Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound
|
Polycystic kidney disease Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Polycystic kidney disease from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
FDA on Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
CDC on Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound in the news |
|
Blogs on Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Polycystic kidney disease echocardiography or ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
USG
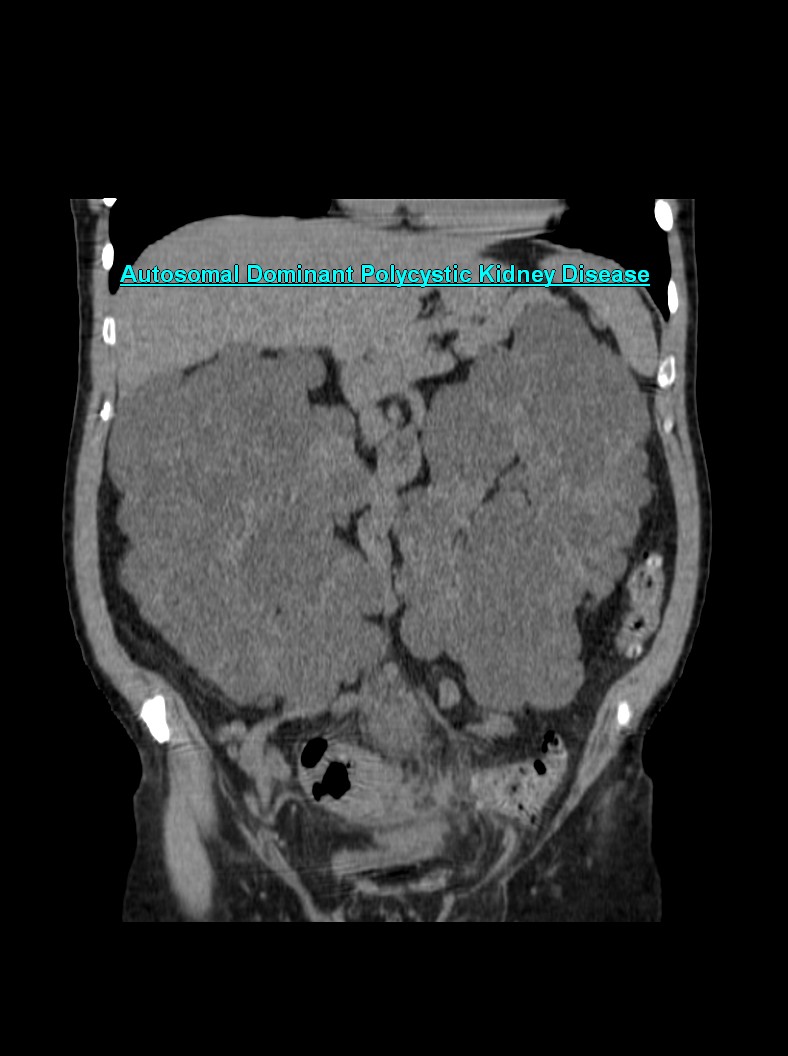
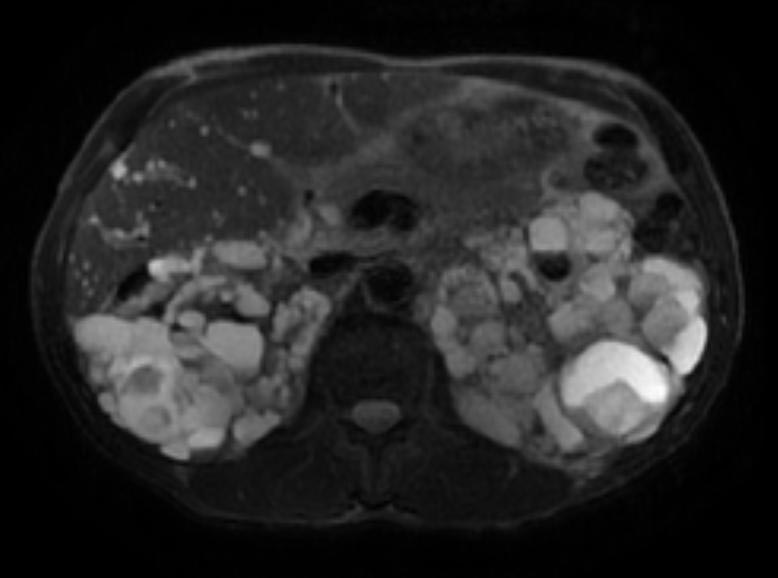
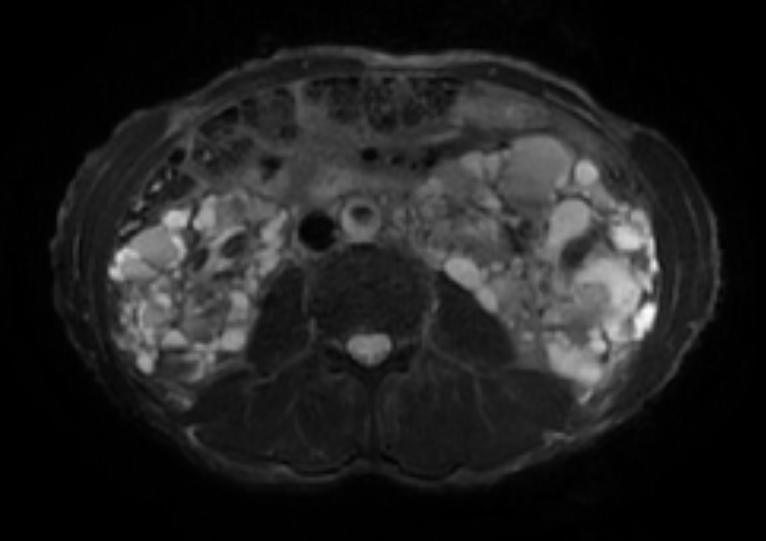
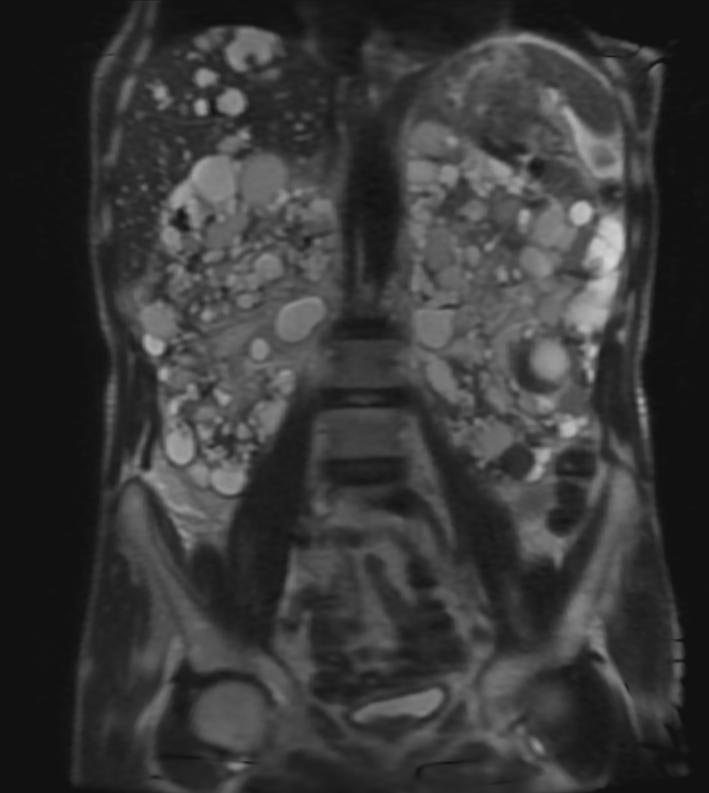
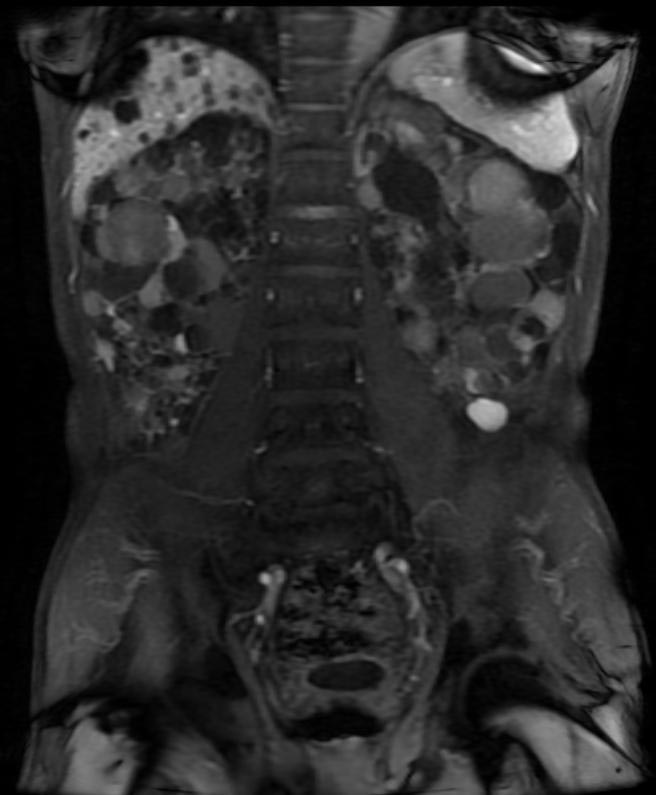
- On a USG, the kidneys are massively enlarged and diffusely echogenic bilaterally.
- Corticomedullary differentiation is absent.
- High-resolution USG (linear-array transducer, 7.5 mHz or greater) allows visualization of numerous cylindrical cysts in the medulla and cortex, which represent ectatic collecting ducts.
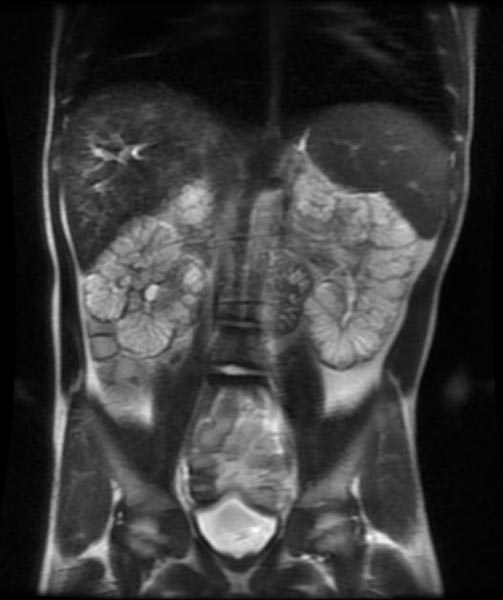
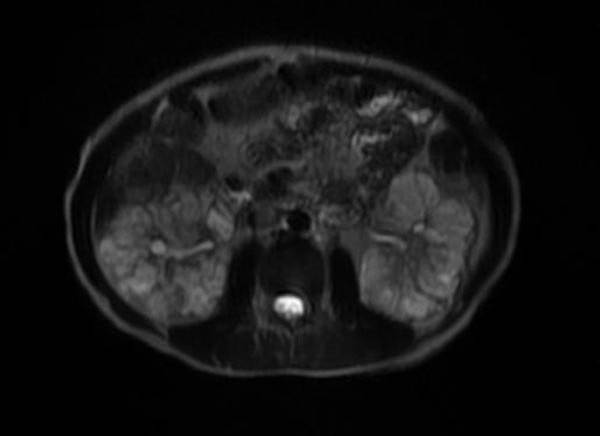

Autosomal dominant form
- Multiple, variably sized cortical and medullary based cysts
- Renomegaly
- Hemorrhagic cysts are often present
Patient #1
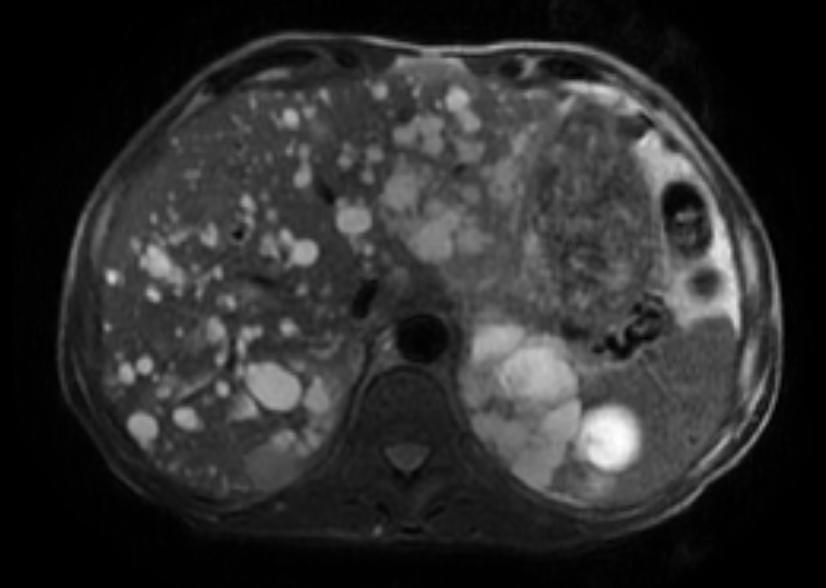
Patient #2
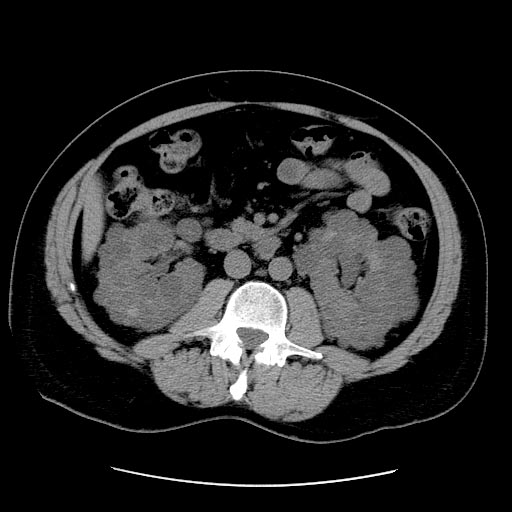


Patient #3
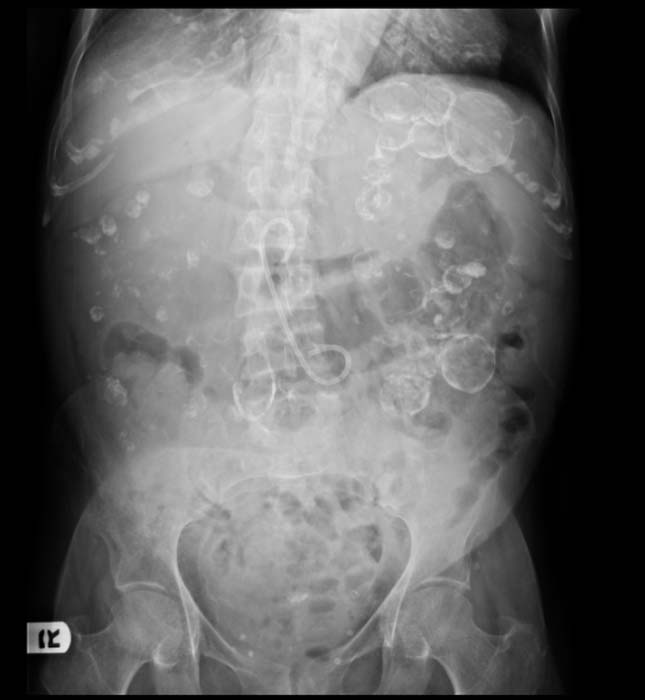
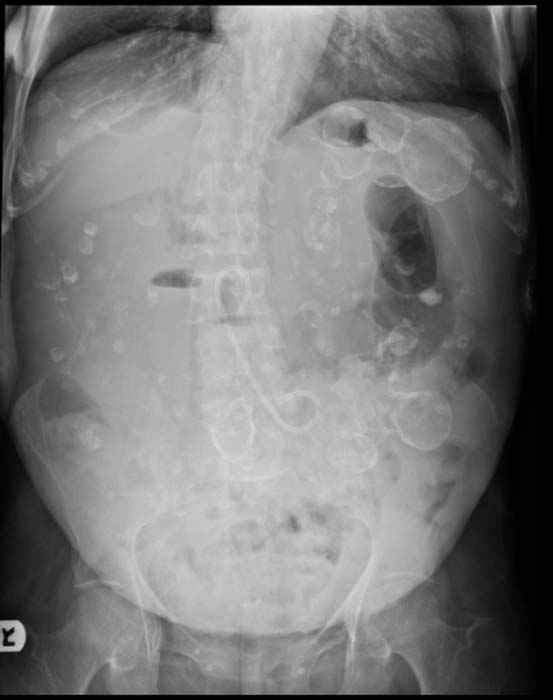
Patient #4