Turner syndrome physical examination: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Physical examination may be suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, congenital heart defects, inflammatory bowel disease, characteristic skeletal deformities and body habitus/skin manifestations. | Physical examination may be suggestive of [[thyroid]] dysfunction, [[congenital heart defects]], [[inflammatory bowel disease]], characteristic [[skeletal deformities]] and [[body habitus]]/skin manifestations. | ||
==Physical Examination== | ==Physical Examination== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Appearance of the Patient=== | ===Appearance of the Patient=== | ||
*Patient may show signs of poor growth velocity and malnutrition indicative of failure to thrive. | *Patient may show signs of poor growth velocity and [[malnutrition]] indicative of [[failure to thrive]]. | ||
*Patients may be hyperactive. | *Patients may be [[hyperactive]]. | ||
*The presence of short stature, a webbed neck, pigmented nevi, puffiness of the hands and feet, a cubitus valgus deformity, genu valgum on physical examination are highly suggestive of Turner syndrome. | *The presence of [[short stature]], a [[webbed neck]], [[pigmented nevi]], puffiness of the hands and feet, a [[cubitus valgus]] deformity, [[genu valgum]] on physical examination are highly suggestive of [[Turner syndrome]]. | ||
<gallery widths=150px> | <gallery widths=150px> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Vital Signs=== | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
*High-grade / low-grade fever | *High-grade / low-grade [[fever]] | ||
*[[Hypothermia]] / hyperthermia may be present | *[[Hypothermia]] / [[hyperthermia]] may be present | ||
*[[Tachycardia]] with regular pulse or irregularly irregular pulse - Hyperthyroidism | *[[Tachycardia]] with [[regular pulse]] or [[irregularly irregular pulse]] - [[Hyperthyroidism]] | ||
*[[Bradycardia]] with regular pulse or irregularly irregular pulse - Hypothyroidism | *[[Bradycardia]] with [[regular pulse]] or [[irregularly irregular pulse]] - [[Hypothyroidism]] | ||
*Tachypnea - Secondary to Acute pulmonary edema from ischemic heart disease | *[[Tachypnea]] - Secondary to [[Acute pulmonary edema]] from [[ischemic heart disease]] | ||
*Hypertension in the upper extremities with hypotension in the lower extremities, decreased post ductal oxygen saturation in the lower extremities, absent lower extremity pulses - Coarctation of aorta | *[[Hypertension]] in the upper extremities with [[hypotension]] in the lower extremities, decreased [[post ductal]] oxygen saturation in the lower extremities, absent lower extremity pulses - [[Coarctation of aorta]] | ||
*Widened pulse pressure + water hammer pulse - Aortic Regurgitation secondary to aortic dissection | *Widened [[pulse]] pressure + [[water hammer pulse]] - [[Aortic Regurgitation]] secondary to [[aortic dissection]] | ||
* | * | ||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
*Lymphedema of hands and feet | *[[Lymphedema]] of hands and feet | ||
*Toe nail cellulitis | *Toe nail [[cellulitis]] | ||
*Vitiligo | *[[Vitiligo]] | ||
*Alopecia | *[[Alopecia]] | ||
*Nail hypoplasia | *Nail [[hypoplasia]] | ||
*Psoriasis - silver scaled erythrematous plaques present on extensor surfaces | *[[Psoriasis]] - silver scaled [[erythrematous plaques]] present on [[extensor]] surfaces | ||
*Pigmented melanocytic nevi - avoid rubbing against clothes. | *Pigmented [[melanocytic nevi]] - avoid rubbing against clothes. | ||
*Hyperconvex nails | *[[Hyperconvex]] nails | ||
*Oslers nodes, Jane way lesions - Infective Endocarditis | *[[Oslers nodes]], Jane way lesions]] - [[Infective Endocarditis]] | ||
===HEENT=== | ===HEENT=== | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
'''Eye''' | '''Eye''' | ||
#Prominent epicanthal folds | #Prominent [[epicanthal folds]] | ||
#Bilateral epicanthus | #[[Bilateral epicanthus]] | ||
#Strabismus | #[[Strabismus]] | ||
#Ptosis | #[[Ptosis]] | ||
#Cataract | #[[Cataract]] | ||
#Nystagmus | #[[Nystagmus]] | ||
#Roth spots - secondary to infective endocarditis | #[[Roth spots]] - secondary to [[infective endocarditis]] | ||
===Neck=== | ===Neck=== | ||
*Pterygium colli | *[[Pterygium colli]] | ||
*Low posterior hair line | *Low posterior hair line | ||
*Loose skin on the nape of newborns | *Loose skin on the nape of newborns | ||
*[[Jugular venous distension]] - Rule out Eisenmengirsation secondary to congenital heart defects, pressure may be transmitted to the internal | *[[Jugular venous distension]] - Rule out [[Eisenmengirsation]] secondary to [[congenital heart defects]], pressure may be transmitted to the [[internal jugular vein]]. | ||
*[[Hepatojugular reflux]] - There is an increased risk of ischemic heart disease and cardiomyopathy secondary to this may cause Right sided heart failure. | *[[Hepatojugular reflux]] - There is an increased risk of [[ischemic heart disease]] and [[cardiomyopathy]] secondary to this may cause Right sided [[heart failure]]. | ||
===Lungs=== | ===Lungs=== | ||
* Pulmonary examination of patients with Turner syndrome is usually normal. | *[[Pulmonary]] examination of patients with [[Turner syndrome]] is usually normal. | ||
*Fine/coarse [[crackles]] upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally (rule out) | *Fine/coarse [[crackles]] upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally (rule out) | ||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
*[[Heart sounds#Fourth heart sound S4|S4]] (rule out) | *[[Heart sounds#Fourth heart sound S4|S4]] (rule out) | ||
*[[Heart sounds#Summation Gallop|Gallops]] (rule out) | *[[Heart sounds#Summation Gallop|Gallops]] (rule out) | ||
*A pansystolic murmur heard over the tricuspid area - Ventricular Septal defect | *A [[pansystolic murmur]] heard over the [[tricuspid]] area - [[Ventricular Septal defect]] | ||
*Early blowing diastolic murmur head over the left upper sternal border - Aortic | *Early blowing [[diastolic murmur]] head over the left upper [[sternal border]] - [[Aortic regurgitation]] secondary to [[aortic dissection]] | ||
*Systolic ejection click followed by a crescendo decrescendo murmur (early P2 and delayed A2) - Early onset aortic stenosis secondary to a bicuspid aortic valve | *[[Systolic ejection click]] followed by a [[crescendo decrescendo murmur]] (early P2 and delayed A2) - Early onset [[aortic stenosis]] secondary to a [[bicuspid aortic valve]] | ||
*Fever + Petechiae + Heart murmur - Infective Endocarditis | *Fever + [[Petechiae]] + [[Heart murmur]] - [[Infective Endocarditis]] | ||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
*Look for signs of inflammatory bowel disease such as fistulas, skin tags and oral aphtous ulcers | *Look for signs of [[inflammatory bowel disease]] such as [[fistulas]], [[skin tags]] and oral [[aphtous ulcers]] | ||
===Back=== | ===Back=== | ||
*Kyphosis | *[[Kyphosis]] | ||
*Scoliosis | *[[Scoliosis]] | ||
===Genitourinary=== | ===Genitourinary=== | ||
*Chronic estrogen deficiency may lead to signs of atrophic vaginitis | *Chronic [[estrogen]] deficiency may lead to signs of [[atrophic vaginitis]] | ||
*Rudimentary uterus | *[[Rudimentary uterus]] | ||
*Palpable mass secondary to dysgerminoma or gonadoblastoma | *Palpable mass secondary to [[dysgerminoma]] or [[gonadoblastoma]] | ||
===Neuromuscular=== | ===Neuromuscular=== | ||
*Neuromuscular examination of patients with Turner syndrome is usually normal. | *[[Neuromuscular]] examination of patients with [[Turner syndrome]] is usually normal. | ||
===Extremities=== | ===Extremities=== | ||
*Shortened limbs | *Shortened limbs | ||
*Shortened 4th metacarpal | *Shortened 4th [[metacarpal]] | ||
*Cubitus valgus deformity | *[[Cubitus valgus]] deformity | ||
*Madelung deformity | *[[Madelung deformity]] | ||
*[[Cyanosis]] - Secondary to structural heart defects | *[[Cyanosis]] - Secondary to structural heart defects | ||
*Pitting [[edema]] of the upper/lower extremities - Hypothyroidism | *Pitting [[edema]] of the upper/lower extremities - [[Hypothyroidism]] | ||
*Muscle atrophy | *[[Muscle atrophy]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:12, 15 September 2020
|
Turner syndrome Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Turner syndrome physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Turner syndrome physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Turner syndrome physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Akash Daswaney, M.B.B.S[2]
Overview
Physical examination may be suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, congenital heart defects, inflammatory bowel disease, characteristic skeletal deformities and body habitus/skin manifestations.
Physical Examination
Appearance of the Patient
- Patient may show signs of poor growth velocity and malnutrition indicative of failure to thrive.
- Patients may be hyperactive.
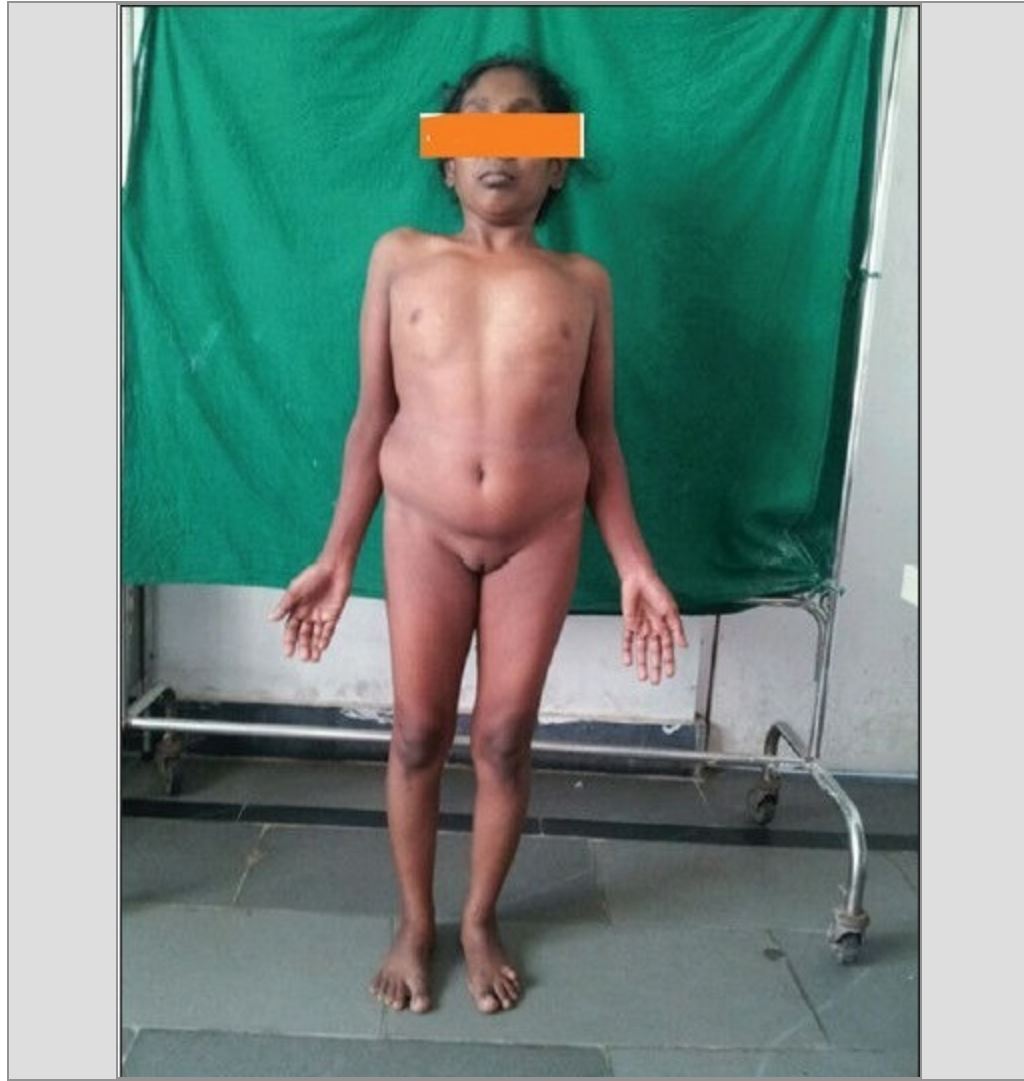
- The presence of short stature, a webbed neck, pigmented nevi, puffiness of the hands and feet, a cubitus valgus deformity, genu valgum on physical examination are highly suggestive of Turner syndrome.
Vital Signs
- High-grade / low-grade fever
- Hypothermia / hyperthermia may be present
- Tachycardia with regular pulse or irregularly irregular pulse - Hyperthyroidism
- Bradycardia with regular pulse or irregularly irregular pulse - Hypothyroidism
- Tachypnea - Secondary to Acute pulmonary edema from ischemic heart disease
- Hypertension in the upper extremities with hypotension in the lower extremities, decreased post ductal oxygen saturation in the lower extremities, absent lower extremity pulses - Coarctation of aorta
- Widened pulse pressure + water hammer pulse - Aortic Regurgitation secondary to aortic dissection
Skin
- Lymphedema of hands and feet
- Toe nail cellulitis
- Vitiligo
- Alopecia
- Nail hypoplasia
- Psoriasis - silver scaled erythrematous plaques present on extensor surfaces
- Pigmented melanocytic nevi - avoid rubbing against clothes.
- Hyperconvex nails
- Oslers nodes, Jane way lesions]] - Infective Endocarditis
HEENT
Ear
- Weber test may be abnormal- Conductive hearing loss or sensorineural hearing loss
- Rinne test may be positive - Conductive hearing loss or sensorineural hearing loss
- External ear canal deformities may be noted.
Eye
- Prominent epicanthal folds
- Bilateral epicanthus
- Strabismus
- Ptosis
- Cataract
- Nystagmus
- Roth spots - secondary to infective endocarditis
Neck
- Pterygium colli
- Low posterior hair line
- Loose skin on the nape of newborns
- Jugular venous distension - Rule out Eisenmengirsation secondary to congenital heart defects, pressure may be transmitted to the internal jugular vein.
- Hepatojugular reflux - There is an increased risk of ischemic heart disease and cardiomyopathy secondary to this may cause Right sided heart failure.
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with Turner syndrome is usually normal.
- Fine/coarse crackles upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally (rule out)
Heart
- Patient has a wide shield shaped chest with inverted nipples.
- S3 (rule out)
- S4 (rule out)
- Gallops (rule out)
- A pansystolic murmur heard over the tricuspid area - Ventricular Septal defect
- Early blowing diastolic murmur head over the left upper sternal border - Aortic regurgitation secondary to aortic dissection
- Systolic ejection click followed by a crescendo decrescendo murmur (early P2 and delayed A2) - Early onset aortic stenosis secondary to a bicuspid aortic valve
- Fever + Petechiae + Heart murmur - Infective Endocarditis
Abdomen
- Look for signs of inflammatory bowel disease such as fistulas, skin tags and oral aphtous ulcers
Back
Genitourinary
- Chronic estrogen deficiency may lead to signs of atrophic vaginitis
- Rudimentary uterus
- Palpable mass secondary to dysgerminoma or gonadoblastoma
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with Turner syndrome is usually normal.
Extremities
- Shortened limbs
- Shortened 4th metacarpal
- Cubitus valgus deformity
- Madelung deformity
- Cyanosis - Secondary to structural heart defects
- Pitting edema of the upper/lower extremities - Hypothyroidism
- Muscle atrophy
References
- ↑ Bucerzan S, Miclea D, Popp R, Alkhzouz C, Lazea C, Pop IV; et al. (2017). "Clinical and genetic characteristics in a group of 45 patients with Turner syndrome (monocentric study)". Ther Clin Risk Manag. 13: 613–622. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S126301. PMC 5422538. PMID 28496331.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Vaddadi S, Murthy RS, Rahul CH, Kumar VL (2013). "A rare case of Turner's syndrome presenting with Mullerian agenesis". J Hum Reprod Sci. 6 (4): 277–9. doi:10.4103/0974-1208.126313. PMC 3963314. PMID 24672170.
![[1]](/images/c/c7/Turner_Syndrome_Phenotype.JPG)
![[2]](/images/0/03/Turner_Syndrome_Phenotype_2.JPG)
![[2]](/images/7/77/Turner_Syndrome_Phenotype_3.JPG)