Acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification
|
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Acute lymphoblastic leukemia from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Raviteja Guddeti, M.B.B.S. [2] Carlos A Lopez, M.D. [3]
Overview
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be classified according to either the French-American-British (FAB) classification or World Health Organization (WHO). According to the French-American-British (FAB) classification, acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be classified into 3 subgroups: ALL-L1 (small uniform cells), ALL-L2 (large varied cells), and ALL-L3 (large varied cells with vacuoles). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), acute lymphoblastic leukemia may also be classified into 3 subgroups: B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (not organ specific), and B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with recurrent genetic abnormalities.
Classification
There are 2 classifications systems between acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the French-American-British (FAB) classification and the World Health Organization (WHO):
French-American-British classification
The French-American-British (FAB) classification of acute lymphoblastic leukemia is divided into 3 subtypes L1 to L3 based on the type of cell from which the leukemia developed and its degree of maturity and morphological classification. Each subtype is then further classified by determining the surface markers of the abnormal lymphocytes, called immunophenotyping. There are 2 main immunologic types: pre-B cell and pre-T cell. The mature B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (L3) is now classified as Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma.
Classification
- ALL-L1: small uniform cells
- ALL-L2: large varied cells
- ALL-L3: large varied cells with vacuoles (bubble-like features)
World Health Organization classification
The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of acute lymphoblastic leukemia attempts to be more clinically useful and to produce more meaningful prognostic information than the French-American-British (FAB) classification criteria. There are 3 different grups of Lymphoblastic leukemias according to the WHO including a classification with recurrent genetic abnormalities.[1]
Group 1
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
Group 2
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (Not organ specific)
Group 3
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with recurrent genetic abnormalities:
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(9;22)(q34;q11.2), BCR-ABL1
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(v;11q23); MLL rearranged
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(12;21)(p13;q22) TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1)
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with hyperdiploidy
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with hypodiploidy
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(5;14)(q31;q32) IL3-IGH
- B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(1;19)(q23;p13.3) TCF3-PBX1
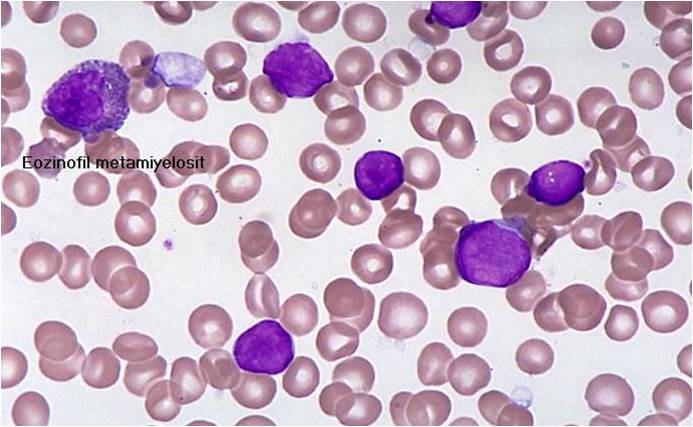
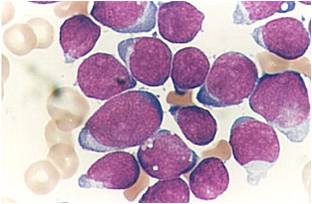
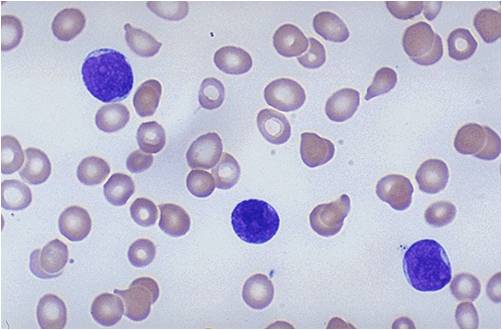
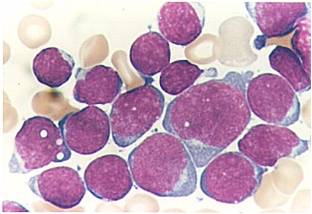
(Images shown below are courtesy of Melih Aktan MD, Istanbul Medical Faculty - Turkey, and Kyoto University - Japan)
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
References
- ↑ Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES (2011). "The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications". Blood. 117 (19): 5019–32. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-01-293050. PMC 3109529. PMID 21300984.