehensive Screening of Gene Function and Networks by DNA Microarray Analysis in Japanese Patients with Idiopathic Portal Hypertension|journal=Mediators of Inflammation|volume=2015|year=2015|pages=1–10|issn=0962-9351|doi=10.1155/2015/349215}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015">{{cite journal|last1=Kotani|first1=Kohei|last2=Kawabe|first2=Joji|last3=Morikawa|first3=Hiroyasu|last4=Akahoshi|first4=Tomohiko|last5=Hashizume|first5=Makoto|last6=Shiomi|first6=Susumu|title=Comprehensive Screening of Gene Function and Networks by DNA Microarray Analysis in Japanese Patients with Idiopathic Portal Hypertension|journal=Mediators of Inflammation|volume=2015|year=2015|pages=1–10|issn=0962-9351|doi=10.1155/2015/349215}}</ref> | ||
|Some roles in modulating tissue response to [[Interleukin 13|IL-13]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5; + |Some roles in modulating tissue response to [[Interleukin 13|IL-13]] | ||
The main effects of [[IL-13]] are:<ref name="pmid12897202">{{cite journal |vauthors=Blackburn MR, Lee CG, Young HW, Zhu Z, Chunn JL, Kang MJ, Banerjee SK, Elias JA |title=Adenosine mediates IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling in the lung and interacts in an IL-13-adenosine amplification pathway |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=112 |issue=3 |pages=332–44 |year=2003 |pmid=12897202 |pmc=166289 |doi=10.1172/JCI16815 |url=}}</ref> | The main effects of [[IL-13]] are:<ref name="pmid12897202">{{cite journal |vauthors=Blackburn MR, Lee CG, Young HW, Zhu Z, Chunn JL, Kang MJ, Banerjee SK, Elias JA |title=Adenosine mediates IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling in the lung and interacts in an IL-13-adenosine amplification pathway |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=112 |issue=3 |pages=332–44 |year=2003 |pmid=12897202 |pmc=166289 |doi=10.1172/JCI16815 |url=}}</ref> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 111: | ||
* [[Fibrosis]] | * [[Fibrosis]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Phospholipase A2|Phospholipase A2 (PL2G10)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Phospholipase A2|Phospholipase A2 (PL2G10)]]''' | ||
|603603 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |603603 | ||
|16p13.12 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |16p13.12 | ||
|Catalyzing the release of [[Fatty acid|fatty acids]] from [[phospholipids]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Catalyzing the release of [[Fatty acid|fatty acids]] from [[phospholipids]] | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
|Identifier of PL2G10 expression: | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Identifier of PL2G10 expression: | ||
* [[Arachidonic acid|Arachidonic acid (AA)]] | * [[Arachidonic acid|Arachidonic acid (AA)]] | ||
* [[Prostaglandins|Prostaglandins (PG)]] | * [[Prostaglandins|Prostaglandins (PG)]] | ||
* [[Leukotrienes|Leukotrienes (LT)]] | * [[Leukotrienes|Leukotrienes (LT)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[CYP4F3|Cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily F, polypeptide 3 (CYP4F3)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[CYP4F3|Cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily F, polypeptide 3 (CYP4F3)]]''' | ||
|601270 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |601270 | ||
|19p13.12 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |19p13.12 | ||
|Catalyzing the omega-[[hydroxylation]] of [[Leukotriene B4|leukotriene B4 (LTB4)]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Catalyzing the omega-[[hydroxylation]] of [[Leukotriene B4|leukotriene B4 (LTB4)]] | ||
|Increased<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Increased<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
| - | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Glutathione peroxidase|Glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Glutathione peroxidase|Glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3)]]''' | ||
|138321 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |138321 | ||
|5q33.1 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |5q33.1 | ||
|Reduction of [[glutathione]] which reduce:<ref name="pmid3015592">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chambers I, Frampton J, Goldfarb P, Affara N, McBain W, Harrison PR |title=The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA |journal=EMBO J. |volume=5 |issue=6 |pages=1221–7 |year=1986 |pmid=3015592 |pmc=1166931 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduction of [[glutathione]] which reduce:<ref name="pmid3015592">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chambers I, Frampton J, Goldfarb P, Affara N, McBain W, Harrison PR |title=The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA |journal=EMBO J. |volume=5 |issue=6 |pages=1221–7 |year=1986 |pmid=3015592 |pmc=1166931 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* [[Hydrogen peroxide]] | * [[Hydrogen peroxide]] | ||
* [[Organic peroxide|Organic hydroperoxide]] | * [[Organic peroxide|Organic hydroperoxide]] | ||
* [[Lipid peroxidation|Lipid peroxides]] | * [[Lipid peroxidation|Lipid peroxides]] | ||
|Increased<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Increased<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
|Protects various organs against [[oxidative stress]]:<ref name="pmid1339300">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chu FF, Esworthy RS, Doroshow JH, Doan K, Liu XF |title=Expression of plasma glutathione peroxidase in human liver in addition to kidney, heart, lung, and breast in humans and rodents |journal=Blood |volume=79 |issue=12 |pages=3233–8 |year=1992 |pmid=1339300 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Protects various organs against [[oxidative stress]]:<ref name="pmid1339300">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chu FF, Esworthy RS, Doroshow JH, Doan K, Liu XF |title=Expression of plasma glutathione peroxidase in human liver in addition to kidney, heart, lung, and breast in humans and rodents |journal=Blood |volume=79 |issue=12 |pages=3233–8 |year=1992 |pmid=1339300 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* [[Liver]] | * [[Liver]] | ||
* [[Kidney]] | * [[Kidney]] | ||
* [[Breast]] | * [[Breast]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Leukotriene B4|Leukotriene B4 (LTB4)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Leukotriene B4|Leukotriene B4 (LTB4)]]''' | ||
|601531 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |601531 | ||
|14q12 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |14q12 | ||
|Include:<ref name="pmid9177352">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yokomizo T, Izumi T, Chang K, Takuwa Y, Shimizu T |title=A G-protein-coupled receptor for leukotriene B4 that mediates chemotaxis |journal=Nature |volume=387 |issue=6633 |pages=620–4 |year=1997 |pmid=9177352 |doi=10.1038/42506 |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Include:<ref name="pmid9177352">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yokomizo T, Izumi T, Chang K, Takuwa Y, Shimizu T |title=A G-protein-coupled receptor for leukotriene B4 that mediates chemotaxis |journal=Nature |volume=387 |issue=6633 |pages=620–4 |year=1997 |pmid=9177352 |doi=10.1038/42506 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Increasing intra-cellular [[calcium]] | * Increasing intra-cellular [[calcium]] | ||
* Elevation of [[Inositol-3-phosphate synthase|inositol 3-phosphate (IP3)]] | * Elevation of [[Inositol-3-phosphate synthase|inositol 3-phosphate (IP3)]] | ||
* Inhibition of [[Adenylate cyclase|adenylyl cyclase]] | * Inhibition of [[Adenylate cyclase|adenylyl cyclase]] | ||
|Mutated | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Mutated | ||
|Increase [[blood flow]] to target [[tissue]] (esp. [[heart]]) about 4 times more.<ref name="pmid16293697">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bäck M, Bu DX, Bränström R, Sheikine Y, Yan ZQ, Hansson GK |title=Leukotriene B4 signaling through NF-kappaB-dependent BLT1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis and intimal hyperplasia |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=102 |issue=48 |pages=17501–6 |year=2005 |pmid=16293697 |pmc=1297663 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0505845102 |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Increase [[blood flow]] to target [[tissue]] (esp. [[heart]]) about 4 times more.<ref name="pmid16293697">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bäck M, Bu DX, Bränström R, Sheikine Y, Yan ZQ, Hansson GK |title=Leukotriene B4 signaling through NF-kappaB-dependent BLT1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis and intimal hyperplasia |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=102 |issue=48 |pages=17501–6 |year=2005 |pmid=16293697 |pmc=1297663 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0505845102 |url=}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Prostaglandin E2 receptor|Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (PTGER2)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Prostaglandin E2 receptor|Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (PTGER2)]]''' | ||
|176804 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |176804 | ||
|14q22.1 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |14q22.1 | ||
|Various biological activities in diverse tissues | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Various biological activities in diverse tissues | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
| - | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Endothelin|Endothelin (EDN1)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Endothelin|Endothelin (EDN1)]]''' | ||
|131240 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |131240 | ||
|6p24.1 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |6p24.1 | ||
|[[Vasoconstriction]]<ref name="pmid15148269">{{cite journal |vauthors=Campia U, Cardillo C, Panza JA |title=Ethnic differences in the vasoconstrictor activity of endogenous endothelin-1 in hypertensive patients |journal=Circulation |volume=109 |issue=25 |pages=3191–5 |year=2004 |pmid=15148269 |doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000130590.24107.D3 |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |[[Vasoconstriction]]<ref name="pmid15148269">{{cite journal |vauthors=Campia U, Cardillo C, Panza JA |title=Ethnic differences in the vasoconstrictor activity of endogenous endothelin-1 in hypertensive patients |journal=Circulation |volume=109 |issue=25 |pages=3191–5 |year=2004 |pmid=15148269 |doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000130590.24107.D3 |url=}}</ref> | ||
|Increased | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Increased | ||
|The most powerful [[vasoconstrictor]] known<ref name="pmid2670930">{{cite journal |vauthors=Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Takuwa Y, Mitsui Y, Kobayashi M, Masaki T |title=The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=264 |issue=25 |pages=14954–9 |year=1989 |pmid=2670930 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |The most powerful [[vasoconstrictor]] known<ref name="pmid2670930">{{cite journal |vauthors=Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Takuwa Y, Mitsui Y, Kobayashi M, Masaki T |title=The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=264 |issue=25 |pages=14954–9 |year=1989 |pmid=2670930 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Endothelin receptor type A|Endothelin receptor type A (EDNRA)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Endothelin receptor type A|Endothelin receptor type A (EDNRA)]]''' | ||
|131243 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |131243 | ||
|4q31.22-q31.23 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |4q31.22-q31.23 | ||
|[[Vasoconstriction]] through binding to [[endothelin]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |[[Vasoconstriction]] through binding to [[endothelin]] | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
|Directly related to [[hypertension]] in patients<ref name="pmid15148269" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Directly related to [[hypertension]] in patients<ref name="pmid15148269" /> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Natriuretic peptides|Natriuretic peptide receptor 3 (NPR3)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Natriuretic peptides|Natriuretic peptide receptor 3 (NPR3)]]''' | ||
|108962 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |108962 | ||
|5p13.3 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |5p13.3 | ||
|Maintenance of: | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Maintenance of: | ||
* [[Blood pressure]] | * [[Blood pressure]] | ||
* [[Extracellular fluid|Extracellular fluid volume]] | * [[Extracellular fluid|Extracellular fluid volume]] | ||
|Increased<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Increased<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
|Released from [[heart muscle]] in response to increase in wall tension. [[Atrial natriuretic peptide|ANP]] can modulate [[blood pressure]] by binding to NPR3<ref name="pmid7477288">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lopez MJ, Wong SK, Kishimoto I, Dubois S, Mach V, Friesen J, Garbers DL, Beuve A |title=Salt-resistant hypertension in mice lacking the guanylyl cyclase-A receptor for atrial natriuretic peptide |journal=Nature |volume=378 |issue=6552 |pages=65–8 |year=1995 |pmid=7477288 |doi=10.1038/378065a0 |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Released from [[heart muscle]] in response to increase in wall tension. [[Atrial natriuretic peptide|ANP]] can modulate [[blood pressure]] by binding to NPR3<ref name="pmid7477288">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lopez MJ, Wong SK, Kishimoto I, Dubois S, Mach V, Friesen J, Garbers DL, Beuve A |title=Salt-resistant hypertension in mice lacking the guanylyl cyclase-A receptor for atrial natriuretic peptide |journal=Nature |volume=378 |issue=6552 |pages=65–8 |year=1995 |pmid=7477288 |doi=10.1038/378065a0 |url=}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Cluster of differentiation|Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Cluster of differentiation|Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44)]]''' | ||
|107269 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |107269 | ||
|11p13 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |11p13 | ||
| | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | | ||
* [[Lymphocyte]] activation | * [[Lymphocyte]] activation | ||
* [[Lymph node]] homing<ref name="pmid1694723">{{cite journal |vauthors=Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B |title=CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate |journal=Cell |volume=61 |issue=7 |pages=1303–13 |year=1990 |pmid=1694723 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * [[Lymph node]] homing<ref name="pmid1694723">{{cite journal |vauthors=Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B |title=CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate |journal=Cell |volume=61 |issue=7 |pages=1303–13 |year=1990 |pmid=1694723 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
| | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | | ||
* Related to [[Fibroblast growth factor|fibroblast growth factor (FGF)]]<ref name="pmid12697740">{{cite journal |vauthors=Nedvetzki S, Golan I, Assayag N, Gonen E, Caspi D, Gladnikoff M, Yayon A, Naor D |title=A mutation in a CD44 variant of inflammatory cells enhances the mitogenic interaction of FGF with its receptor |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=111 |issue=8 |pages=1211–20 |year=2003 |pmid=12697740 |doi=10.1172/JCI17100 |url=}}</ref> | * Related to [[Fibroblast growth factor|fibroblast growth factor (FGF)]]<ref name="pmid12697740">{{cite journal |vauthors=Nedvetzki S, Golan I, Assayag N, Gonen E, Caspi D, Gladnikoff M, Yayon A, Naor D |title=A mutation in a CD44 variant of inflammatory cells enhances the mitogenic interaction of FGF with its receptor |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=111 |issue=8 |pages=1211–20 |year=2003 |pmid=12697740 |doi=10.1172/JCI17100 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Increased expression during [[collateral]] [[arteriogenesis]]<ref name="pmid15023889">{{cite journal |vauthors=van Royen N, Voskuil M, Hoefer I, Jost M, de Graaf S, Hedwig F, Andert JP, Wormhoudt TA, Hua J, Hartmann S, Bode C, Buschmann I, Schaper W, van der Neut R, Piek JJ, Pals ST |title=CD44 regulates arteriogenesis in mice and is differentially expressed in patients with poor and good collateralization |journal=Circulation |volume=109 |issue=13 |pages=1647–52 |year=2004 |pmid=15023889 |doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000124066.35200.18 |url=}}</ref> | * Increased expression during [[collateral]] [[arteriogenesis]]<ref name="pmid15023889">{{cite journal |vauthors=van Royen N, Voskuil M, Hoefer I, Jost M, de Graaf S, Hedwig F, Andert JP, Wormhoudt TA, Hua J, Hartmann S, Bode C, Buschmann I, Schaper W, van der Neut R, Piek JJ, Pals ST |title=CD44 regulates arteriogenesis in mice and is differentially expressed in patients with poor and good collateralization |journal=Circulation |volume=109 |issue=13 |pages=1647–52 |year=2004 |pmid=15023889 |doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000124066.35200.18 |url=}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Transforming growth factor-β|Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[Transforming growth factor-β|Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β]]''' | ||
|190180 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |190180 | ||
|19q13.2 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |19q13.2 | ||
| | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | | ||
* [[Transformation|Tissue transformation]] | * [[Transformation|Tissue transformation]] | ||
* [[Apoptosis]] regulation<ref name="pmid11586292">{{cite journal |vauthors=Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A |title=TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression |journal=Nat. Genet. |volume=29 |issue=2 |pages=117–29 |year=2001 |pmid=11586292 |doi=10.1038/ng1001-117 |url=}}</ref> | * [[Apoptosis]] regulation<ref name="pmid11586292">{{cite journal |vauthors=Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A |title=TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression |journal=Nat. Genet. |volume=29 |issue=2 |pages=117–29 |year=2001 |pmid=11586292 |doi=10.1038/ng1001-117 |url=}}</ref> | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5; + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
|Hyper-expressed in African-American hypertensive patients<ref name="pmid10725360">{{cite journal |vauthors=Suthanthiran M, Li B, Song JO, Ding R, Sharma VK, Schwartz JE, August P |title=Transforming growth factor-beta 1 hyperexpression in African-American hypertensives: A novel mediator of hypertension and/or target organ damage |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=97 |issue=7 |pages=3479–84 |year=2000 |pmid=10725360 |pmc=16265 |doi=10.1073/pnas.050420897 |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5; + |Hyper-expressed in African-American hypertensive patients<ref name="pmid10725360">{{cite journal |vauthors=Suthanthiran M, Li B, Song JO, Ding R, Sharma VK, Schwartz JE, August P |title=Transforming growth factor-beta 1 hyperexpression in African-American hypertensives: A novel mediator of hypertension and/or target organ damage |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=97 |issue=7 |pages=3479–84 |year=2000 |pmid=10725360 |pmc=16265 |doi=10.1073/pnas.050420897 |url=}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 4 (ENTPD4)''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 4 (ENTPD4)''' | ||
|607577 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |607577 | ||
|8p21.3 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |8p21.3 | ||
|Increasing [[phosphatase]] activity in [[intracellular]] membrane-bound [[nucleosides]] | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Increasing [[phosphatase]] activity in [[intracellular]] membrane-bound [[nucleosides]] | ||
|Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced<ref name="KotaniKawabe2015" /> | ||
| - | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[ABCC1|ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 1 (ABCC1)]]''' | | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" + |'''[[ABCC1|ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 1 (ABCC1)]]''' | ||
|158343 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |158343 | ||
|16p13.11 | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" align="center" + |16p13.11 | ||
|[[Multidrug resistance|Multi-drug resistance]] in [[small cell lung cancer]]<ref name="pmid1360704">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cole SP, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach JH, Mackie JE, Grant CE, Almquist KC, Stewart AJ, Kurz EU, Duncan AM, Deeley RG |title=Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line |journal=Science |volume=258 |issue=5088 |pages=1650–4 |year=1992 |pmid=1360704 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |[[Multidrug resistance|Multi-drug resistance]] in [[small cell lung cancer]]<ref name="pmid1360704">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cole SP, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach JH, Mackie JE, Grant CE, Almquist KC, Stewart AJ, Kurz EU, Duncan AM, Deeley RG |title=Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line |journal=Science |volume=258 |issue=5088 |pages=1650–4 |year=1992 |pmid=1360704 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
|Reduced | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + |Reduced | ||
| - | | style="background:#F5F5F5;" + | - | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 237: | Line 230: | ||
==Gross Pathology== | ==Gross Pathology== | ||
{| | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
| colspan="3" | | |||
*On [[gross pathology]], [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]], [[splenomegaly]], and [[esophageal varices]] are characteristic findings in portal hypertension. | |||
|- | |||
| | | | ||
=== Cirrhosis === | === Cirrhosis === | ||
On [[gross pathology]] there are two types of [[cirrhosis]]: | On [[gross pathology]] there are two types of [[cirrhosis]]: | ||
* Micronodular [[cirrhosis]] which is uniform and diffuse, mostly due to [[alcohol]]. | * Micronodular [[cirrhosis]] which is uniform and diffuse, mostly due to [[alcohol]]. | ||
* Macronodular [[cirrhosis]] which is irregular, mostly due to [[viral hepatitis]]. | * Macronodular [[cirrhosis]] which is irregular, mostly due to [[viral hepatitis]]. | ||
< | | | ||
< | [[image:Cirrosi micronodular.1427.jpg|thumb|200px|Micronodular cirrhosis - By Amadalvarez (Own work), via Wikimedia Commons<ref><CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)></ref>]] | ||
| | |||
[[image:Fig78x.jpg|thumb|200px|Macronodular cirrhosis- By Amadalvarez (Own work), via Wikimedia Commons<ref name="urlwww.meddean.luc.edu">{{cite web |url=http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/orfpath/images/fig78x.jpg |title=www.meddean.luc.edu |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
=== Splenomegaly === | === Splenomegaly === | ||
On [[gross pathology]], diffuse enlargement and [[congestion]] of the [[spleen]] are characteristic findings of [[splenomegaly]]. | On [[gross pathology]], diffuse enlargement and [[congestion]] of the [[spleen]] are characteristic findings of [[splenomegaly]]. | ||
< | | colspan="2" | | ||
< | [[image:Esplenomegalia i hiperplasia linfoide folicular reactiva. IMG 2865.jpg|thumb|200px|center|Splenomegaly - By Amadalvarez (Own work), via Wikimedia Commons<ref>Amadalvarez - <span class="int-own-work" lang="en">Own work</span>, <"https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0" title="Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0">CC BY-SA 4.0, <"https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=49669333">Link</ref>]] | ||
< | |- | ||
| | |||
=== Esophageal Varices === | === Esophageal Varices === | ||
On gross pathology, prominent, congested, and tortoise [[veins]] in the lower parts of [[esophagus]] are characteristic findings of [[esophageal varices]]. | On gross pathology, prominent, congested, and tortoise [[veins]] in the lower parts of [[esophagus]] are characteristic findings of [[esophageal varices]]. | ||
< | |colspan="2"| | ||
< | [[image:F21. Venous enlargement in hepatic cirrhosis. Alfred Kast Wellcome L0074357.jpg|thumb|200px|center|Esophageal varices- By Amadalvarez (Own work), via Wikimedia Commons<ref><http://wellcomeimages.org/indexplus/obf_images/29/b4/13f38971164f946a97f9d32ddd93.jpg>Gallery: <"http://wellcomeimages.org/indexplus/image/L0074357.html"><"http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0> CC BY 4.0, <"https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=36297209"></ref>]] | ||
< | |} | ||
==Microscopic Pathology== | ==Microscopic Pathology== | ||
| Line 309: | Line 301: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | [[Category:Hepatology]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:15, 23 February 2018
| https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Mf_8TawJ9w%7C500}} |
|
Portal Hypertension Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Portal hypertension pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Portal hypertension pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Portal hypertension pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Eiman Ghaffarpasand, M.D. [2]
Overview
The exact pathogenesis in portal hypertension is disturbance in normal physiology of portocaval circulation. The main factors that affect the pressure gradient in blood vessels are blood flow (Q) and vessel radius (r) in a direct and inverse way, respectively. Portal hypertension is related to elevation of portal vasculature resistance. Peripheral vasodilatation is the basis for decreased systemic vascular resistance and mean arterial pressure, plasma volume expansion, elevated splanchnic blood flow, and elevated cardiac index. Fourteen different genes are involved in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension. Homozygous missense mutation in DGUOK gene is found to be related with non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. On gross pathology, cirrhotic liver, splenomegaly, and esophageal varices are characteristic findings in portal hypertension. The main microscopic histopathological findings in portal hypertension are related to cirrhosis, esophageal varices, hepatic amyloidosis, and congestive hepatopathy due to heart failure or Budd-Chiari syndrome.
Pathophysiology
- Portal hypertension is caused by conditions classified as pre-hepatic, intra-hepatic, and post-hepatic disorders.
- Intra-hepatic portal hypertension causes are pre-sinusoidal, sinusoidal, and post-sinusoidal disorders.
- The exact pathogenesis in portal hypertension is disturbance in normal physiology of portocaval circulation.
Physiology
- Ohm's law in vascular system defines the pressure gradient (ΔP) in blood vessels as equal to product of blood flow (Q) and vascular resistance (R):

- Vascular resistance (R) has to be measured through Pouseuille’s law formula:

η= Viscosity; L= Length of vessel; r= Radius of vessel; π=22/7
- When the (R) measurement formula is integrated in Ohm's law it becomes as the following:

- Length of blood vessels (L) never differs in normal physiologic condition.
- Blood viscosity (η) does not change, unless dramatic changes in hematocrit happen.
- The main factors that affect the pressure gradient in blood vessels are blood flow (Q) and vessel radius (r) in a direct and inverse way, respectively.
| • Anatomical (irreversible component) • Functional/vascular tone (reversible component) | • Opening of pre-existing vascular channels • Formation of new vascular channels | • Systemic vasodilation (r) • Increasing plasma volume (Q) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| lntra-hepatic resistance (r) | Portosystemic collaterals (Q) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Increased resistance to portal blood flow (R) | Increased systemic/splanchnic blood flow (Q) (hyperdynamic circulation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevated portal pressure (P) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Portal hypertension | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pathogenesis
Increased resistance
- Portal hypertension is related to elevation of portal vasculature resistance.
- Increased resistance in portal system can be due to both intra-hepatic and also portosystemic collaterals resistances.
- Intra-hepatic resistance
- The main factor in intra-hepatic resistance is hepatic vascular compliance, which is greatly decreased in various liver diseases, such as liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
- Portal hypertension occurs when compliance is decreased and blood flow is increased in liver.[1]
- Pre-hepatic and post-hepatic portal hypertension are due to some secondary obstruction before or after liver vasculature, respectively.[2]
- Schistosomiasis causes both pre-sinusoidal and sinusoidal pathologies. The granulomas compress the pre-sinusoidal veins. In late stages sinusoidal resistance is also increased.[3]
- Alcoholic hepatitis causes both sinusoidal and post-sinusoidal pathologies.[4][5]
- Hepatic vascular endothelium synthesizes and secretes both vasodilator (e.g., nitric oxide, prostacyclins) and vasoconstrictor (e.g., endothelin and prostanoids) chemicals.[6][7]
- Increased resistance due to the elevation of vascular tone may be caused by excess of vasoconstrictors or lack of vasodilators.
- It is postulated that in cirrhotic liver the nitric oxide level is lower and the response to endothelin response in myofibrils is higher than normal liver.[8]
- Portosystemic collateral resistance
- Collateral formation is the consequence of portal hypertension which is also the main contributor to esophageal varices.
- The main purpose of the collaterals is to decompress and bypass the portal blood flow.
- However, the resistance in collaterals is less than the normal liver.
- Thus, portosystemic collaterals can not lead to a complete decompression.
- Portosystemic collateraling occurs between the short gastric, coronary veins, and the esophageal azygos and the intercostal veins; the superior, the middle, and the inferior hemorrhoidal veins; the paraumbilical venous plexus and the venous system of abdominal organs juxtaposed with the retroperitoneum and abdominal wall; the left renal vein, the splanchnic, the adrenal, and the spermatic veins.[9]
- Intra-hepatic resistance
Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertension
- Peripheral vasodilatation is the basis for decreased systemic vascular resistance and mean arterial pressure, plasma volume expansion, elevated splanchnic blood flow, and elevated cardiac index.[10]
- Systemic vasodilation
- Three main mechanisms which contribute to the peripheral vasodilation are as following:
- Increased vasodilators production in systemic circulation[11]
- Increased vasodilators production in local endothelium[12]
- Decreased vascular response to local vasoconstrictors[13]
- Three main mechanisms which contribute to the peripheral vasodilation are as following:
- Plasma volume
- There are several events which contribute to the hyperdynamic circulation such as:
- Initial vasodilatation, induced by systemic and local endothelial factors
- Subsequent plasma volume expansion[14]
- There are several events which contribute to the hyperdynamic circulation such as:
Genetics
- Genes are involved in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension include the following:
| Gene | OMIM number | Chromosome | Function | Gene expression in portal hypertension | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK) | 601465 | 2p13.1 | DNA replication | Point mutation | Mutation leads to:[15]
Homozygous missense mutation leads to:[16] |
| Adenosine deaminase (ADA) | 608958 | 20q13.12 | Irreversible deamination of adenosine and deoxyadenosine in the purine catabolic pathway | Reduced[17] | Some roles in modulating tissue response to IL-13
The main effects of IL-13 are:[18]
|
| Phospholipase A2 (PL2G10) | 603603 | 16p13.12 | Catalyzing the release of fatty acids from phospholipids | Reduced[17] | Identifier of PL2G10 expression: |
| Cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily F, polypeptide 3 (CYP4F3) | 601270 | 19p13.12 | Catalyzing the omega-hydroxylation of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) | Increased[17] | - |
| Glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3) | 138321 | 5q33.1 | Reduction of glutathione which reduce:[19] | Increased[17] | Protects various organs against oxidative stress:[20] |
| Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) | 601531 | 14q12 | Include:[21]
|
Mutated | Increase blood flow to target tissue (esp. heart) about 4 times more.[22] |
| Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (PTGER2) | 176804 | 14q22.1 | Various biological activities in diverse tissues | Reduced[17] | - |
| Endothelin (EDN1) | 131240 | 6p24.1 | Vasoconstriction[23] | Increased | The most powerful vasoconstrictor known[24] |
| Endothelin receptor type A (EDNRA) | 131243 | 4q31.22-q31.23 | Vasoconstriction through binding to endothelin | Reduced[17] | Directly related to hypertension in patients[23] |
| Natriuretic peptide receptor 3 (NPR3) | 108962 | 5p13.3 | Maintenance of: | Increased[17] | Released from heart muscle in response to increase in wall tension. ANP can modulate blood pressure by binding to NPR3[25] |
| Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) | 107269 | 11p13 |
|
Reduced[17] |
|
| Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β | 190180 | 19q13.2 |
|
Reduced[17] | Hyper-expressed in African-American hypertensive patients[30] |
| Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 4 (ENTPD4) | 607577 | 8p21.3 | Increasing phosphatase activity in intracellular membrane-bound nucleosides | Reduced[17] | - |
| ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 1 (ABCC1) | 158343 | 16p13.11 | Multi-drug resistance in small cell lung cancer[31] | Reduced | - |
Associated Conditions
| Portal Hypertension associated conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunological disorders | Infections | Medication and toxins | Genetic disorders | Prothrombotic conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Common variable immunodeficiency syndrome[32] • Connective tissue diseases[33] • Crohn’s disease[34] • Solid organ transplant •• Renal transplantation[35] •• Liver transplantation[36] • Hashimoto's thyroiditis[37] • Autoimmune disease[38] | • Bacterial intestinal infections • Recurrent E.coli infection[39] • Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection[40] • Antiretroviral therapy[41] | • Thiopurine derivatives •• Didanosine •• Azathioprine[42] •• Cis-thioguanine[43] • Arsenicals[44] • Vitamin A[45] | • Adams-Olivier syndrome[46] • Turner syndrome[47] • Phosphomannose isomerase deficiency[48] • Familial cases[49] | • Inherited thrombophilias [50] • Myeloproliferative neoplasm[50] • Antiphospholipid syndrome[50] • Sickle cell disease[51] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross Pathology
| ||
CirrhosisOn gross pathology there are two types of cirrhosis:
|
 |
 |
SplenomegalyOn gross pathology, diffuse enlargement and congestion of the spleen are characteristic findings of splenomegaly. |
 | |
Esophageal VaricesOn gross pathology, prominent, congested, and tortoise veins in the lower parts of esophagus are characteristic findings of esophageal varices. |
 | |
Microscopic Pathology
| |
CirrhosisRobbins definition of microscopic histopathological findings in cirrhosis includes (all three is needed for diagnosis):[56] |
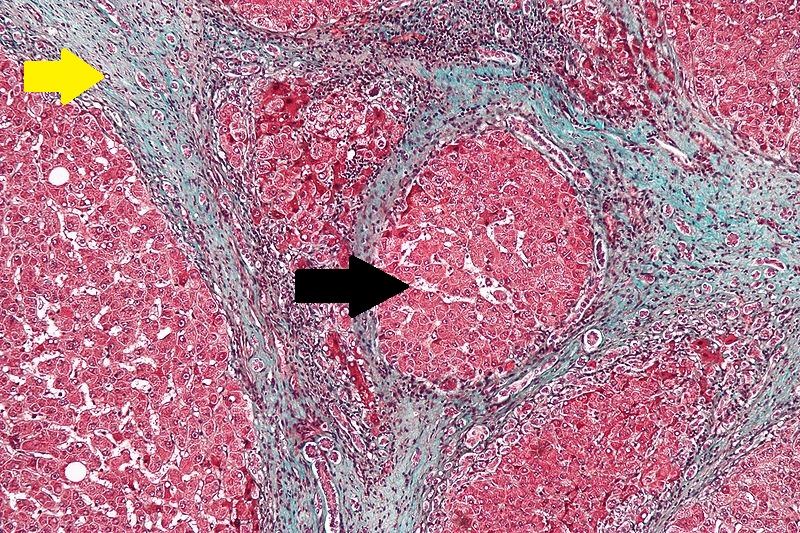 |
Esophageal varicesThe main microscopic histopathological findings in esophageal varices are:
|
 |
Hepatic amyloidosisThe main microscopic histopathological findings in hepatic amyloidosis is amorphous extracellular pink stuff on H&E staining. |
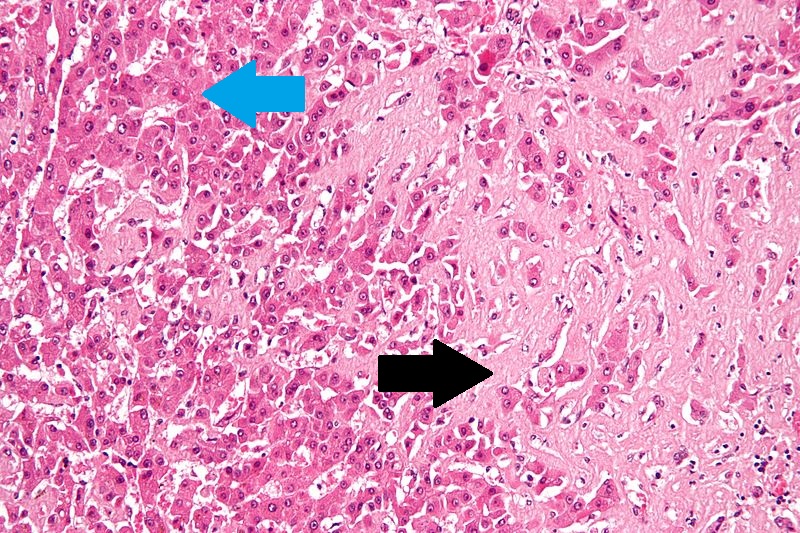 |
Congestive hepatopathyThe main microscopic histopathological findings in congestive hepatopathy (due to heart failure or Budd-Chiari syndrome) are:
|
 |
References
- ↑ Greenway CV, Stark RD (1971). "Hepatic vascular bed". Physiol. Rev. 51 (1): 23–65. PMID 5543903.
- ↑ Schiff, Eugene (2012). Schiff's diseases of the liver. Chichester, West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780470654682.
- ↑ Beker, Simón G.; Valencia-Parparcén, Joel (1968). "Portal hypertension syndrome". The American Journal of Digestive Diseases. 13 (12): 1047–1054. doi:10.1007/BF02233549. ISSN 0002-9211.
- ↑ SCHAFFNER F, POPER H (1963). "Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man". Gastroenterology. 44: 239–42. PMID 13976646.
- ↑ Reynolds TB, Hidemura R, Michel H, Peters R (1969). "Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease". Ann. Intern. Med. 70 (3): 497–506. PMID 5775031.
- ↑ Rubanyi GM (1991). "Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors". J. Cell. Biochem. 46 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1002/jcb.240460106. PMID 1874796.
- ↑ Epstein, Franklin H.; Vane, John R.; Änggård, Erik E.; Botting, Regina M. (1990). "Regulatory Functions of the Vascular Endothelium". New England Journal of Medicine. 323 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ Rockey DC, Weisiger RA (1996). "Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance". Hepatology. 24 (1): 233–40. doi:10.1002/hep.510240137. PMID 8707268.
- ↑ Mosca P, Lee FY, Kaumann AJ, Groszmann RJ (1992). "Pharmacology of portal-systemic collaterals in portal hypertensive rats: role of endothelium". Am. J. Physiol. 263 (4 Pt 1): G544–50. PMID 1415713.
- ↑ Colombato LA, Albillos A, Groszmann RJ (1992). "Temporal relationship of peripheral vasodilatation, plasma volume expansion and the hyperdynamic circulatory state in portal-hypertensive rats". Hepatology. 15 (2): 323–8. PMID 1735537.
- ↑ Genecin P, Polio J, Colombato LA, Ferraioli G, Reuben A, Groszmann RJ (1990). "Bile acids do not mediate the hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertensive rats". Am. J. Physiol. 259 (1 Pt 1): G21–5. PMID 2372062.
- ↑ Casadevall, María; Panés, Julián; Piqué, Josep M.; Marroni, Norma; Bosch, Jaume; Whittle, Brendan J. R. (1993). "Involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandins in gastric mucosal hyperemia of portal-hypertensive anesthetized rats". Hepatology. 18 (3): 628–634. doi:10.1002/hep.1840180323. ISSN 0270-9139.
- ↑ Sieber CC, Groszmann RJ (1992). "In vitro hyporeactivity to methoxamine in portal hypertensive rats: reversal by nitric oxide blockade". Am. J. Physiol. 262 (6 Pt 1): G996–1001. PMID 1616049.
- ↑ Albillos A, Colombato LA, Lee FY, Groszmann RJ (1993). "Octreotide ameliorates vasodilatation and Na+ retention in portal hypertensive rats". Gastroenterology. 104 (2): 575–9. PMID 8425700.
- ↑ Mandel H, Szargel R, Labay V, Elpeleg O, Saada A, Shalata A, Anbinder Y, Berkowitz D, Hartman C, Barak M, Eriksson S, Cohen N (2001). "The deoxyguanosine kinase gene is mutated in individuals with depleted hepatocerebral mitochondrial DNA". Nat. Genet. 29 (3): 337–41. doi:10.1038/ng746. PMID 11687800.
- ↑ Vilarinho S, Sari S, Yilmaz G, Stiegler AL, Boggon TJ, Jain D, Akyol G, Dalgic B, Günel M, Lifton RP (2016). "Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension". Hepatology. 63 (6): 1977–86. doi:10.1002/hep.28499. PMC 4874872. PMID 26874653.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 17.7 17.8 17.9 Kotani, Kohei; Kawabe, Joji; Morikawa, Hiroyasu; Akahoshi, Tomohiko; Hashizume, Makoto; Shiomi, Susumu (2015). "Comprehensive Screening of Gene Function and Networks by DNA Microarray Analysis in Japanese Patients with Idiopathic Portal Hypertension". Mediators of Inflammation. 2015: 1–10. doi:10.1155/2015/349215. ISSN 0962-9351.
- ↑ Blackburn MR, Lee CG, Young HW, Zhu Z, Chunn JL, Kang MJ, Banerjee SK, Elias JA (2003). "Adenosine mediates IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling in the lung and interacts in an IL-13-adenosine amplification pathway". J. Clin. Invest. 112 (3): 332–44. doi:10.1172/JCI16815. PMC 166289. PMID 12897202.
- ↑ Chambers I, Frampton J, Goldfarb P, Affara N, McBain W, Harrison PR (1986). "The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA". EMBO J. 5 (6): 1221–7. PMC 1166931. PMID 3015592.
- ↑ Chu FF, Esworthy RS, Doroshow JH, Doan K, Liu XF (1992). "Expression of plasma glutathione peroxidase in human liver in addition to kidney, heart, lung, and breast in humans and rodents". Blood. 79 (12): 3233–8. PMID 1339300.
- ↑ Yokomizo T, Izumi T, Chang K, Takuwa Y, Shimizu T (1997). "A G-protein-coupled receptor for leukotriene B4 that mediates chemotaxis". Nature. 387 (6633): 620–4. doi:10.1038/42506. PMID 9177352.
- ↑ Bäck M, Bu DX, Bränström R, Sheikine Y, Yan ZQ, Hansson GK (2005). "Leukotriene B4 signaling through NF-kappaB-dependent BLT1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis and intimal hyperplasia". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (48): 17501–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505845102. PMC 1297663. PMID 16293697.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Campia U, Cardillo C, Panza JA (2004). "Ethnic differences in the vasoconstrictor activity of endogenous endothelin-1 in hypertensive patients". Circulation. 109 (25): 3191–5. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000130590.24107.D3. PMID 15148269.
- ↑ Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Takuwa Y, Mitsui Y, Kobayashi M, Masaki T (1989). "The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (25): 14954–9. PMID 2670930.
- ↑ Lopez MJ, Wong SK, Kishimoto I, Dubois S, Mach V, Friesen J, Garbers DL, Beuve A (1995). "Salt-resistant hypertension in mice lacking the guanylyl cyclase-A receptor for atrial natriuretic peptide". Nature. 378 (6552): 65–8. doi:10.1038/378065a0. PMID 7477288.
- ↑ Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B (1990). "CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate". Cell. 61 (7): 1303–13. PMID 1694723.
- ↑ Nedvetzki S, Golan I, Assayag N, Gonen E, Caspi D, Gladnikoff M, Yayon A, Naor D (2003). "A mutation in a CD44 variant of inflammatory cells enhances the mitogenic interaction of FGF with its receptor". J. Clin. Invest. 111 (8): 1211–20. doi:10.1172/JCI17100. PMID 12697740.
- ↑ van Royen N, Voskuil M, Hoefer I, Jost M, de Graaf S, Hedwig F, Andert JP, Wormhoudt TA, Hua J, Hartmann S, Bode C, Buschmann I, Schaper W, van der Neut R, Piek JJ, Pals ST (2004). "CD44 regulates arteriogenesis in mice and is differentially expressed in patients with poor and good collateralization". Circulation. 109 (13): 1647–52. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000124066.35200.18. PMID 15023889.
- ↑ Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A (2001). "TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression". Nat. Genet. 29 (2): 117–29. doi:10.1038/ng1001-117. PMID 11586292.
- ↑ Suthanthiran M, Li B, Song JO, Ding R, Sharma VK, Schwartz JE, August P (2000). "Transforming growth factor-beta 1 hyperexpression in African-American hypertensives: A novel mediator of hypertension and/or target organ damage". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (7): 3479–84. doi:10.1073/pnas.050420897. PMC 16265. PMID 10725360.
- ↑ Cole SP, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach JH, Mackie JE, Grant CE, Almquist KC, Stewart AJ, Kurz EU, Duncan AM, Deeley RG (1992). "Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line". Science. 258 (5088): 1650–4. PMID 1360704.
- ↑ Fuss IJ, Friend J, Yang Z, He JP, Hooda L, Boyer J, Xi L, Raffeld M, Kleiner DE, Heller T, Strober W (2013). "Nodular regenerative hyperplasia in common variable immunodeficiency". J. Clin. Immunol. 33 (4): 748–58. doi:10.1007/s10875-013-9873-6. PMC 3731765. PMID 23420139.
- ↑ Vaiphei K, Bhatia A, Sinha SK (2011). "Liver pathology in collagen vascular disorders highlighting the vascular changes within portal tracts". Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 54 (1): 25–31. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.77319. PMID 21393872.
- ↑ De Boer NK, Tuynman H, Bloemena E, Westerga J, Van Der Peet DL, Mulder CJ, Cuesta MA, Meuwissen SG, Van Nieuwkerk CM, Van Bodegraven AA (2008). "Histopathology of liver biopsies from a thiopurine-naïve inflammatory bowel disease cohort: prevalence of nodular regenerative hyperplasia". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 43 (5): 604–8. doi:10.1080/00365520701800266. PMID 18415755.
- ↑ Allison MC, Mowat A, McCruden EA, McGregor E, Burt AD, Briggs JD, Junor BJ, Follett EA, MacSween RN, Mills PR (1992). "The spectrum of chronic liver disease in renal transplant recipients". Q. J. Med. 83 (301): 355–67. PMID 1438671.
- ↑ Gane E, Portmann B, Saxena R, Wong P, Ramage J, Williams R (1994). "Nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver graft after liver transplantation". Hepatology. 20 (1 Pt 1): 88–94. PMID 8020909.
- ↑ Imai Y, Minami Y, Miyoshi S, Kawata S, Saito R, Noda S, Tamura S, Nishikawa M, Tajima K, Tarui S (1986). "Idiopathic portal hypertension associated with Hashimoto's disease: report of three cases". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 81 (9): 791–5. PMID 2944377.
- ↑ Li X, Gao W, Chen J, Tang W (2000). "[Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension associated with autoimmune disease]". Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi (in Chinese). 38 (2): 101–3. PMID 11831999.
- ↑ Kono K, Ohnishi K, Omata M, Saito M, Nakayama T, Hatano H, Nakajima Y, Sugita S, Okuda K (1988). "Experimental portal fibrosis produced by intraportal injection of killed nonpathogenic Escherichia coli in rabbits". Gastroenterology. 94 (3): 787–96. PMID 3276575.
- ↑ Siramolpiwat S, Seijo S, Miquel R, Berzigotti A, Garcia-Criado A, Darnell A, Turon F, Hernandez-Gea V, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagán JC (2014). "Idiopathic portal hypertension: natural history and long-term outcome". Hepatology. 59 (6): 2276–85. doi:10.1002/hep.26904. PMID 24155091.
- ↑ Maida I, Garcia-Gasco P, Sotgiu G, Rios MJ, Vispo ME, Martin-Carbonero L, Barreiro P, Mura MS, Babudieri S, Albertos S, Garcia-Samaniego J, Soriano V (2008). "Antiretroviral-associated portal hypertension: a new clinical condition? Prevalence, predictors and outcome". Antivir. Ther. (Lond.). 13 (1): 103–7. PMID 18389904.
- ↑ Vernier-Massouille G, Cosnes J, Lemann M, Marteau P, Reinisch W, Laharie D, Cadiot G, Bouhnik Y, De Vos M, Boureille A, Duclos B, Seksik P, Mary JY, Colombel JF (2007). "Nodular regenerative hyperplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with azathioprine". Gut. 56 (10): 1404–9. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.114363. PMC 2000290. PMID 17504943.
- ↑ Calabrese E, Hanauer SB (2011). "Assessment of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension associated with thiopurine therapy in inflammatory bowel disease". J Crohns Colitis. 5 (1): 48–53. doi:10.1016/j.crohns.2010.08.007. PMID 21272804.
- ↑ Nevens F, Fevery J, Van Steenbergen W, Sciot R, Desmet V, De Groote J (1990). "Arsenic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. A report of eight cases". J. Hepatol. 11 (1): 80–5. PMID 2398270.
- ↑ Geubel AP, De Galocsy C, Alves N, Rahier J, Dive C (1991). "Liver damage caused by therapeutic vitamin A administration: estimate of dose-related toxicity in 41 cases". Gastroenterology. 100 (6): 1701–9. PMID 2019375.
- ↑ Girard M, Amiel J, Fabre M, Pariente D, Lyonnet S, Jacquemin E (2005). "Adams-Oliver syndrome and hepatoportal sclerosis: occasional association or common mechanism?". Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 135 (2): 186–9. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.30724. PMID 15832360.
- ↑ Roulot D (2013). "Liver involvement in Turner syndrome". Liver Int. 33 (1): 24–30. doi:10.1111/liv.12007. PMID 23121401.
- ↑ de Lonlay P, Seta N (2009). "The clinical spectrum of phosphomannose isomerase deficiency, with an evaluation of mannose treatment for CDG-Ib". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1792 (9): 841–3. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.11.012. PMID 19101627.
- ↑ Sarin SK, Mehra NK, Agarwal A, Malhotra V, Anand BS, Taneja V (1987). "Familial aggregation in noncirrhotic portal fibrosis: a report of four families". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 82 (11): 1130–3. PMID 3499813.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 Bayan K, Tüzün Y, Yilmaz S, Canoruc N, Dursun M (2009). "Analysis of inherited thrombophilic mutations and natural anticoagulant deficiency in patients with idiopathic portal hypertension". J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 28 (1): 57–62. doi:10.1007/s11239-008-0244-8. PMID 18685811.
- ↑ Kumar S, Joshi R, Jain AP (2007). "Portal hypertension associated with sickle cell disease". Indian J Gastroenterol. 26 (2): 94. PMID 17558079.
- ↑ <CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)>
- ↑ "www.meddean.luc.edu".
- ↑ Amadalvarez - Own work, <"https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0" title="Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0">CC BY-SA 4.0, <"https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=49669333">Link
- ↑ <http://wellcomeimages.org/indexplus/obf_images/29/b4/13f38971164f946a97f9d32ddd93.jpg>Gallery: <"http://wellcomeimages.org/indexplus/image/L0074357.html"><"http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0> CC BY 4.0, <"https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=36297209">
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard (2012). Pocket companion to Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ "File:Cirrhosis high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology".
- ↑ "Esophageal varices - Libre Pathology".
- ↑ "File:Hepatic amyloidosis - high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology".
- ↑ "File:2 CEN NEC 1 680x512px.tif - Libre Pathology".