Pulmonary hypertension pathophysiology
|
Pulmonary Hypertension Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pulmonary hypertension pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pulmonary hypertension pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pulmonary hypertension pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Assistant Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ralph Matar; Rim Halaby
Overview
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a pathological condition of the pulmonary vasculature present in several disease states that presents with elevated mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) as measured by right heart catheterization at rest. The factors that are in involved in the pathophysiology of the increase in the mean pulmonary arterial pressure are: increase in pulmonary vascular resistance, increase in the right-sided cardiac output and increase in the mean pulmonary venous pressure. To note that “pulmonary arterial hypertension” (PAH) refers to group 1 PAH in the updated WHO classification. “pulmonary hypertension” (PH) refers to any of group 2 PH through group 5 PH. PH is also used when referring to all five groups collectively. Pulmonary arterial hypertension is characterized by endothelial dysfunction resulting from an imbalance between apoptosis and proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells favoring the proliferation. The other are caused by hemodynamic changes that result in increased pulmonary blood pressure or architectural changes to the lung or its vasculature that result in the same outcome.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10]
PH is defined as an elevated mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) ≥ 25 mmHg as measured by right heart catheterization at rest. The elevation in PAP results from an elevation in the pulmonary vascular resistance caused by a multifactorial pathogenesis involving genetic and environmental factors.
Pulmonary hypertension has several pathophysiologic mechanisms depending on the underlying etiology. Nevertheless, the following sequence of events is almost always present:
- Vasoconstriction (ocurring early in the disease);
- Thrombosis (during the evolution of the disease);
- Remodeling (then takes place and becomes the most important factor).[3]
- An initiating factor leads to increased resistance in the pulmonary vasculature causing narrowing of the vessels and impaired blood flow.
- As a consequence, the right ventricle adapts by increasing right ventricular systolic pressures to preserve the cardiac output from the right heart.
- Over time, increasing right ventricular systolic pressures will subsequently result in chronic changes in the pulmonary circulation and the affected blood vessels progressively become stiffer and thicker, further increasing the blood pressure within the lungs and impairing blood flow.
- In addition, the increased workload of the heart causes thickening and enlargement of the right ventricle, making the heart less able to pump blood through the lungs, causing right heart failure. Factors that might affect the ability of the right ventricle to adapt to an increased pulmonary vascular resistance are:
- Age of the patient at onset
- Rapidity of onset of pulmonary hypertension
- Coexisting hypoxemia
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Molecular and Cellular Changes
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension is characterized by endothelial dysfunction resulting from an imbalance between apoptosis and proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells favoring the proliferation.
- There is also thickened and disordered adventitia due to excessive amounts of adventitial metalloproteinases.
- Several pathways are implicated in development of vascular remodeling, which is the hallmark of pathologic changes in pulmonary hypertension:
1. Vasoconstriction-mediated remodeling
- Imbalance of vasoactive signals is suggested in the pathogenesis of remodeling.
- Reduced levels of vasodilatory mediators, in particular prostaglandin I2, nitric oxide, and cyclic guanine monophosphate, and elevated levels of vasocontricting molecules such as endothelin 1, thromboxane, and 5-hydroxytryptamine contribute to alterations in the vascular tone.
- Down regulation of the voltage-gated potassium channels has also been linked with altered pulmonary vascular tone, dysregulation of cellular homeostasis, and induction of proliferative sequelae in vascular smooth muscle cells.
- May occur in response to hypoxia;
- May be reversible - patients treated early in the disease with calcium channel blockers seem to have a much better prognosis.[3]
2. Thrombosis-mediated remodeling
- Thrombin plays a key role in mediating vascular remodeling by activating platelet, upregulating angiogenesis-related genes (including tissue factor [TF], basic fibroblast growth factor [bFGF], and matrix metalloproteinase-2), and transactivating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by inducing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the expression of the hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha.
- Upregulation of TF in the vasculature leads to initiation of coagulation cascade and migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells upon vascular injury.
- In addition, platelet activation by thrombin results in the release of granules containing substances that promote mitogenesis and vasoconstriction including VEGF, bFGF, platelet-derived growth factor, and serotonin, which also contribute to increased endothelial cell migration and proliferation.
3. Proliferation-mediated remodeling
- Serotonin exerts both vasoconstrictive and mitogenic effects on smooth muscle cells (SMC).
- Serotonin m bind to 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A and 2B receptors or may enter SMC via serotonin transporter which induces generation of ROS, rho kinase, and mitogen-activated protein kinases.
- This in turn leads to the expression of growth factors and proliferation. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) is also involved in the SMC proliferation.
- Upon binding of BMP to its heterodimerized receptors, a group of cytoplasmic proteins known as receptor-mediated Smads are phosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus where they upregulate genes related to anti-proliferation.
- Serotonin is shown to antagonize the BMP/Smad pathway thus facilitating the proliferation of smooth muscle cells.
4. Inflammation-mediated remodeling
- Influx of inflammatory effector cells is stimulated by the release of chemokines such as CCL5 and CX3CL1.
- On the other hand, endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell dysfunction contributes to the release of vasomotor and growth factors, activation of transcription factors, influx of calcium, and dysfunction of mitochondria.
- The net effect is a shift of balance in favor of proliferation and suppressed apoptosis, leading to remodeling of the pulmonary vasculature.
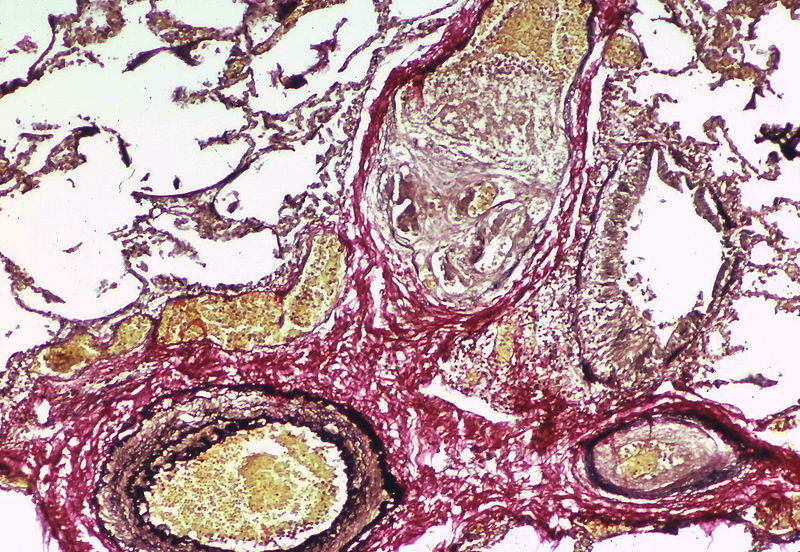
Shown below is an image depicting remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Genetic Mutations
TGF-β Receptor Pathway
- Bone morphogenetic protein receptor II (BMPR2) gene encodes a serine/threonine kinase that functions as a receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins which forms a heterodimer cytoplasmic complex of two type II and two type I receptors. The downstream signaling involves activation of SMAD transcription factor which mediates anti-proliferation in smooth muscle cells.
- Activin-like kinase 1 gene mutations are detected in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Mutation would cause growth-promoting alterations.
Serotoninergic Pathway
- 5- Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) transporter mutations have also been associated with the proliferation of smooth muscle cells of pulmonary arteries.[11]
Genetics
Familial PAH often results from a mutation in the bone morphogenic protein receptor-2 (BMPR2) and is inherited as an autosomal dominant disease with incomplete penetrance and anticipation.[12]
Associated conditions
- PAH is also associated with:[13]
- Congenital heart disease (30% of untreated cases)
- Connective tissue diseases (12% of patients with scleroderma and up to 21% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis)
- HIV (0.5%)
- Portal hypertension (2-6%)
- Sickle cell disease (20 to 40%)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (4 to 14%)
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Myeloproliferative disorders
- Drugs and toxins
Histopathology
PH is a pathological condition present in different disease states that share similar clinical manifestation and some common histopathological features. Shown below is a table that summarizes the classification of PH based on histopathology findings.[14]
| Class | Histopathological findings[14] | Images |
|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary arteriopathy | Constrictive lesions in pulmonary arteries
Complex lesions in pulmonary arteries
|
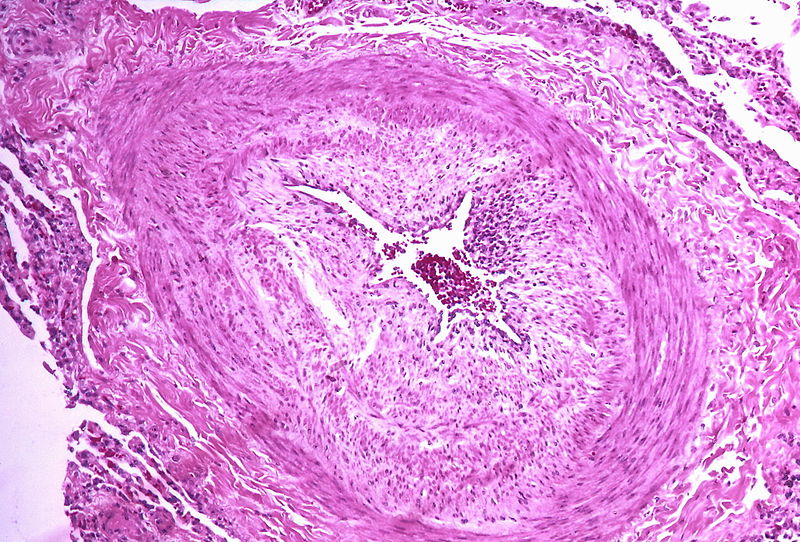 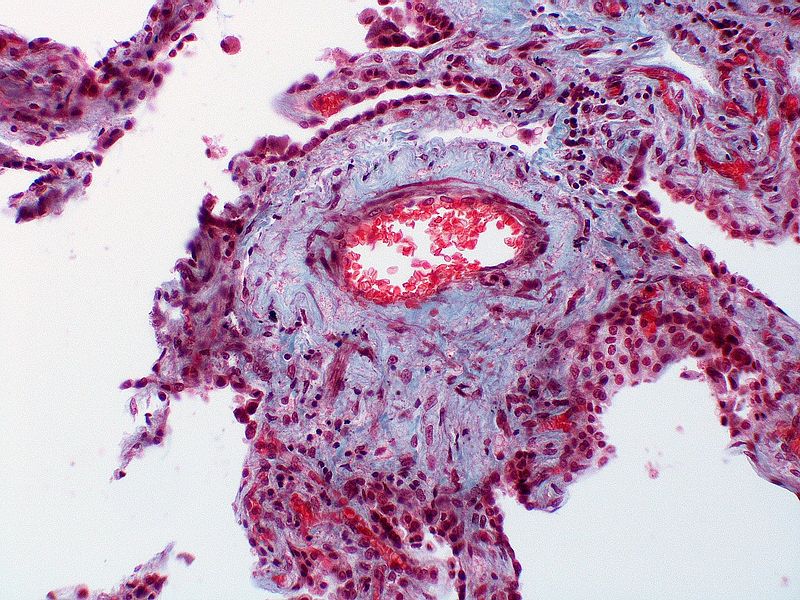 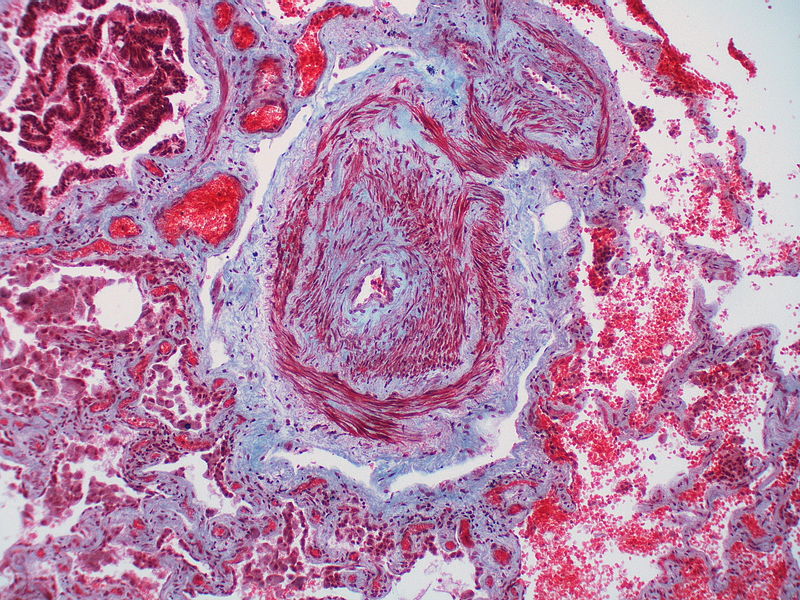 |
| Pulmonary arteriopathy with venous-venular changes | Changes similar to pulmonary arteriopathy PLUS Changes in venules and veins |
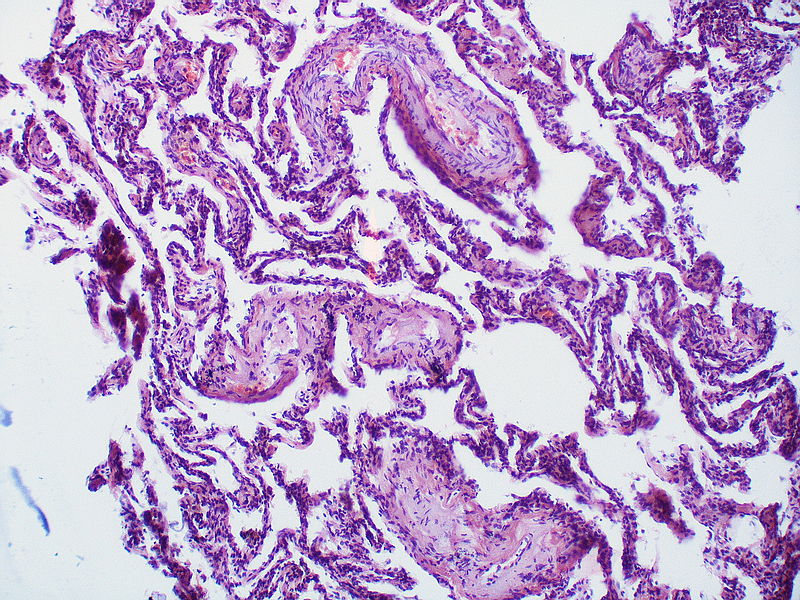 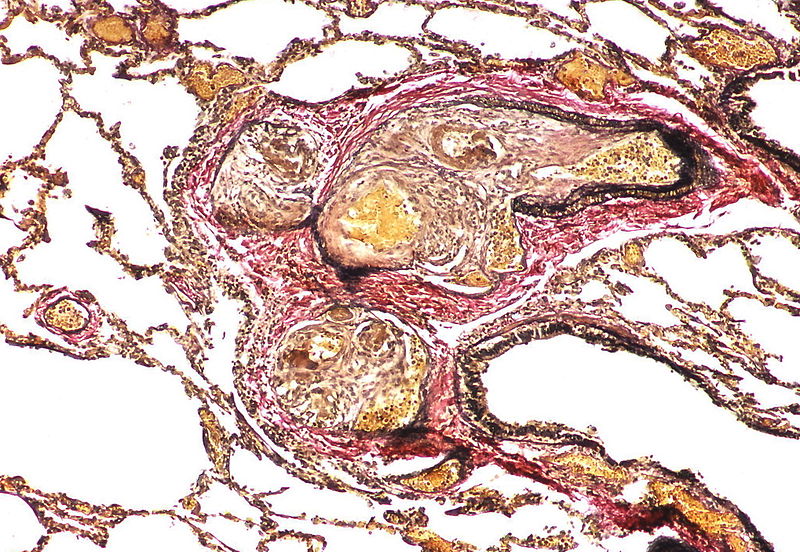 |
| Pulmonary occlusive venopathy (with or without arteriopathy) |
Changes in venules and veins
Changes in the capillaries
Changes in the interstitium |
|
| Pulmonary microvasculopathy (with or without arteriopathy and/on venopathy) |
Changes in the capillaries
Changes in the interstitium |
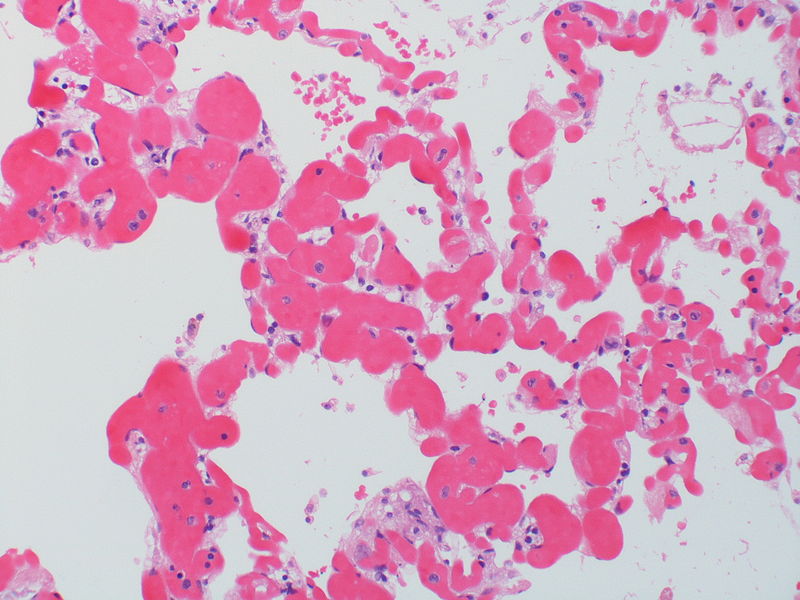 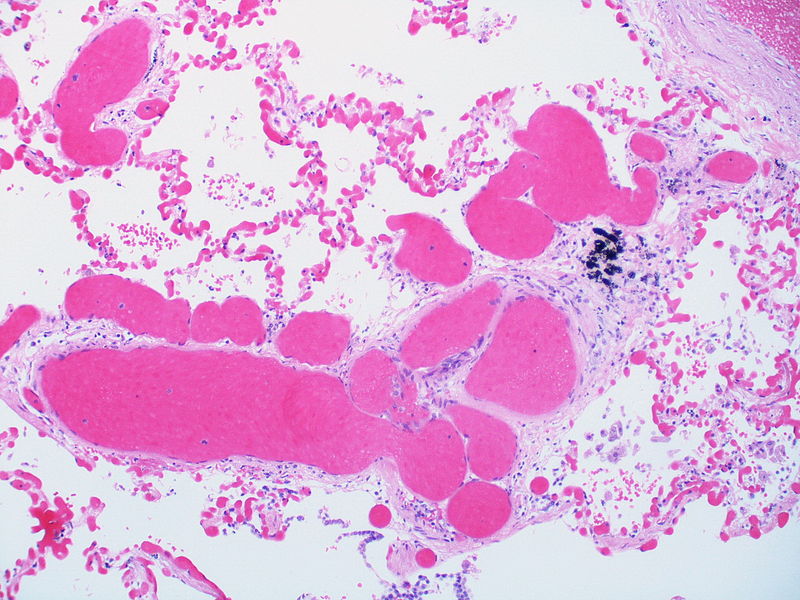 |
| Unclassified | Non specific changes |
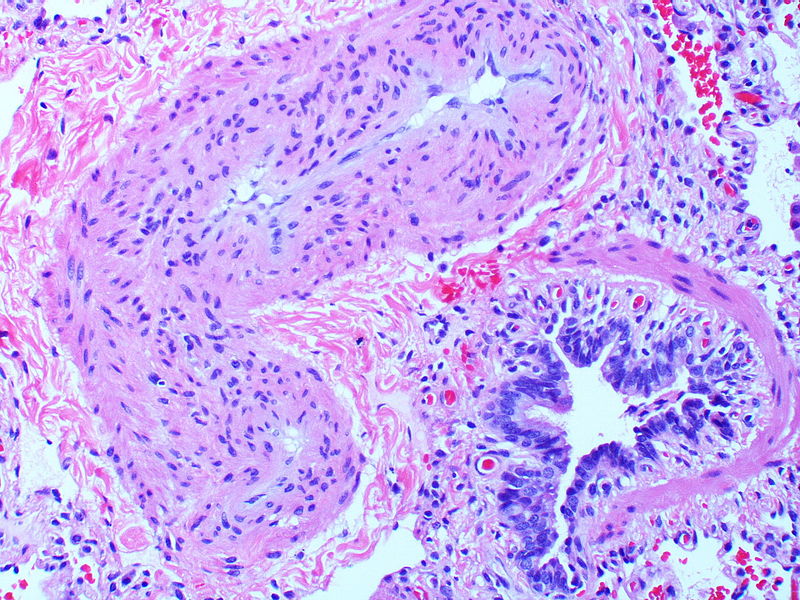
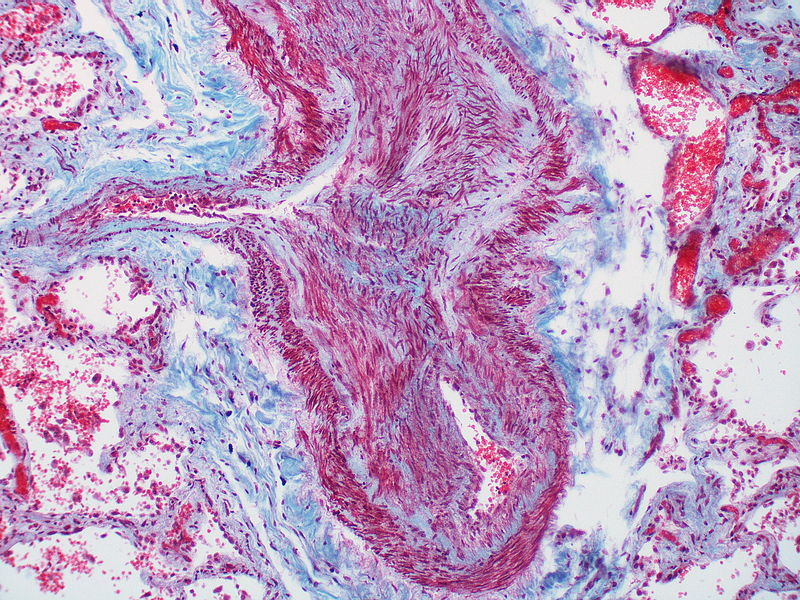
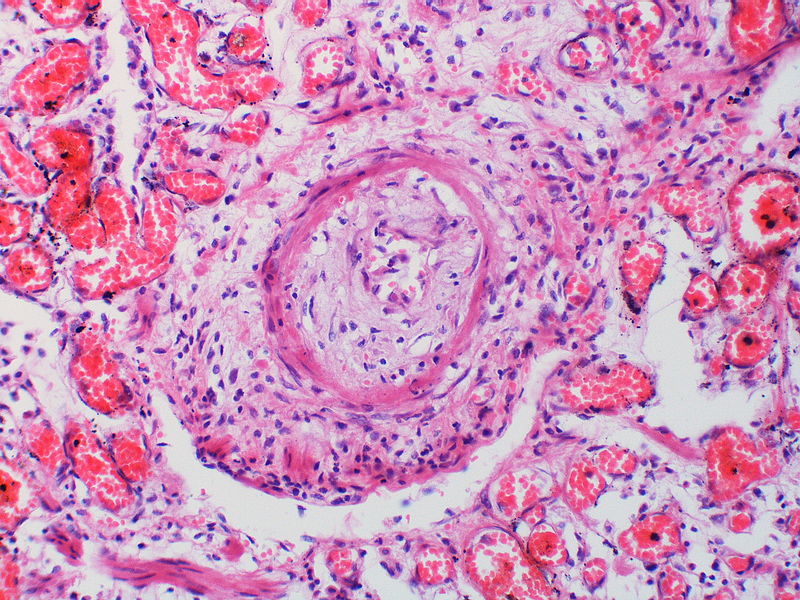
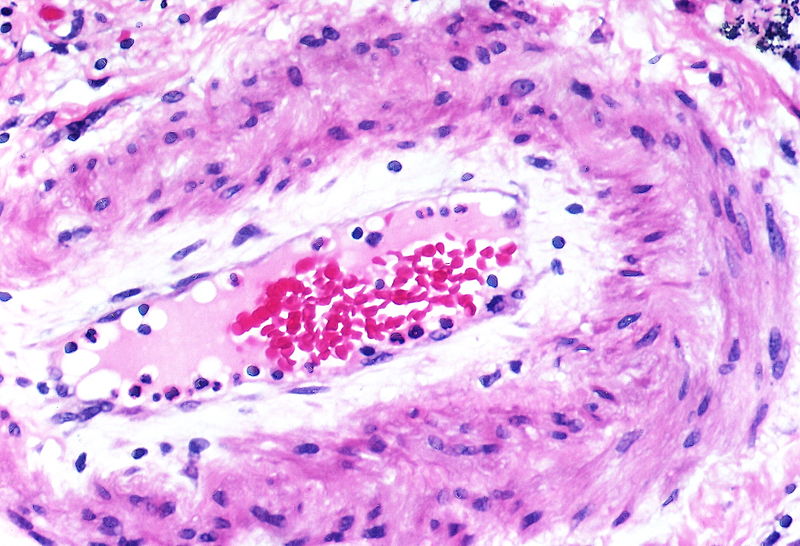
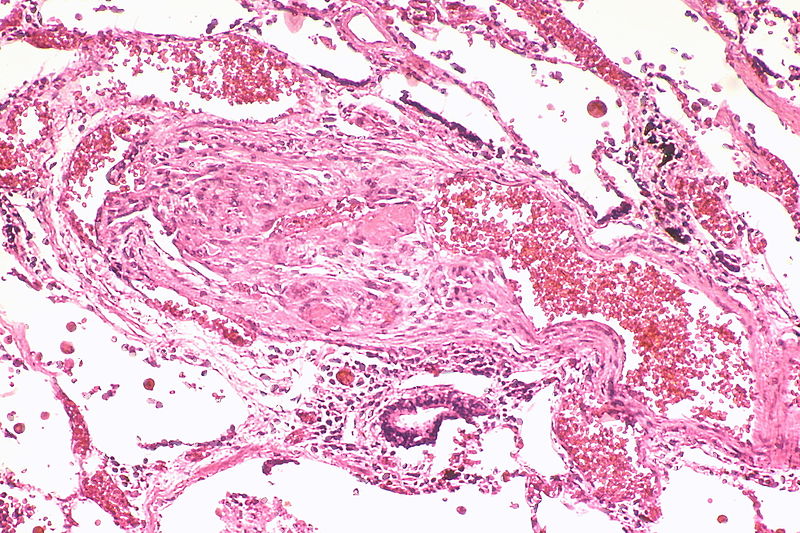
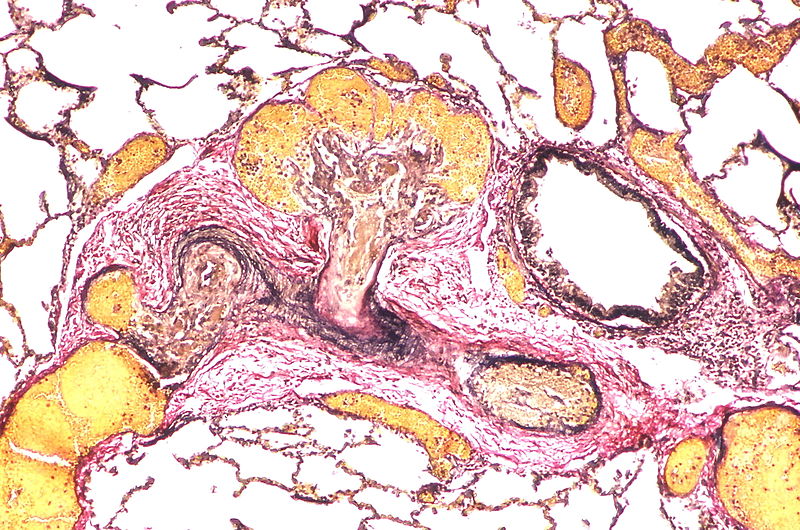
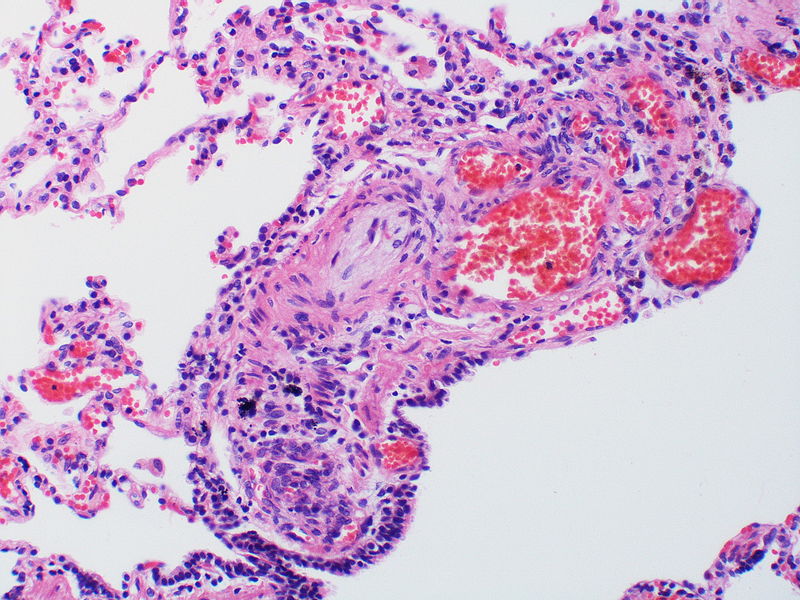
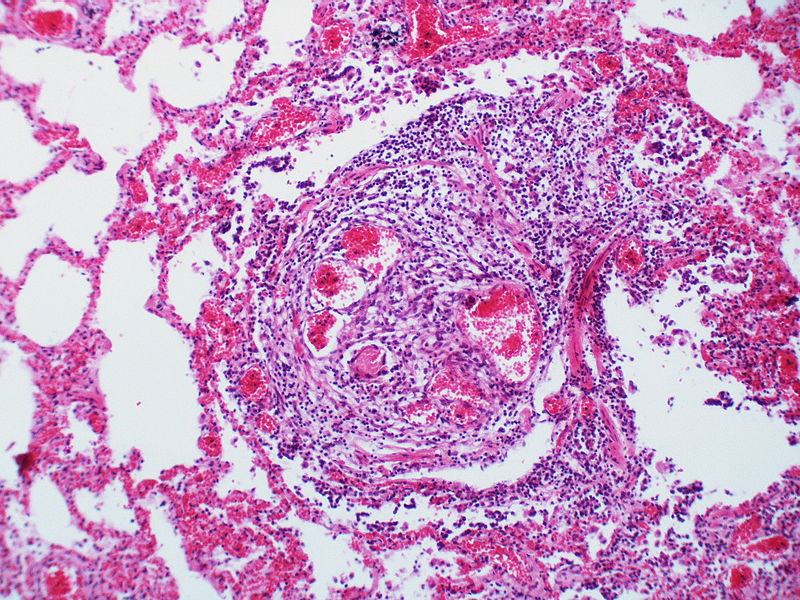
Gallery
The images below are courtesy of Dr. Yale Rosen (Source:Wikimedia Commons).
-
Marked intimal and medial thickening
-
Medial muscle layer thickening involving multiple pulmonary arteries.
-
This arteriole exhibits fibrinoid necrosis.
-
Pronounced thickening of the medial muscle layer.
-
Marked intimal and medial thickening.
-
This artery exhibits marked intimal thickening The red-staining cells in the intima are probably myofibroblasts. Masson trichrome stain.
-
Marked adventitial thickening. Masson trichrome stain.
-
This artery exhibits marked intimal thickening as well as adventitial thickening. The red-staining cells in the intima are probably myofibroblasts. Masson trichrome stain.
-
Pulmonary hypertension associated with pulmonary hemangiomatosis. A muscular pulmonary artery surrounded by angiomatous vessels exhibits marked intimal and adventitial thickening.
-
There is thickening of the medial muscle layer as well as mild intimal thickening.
-
Alveolar capillary proliferation as well as the proliferation of larger blood vessels, probably venules.
-
This artery exhibits vasculitis characterized by focal necrosis of the wall accompanied by inflammation.
-
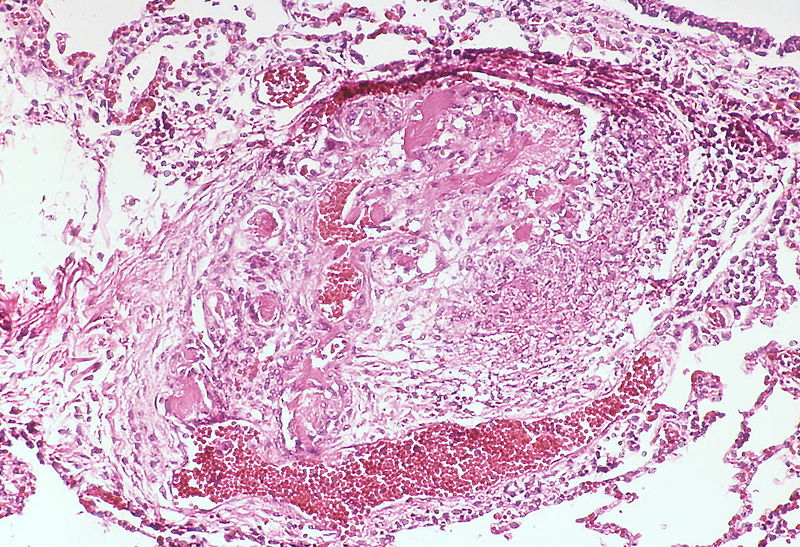
A large dilatation lesion is present on the right side of this image adjacent to an angiomatoid lesion.
-
Two angiomatoid lesions are present. A large dilatation lesion is a present adjacent to the angiomatoid lesion that is located just above center.
-
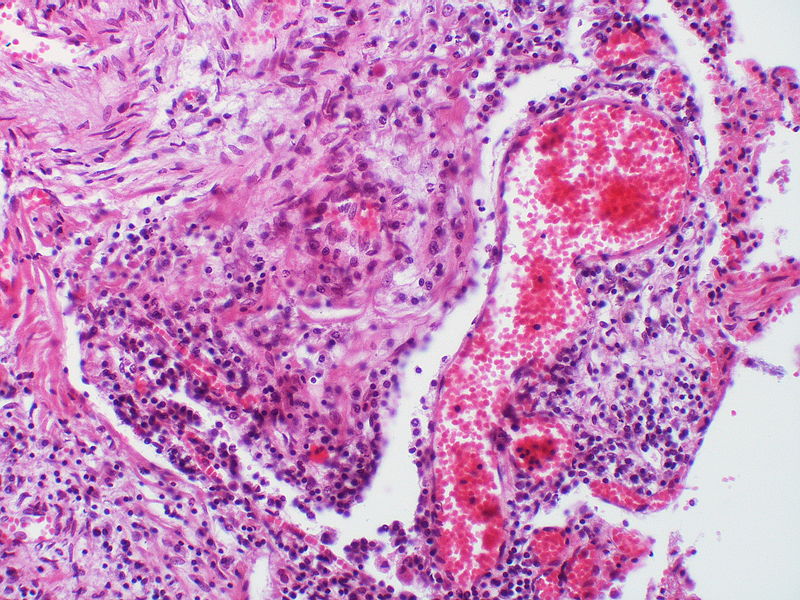
There is angiomatoid (plexiform) lesion.
-
The appearance suggests multiple lesions but a single lesion cannot be excluded. Note the destruction of the arterial wall at the site of the angiomatoid lesion. Destructive arterial changes are frequently associated with angiomatoid lesions. There is an elastic stain.
-
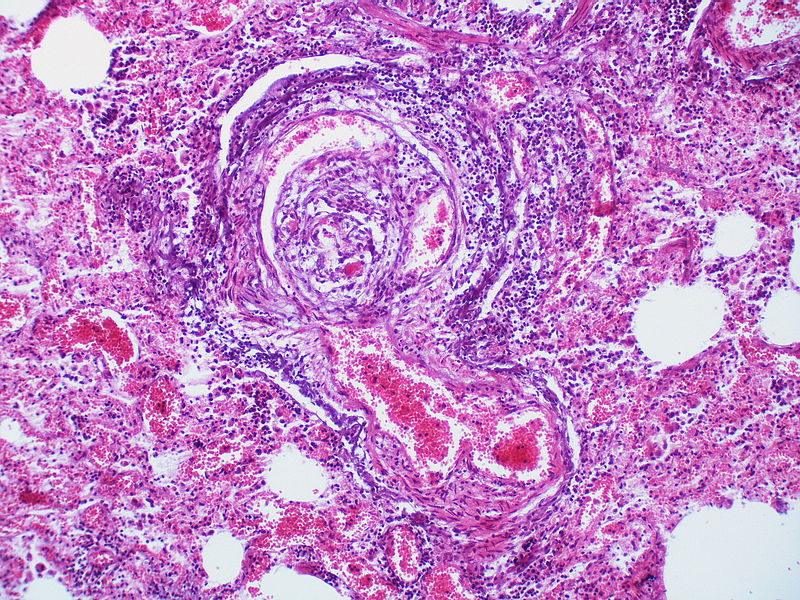
This angiomatoid lesion is accompanied by inflammation which is frequently associated with these lesions.
-
There is a proliferation of alveolar wall capillaries which are markedly dilated.
-
A dilatation lesion is seen in the left lower quadrant adjacent to the angiomatoid lesion. There is an elastic stain.
-
This angiomatoid lesion contains multiple thrombi within the vascular spaces. A large dilatation lesion is a present adjacent to the bottom of the angiomatoid lesion.
-
A dilatation lesion is present adjacent to the right side of the angiomatoid lesion.
-
There is a disappearance of the arterial wall at the site of the angiomatoid lesions. Arterial wall destruction is a frequent finding in association with angiomatoid lesions. A dilatation lesion encircles the angiomatoid lesion
References
- ↑ Marcos E, Fadel E, Sanchez O, Humbert M, Dartevelle P, Simonneau G, Hamon M, Adnot S, Eddahibi S (May 2004). "Serotonin-induced smooth muscle hyperplasia in various forms of human pulmonary hypertension". Circ. Res. 94 (9): 1263–70. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000126847.27660.69. PMID 15059929.
- ↑ Eddahibi S, Fabre V, Boni C, Martres MP, Raffestin B, Hamon M, Adnot S (February 1999). "Induction of serotonin transporter by hypoxia in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells. Relationship with the mitogenic action of serotonin". Circ. Res. 84 (3): 329–36. PMID 10024307.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Huber LC, Bye H, Brock M (2015). "The pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension--an update". Swiss Med Wkly. 145: w14202. doi:10.4414/smw.2015.14202. PMID 26479975.
- ↑ Peacock A (March 2013). "Pulmonary hypertension". Eur Respir Rev. 22 (127): 20–5. doi:10.1183/09059180.00006912. PMID 23457160.
- ↑ Tuder RM, Stacher E, Robinson J, Kumar R, Graham BB (December 2013). "Pathology of pulmonary hypertension". Clin. Chest Med. 34 (4): 639–50. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2013.08.009. PMID 24267295.
- ↑ Michelakis ED (June 2014). "Pulmonary arterial hypertension: yesterday, today, tomorrow". Circ. Res. 115 (1): 109–14. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.301132. PMID 24951761.
- ↑ Douwes JM, Berger RM (February 2011). "The maze of vasodilator response criteria". Pediatr Cardiol. 32 (2): 245–6. doi:10.1007/s00246-010-9849-8. PMID 21110189.
- ↑ Ranchoux B, Antigny F, Rucker-Martin C, Hautefort A, Péchoux C, Bogaard HJ, Dorfmüller P, Remy S, Lecerf F, Planté S, Chat S, Fadel E, Houssaini A, Anegon I, Adnot S, Simonneau G, Humbert M, Cohen-Kaminsky S, Perros F (March 2015). "Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary hypertension". Circulation. 131 (11): 1006–18. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008750. PMID 25593290.
- ↑ Hopper RK, Moonen JR, Diebold I, Cao A, Rhodes CJ, Tojais NF, Hennigs JK, Gu M, Wang L, Rabinovitch M (May 2016). "In Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, Reduced BMPR2 Promotes Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via HMGA1 and Its Target Slug". Circulation. 133 (18): 1783–94. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020617. PMC 4856565. PMID 27045138.
- ↑ Jobe AH, Bancalari E (June 2001). "Bronchopulmonary dysplasia". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163 (7): 1723–9. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.163.7.2011060. PMID 11401896.
- ↑ Eddahibi S, Humbert M, Fadel E, Raffestin B, Darmon M, Capron F; et al. (2001). "Serotonin transporter overexpression is responsible for pulmonary artery smooth muscle hyperplasia in primary pulmonary hypertension". J Clin Invest. 108 (8): 1141–50. doi:10.1172/JCI12805. PMC 209526. PMID 11602621.
- ↑ Rich, S.; Dantzker, DR.; Ayres, SM.; Bergofsky, EH.; Brundage, BH.; Detre, KM.; Fishman, AP.; Goldring, RM.; Groves, BM. (1987). "Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study". Ann Intern Med. 107 (2): 216–23. PMID 3605900. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ ACCF/AHA 2009 Expert Consensus Document on Pulmonary Hypertension
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Pietra GG, Capron F, Stewart S, Leone O, Humbert M, Robbins IM; et al. (2004). "Pathologic assessment of vasculopathies in pulmonary hypertension". J Am Coll Cardiol. 43 (12 Suppl S): 25S–32S. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.033. PMID 15194175.