Pneumonia differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{CMG}}; | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{HQ}}, [[Priyamvada Singh|Priyamvada Singh, M.D.]] [mailto:psingh13579@gmail.com] {{HK}} | ||
{{ | [[Image:Home_logo1.png|right|250px|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Pneumonia]] | ||
==Overview== | |||
Pneumonia should be differentiated from other conditions that cause [[cough]], [[fever]], [[shortness of breath]] and [[tachypnea]], such as [[asthma]], [[COPD]], [[CHF]], [[cancer]], [[GERD]], [[pulmonary emboli]]. | |||
==Differentiating Pneumonia from other Diseases== | |||
{| style="border: 0px; font-size: 90%; margin: 3px; width: 700px;" align=center | |||
|valign=top| | |||
|+'''Differential Diagnosis of Pneumonia''' <ref name="pmid1458569">{{cite journal| author=Schiele F, Muller J, Colinet E, Siest G, Arzoglou P, Brettschneider H et al.| title=Interlaboratory study of the IFCC method for alanine aminotransferase performed with use of a partly purified reference material. | journal=Clin Chem | year= 1992 | volume= 38 | issue= 12 | pages= 2365-71 | pmid=1458569 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1458569 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11113658">{{cite journal| author=Castro-Guardiola A, Armengou-Arxé A, Viejo-Rodríguez A, Peñarroja-Matutano G, Garcia-Bragado F| title=Differential diagnosis between community-acquired pneumonia and non-pneumonia diseases of the chest in the emergency ward. | journal=Eur J Intern Med | year= 2000 | volume= 11 | issue= 6 | pages= 334-339 | pmid=11113658 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11113658 }} </ref><ref name="Ahnsjö1935">{{cite journal|last1=Ahnsjö|first1=Sven|title=Contribution to the Differential Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Childhood|journal=Acta Paediatrica|volume=17|issue=3|year=1935|pages=439–446|issn=0803-5253|doi=10.1111/j.1651-2227.1935.tb07697.x}}</ref> | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Disease}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 500px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Findings}} | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Acute bronchitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | No infiltrates seen on the chest X-ray. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Asthma]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Past medical history, no infiltrates seen on chest X-ray. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Bronchiolitis obliterans]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Should be suspected in patients with pneumonia who do not respond to antibiotics treatment. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Congestive heart failure]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Bilateral [[pulmonary edema]], shortness of breath. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[COPD]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Past medical history, no infiltrates on chest X-ray, fever is uncommon. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Empyema]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | CXR showing features of [[pleural effusion]], inflammatory markers on [[thoracocentesis]]. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Endocarditis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Finding of septic [[pulmonary emboli]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Gastroesophageal reflux disease]] (GERD) | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Normal chest X-ray, symptoms are worse during night and associated with meals. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Lung abscess]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Chest X-ray shows signs of [[lung abscess]]. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Lung cancer]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Weight loss, clear sputum. CT scan and biopsy are helpful in ruling out malignancy. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Pertussis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Productive cough for weeks, nasopharyngeal aspirate aids in diagnosis. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Pulmonary embolus]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | A high degree of suspicion should be kept for [[pulmonary embolus]]. Chest X-ray may be normal. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Sinusitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Sinus tenderness, post nasal drip. | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" | [[Vasculitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | Systemic manifestations of [[collagen vascular disease]] may be seen. | |||
|} | |||
==Differential diagnosis== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Causes of | |||
Lung Cavities | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Differentiating Features | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Differentiating Radiological Findings | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Diagnosis Confirmation | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Malignancy]] ([[Lung cancer|Primary lung cance<nowiki/>r]])<ref name="pmid4353362">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chaudhuri MR |title=Primary pulmonary cavitating carcinomas |journal=Thorax |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=354–66 |year=1973 |pmid=4353362 |pmc=470041 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Elderly male or female <ref name="pmid4353362">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chaudhuri MR |title=Primary pulmonary cavitating carcinomas |journal=Thorax |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=354–66 |year=1973 |pmid=4353362 |pmc=470041 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Chronic smokers | |||
*Presents with a [[low-grade fever]], absence of [[leukocytosis]], systemic complaints [[weight loss]], [[fatigue]] | |||
*Absence of factors that predispose to [[gastric content aspiration]], no response to [[antibiotics]] within 10 days | |||
*[[Hemoptysis]] is commonly associated with [[bronchogenic carcinoma]] | |||
| | |||
*A coin-shaped lesion with thick wall(>15mm) is seen on CXR with less ground glass opacities <ref name="pmid8572761">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mouroux J, Padovani B, Elkaïm D, Richelme H |title=Should cavitated bronchopulmonary cancers be considered a separate entity? |journal=Ann. Thorac. Surg. |volume=61 |issue=2 |pages=530–2 |year=1996 |pmid=8572761 |doi=10.1016/0003-4975(95)00973-6 |url=}}</ref> <ref name="pmid16183941">{{cite journal |vauthors=Onn A, Choe DH, Herbst RS, Correa AM, Munden RF, Truong MT, Vaporciyan AA, Isobe T, Gilcrease MZ, Marom EM |title=Tumor cavitation in stage I non-small cell lung cancer: epidermal growth factor receptor expression and prediction of poor outcome |journal=Radiology |volume=237 |issue=1 |pages=342–7 |year=2005 |pmid=16183941 |doi=10.1148/radiol.2371041650 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[Bronchoalveolar lavage]] [[cytology]] shows malignant cells | |||
| | |||
*[[Biopsy]] of lung | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*Pulmonary [[Tuberculosis, pulmonary|Tuberculosis]] | |||
| | |||
*Mostly in endemic areas | |||
*Symptoms include [[productive cough]],[[night sweats]], [[fever]] and [[weight loss]] | |||
| | |||
*CXR and CT demonstrates [[Internal|cavities]] in the upper lobe of the lung | |||
| | |||
*[[Sputum]] smear positive for [[acid-fast bacilli]] and nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT) is used on sputum or any sterile fluid for rapid diagnosis and is positive for mycobacteria. | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Necrotizing Pulmonary Infections|Necrotizing]] [[Pneumonia]] | |||
| | |||
*Any age group | |||
*Acute, [[fulminant]] life threating complication of prior infection | |||
*>100.4F fever, with [[Hemodynamically unstable|hemodynamic]] instability | |||
*Worsening [[pneumonia]]-like symptoms | |||
| | |||
*CXR demonstrates multiple cavitary lesions | |||
*[[Pleural effusion]] and [[empyema]] are common findings | |||
| | |||
*[[Complete blood count|CBC]] is positive for causative organism | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*Loculated [[empyema]] | |||
| | |||
* Children and elderly are at risk | |||
*Pleuritic [[chest pain]], [[dry cough]], [[fever]] with chills | |||
*Dullness to [[Percussion of the lungs|percussion]] decreased [[breath sounds]], and reduced vocal resonance on examination | |||
| | |||
*[[Empyema]] appears lenticular in shape and has a thin wall with smooth luminal margins | |||
| | |||
*[[Thoracocentesis]] | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] ([[Wegener's granulomatosis|Wegener's]])<ref name="pmid10377211">{{cite journal |vauthors=Langford CA, Hoffman GS |title=Rare diseases.3: Wegener's granulomatosis |journal=Thorax |volume=54 |issue=7 |pages=629–37 |year=1999 |pmid=10377211 |pmc=1745525 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Women are more commonly effected than man.<ref name="pmid12541109">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee KS, Kim TS, Fujimoto K, Moriya H, Watanabe H, Tateishi U, Ashizawa K, Johkoh T, Kim EA, Kwon OJ |title=Thoracic manifestation of Wegener's granulomatosis: CT findings in 30 patients |journal=Eur Radiol |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=43–51 |year=2003 |pmid=12541109 |doi=10.1007/s00330-002-1422-2 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Kidneys are also involved | |||
*Upper respiratory tract symptoms , perforation of [[nasal septum]], [[chronic sinusitis]], [[otitis media]], [[mastoiditis]]. | |||
*Lower respiratory tract symptoms, [[hemoptysis]], [[cough]], [[dyspnea]]. | |||
*Renal symptoms, [[hematuria]], red cell [[casts]] | |||
| | |||
*Pulmonary nodules with cavities and infiltrates are a frequent manifestation on CXR | |||
| | |||
*Positive for [[P-ANCA]] | |||
*Biopsy of the tissue involved shows necrotizing [[granulomas]] <ref name="pmid10377211">{{cite journal |vauthors=Langford CA, Hoffman GS |title=Rare diseases.3: Wegener's granulomatosis |journal=Thorax |volume=54 |issue=7 |pages=629–37 |year=1999 |pmid=10377211 |pmc=1745525 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Rheumatoid nodule]] | |||
| | |||
*Elderly females of 40-50 age group | |||
*Manifestation of [[rheumatoid arthritis]] | |||
*Presents with other systemic symptoms including symmetric [[arthritis]] of the small joints of the hands and feet with morning stiffness are common manifestations. | |||
| | |||
*Pulmonary nodules with cavitation are located in the upper lobe ([[Caplan syndrome]]) on Xray. | |||
| | |||
*Positive for both [[rheumatoid factor]] and anticyclic citrullinated peptide [[Antibody|antibody.]] | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Sarcoidosis]] | |||
| | |||
*More common in African-American females | |||
*Often [[asymptomatic]] except for [[Lymphadenopathy|enlarged lymph nodes]]<ref name="pmid11734441">{{cite journal |vauthors=Baughman RP, Teirstein AS, Judson MA, Rossman MD, Yeager H, Bresnitz EA, DePalo L, Hunninghake G, Iannuzzi MC, Johns CJ, McLennan G, Moller DR, Newman LS, Rabin DL, Rose C, Rybicki B, Weinberger SE, Terrin ML, Knatterud GL, Cherniak R |title=Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis |journal=Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. |volume=164 |issue=10 Pt 1 |pages=1885–9 |year=2001 |pmid=11734441 |doi=10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104046 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Associated with [[restrictive lung disease]] | |||
*[[Erythema nodosum]] | |||
*[[Lupus pernio]] (skin lesions on face resembling lupus) | |||
*[[Bell's palsy|Bell palsy]] | |||
*[[Epithelioid]] [[granuloma]]<nowiki/>s containing microscopic [[Schaumann bodies|Schaumann]] and asteroid bodies | |||
| | |||
*On CXR bilateral [[Lymphadenopathy|adenopathy]] and coarse reticular opacities are seen. | |||
*CT of the chest demonstrates extensive [[Hilar lymphadenopathy|hilar]] and mediastinal adenopathy | |||
*Additional findings on CT include [[fibrosis]] (honeycomb, linear, or associated with bronchial distortion), pleural thickening, and ground-glass opacities.<ref name="pmid2748828">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brauner MW, Grenier P, Mompoint D, Lenoir S, de Crémoux H |title=Pulmonary sarcoidosis: evaluation with high-resolution CT |journal=Radiology |volume=172 |issue=2 |pages=467–71 |year=1989 |pmid=2748828 |doi=10.1148/radiology.172.2.2748828 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Biopsy of lung shows non-[[caseating]] [[granuloma]] | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Bronchiolitis obliterans]] ([[Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia]])<ref name="pmid9724431">{{cite journal |vauthors=Murphy J, Schnyder P, Herold C, Flower C |title=Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia simulating bronchial carcinoma |journal=Eur Radiol |volume=8 |issue=7 |pages=1165–9 |year=1998 |pmid=9724431 |doi=10.1007/s003300050527 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19561910">{{cite journal |vauthors=Al-Ghanem S, Al-Jahdali H, Bamefleh H, Khan AN |title=Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: pathogenesis, clinical features, imaging and therapy review |journal=Ann Thorac Med |volume=3 |issue=2 |pages=67–75 |year=2008 |pmid=19561910 |pmc=2700454 |doi=10.4103/1817-1737.39641 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Rare condition and mimics [[asthma]], [[pneumonia]] and [[emphysema]] | |||
*It is caused by [[drug]] or [[toxin]] exposure, [[autoimmune diseases]], [[viral infections]], or [[radiation injury]] | |||
*People working in industries are at high risk | |||
*Presents with [[Fever|feve]]<nowiki/>r, [[cough]], [[wheezing]] and [[shortness of breath]] over weeks to months,<ref name="pmid2805873">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cordier JF, Loire R, Brune J |title=Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Definition of characteristic clinical profiles in a series of 16 patients |journal=Chest |volume=96 |issue=5 |pages=999–1004 |year=1989 |pmid=2805873 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Common appearance on CT is patchy [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation,]]<nowiki/>often accompanied by ground-glass opacities and nodules.<ref name="pmid8109493">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee KS, Kullnig P, Hartman TE, Müller NL |title=Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: CT findings in 43 patients |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=162 |issue=3 |pages=543–6 |year=1994 |pmid=8109493 |doi=10.2214/ajr.162.3.8109493 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Biopsy of the lung <ref name="pmid19561910">{{cite journal |vauthors=Al-Ghanem S, Al-Jahdali H, Bamefleh H, Khan AN |title=Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: pathogenesis, clinical features, imaging and therapy review |journal=Ann Thorac Med |volume=3 |issue=2 |pages=67–75 |year=2008 |pmid=19561910 |pmc=2700454 |doi=10.4103/1817-1737.39641 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[Pulmonary function tests]] demonstrate low fev1/fvc | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
*[[Langerhans cell histiocytosis|Langerhans]] cell [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis|Histiocytosis]]<ref name="pmid22429393">{{cite journal |vauthors=Suri HS, Yi ES, Nowakowski GS, Vassallo R |title=Pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis |journal=Orphanet J Rare Dis |volume=7 |issue= |pages=16 |year=2012 |pmid=22429393 |pmc=3342091 |doi=10.1186/1750-1172-7-16 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Exclusively afflicts smokers, with a peak age of onset of between 20 and 40 years. | |||
*Clinical presentation varies, but symptoms generally include months of dry [[cough]], [[fever]], [[night sweats]] and [[weight loss]]. | |||
*Skin is involved in 80% of the cases, scaly [[erythematous rash]] is typical. | |||
| | |||
*Thin-walled cystic cavities are the usual radiographic manifestation, observed in over 50% of patients by either CXR or CT scans.<ref name="pmid2787035">{{cite journal |vauthors=Moore AD, Godwin JD, Müller NL, Naidich DP, Hammar SP, Buschman DL, Takasugi JE, de Carvalho CR |title=Pulmonary histiocytosis X: comparison of radiographic and CT findings |journal=Radiology |volume=172 |issue=1 |pages=249–54 |year=1989 |pmid=2787035 |doi=10.1148/radiology.172.1.2787035 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
*Biopsy of the lung | |||
|} | |||
'''Table 1: Differentiating psittacosis from other diseases''' | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Clinical feature | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Cough]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Sputum]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Dyspnea]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Sore throat]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Headache]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Confusion]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Diarrhea]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Chest radiograph changes | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Hyponatremia | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |[[Leukopenia]] | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Abnormal Liver function tests | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Treatment | |||
|- | |||
|Psittacosis | |||
| ++ | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| - | |||
| +++ | |||
| + | |||
|Minimal | |||
| | |||
* No changes seen | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| - | |||
|[[Doxycycline]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Chlamydia pneumoniae|''C.pneumoniae'']] pneumonia | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| +++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
* Minimal changes observed | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
|[[Doxycycline]], [[Azithromycin]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Mycoplasma pneumoniae|''M. pneumoniae'']] pneumonia | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
* Bronchial wall thickening | |||
* Centrilobular nodules | |||
* [[Ground glass opacification on CT|Ground-glass attenuation]] | |||
* [[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
|[[Doxycycline]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Legionella pneumophila|''L. Pneumophila'']] infection | |||
| + | |||
| +++ | |||
| +++ | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
|Often Multifocal | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
| ++ | |||
|[[Doxycycline]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Influenza (Flu) (For Patients)|Influenza]] | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| +/- | |||
| +/- | |||
| | |||
* Bi-basal air-space opacities | |||
* Perihilar [[reticular]] and [[Alveolar|alveolar infiltrates]] | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
|[[zanamivir]], [[oseltamivir]], | |||
|- | |||
|[[Endocarditis]] | |||
| ++ | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
* Hazy opacities at [[lung]] | |||
bases bilaterally | |||
| - | |||
| +/- | |||
| +/- | |||
|[[Vancomycin]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Coxiella burnetii infection|''Coxiella burnetii'' infection]] | |||
| ++ | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| +/- | |||
| - | |||
| +/- | |||
|Minimal | |||
| | |||
* [[Segmental analysis (biology)|Segmental]] or [[Lobar pneumonia|lobar]] opacification | |||
* Occasional [[pleural effusions]] | |||
| - | |||
| +/- | |||
|=/- | |||
|[[Doxycycline]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Leptospirosis]] | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| ++ | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
* Multiple ill-defined [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] in both lungs. | |||
| +++ | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|[[Doxycycline]], [[azithromycin]], [[amoxicillin]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Brucellosis]] | |||
| ++ | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| - | |||
| ++ | |||
| + | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
* Soft [[Miliary TB|miliary]] mottling | |||
* [[Parenchymal lung disease|Parenchymal nodules]] | |||
* [[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] | |||
* [[Chronic (medical)|Chronic]] [[diffuse]] changes | |||
* [[Hilar]] or [[Paratracheal lymph nodes|paratracheal]] [[lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Pneumothorax]]. | |||
| -/+ | |||
| +/- | |||
| +/- | |||
|[[Doxycycline]], [[rifampin]] | |||
|} | |||
Key; | |||
+, occurs in some cases | |||
++, occurs in many cases, | |||
+++, occurs frequently | |||
Pnemonia must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [[atypical pneumonia]] such as Q fever and legionella pneumonia: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Disease | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Prominent clinical features | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Lab findings | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Chest X-ray | |||
|- | |||
|Q fever | |||
| | |||
* Q fever is characterized by abrupt onset of [[fever]], [[myalgia]], [[headache]], and other constitutional symptoms. | |||
* [[Cough]] is the most prominent respiratory symptom and it is usually dry.<ref name="pmid23422417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Irfan M, Farooqi J, Hasan R |title=Community-acquired pneumonia |journal=Curr Opin Pulm Med |volume=19 |issue=3 |pages=198–208 |year=2013 |pmid=23422417 |doi=10.1097/MCP.0b013e32835f1d12 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* [[Cough]] is associated with [[dyspnea]] and [[pleuritic chest pain]]. | |||
| | |||
* [[Antibody]] detection using [[Immunofluorescence|indirect immunofluorescence]] (IIF) is the preferred method for diagnosis. | |||
* [[Polymerase chain reaction|PCR]] can be used if IIF is negative, or very early once disease is suspected. | |||
* [[Coxiella burnetii|''C. burnetii'']] does not grow on ordinary blood cultures, but can be cultivated on special media such as embryonated eggs or cell culture. | |||
* A two-to-three fold increase in [[Aspartate transaminase|AST]] and [[ALT]] is seen in most patients. | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Q fever.gif|center|300px|thumb|Q fever pneumonia - - Case courtesy of Royal Melbourne Hospital Respiratory, Radiopaedia.org, rID 21993 ]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[mycoplasma pneumonia|''Mycoplasma'' pneumonia]] | |||
| | |||
* [[mycoplasma pneumonia|''Mycoplasma'' pneumonia]] can be [[asymptomatic]]. | |||
* [[Headache]], [[Nausea and vomiting|nausea]], and [[malaise]] usually precede the onset of symptoms.<ref name="pmid23422417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Irfan M, Farooqi J, Hasan R |title=Community-acquired pneumonia |journal=Curr Opin Pulm Med |volume=19 |issue=3 |pages=198–208 |year=2013 |pmid=23422417 |doi=10.1097/MCP.0b013e32835f1d12 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* [[Cough]] is intractable and nonproductive. | |||
| | |||
* Postitve [[Coombs test]] | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] | |||
* [[Thrombocytosis]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Atypical-pneumonia-mycoplasma - Case courtesy of Dr Alborz Jahangiri, Radiopaedia.org, rID 45781.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Mycoplasma pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Alborz Jahangiri, Radiopaedia.org, rID 45781]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Legionellosis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Legionellosis]] is characterized by cough that is slightly productive.<ref name="pmid23422417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Irfan M, Farooqi J, Hasan R |title=Community-acquired pneumonia |journal=Curr Opin Pulm Med |volume=19 |issue=3 |pages=198–208 |year=2013 |pmid=23422417 |doi=10.1097/MCP.0b013e32835f1d12 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Constitutional symptoms such as [[chills]], [[myalgia]], and [[arthralgia]]. | |||
* Gastrointestinal symptoms such as [[diarrhea]], [[nausea]], and [[vomiting]]. | |||
| | |||
* Labs are nonspecific for diagnosing [[legionellosis]] | |||
* [[Renal dysfunction|Renal]] and [[hepatic dysfunction]] | |||
* [[Thrombocytopenia]] and [[leukocytosis]] | |||
* [[Hyponatremia]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Legionella-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Henry Knipe, Radiopaedia.org, rID 31816.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Legionella pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Henry Knipe, Radiopaedia.org, rID 31816 ]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Chlamydia pneumonia]] | |||
| | |||
* There are no specific clinical features of [[chlamydia pneumonia]]. | |||
* Symptoms appear gradually. | |||
* [[Chlamydia infection]] is usually associated with [[upper respiratory tract]] symptoms ([[pharyngitis]], [[sinusitis]], etc). | |||
* It might be associated with extrapulmonary maifestations such as [[meningitis]] and [[Guillain-Barre syndrome]].<ref name="pmid23422417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Irfan M, Farooqi J, Hasan R |title=Community-acquired pneumonia |journal=Curr Opin Pulm Med |volume=19 |issue=3 |pages=198–208 |year=2013 |pmid=23422417 |doi=10.1097/MCP.0b013e32835f1d12 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* [[Chlamydia pneumonia]] is usually associated with normal [[WBC|WBC count.]] | |||
* Diagnosed with the presence of [[Antibody|antichlamydial antibody]] (through [[complement fixation]] or direct immunofluoroscence) or direct antigen detection. | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Chlamydia-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopaedia.org, rID 14567.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Chlamydia-pneumonia - Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopaedia.org, rID 14567]] | |||
|} | |||
==Other differentials== | |||
Pneumonia should be differentiated from other diseases presenting with [[cough]], [[fever]], [[shortness of breath]] and [[tachypnea]]. The differentials include the following:<ref name="pmid24550636">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brenes-Salazar JA |title=Westermark's and Palla's signs in acute and chronic pulmonary embolism: Still valid in the current computed tomography era |journal=J Emerg Trauma Shock |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=57–8 |year=2014 |pmid=24550636 |pmc=3912657 |doi=10.4103/0974-2700.125645 |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlCT Angiography of Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnostic Criteria and Causes of Misdiagnosis | RadioGraphics">{{cite web |url=http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.245045008 |title=CT Angiography of Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnostic Criteria and Causes of Misdiagnosis | RadioGraphics |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23940438">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A |title=Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism |journal=Exp Clin Cardiol |volume=18 |issue=2 |pages=129–38 |year=2013 |pmid=23940438 |pmc=3718593 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlPulmonary Embolism: Symptoms - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health">{{cite web |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0022657/ |title=Pulmonary Embolism: Symptoms - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20118395">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ramani GV, Uber PA, Mehra MR |title=Chronic heart failure: contemporary diagnosis and management |journal=Mayo Clin. Proc. |volume=85 |issue=2 |pages=180–95 |year=2010 |pmid=20118395 |pmc=2813829 |doi=10.4065/mcp.2009.0494 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18215495">{{cite journal |vauthors=Blinderman CD, Homel P, Billings JA, Portenoy RK, Tennstedt SL |title=Symptom distress and quality of life in patients with advanced congestive heart failure |journal=J Pain Symptom Manage |volume=35 |issue=6 |pages=594–603 |year=2008 |pmid=18215495 |pmc=2662445 |doi=10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.06.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19168510">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hawkins NM, Petrie MC, Jhund PS, Chalmers GW, Dunn FG, McMurray JJ |title=Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: diagnostic pitfalls and epidemiology |journal=Eur. J. Heart Fail. |volume=11 |issue=2 |pages=130–9 |year=2009 |pmid=19168510 |pmc=2639415 |doi=10.1093/eurjhf/hfn013 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid9465867">{{cite journal |vauthors=Takasugi JE, Godwin JD |title=Radiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |journal=Radiol. Clin. North Am. |volume=36 |issue=1 |pages=29–55 |year=1998 |pmid=9465867 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid14651761">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wedzicha JA, Donaldson GC |title=Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |journal=Respir Care |volume=48 |issue=12 |pages=1204–13; discussion 1213–5 |year=2003 |pmid=14651761 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23833163">{{cite journal |vauthors=Nakawah MO, Hawkins C, Barbandi F |title=Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the overlap syndrome |journal=J Am Board Fam Med |volume=26 |issue=4 |pages=470–7 |year=2013 |pmid=23833163 |doi=10.3122/jabfm.2013.04.120256 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20511488">{{cite journal |vauthors=Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA, Sinak LJ, Hayes SN, Melduni RM, Oh JK |title=Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management |journal=Mayo Clin. Proc. |volume=85 |issue=6 |pages=572–93 |year=2010 |pmid=20511488 |pmc=2878263 |doi=10.4065/mcp.2010.0046 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23610095">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bogaert J, Francone M |title=Pericardial disease: value of CT and MR imaging |journal=Radiology |volume=267 |issue=2 |pages=340–56 |year=2013 |pmid=23610095 |doi=10.1148/radiol.13121059 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11680112">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gharib AM, Stern EJ |title=Radiology of pneumonia |journal=Med. Clin. North Am. |volume=85 |issue=6 |pages=1461–91, x |year=2001 |pmid=11680112 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23507061">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schmidt WA |title=Imaging in vasculitis |journal=Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol |volume=27 |issue=1 |pages=107–18 |year=2013 |pmid=23507061 |doi=10.1016/j.berh.2013.01.001 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16891436">{{cite journal |vauthors=Suresh E |title=Diagnostic approach to patients with suspected vasculitis |journal=Postgrad Med J |volume=82 |issue=970 |pages=483–8 |year=2006 |pmid=16891436 |pmc=2585712 |doi=10.1136/pgmj.2005.042648 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid123074">{{cite journal |vauthors=Stein PD, Dalen JE, McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA, Wenger NK, Willis PW |title=The electrocardiogram in acute pulmonary embolism |journal=Prog Cardiovasc Dis |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=247–57 |year=1975 |pmid=123074 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23413894">{{cite journal |vauthors=Warnier MJ, Rutten FH, Numans ME, Kors JA, Tan HL, de Boer A, Hoes AW, De Bruin ML |title=Electrocardiographic characteristics of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |journal=COPD |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=62–71 |year=2013 |pmid=23413894 |doi=10.3109/15412555.2012.727918 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23000104">{{cite journal |vauthors=Stein PD, Matta F, Ekkah M, Saleh T, Janjua M, Patel YR, Khadra H |title=Electrocardiogram in pneumonia |journal=Am. J. Cardiol. |volume=110 |issue=12 |pages=1836–40 |year=2012 |pmid=23000104 |doi=10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.019 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26209947">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hazebroek MR, Kemna MJ, Schalla S, Sanders-van Wijk S, Gerretsen SC, Dennert R, Merken J, Kuznetsova T, Staessen JA, Brunner-La Rocca HP, van Paassen P, Cohen Tervaert JW, Heymans S |title=Prevalence and prognostic relevance of cardiac involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis |journal=Int. J. Cardiol. |volume=199 |issue= |pages=170–9 |year=2015 |pmid=26209947 |doi=10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.087 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20112390">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dennert RM, van Paassen P, Schalla S, Kuznetsova T, Alzand BS, Staessen JA, Velthuis S, Crijns HJ, Tervaert JW, Heymans S |title=Cardiac involvement in Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=62 |issue=2 |pages=627–34 |year=2010 |pmid=20112390 |doi=10.1002/art.27263 |url=}}</ref> | |||
<small> | |||
{| | |||
|- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | |||
! rowspan="2" |<small>Diseases</small> | |||
! colspan="3" |<small>Diagnostic tests</small> | |||
! colspan="3" |<small>Physical Examination</small> | |||
| colspan="7" |<small>Symptoms | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="2" |<small>Past medical history</small> | |||
! rowspan="2" |<small>Other Findings</small> | |||
|- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | |||
!<small>CT scan and MRI</small> | |||
!<small>EKG</small> | |||
!<small>Chest X-ray</small> | |||
!<small>Tachypnea</small> | |||
!<small>Tachycardia</small> | |||
!<small>Fever</small> | |||
!<small>Chest Pain</small> | |||
!<small>Hemoptysis</small> | |||
!<small>Dyspnea on Exertion</small> | |||
!<small>Wheezing</small> | |||
!<small>Chest Tenderness</small> | |||
!<small>Nasalopharyngeal Ulceration</small> | |||
!<small>Carotid Bruit</small> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pulmonary embolism]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align:center" | | |||
* On [[CT angiography]]: | |||
** Intra-luminal filling defect | |||
*On [[MRI]]: | |||
** Narrowing of involved [[Blood vessel|vessel]] | |||
** No contrast seen distal to [[obstruction]] | |||
** Polo-mint sign (partial filling defect surrounded by contrast) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Pulmonary embolism electrocardiogram|S1Q3T3]] pattern representing acute [[right heart]] strain | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Fleischner sign]] (enlarged pulmonary artery), [[Hampton's hump|Hampton hump]], [[Westermark's sign]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (Low grade) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (In case of massive PE) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Hypercoagulating conditions ([[Factor V Leiden]], [[thrombophilia]], [[deep vein thrombosis]], immobilization, [[malignancy]], [[pregnancy]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* May be associated with [[metabolic alkalosis]] and [[syncope]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | [[Congestive heart failure]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | |||
** [[Mediastinal lymphadenopathy]] | |||
** Hazy [[mediastinal]] fat | |||
*On [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]]: | |||
** Abnormality of [[cardiac]] chambers ([[Hypertrophy (medical)|hypertrophy]], dilation) | |||
** Delayed enhancement [[MRI]] may help characterize the [[myocardial]] [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] ([[fibrosis]]) | |||
** Late enhancement of contrast in conditions such as [[myocarditis]], [[sarcoidosis]], [[amyloidosis]], [[Anderson-Fabry disease|Anderson-Fabry]]'s disease, [[Chagas disease]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Goldberg's criteria may aid in diagnosis of left ventricular dysfunction: (High specificity) | |||
**[[S wave|S]]V1 or [[S wave|S]]V2 + [[R wave|R]]V5 or [[R wave|R]]V6 ≥3.5 mV | |||
**Total [[QRS complex|QRS]] amplitude in each of the limb leads ≤0.8 mV | |||
** [[R wave|R]]/[[S wave|S]] ratio <1 in lead V4 | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Cardiomegaly]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Previous [[myocardial infarction]] | |||
*[[Hypertension]] ([[Systemic hypertension|systemic]] and [[Pulmonary hypertension|pulmonary]]) | |||
*[[Cardiac arrhythmia|Cardiac arrythmias]] | |||
*[[Viral]] infections ([[myocarditis]]) | |||
*[[Congenital heart disease|Congenital heart defects]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Right heart failure]] associated with: | |||
**[[Hepatomegaly]] | |||
**Positive hepato-jugular reflex | |||
**Increased [[jugular venous pressure]] | |||
**[[Peripheral edema]] | |||
*[[Left heart failure]] associated with: | |||
**[[Pulmonary edema]] | |||
**Eventual [[right heart failure]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Percarditis]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On contrast enhanced [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | |||
**Enhancement of the [[pericardium]] (due to [[inflammation]]) | |||
**[[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
**[[Pericardial calcification]] | |||
*On [[gadolinium]]-enhanced fat-saturated [[Magnetic resonance imaging|T1-weighted MRI]]: | |||
**[[Pericardial]] enhancement (due to [[inflammation]]) | |||
**[[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*ST elevation | |||
*PR depression | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Large collection of fluid inside the pericardial sac (pericardial effusion) | |||
*Calcification of pericardial sac | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (Low grade) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (Relieved by sitting up and leaning forward) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Infections: | |||
**[[Viral]] (Coxsackie virus, [[Herpes simplex virus|Herpes virus]], [[Mumps virus]], [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]]) | |||
**[[Bacteria]] ([[Mycobacterium tuberculosis]]-common in developing countries) | |||
**[[Fungal]] ([[Histoplasmosis]]) | |||
*Idiopathic in a large number of cases | |||
*[[Autoimmune]] | |||
*[[Uremia]] | |||
*[[Malignancy]] | |||
*Previous [[myocardial infarction]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*May be clinically classified into: | |||
**Acute (< 6 weeks) | |||
**Sub-acute (6 weeks - 6 months) | |||
**Chronic (> 6 months) | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pneumonia]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: (not generally indicated) | |||
**[[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] ([[alveolar]]/lobar pneumonia) | |||
**Peribronchial [[nodules]] ([[bronchopneumonia]]) | |||
**[[Ground glass opacification on CT|Ground-glass opacity]] (GGO) | |||
**[[Abscess]] | |||
**[[Pleural effusion]] | |||
**On [[MRI]]: | |||
*Not indicated | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Prolonged [[PR interval]] | |||
*Transient [[T wave]] inversions | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] ([[alveolar]]/lobar [[pneumonia]]) | |||
*Peribronchial [[nodules]] (bronchopneumonia) | |||
*Ground-glass opacity (GGO) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Ill-contact | |||
*Travelling | |||
*[[Smoking]] | |||
*[[Diabetes mellitus|Diabetic]] | |||
*Recent hospitalization | |||
*[[Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Requires [[Sputum|sputum stain]] and culture for diagnosis | |||
*[[Empiric therapy|Empiric management]] usually started before [[Culture collection|culture]] results | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Vasculitis]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: ([[Takayasu's arteritis|Takayasu arteritis]]) | |||
**[[Blood vessel|Vessel]] wall thickening | |||
**Luminal narrowing of [[pulmonary artery]] | |||
**Masses or nodules ([[Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody|ANCA]]-associated granulomatous vasculitis) | |||
*On [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]]: | |||
Homogeneous, circumferential [[Blood vessel|vessel]] wall [[swelling]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Bundle branch block|Right or left bundle-branch block]] ([[Churg-Strauss syndrome]]) | |||
*[[Atrial fibrillation]] ([[Churg-Strauss syndrome]]) | |||
*Non-specific [[ST interval|ST segment]] and [[T wave]] changes | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Nodule (medicine)|Nodules]] | |||
*[[Cavitation]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Takayasu's arteritis|Takayasu arteritis]] usually found in persons aged 4-60 years with a mean of 30 | |||
*[[Giant-cell arteritis]] usually occurrs in persons aged > 60 years | |||
*[[Churg-Strauss syndrome]] may present with [[asthma]], [[sinusitis]], transient [[pulmonary]] infiltrates and neuropathy alongwith [[cardiac]] involvement | |||
*Granulomatous vasculitides may present with [[nephritis]] and [[upper airway]] ([[nasopharyngeal]]) destruction | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] (COPD) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | |||
**[[Chronic bronchitis]] may show [[bronchial]] wall thickening, scarring with bronchovascular irregularity, [[fibrosis]] | |||
**[[Emphysema]] may show [[alveolar]] septal destruction and airspace enlargement (Centrilobular- upper lobe, panlobular- lower lobe) | |||
**Giant bubbles | |||
*On [[MRI]]: | |||
**Increased diameter of [[pulmonary arteries]] | |||
**Peripheral [[pulmonary]] [[vasculature]] attentuation | |||
**Loss of retrosternal airspace due to right ventricular enlargement | |||
**Hyperpolarized Helium MRI may show progressively poor ventilation and destruction of lung | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Multifocal atrial tachycardia]] (atleast 3 distinct [[P waves|P wave]] morphologies) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Enlarged [[lung]] shadows ([[emphysema]]) | |||
*Flattening of [[diaphragm]] ([[emphysema]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Smoking]] | |||
*[[Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency|Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency]] | |||
*Increased [[sputum]] production ([[chronic bronchitis]]) | |||
*[[Cough]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency|Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency]] may be associated with [[hepatomegaly]] | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Pulmonology]] | [[Category:Pulmonology]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | [[Category:Pediatrics]] | ||
[[Category:Patient information]] | [[Category:Patient information]] | ||
[[Category:Needs overview]] | [[Category:Needs overview]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:45, 29 July 2020
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Hamid Qazi, MD, BSc [2], Priyamvada Singh, M.D. [3] Syed Hassan A. Kazmi BSc, MD [4]

Overview
Pneumonia should be differentiated from other conditions that cause cough, fever, shortness of breath and tachypnea, such as asthma, COPD, CHF, cancer, GERD, pulmonary emboli.
Differentiating Pneumonia from other Diseases
| Disease | Findings |
|---|---|
| Acute bronchitis | No infiltrates seen on the chest X-ray. |
| Asthma | Past medical history, no infiltrates seen on chest X-ray. |
| Bronchiolitis obliterans | Should be suspected in patients with pneumonia who do not respond to antibiotics treatment. |
| Congestive heart failure | Bilateral pulmonary edema, shortness of breath. |
| COPD | Past medical history, no infiltrates on chest X-ray, fever is uncommon. |
| Empyema | CXR showing features of pleural effusion, inflammatory markers on thoracocentesis. |
| Endocarditis | Finding of septic pulmonary emboli |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) | Normal chest X-ray, symptoms are worse during night and associated with meals. |
| Lung abscess | Chest X-ray shows signs of lung abscess. |
| Lung cancer | Weight loss, clear sputum. CT scan and biopsy are helpful in ruling out malignancy. |
| Pertussis | Productive cough for weeks, nasopharyngeal aspirate aids in diagnosis. |
| Pulmonary embolus | A high degree of suspicion should be kept for pulmonary embolus. Chest X-ray may be normal. |
| Sinusitis | Sinus tenderness, post nasal drip. |
| Vasculitis | Systemic manifestations of collagen vascular disease may be seen. |
Differential diagnosis
| Causes of
Lung Cavities |
Differentiating Features | Differentiating Radiological Findings | Diagnosis Confirmation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
||
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Table 1: Differentiating psittacosis from other diseases
| Clinical feature | Cough | Sputum | Dyspnea | Sore throat | Headache | Confusion | Diarrhea | Chest radiograph changes | Hyponatremia | Leukopenia | Abnormal Liver function tests | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psittacosis | ++ | - | + | - | +++ | + | Minimal |
|
- | + | - | Doxycycline |
| C.pneumoniae pneumonia | + | + | + | +++ | ++ | + | - |
|
- | - | - | Doxycycline, Azithromycin |
| M. pneumoniae pneumonia | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | - | - | - |
|
- | - | + | Doxycycline |
| L. Pneumophila infection | + | +++ | +++ | - | + | ++ | + | Often Multifocal | ++ | + | ++ | Doxycycline |
| Influenza | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +/- | +/- |
|
- | - | - | zanamivir, oseltamivir, |
| Endocarditis | ++ | ++ | + | - | - | - | - |
bases bilaterally |
- | +/- | +/- | Vancomycin |
| Coxiella burnetii infection | ++ | - | + | +/- | - | +/- | Minimal |
|
- | +/- | =/- | Doxycycline |
| Leptospirosis | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | - |
|
+++ | Doxycycline, azithromycin, amoxicillin | ||
| Brucellosis | ++ | - | + | - | ++ | + | - |
|
-/+ | +/- | +/- | Doxycycline, rifampin |
Key;
+, occurs in some cases
++, occurs in many cases,
+++, occurs frequently
Pnemonia must be differentiated from other diseases that cause atypical pneumonia such as Q fever and legionella pneumonia:
| Disease | Prominent clinical features | Lab findings | Chest X-ray |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q fever |
|
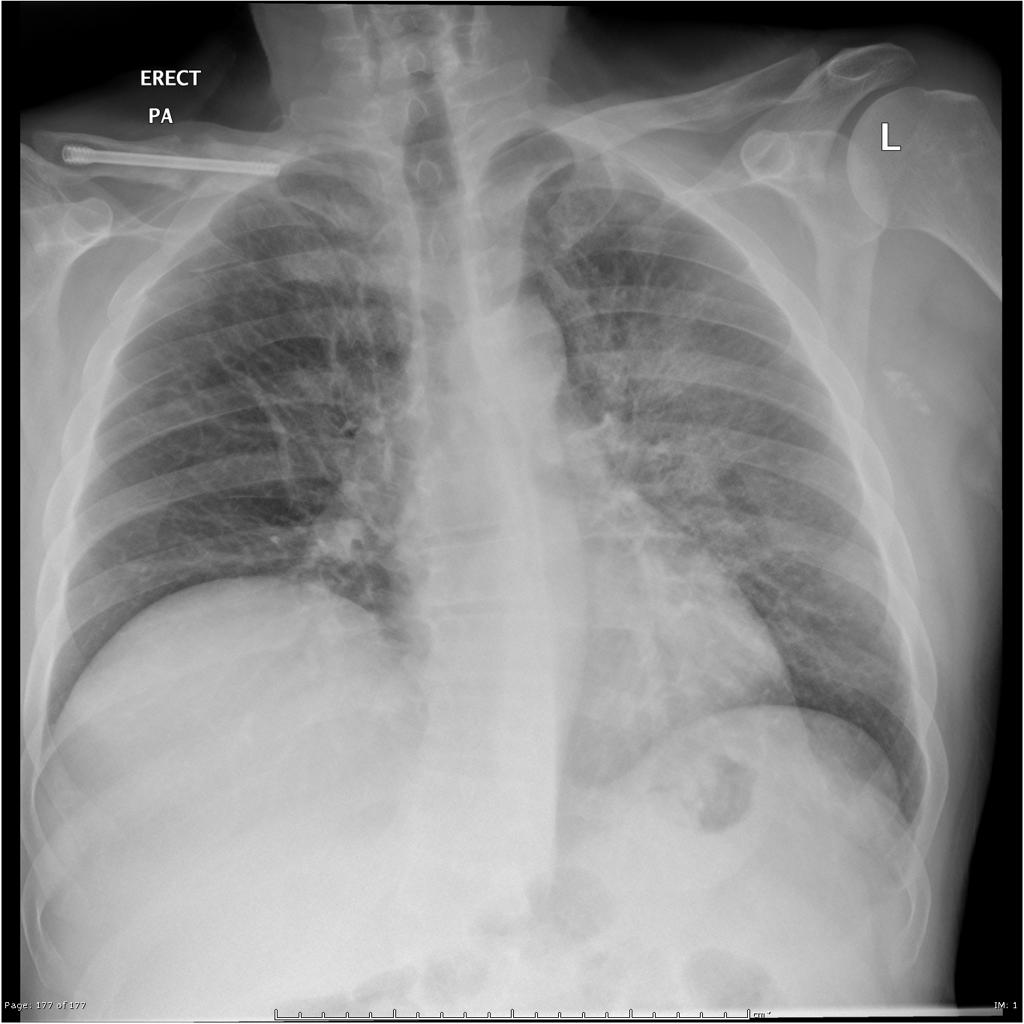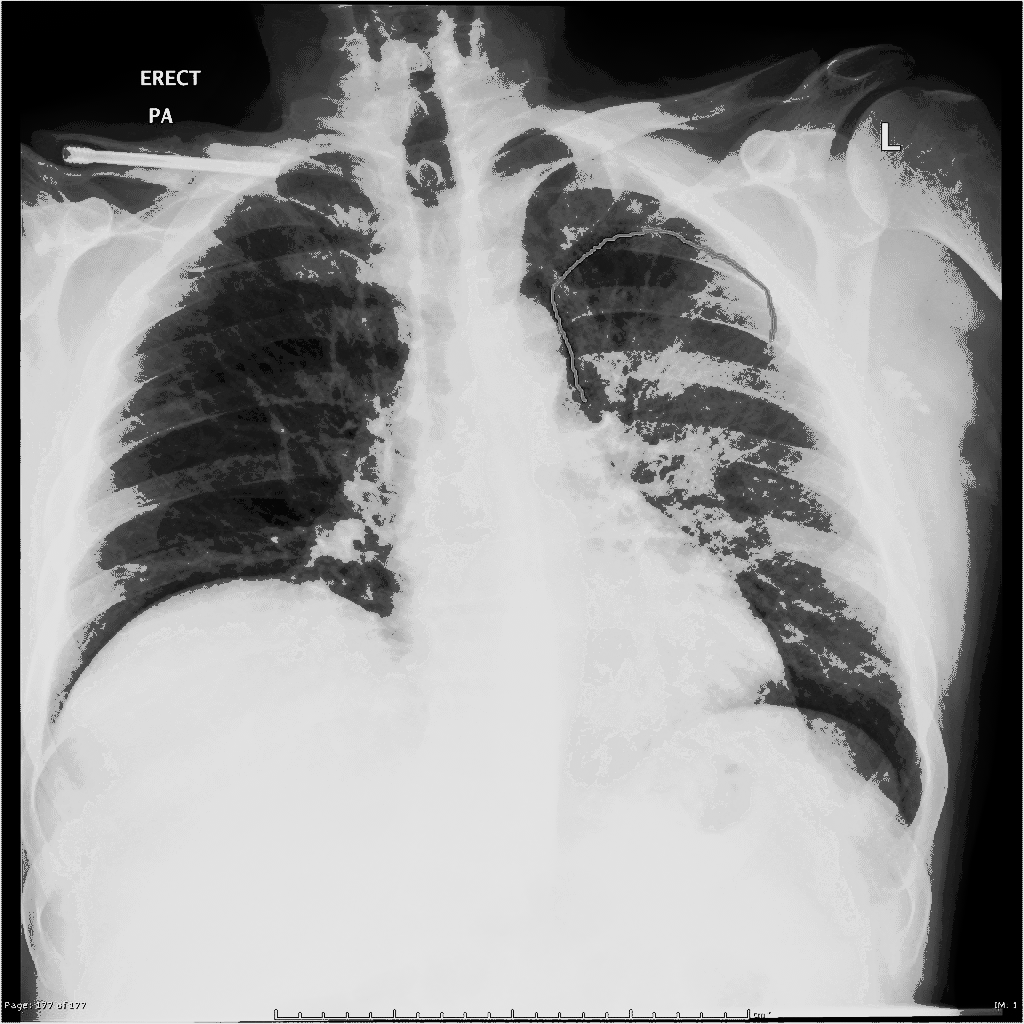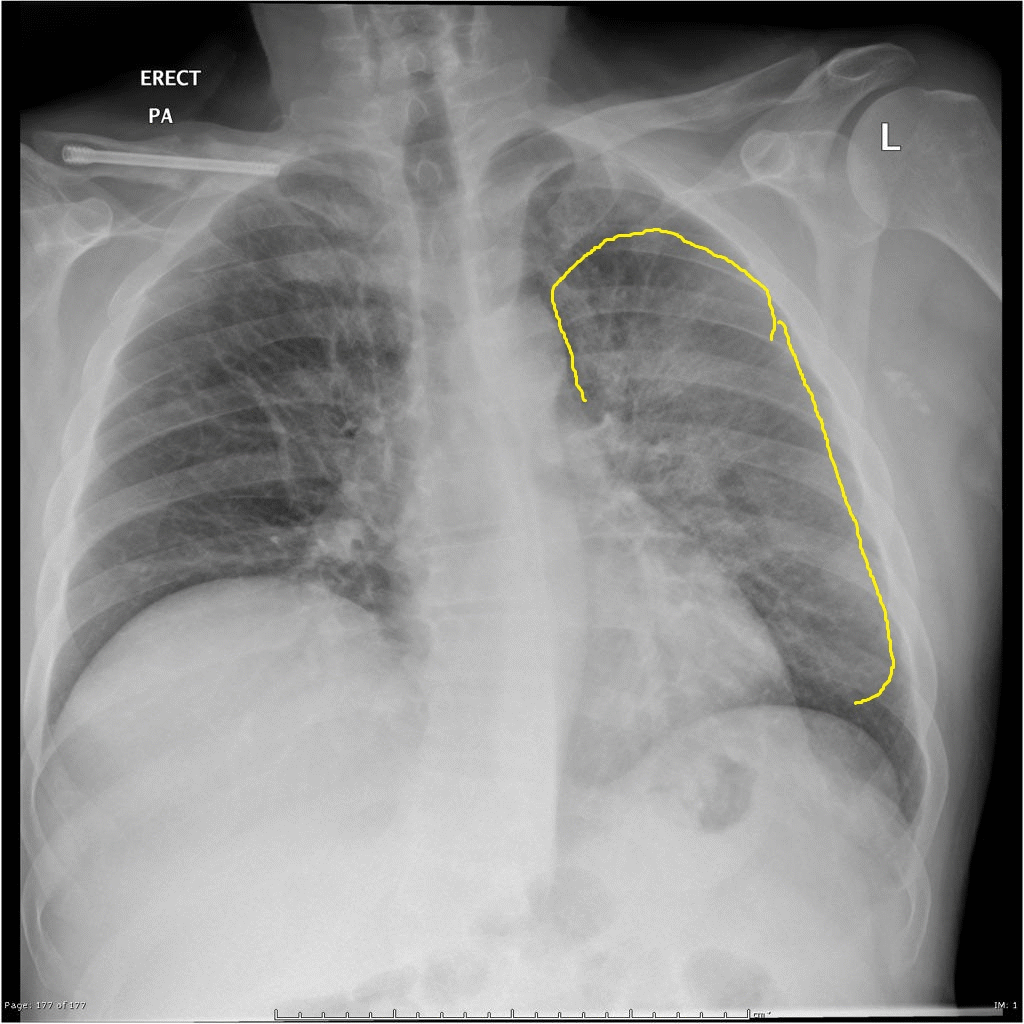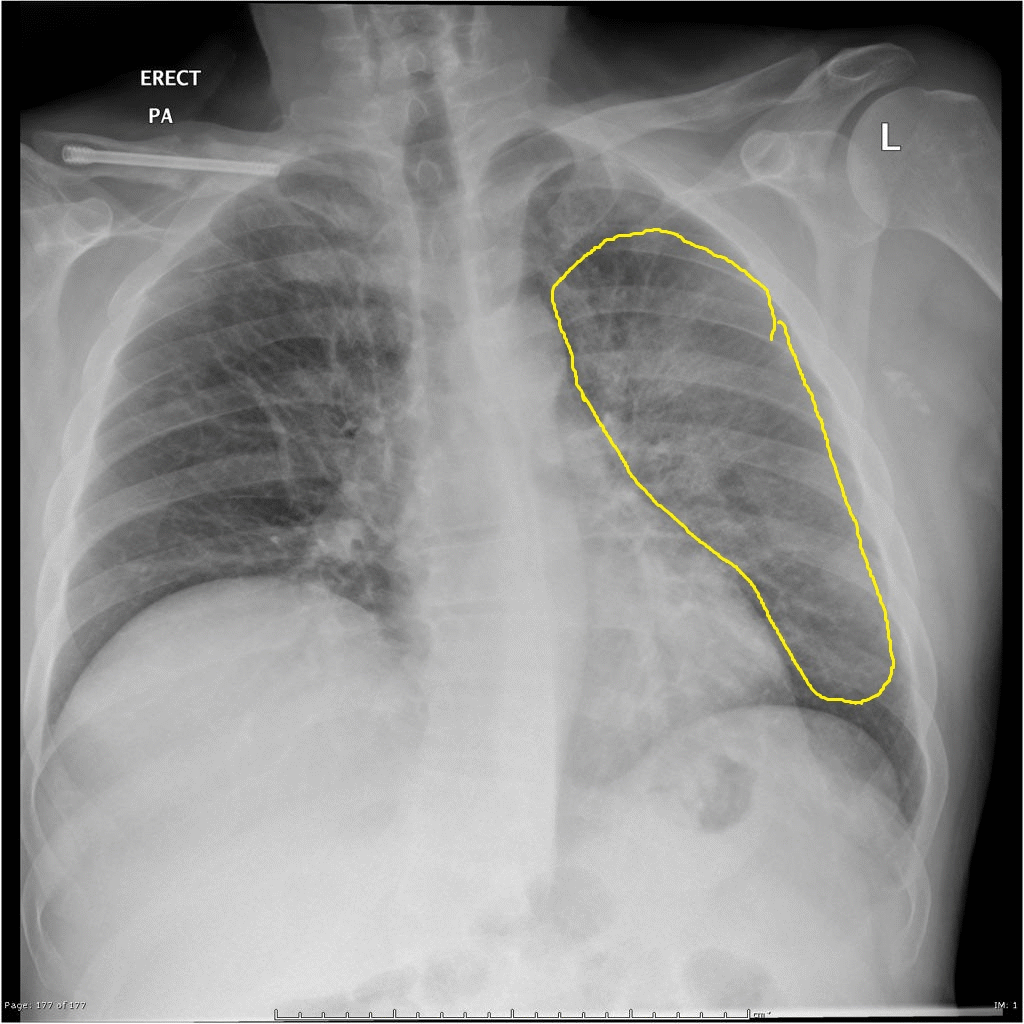 | |
| Mycoplasma pneumonia |
|
|
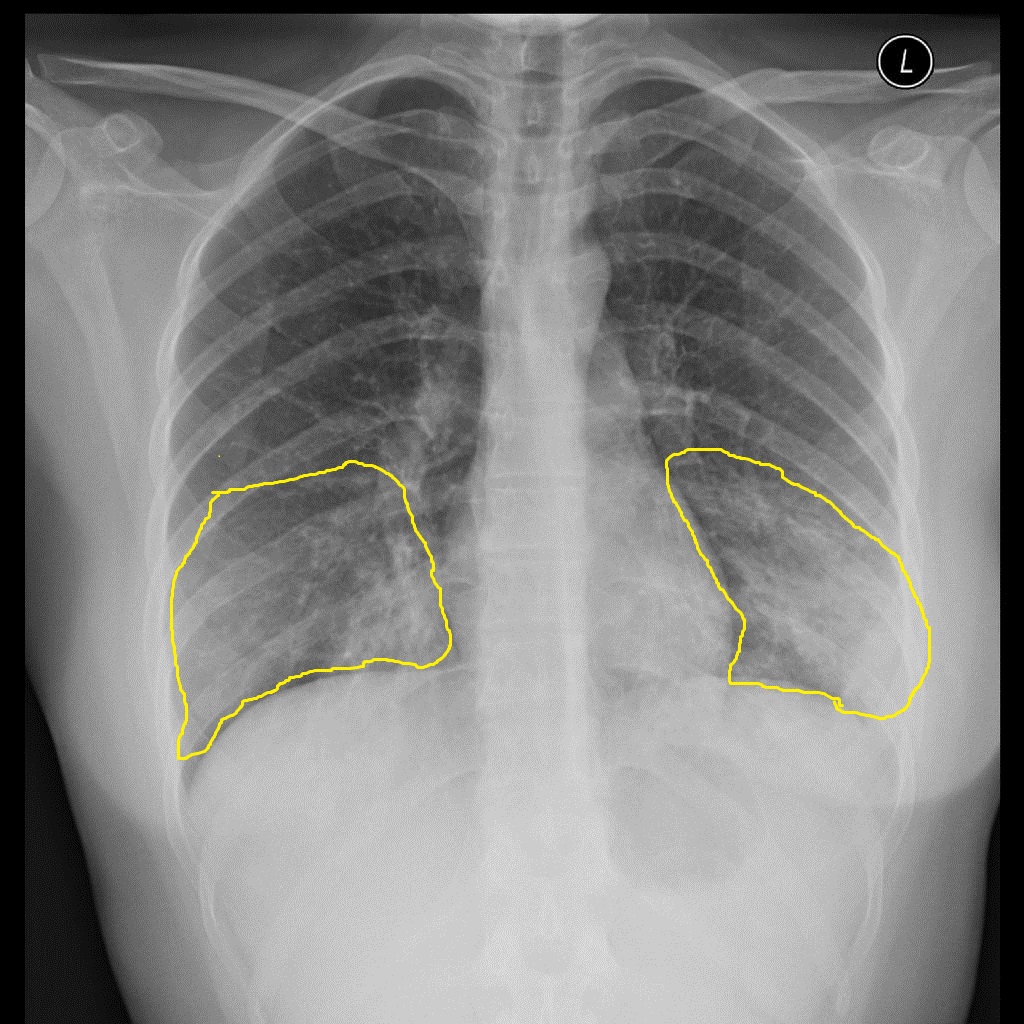 |
| Legionellosis |
|
|
 |
| Chlamydia pneumonia |
|
|
 |
Other differentials
Pneumonia should be differentiated from other diseases presenting with cough, fever, shortness of breath and tachypnea. The differentials include the following:[18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37]
| Diseases | Diagnostic tests | Physical Examination | Symptoms | Past medical history | Other Findings | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT scan and MRI | EKG | Chest X-ray | Tachypnea | Tachycardia | Fever | Chest Pain | Hemoptysis | Dyspnea on Exertion | Wheezing | Chest Tenderness | Nasalopharyngeal Ulceration | Carotid Bruit | |||
| Pulmonary embolism |
|
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ (Low grade) | ✔ | ✔ (In case of massive PE) | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
|
|
| Congestive heart failure |
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
|
| ||
| Percarditis |
|
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ (Low grade) | ✔ (Relieved by sitting up and leaning forward) | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
|
|
| Pneumonia |
|
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | - | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | - |
|
|
| Vasculitis |
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | - | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
||
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) |
|
|
✔ | ✔ | - | - | - | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | - |
|
| |
References
- ↑ Schiele F, Muller J, Colinet E, Siest G, Arzoglou P, Brettschneider H; et al. (1992). "Interlaboratory study of the IFCC method for alanine aminotransferase performed with use of a partly purified reference material". Clin Chem. 38 (12): 2365–71. PMID 1458569.
- ↑ Castro-Guardiola A, Armengou-Arxé A, Viejo-Rodríguez A, Peñarroja-Matutano G, Garcia-Bragado F (2000). "Differential diagnosis between community-acquired pneumonia and non-pneumonia diseases of the chest in the emergency ward". Eur J Intern Med. 11 (6): 334–339. PMID 11113658.
- ↑ Ahnsjö, Sven (1935). "Contribution to the Differential Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Childhood". Acta Paediatrica. 17 (3): 439–446. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1935.tb07697.x. ISSN 0803-5253.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Chaudhuri MR (1973). "Primary pulmonary cavitating carcinomas". Thorax. 28 (3): 354–66. PMC 470041. PMID 4353362.
- ↑ Mouroux J, Padovani B, Elkaïm D, Richelme H (1996). "Should cavitated bronchopulmonary cancers be considered a separate entity?". Ann. Thorac. Surg. 61 (2): 530–2. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(95)00973-6. PMID 8572761.
- ↑ Onn A, Choe DH, Herbst RS, Correa AM, Munden RF, Truong MT, Vaporciyan AA, Isobe T, Gilcrease MZ, Marom EM (2005). "Tumor cavitation in stage I non-small cell lung cancer: epidermal growth factor receptor expression and prediction of poor outcome". Radiology. 237 (1): 342–7. doi:10.1148/radiol.2371041650. PMID 16183941.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Langford CA, Hoffman GS (1999). "Rare diseases.3: Wegener's granulomatosis". Thorax. 54 (7): 629–37. PMC 1745525. PMID 10377211.
- ↑ Lee KS, Kim TS, Fujimoto K, Moriya H, Watanabe H, Tateishi U, Ashizawa K, Johkoh T, Kim EA, Kwon OJ (2003). "Thoracic manifestation of Wegener's granulomatosis: CT findings in 30 patients". Eur Radiol. 13 (1): 43–51. doi:10.1007/s00330-002-1422-2. PMID 12541109.
- ↑ Baughman RP, Teirstein AS, Judson MA, Rossman MD, Yeager H, Bresnitz EA, DePalo L, Hunninghake G, Iannuzzi MC, Johns CJ, McLennan G, Moller DR, Newman LS, Rabin DL, Rose C, Rybicki B, Weinberger SE, Terrin ML, Knatterud GL, Cherniak R (2001). "Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164 (10 Pt 1): 1885–9. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104046. PMID 11734441.
- ↑ Brauner MW, Grenier P, Mompoint D, Lenoir S, de Crémoux H (1989). "Pulmonary sarcoidosis: evaluation with high-resolution CT". Radiology. 172 (2): 467–71. doi:10.1148/radiology.172.2.2748828. PMID 2748828.
- ↑ Murphy J, Schnyder P, Herold C, Flower C (1998). "Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia simulating bronchial carcinoma". Eur Radiol. 8 (7): 1165–9. doi:10.1007/s003300050527. PMID 9724431.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Al-Ghanem S, Al-Jahdali H, Bamefleh H, Khan AN (2008). "Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: pathogenesis, clinical features, imaging and therapy review". Ann Thorac Med. 3 (2): 67–75. doi:10.4103/1817-1737.39641. PMC 2700454. PMID 19561910.
- ↑ Cordier JF, Loire R, Brune J (1989). "Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Definition of characteristic clinical profiles in a series of 16 patients". Chest. 96 (5): 999–1004. PMID 2805873.
- ↑ Lee KS, Kullnig P, Hartman TE, Müller NL (1994). "Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: CT findings in 43 patients". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 162 (3): 543–6. doi:10.2214/ajr.162.3.8109493. PMID 8109493.
- ↑ Suri HS, Yi ES, Nowakowski GS, Vassallo R (2012). "Pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis". Orphanet J Rare Dis. 7: 16. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-7-16. PMC 3342091. PMID 22429393.
- ↑ Moore AD, Godwin JD, Müller NL, Naidich DP, Hammar SP, Buschman DL, Takasugi JE, de Carvalho CR (1989). "Pulmonary histiocytosis X: comparison of radiographic and CT findings". Radiology. 172 (1): 249–54. doi:10.1148/radiology.172.1.2787035. PMID 2787035.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 Irfan M, Farooqi J, Hasan R (2013). "Community-acquired pneumonia". Curr Opin Pulm Med. 19 (3): 198–208. doi:10.1097/MCP.0b013e32835f1d12. PMID 23422417.
- ↑ Brenes-Salazar JA (2014). "Westermark's and Palla's signs in acute and chronic pulmonary embolism: Still valid in the current computed tomography era". J Emerg Trauma Shock. 7 (1): 57–8. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.125645. PMC 3912657. PMID 24550636.
- ↑ "CT Angiography of Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnostic Criteria and Causes of Misdiagnosis | RadioGraphics".
- ↑ Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A (2013). "Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism". Exp Clin Cardiol. 18 (2): 129–38. PMC 3718593. PMID 23940438.
- ↑ "Pulmonary Embolism: Symptoms - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health".
- ↑ Ramani GV, Uber PA, Mehra MR (2010). "Chronic heart failure: contemporary diagnosis and management". Mayo Clin. Proc. 85 (2): 180–95. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0494. PMC 2813829. PMID 20118395.
- ↑ Blinderman CD, Homel P, Billings JA, Portenoy RK, Tennstedt SL (2008). "Symptom distress and quality of life in patients with advanced congestive heart failure". J Pain Symptom Manage. 35 (6): 594–603. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.06.007. PMC 2662445. PMID 18215495.
- ↑ Hawkins NM, Petrie MC, Jhund PS, Chalmers GW, Dunn FG, McMurray JJ (2009). "Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: diagnostic pitfalls and epidemiology". Eur. J. Heart Fail. 11 (2): 130–9. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfn013. PMC 2639415. PMID 19168510.
- ↑ Takasugi JE, Godwin JD (1998). "Radiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Radiol. Clin. North Am. 36 (1): 29–55. PMID 9465867.
- ↑ Wedzicha JA, Donaldson GC (2003). "Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Respir Care. 48 (12): 1204–13, discussion 1213–5. PMID 14651761.
- ↑ Nakawah MO, Hawkins C, Barbandi F (2013). "Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the overlap syndrome". J Am Board Fam Med. 26 (4): 470–7. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2013.04.120256. PMID 23833163.
- ↑ Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA, Sinak LJ, Hayes SN, Melduni RM, Oh JK (2010). "Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management". Mayo Clin. Proc. 85 (6): 572–93. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0046. PMC 2878263. PMID 20511488.
- ↑ Bogaert J, Francone M (2013). "Pericardial disease: value of CT and MR imaging". Radiology. 267 (2): 340–56. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121059. PMID 23610095.
- ↑ Gharib AM, Stern EJ (2001). "Radiology of pneumonia". Med. Clin. North Am. 85 (6): 1461–91, x. PMID 11680112.
- ↑ Schmidt WA (2013). "Imaging in vasculitis". Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 27 (1): 107–18. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2013.01.001. PMID 23507061.
- ↑ Suresh E (2006). "Diagnostic approach to patients with suspected vasculitis". Postgrad Med J. 82 (970): 483–8. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2005.042648. PMC 2585712. PMID 16891436.
- ↑ Stein PD, Dalen JE, McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA, Wenger NK, Willis PW (1975). "The electrocardiogram in acute pulmonary embolism". Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 17 (4): 247–57. PMID 123074.
- ↑ Warnier MJ, Rutten FH, Numans ME, Kors JA, Tan HL, de Boer A, Hoes AW, De Bruin ML (2013). "Electrocardiographic characteristics of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". COPD. 10 (1): 62–71. doi:10.3109/15412555.2012.727918. PMID 23413894.
- ↑ Stein PD, Matta F, Ekkah M, Saleh T, Janjua M, Patel YR, Khadra H (2012). "Electrocardiogram in pneumonia". Am. J. Cardiol. 110 (12): 1836–40. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.019. PMID 23000104.
- ↑ Hazebroek MR, Kemna MJ, Schalla S, Sanders-van Wijk S, Gerretsen SC, Dennert R, Merken J, Kuznetsova T, Staessen JA, Brunner-La Rocca HP, van Paassen P, Cohen Tervaert JW, Heymans S (2015). "Prevalence and prognostic relevance of cardiac involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis". Int. J. Cardiol. 199: 170–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.087. PMID 26209947.
- ↑ Dennert RM, van Paassen P, Schalla S, Kuznetsova T, Alzand BS, Staessen JA, Velthuis S, Crijns HJ, Tervaert JW, Heymans S (2010). "Cardiac involvement in Churg-Strauss syndrome". Arthritis Rheum. 62 (2): 627–34. doi:10.1002/art.27263. PMID 20112390.