Pleural empyema: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| MeshID = D016724 | | MeshID = D016724 | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pleural_empyema}} | ||
'''For the WikiPatient page for this topic, click [[Pleural empyema (patient information)|here]]''' | '''For the WikiPatient page for this topic, click [[Pleural empyema (patient information)|here]]''' | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Definitive treatment for empyema entails drainage of the infected pleural fluid. A [[chest tube]] may be inserted, often using ultrasound guidance. [[Intravenous]] [[antibiotic]]s are given. If this is insufficient, surgical [[debridement]] of the pleural space may be required. | Definitive treatment for empyema entails drainage of the infected pleural fluid. A [[chest tube]] may be inserted, often using ultrasound guidance. [[Intravenous]] [[antibiotic]]s are given. If this is insufficient, surgical [[debridement]] of the pleural space may be required. | ||
{{Respiratory pathology}} | {{Respiratory pathology}} | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 24 September 2012
| Pleural empyema | |
 | |
|---|---|
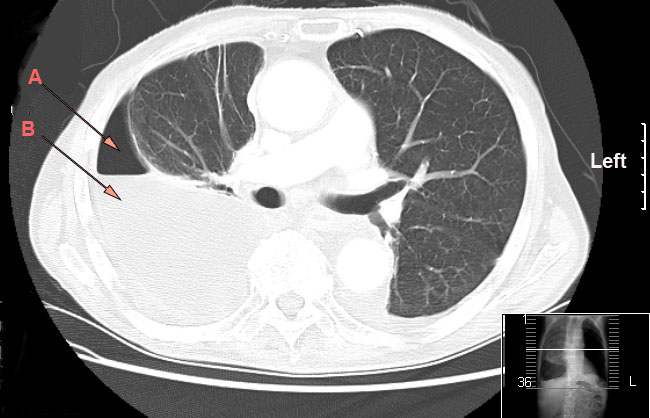
| CT chest showing large right sided hydro-pneumothorax from pleural empyema. Arrows A: air, B: fluid | |
| ICD-10 | J86 |
| ICD-9 | 510 |
| DiseasesDB | 4200 |
| MedlinePlus | 000123 |
| MeSH | D016724 |
|
Pleural empyema Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pleural empyema On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pleural empyema |
For the WikiPatient page for this topic, click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
A pleural empyema (also known as a pyothorax or purulent pleuritis) is an accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity. Most pleural empyemas arise from an infection within the lung (pneumonia), often associated with parapneumonic effusions. There are three stages: exudative, fibrinopurulent and organizing. In the exudative stage, the pus accumulates. This is followed by the fibrinopurulent stage in which there is loculation of the pleural fluid (the creation of grapelike pus pockets). In the final organizing stage, scarring of the pleural space may lead to lung entrapment.
Symptoms
Symptoms of empyema may vary in severity. Typical symptoms include: fever, chest pain or discomfort, cough, sweating and shortness of breath.
Clubbing of the fingernails may be present. There is a dull percussion note and reduced breath sounds on the affected side of the chest. Other diagnostic tools include chest x-ray, CT scan, and ultrasonography.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is confirmed by thoracentesis; frank pus may be aspirated from the pleural space. The pleural fluid typically has a low pH (<7.20), low glucose (<60 mg/dL), and contains infectious organisms.
Treatment
Definitive treatment for empyema entails drainage of the infected pleural fluid. A chest tube may be inserted, often using ultrasound guidance. Intravenous antibiotics are given. If this is insufficient, surgical debridement of the pleural space may be required.
Template:Respiratory pathology Template:SIB
de:Empyem et:Empüeem nl:Empyeem