COVID-19-associated abdominal pain: Difference between revisions
Aditya Ganti (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 167: | Line 167: | ||
*In an unexplained [[abdominal pain]], [[CXR]], Chest [[CT scan]] or nasopharyngeal swab [[RT-PCR]] should be performed to diagnose the infection and treat it timely. | *In an unexplained [[abdominal pain]], [[CXR]], Chest [[CT scan]] or nasopharyngeal swab [[RT-PCR]] should be performed to diagnose the infection and treat it timely. | ||
*For the prevention of transmission through [[gastrointestinal]] tract (presence of viral RNA in the stool raise suspicion for [[fecal-oral route|fecal-oral transmission]]) | *For the prevention of transmission through [[gastrointestinal]] tract (presence of viral RNA in the stool raise suspicion for [[fecal-oral route|fecal-oral transmission]]) | ||
**Use of [[personal protective equipment]] (PPE) by the personnel handling the fecal matter. | **Use of [[personal protective equipment]] (PPE) by the personnel handling the fecal matter or visiting the [[patient]]. Protective eyewear (such as goggles or a face shield) used by healthcare personnel should cover the front and sides of the face with no gaps between glasses and the face.<ref name="urlInfection Control: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) | CDC">{{cite web |url=https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/infection-control-recommendations.html |title=Infection Control: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) | CDC |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>. | ||
**Screening of fecal [[Microbiome|microbiota]] [[transplant]] donors for [[COVID-19]] is also recommended.<ref name="pmid32240618">{{cite journal |vauthors=Green CA, Quraishi MN, Shabir S, Sharma N, Hansen R, Gaya DR, Hart AL, Loman NJ, Iqbal TH |title=Screening faecal microbiota transplant donors for SARS-CoV-2 by molecular testing of stool is the safest way forward |journal=Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol |volume=5 |issue=6 |pages=531 |date=June 2020 |pmid=32240618 |pmc=7225406 |doi=10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30089-3 |url=}}</ref> | **Screening of fecal [[Microbiome|microbiota]] [[transplant]] donors for [[COVID-19]] is also recommended.<ref name="pmid32240618">{{cite journal |vauthors=Green CA, Quraishi MN, Shabir S, Sharma N, Hansen R, Gaya DR, Hart AL, Loman NJ, Iqbal TH |title=Screening faecal microbiota transplant donors for SARS-CoV-2 by molecular testing of stool is the safest way forward |journal=Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol |volume=5 |issue=6 |pages=531 |date=June 2020 |pmid=32240618 |pmc=7225406 |doi=10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30089-3 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*If a [[patient]] with [[inflammatory bowel disease|IBDs]] takes ⩾20 mg/day of prednisone, they should reduce the dose or taper the dse to discontinue to prevent [[COVID-19]] infection. In case of positive test for [[COVID-19]] infection, drug should be tapered to discontinue.<ref name="SuShen2020">{{cite journal|last1=Su|first1=Song|last2=Shen|first2=Jun|last3=Zhu|first3=Liangru|last4=Qiu|first4=Yun|last5=He|first5=Jin-Shen|last6=Tan|first6=Jin-Yu|last7=Iacucci|first7=Marietta|last8=Ng|first8=Siew C|last9=Ghosh|first9=Subrata|last10=Mao|first10=Ren|last11=Liang|first11=Jie|title=Involvement of digestive system in COVID-19: manifestations, pathology, management and challenges|journal=Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology|volume=13|year=2020|pages=175628482093462|issn=1756-2848|doi=10.1177/1756284820934626}}</ref> | *If a [[patient]] with [[inflammatory bowel disease|IBDs]] takes ⩾20 mg/day of prednisone, they should reduce the dose or taper the dse to discontinue to prevent [[COVID-19]] infection. In case of positive test for [[COVID-19]] infection, drug should be tapered to discontinue.<ref name="SuShen2020">{{cite journal|last1=Su|first1=Song|last2=Shen|first2=Jun|last3=Zhu|first3=Liangru|last4=Qiu|first4=Yun|last5=He|first5=Jin-Shen|last6=Tan|first6=Jin-Yu|last7=Iacucci|first7=Marietta|last8=Ng|first8=Siew C|last9=Ghosh|first9=Subrata|last10=Mao|first10=Ren|last11=Liang|first11=Jie|title=Involvement of digestive system in COVID-19: manifestations, pathology, management and challenges|journal=Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology|volume=13|year=2020|pages=175628482093462|issn=1756-2848|doi=10.1177/1756284820934626}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 22 July 2020
For COVID-19 frequently asked outpatient questions, click here
For COVID-19 frequently asked inpatient questions, click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Javaria Anwer M.D.[2]
Synonyms and keywords: COVID-19 associated abdominal pain, COVID associated abdominal pain, COVID likned abdominal pain, COVID-19 linked abdominal pain, coronavirus associated abdominal pain, coronavirus related belly pain, abdominal pain associated with COVID-19, abdominal pain associated with SARS CoV2, SARS CoV2 related abdominal pain, SARS CoV2 linked abdomin pain, abdominal pain and COVID-19, abdominal pain and SARS CoV2 ,abdominal pain in COVID, abdomin pain in COVID, abdominal pain in nCoV, abdominal discomfort in COVID-19, abdominal discomfort in SARS CoV2.
Overview
Abdominal pain is a vast entity and sometimes a challenge due to its various potential diagnoses. Although COVID-19 is mainly a respiratory disease, abdominal pain is one of the symptoms of COVID-19 infection. A potential explanation for abdominal pain in COVID-19 is the presence of cellular ACE2 in esophagus, ileum and colon. Patients may present with global, epigastric, ileac fossa or epigastric pain. Cases of abdominal pain in COVID-19 infection may present as acute appendicitis, acute pancreatitis, upper GI bleed, gut perforation. In an unexplained abdominal pain it is important to suspect coronavirus-19 infection and take nasopharyngeal RT-PCR or CXR or chest CT as positive findings of these tests have been demonstrated in patients presenting with mere abdominal symptoms. Abdominal scans may show signs of mucosal inflammation. Contact tracing is an important secondary prevention step.
Historical Perspective
- COVID-19 was first discovered in a cluster of cases of pneumonia in Wuhan, China, reported on December 30th, 2019 by Wuhan Municipal Health Commission, China.
- Three bronchoalveolar lavage samples collected from a patient with pneumonia of unknown etiology – a surveillance definition established following the SARS outbreak of 2002-2003 – in Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) assays on these samples were positive for pan-Betacoronavirus. Nanopore sequencing and bioinformatic analyses indicated that the virus had features typical of the coronavirus family and belonged to the Betacoronavirus 2B lineage.A novel coronavirus was eventually identified.[1]
- The first disease outbreak news on the new virus was first published by WHO on 5th January 2020.[2]
- COVID-19-associated abdominal pain was first described as one of the less common symptoms of COVID-19 in a study published by Wang D et al. on Feb 3rd, 2020.[3] Still COVID-19 was primarily known as a respiratory disease. In the initial phase of the pandemic, the screening criteria for COVID‐19 did not include symptoms of abdominal pain.
- On March 12, 2020, WHO declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.
- With the increasing evidence and ongoing research, abdominal pain is now reported to be a common symptom in patients with COVID-19, and the viral infection is suspected in a patient presenting with abdominal pain. Research is underway to develop a better understanding of the etiology, risk factors, and treatment of abdominal pain associated with COVID-19.
Classification
There is no established system for the classification of abdominal pain in COVID-19. But a differentiation can be made based on the organ injury related to COVID-19 causing abdominal pain.
Pathophysiology
- The exact pathogenesis of COVID-19-associated abdominal pain is not fully understood.
- It is thought that COVID-19-associated abdominal pain is the result of either ACE 2 receptor mediated SARS-CoV2 infectivity and direct viral damage or colonic ischemia.
- The abdominal pain can be due to direct viral infection of the gastrointestinal tract via cellular ACE 2 receptors in several abdominal organs, making them susceptible to viral infection.
- ACE 2 acts as the SARS-CoV2 receptor for infectivity and the entrance into the cell.
- Research has shown ACE 2 receptors in esophageal epithelial cells, ileal and colon enterocytes making them vulnerable to COVID-19 infection.
- The detection of viral nucleocapsid protein in gastrointestinal epithelial cells and viral RNA in fecal specimens reflects the infectivity and chance of direct viral damage of organs.[4][5][6]
- The entry of the virus causes disruption of the enterocytes and may lead to inflammation, impaired cell permeability, and cellular damage.
- The severe abdominal pain associated colonic ischemia leading to gut perforation is due to nociceptor stimulation with cell destruction products and pH changes due to ischemia.
- Colon being the watreshed area is susceptible to hypoperfusion probably due to hypotension or clotting or due to reperfusion injury.
- Within 3-4 hours after the onset of ischemia, the necrosis of the mucosal villi starts leading to transmural infarct in 6 hours and eventually perforation.[7]
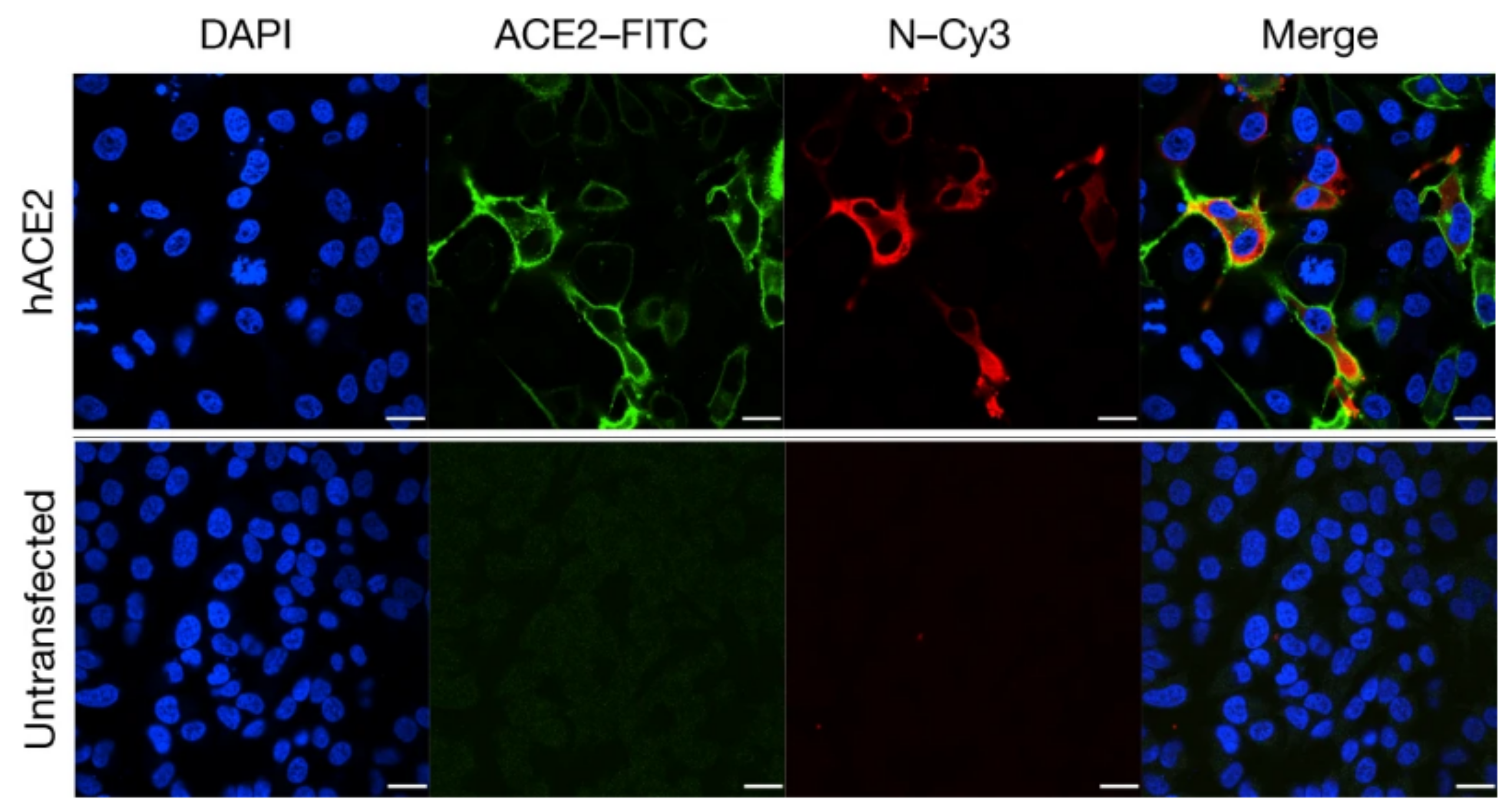
Transfection of HeLa cells with the ACE2 receptor makes them susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. hACE2, human ACE2;green, ACE2;red, viral protein (N);blue, DAPI (nuclei). Scale bars, 10 μm-By Peng Zhou et al - https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-2012-7, CC BY 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=91229428.jpg
Causes
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
- COVID-19 associated abdominal pain may be caused by:
- COVID-19-associated diarrhea
- COVID-19-associated hepatic injury
- COVID-19 associated acute abdomen (acute peritonitis and gut perforation)[8]
- COVID-19 associated pancreatitis[9][10]
- Anxiety associated with patient condition
Differentiating COVID-19 associated abdominal pain from other Diseases
- For further information about the differential diagnosis, click here.
- To view the differential diagnosis of COVID-19, click here
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Based upon the meta-analysis including 78 studies the Weighted Pooled Prevalence (WPP) of abdominal pain associated with COVID-19 is approximately 6.2% (2.6%-10.3%). Although the data comes from four studies, the WPP of abdominal pain at illness onset was 4.1% and at admission was 7.3%.[11]
Age
Very limited data is available about the detailed demographics of the patients having abdominal pain as one of the symptoms of COVID-19 infection. The age bracket of patients abdominal pain as their main symptoms reported average age to be 48 years, 50 years and 53 years respectively.[12][13] The close observation gives us an idea of the age range mostly affected.
Gender
In a retrospective study data from 1141 patients in China, among patients presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms, 56% were male.
Race
Data from 12797 patients showed a higher weighted pooled prevalence of abdominal pain associated with COVID-19 in the non-Chinese subgroup.
Risk Factors
- The most potent risk factor in the development of the COVID-19 associated abdominal pain is COVID-19 infection itself.
- The incidence of abdominal pain is higher in patients with severe COVID-19.[14]
Screening
There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine screening for COVID-19 associated abdominal pain.
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- The appearance of abdominal pain has no fixed pattern of appearance in the COVID-19 clinical course.
- A complication reported is gut perforation due to ischemia. Patients may present with gut perforation as the first sign of COVID-19 infection.[15]
- Upper GI bleed (due to esophageal mucosal damage as seen on endoscopy) has been reported in 4% of patients with other GI symptoms such as abdominal pain related to novel coronavirus infection. It is not known whether bleeding is a complication of other entities or a separate phenomenon in COVID-19 infection but has been mentioned together with abdominal pain. The esophagus, stomach, duodenum and stool have been tested positive for viral RNA.[16][17]
- Prognosis: In a meta-analysis by Mao R. et al. the odds ratio for severe disease in patients with anorexia as one of the gastrointestinal symptoms were 7.10.[18]
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Criteria
- There are no established diagnostic criteria to identify the cause of abdominal pain in SARS-CoV2 patient. Abdominal ultrasound or CT scan, and blood tests showing deranged liver functions can give a clue of possible gastrointestinal involvement.
History and Symptoms
- The patient may have abdominal pain as an accompanying symptom along with other SARS-CoV2 infection symptoms such as anorexia, fever, cough, and malaise. Very few patients present with abdominal pain as the sole symptom and high suspicion is required in order to reach the diagnosis.
- A patient with COVID-19 can have right iliac fossa, left iliac fossa, global, epigastric and umbilical pain.[12]
Physical Examination
- Patients with abdominal pain associated with COVID-19 may appear in distress due to their general condition or the severity of abdominal pain. A person with pancreatitis will appear dehydrated, lethargic and in severe pain.
- Coffee ground gastric emesis indicates a possible upper GI bleed.[16]
- Vital signs:
- Heart rate/ Pulse: Tachycardia may be due to fever, pain or shock or anxiety.
- Blood pressure: Depending upon the cause of abdominal pain a patient with mild disease may have a normal blood pressure with other presenting with shock due to gut perforation and resulting sepsis.
- Respiratory rate: Tachypnea maybe due to high metabolic rate such as in fever and sepsis due to COVID-19 along with inefficient ventilation.[19] Inefficient ventilation can be due to COVID-19 lung infection such as pneumonia or ARDS. Shallow breathing can be due to severe respiratory distress or abdominal pain.[20]
- Temperature: The patient can be febrile due to COVID-19 infection, hypothermic, or have a normal temperature.
- On Abdominal exam:[21][10]
- Inspection: Cullen's sign indicated acute pancreatitis but it has not been reported in COVID-19 associated acute pancreatitis cases.
- Auscultation: Accompanying gastrointestinal infection may present as increased bowel sounds due to enteritis. Decreased bowel sounds or absent bowel sounds after a period of increased bowel sounds may indicate gut rupture.
- Palpation:
- Based of a few case reports generalised abdominal or epigastric tenderness or right iliac fossa tenderness may accompany the symptom sometimes presenting exactly as acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis.
- Guarding (muscles contract as pressure is applied), rigidity (rigid abdominal wall- indicates peritoneal inflammation), and rebound tenderness (release of pressure causes pain) may point towards peritonitis a complication of acute appendicitis, gut perforation or rarely pancreatitis. The sign is important in leading decision making regarding the patient's need for surgery.
- Murphy's sign is important in the diagnosis of cholecystitis which has been reported with COVID-19.
- Percussion: No significant findings associated with COVID-19 associated abdominal pain have been reported.
- The physical exam findings associated with COVID-19 can be viewed by clicking here.
Laboratory Findings
- Laboratory findings consistent with the presence of infectious virions in the GI or respiratory tract detected via reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) indicate direct veal infectivity.
- There are no specific laboratory findings associated with abdominal pain in COVID-19 patients. Biochemical markers of liver injury such as bilirubin, CRP, ALT, AST and Gamma GT may be increased in blood tests.[20]
- Serum potassium levels are normal in patients but an important test to exclude life-threatening conditions in patients presenting with abdominal pain.
- Complete blood count provides information about the infectious status of the patient via leukicytosis such as in upper GI bleed and peritonitis, or lymphocytes indicating viral infection.
- Value of CRP and procalcitonin provide information on the inflammation and superimposed bacterial source of infection.[20]
- D-Dimer levels give information on active bleeding in the body such as acute abdomen and upper upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Renal function tests are deranged in a dehydrated person (increased urea) and patient with upper gastrointestinal bleeding or gut perforation as a complication of COVID-19 (increased BUN and creatinine).[15]
- Fecal occult blood test has been found positive in patients with upper GI bleed.[16]
- In a patient with upper GI bleed upper GI endoscopy may reveal esophageal ulcers and sample for immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescent staining can help detect the virus.[16]
Electrocardiogram
- There are no ECG findings associated with COVID-19 associated abdominal pain.
- The electrocardiogram findings on COVID-19 can be viewed by clicking here.
X-ray
- A Chest X-ray may be normal or show consolidation, bilateral perihilar and interstitial opacities opacities with air bronchograms.
- Abdominal X-ray has been reported to be normal in a few studies available.[10][21]
- The x-ray finidings on COVID-19 can be viewed by clicking here.
Echocardiography or Ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the abdomen may or may not show any abnormal findings. A case of bowel inflammatory signs (peri-intestinal inflammatory reaction) has been reported in a patient with abdominal pain associated with COVID-19.[20]
- The echocardiographic findings on COVID-19 can be viewed by clicking here.
CT scan
- CT scan abdomen maybe normal or confirm the peri-intestinal inflammatory reaction in a patient with pancreatitis associated with COVID.[20]
- CT scan of abdomen reals extensive pneumoperitoneum and of chest shows pneumothorax in a patient with gut perforation associated with COVID-19.[15]
- In COVID-19 patients with abdominal pain the CT scan chest can shows ground-glass opacities.[12]
- The CT scan findings in COVID-19 can be viewed by clicking here.
MRI
- There are no MRI findings associated with COVOD-19 associated abdominal pain.
- The MRI findings in COVID-19 can be viewed by clicking here.
Other Imaging Findings
A study by Poggiali et al. strongly recommends bedside lung ultrasound to detect the signs of respiratory COVID-19 infection even when there are no respiratory symptoms.[20]
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- The mainstay of therapy for COVID-19 associated abdominal pain is antiviral therapy, including lopinavir and ritonavir tablets. Treating the infection treats the direct cause of gut damage. The recommended medical therapy is based upon expert opinion rather than randomized control trials.
- Supportive care such as IV fluid therapy is essential especially if vomiting accompanies anorexia.
- Associated vomiting is treated with antiemetic drugs and diarrhea is treated with antidiarrheal drugs such as loperamide if C.difficile infection has been ruled out.
- Response to medical therapy can be monitored with the patient's general condition, symptoms, vital signs, and US of the abdomen or CT scan abdomen if required.
- There are no formal recommendations for the treatment of abdominal pain that is COVID-19 related. But NSAIDS given in the infection, serve the purpose. An acute abdomen is treated with surgery but if required the generalized abdominal pain is treated with opioids. The side effect of respiratory depression of increased opioids should be kept in mind.
- Although the COVID-19 infection and IBDs mimic in some parameters, glucocorticoids such as prednisone treatment should not be abruptly discontinued but tapered to a possible minimum dose.[22]
- UpperGI bleed can be stopped with the use of octreotide and esomeprazole.[16]
Surgery
- An acute abdomen associated with COVID-19 having complications such as gut perforation requires surgery. The reported procedures performed include exploratory laparotomy, followed by GI repair or partial resection.[8]
Primary Prevention
- There are no available vaccines for the prevention of COVID-19. There have been rigorous efforts in order to develop a vaccine for novel coronavirus and several vaccines are in the later phases of trials.[23]
- The only prevention for COVID-19 associated abdominal pain is the prevention and early diagnosis of the coronavirus-19 infection itself. According to the CDC, the effective measure for primary prevention of COVID-19 include:[24]
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or using a alcohol based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Staying at least 6 feet (about 2 arms’ length) from other people who do not live with you.
- Covering your mouth and nose with a cloth face cover when around others and covering sneezes and coughs.
- Cleaning and disinfecting.
Secondary prevention
Effective measures for the secondary prevention of COVID-19 associated abdominal pain include the following:
- Contact tracing helps reduce the spread of the disease.[25]
- In an unexplained abdominal pain, CXR, Chest CT scan or nasopharyngeal swab RT-PCR should be performed to diagnose the infection and treat it timely.
- For the prevention of transmission through gastrointestinal tract (presence of viral RNA in the stool raise suspicion for fecal-oral transmission)
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by the personnel handling the fecal matter or visiting the patient. Protective eyewear (such as goggles or a face shield) used by healthcare personnel should cover the front and sides of the face with no gaps between glasses and the face.[26].
- Screening of fecal microbiota transplant donors for COVID-19 is also recommended.[27]
- If a patient with IBDs takes ⩾20 mg/day of prednisone, they should reduce the dose or taper the dse to discontinue to prevent COVID-19 infection. In case of positive test for COVID-19 infection, drug should be tapered to discontinue.[14]
References
- ↑ "www.who.int" (PDF).
- ↑ "WHO Timeline - COVID-19".
- ↑ Wang, Dawei; Hu, Bo; Hu, Chang; Zhu, Fangfang; Liu, Xing; Zhang, Jing; Wang, Binbin; Xiang, Hui; Cheng, Zhenshun; Xiong, Yong; Zhao, Yan; Li, Yirong; Wang, Xinghuan; Peng, Zhiyong (2020). "Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China". JAMA. 323 (11): 1061. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585. ISSN 0098-7484.
- ↑ Zou, Xin; Chen, Ke; Zou, Jiawei; Han, Peiyi; Hao, Jie; Han, Zeguang (2020). "Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection". Frontiers of Medicine. 14 (2): 185–192. doi:10.1007/s11684-020-0754-0. ISSN 2095-0217.
- ↑ Tian Y, Rong L, Nian W, He Y (May 2020). "Review article: gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of faecal transmission". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 51 (9): 843–851. doi:10.1111/apt.15731. PMC 7161803 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32222988 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q, Zhong JC, Turner AJ, Raizada MK, Grant MB, Oudit GY (May 2020). "Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2". Circ. Res. 126 (10): 1456–1474. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015. PMC 7188049 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32264791 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Mastoraki A, Mastoraki S, Tziava E, Touloumi S, Krinos N, Danias N, Lazaris A, Arkadopoulos N (February 2016). "Mesenteric ischemia: Pathogenesis and challenging diagnostic and therapeutic modalities". World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 7 (1): 125–30. doi:10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.125. PMC 4753178. PMID 26909235.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Gao Y, Xi H, Chen L (July 2020). "Emergency Surgery in Suspected COVID-19 Patients With Acute Abdomen: Case Series and Perspectives". Ann. Surg. 272 (1): e38–e39. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003961. PMC 7188052 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32301807 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Aloysius MM, Thatti A, Gupta A, Sharma N, Bansal P, Goyal H (May 2020). "COVID-19 presenting as acute pancreatitis". Pancreatology. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2020.05.003. PMC 7207100 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32444169 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Hadi A, Werge M, Kristiansen KT, Pedersen UG, Karstensen JG, Novovic S, Gluud LL (June 2020). "Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) associated with severe acute pancreatitis: Case report on three family members". Pancreatology. 20 (4): 665–667. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2020.04.021. PMC 7199002 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32387082 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Tariq, Raseen; Saha, Srishti; Furqan, Fateeha; Hassett, Leslie; Pardi, Darrell; Khanna, Sahil (2020). "Prevalence and Mortality of COVID-19 patients with Gastrointestinal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.003. ISSN 0025-6196.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Saeed, U.; Sellevoll, H. B.; Young, V. S.; Sandbaek, G.; Glomsaker, T.; Mala, T. (2020). "Covid-19 may present with acute abdominal pain". British Journal of Surgery. 107 (7): e186–e187. doi:10.1002/bjs.11674. ISSN 0007-1323.
- ↑ Luo S, Zhang X, Xu H (June 2020). "Don't Overlook Digestive Symptoms in Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)". Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18 (7): 1636–1637. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043. PMC 7154217 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32205220 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 14.0 14.1 Su, Song; Shen, Jun; Zhu, Liangru; Qiu, Yun; He, Jin-Shen; Tan, Jin-Yu; Iacucci, Marietta; Ng, Siew C; Ghosh, Subrata; Mao, Ren; Liang, Jie (2020). "Involvement of digestive system in COVID-19: manifestations, pathology, management and challenges". Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology. 13: 175628482093462. doi:10.1177/1756284820934626. ISSN 1756-2848.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Corrêa Neto, Isaac José Felippe; Viana, Kaline Fortes; Silva, Milena Braga Soares da; Silva, Leandro Mariano da; Oliveira, Gustavo de; Cecchini, Angelo Rossi da Silva; Rolim, Alexander Sá; Robles, Laercio (2020). "Perforated acute abdomen in a patient with COVID-19: an atypical manifestation of the disease". Journal of Coloproctology. doi:10.1016/j.jcol.2020.05.011. ISSN 2237-9363.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 Xiao F, Tang M, Zheng X, Liu Y, Li X, Shan H (May 2020). "Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2". Gastroenterology. 158 (6): 1831–1833.e3. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055. PMC 7130181 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32142773 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, Yu T, Wang Y, Pan S, Zou X, Yuan S, Shang Y (May 2020). "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study". Lancet Respir Med. 8 (5): 475–481. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. PMC 7102538 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32105632 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Mao, Ren; Qiu, Yun; He, Jin-Shen; Tan, Jin-Yu; Li, Xue-Hua; Liang, Jie; Shen, Jun; Zhu, Liang-Ru; Chen, Yan; Iacucci, Marietta; Ng, Siew C; Ghosh, Subrata; Chen, Min-Hu (2020). "Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 5 (7): 667–678. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6. ISSN 2468-1253.
- ↑ Telias, Irene; Katira, Bhushan H.; Brochard, Laurent (2020). "Is the Prone Position Helpful During Spontaneous Breathing in Patients With COVID-19?". JAMA. 323 (22): 2265. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8539. ISSN 0098-7484.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 Poggiali E, Ramos PM, Bastoni D, Vercelli A, Magnacavallo A (2020). "Abdominal Pain: A Real Challenge in Novel COVID-19 Infection". Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 7 (4): 001632. doi:10.12890/2020_001632. PMC 7162568 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32309266 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 21.0 21.1 Abdalhadi A, Alkhatib M, Mismar AY, Awouda W, Albarqouni L (2020). "Can COVID 19 present like appendicitis?". IDCases. 21: e00860. doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00860. PMC 7265835 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32523872 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Queiroz N, Barros LL, Azevedo M, Oba J, Sobrado CW, Carlos AS, Milani LR, Sipahi AM, Damião A (2020). "Management of inflammatory bowel disease patients in the COVID-19 pandemic era: a Brazilian tertiary referral center guidance". Clinics (Sao Paulo). 75: e1909. doi:10.6061/clinics/2020/e1909. PMC 7153358 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32321117 Check|pmid=value (help). Vancouver style error: initials (help) - ↑ "NIH clinical trial of investigational vaccine for COVID-19 begins | National Institutes of Health (NIH)".
- ↑ "How to Protect Yourself & Others | CDC".
- ↑ "Contact Tracing for COVID-19 | CDC".
- ↑ Green CA, Quraishi MN, Shabir S, Sharma N, Hansen R, Gaya DR, Hart AL, Loman NJ, Iqbal TH (June 2020). "Screening faecal microbiota transplant donors for SARS-CoV-2 by molecular testing of stool is the safest way forward". Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5 (6): 531. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30089-3. PMC 7225406 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32240618 Check|pmid=value (help).