Xanthelasma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
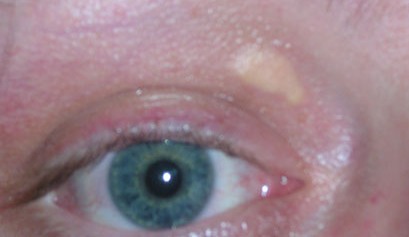
'''Xanthelasma''' (or '''xanthelasma palpebrarum''') is a sharply demarcated yellowish collection of [[cholesterol]] underneath the skin, usually on or around the [[eyelids]] | '''Xanthelasma''' (or '''xanthelasma palpebrarum''') is a sharply demarcated yellowish collection of [[cholesterol]] underneath the skin, usually on or around the [[eyelids]]. The plural is "xanthelasmata". The root of the word is from Greek xanthos, ξανθος, "yellow". | ||
== | Xanthelasma are distinct from [[xanthoma]] which are larger and nodular, lesions.<ref>{{cite book |author=Shields, Carol; Shields, Jerry |title=Eyelid, conjunctival, and orbital tumors: atlas and textbook |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |location=Hagerstwon, MD |year=2008 |pages= |isbn=0-7817-7578-7 |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref> Still, it is often classified simply as a subtype of ''xanthoma''.<ref>[http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/xanthelasma thefreedictionary.com > xanthelasma] Citing: The American Heritage Medical Dictionary Copyright 2007, 2004 and Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009</ref> | ||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | |||
They are common in people of Asian extraction and those from the Mediterranean region. | |||
==Natural History, Complications, Prognosis== | |||
The lesions are not harmful or painful. If there is no [[family history]] of xanthelasmata, the lesion may indicate that the cholesterol is elevated, and may be associated with an increased risk of [[atherosclerosis]]. | |||
==Differential Diagnosis of Associated Conditions== | |||
* [[Hypercholesterolemia|High cholesterol levels]] (specifically [[familial hypercholesterolemia]]) | * [[Hypercholesterolemia|High cholesterol levels]] (specifically [[familial hypercholesterolemia]]) | ||
* [[Primary biliary cirrhosis]] | * [[Primary biliary cirrhosis]] | ||
* [[Menopause]] | * [[Menopause]] | ||
* [[Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes]] | ||
==Treatment== | |||
These minor growths may be disfiguring and can be removed. Xanthelasmata can be removed with [[trichloroacetic acid]] peel, surgery, lasers or [[cryotherapy]]. Removal can cause scarring and pigment changes, but it is unusual after treatment with trichloroacetic acid. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 20:52, 13 September 2011
| Xanthelasma | |
 | |
|---|---|
| ICD-10 | H02.6 |
| ICD-9 | 374.51 |
| DiseasesDB | 28519 |
| MedlinePlus | 001447 |
| eMedicine | oph/610 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
Xanthelasma (or xanthelasma palpebrarum) is a sharply demarcated yellowish collection of cholesterol underneath the skin, usually on or around the eyelids. The plural is "xanthelasmata". The root of the word is from Greek xanthos, ξανθος, "yellow".
Xanthelasma are distinct from xanthoma which are larger and nodular, lesions.[1] Still, it is often classified simply as a subtype of xanthoma.[2]
Epidemiology and Demographics
They are common in people of Asian extraction and those from the Mediterranean region.
Natural History, Complications, Prognosis
The lesions are not harmful or painful. If there is no family history of xanthelasmata, the lesion may indicate that the cholesterol is elevated, and may be associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
Differential Diagnosis of Associated Conditions
- High cholesterol levels (specifically familial hypercholesterolemia)
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Menopause
- Diabetes
Treatment
These minor growths may be disfiguring and can be removed. Xanthelasmata can be removed with trichloroacetic acid peel, surgery, lasers or cryotherapy. Removal can cause scarring and pigment changes, but it is unusual after treatment with trichloroacetic acid.
See also
- Xanthoma (similar collections of cholesterol around tendons)
External links
References
- Lang, Gerhard K Ophthalmology Thieme. Stuttgart. 2000.
Template:Skin and subcutaneous tissue symptoms and signs Template:Nervous and musculoskeletal system symptoms and signs Template:Urinary system symptoms and signs Template:Cognition, perception, emotional state and behaviour symptoms and signs Template:Speech and voice symptoms and signs Template:General symptoms and signs
da:Xantelasma de:Xanthelasma nl:Xanthelasma sv:Xantelasma
Template:WH Template:WikiDoc Sources
- ↑ Shields, Carol; Shields, Jerry (2008). Eyelid, conjunctival, and orbital tumors: atlas and textbook. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-7578-7.
- ↑ thefreedictionary.com > xanthelasma Citing: The American Heritage Medical Dictionary Copyright 2007, 2004 and Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009