Remdesivir
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi, M.D.
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Remdesivir is an adenosine nucleotide prodrug that is FDA authorized for the treatment of suspected or laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults and pediatric patients hospitalized with severe disease under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA). Common adverse reactions include nausea, constipation, pyrexia, acute respiratory failure, anemia (decreased hemoglobin), acute kidney injury (decreased eGFR, decreased creatinine clearance, or increased creatinine), hyperglycemia (increased blood glucose), and increased transaminases.
Adult Indications and Dosage
Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Suspected or Laboratory Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severe Disease
Remdesivir is authorized for use under an EUA for treatment of patients hospitalized with suspected or laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe disease. Severe disease is defined as patients with an oxygen saturation (SpO2) ≤94% on room air or requiring supplemental oxygen or requiring mechanical ventilation or requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Specifically, remdesivir is only authorized for hospitalized adult and pediatric patients for whom use of an intravenous (IV) agent is clinically appropriate.
Dosage
- The recommended dosage in adults is a single loading dose of remdesivir 200 mg on Day 1 followed by once-daily maintenance doses of remdesivir 100 mg from Day 2 via IV infusion.
- For patients requiring invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, total treatment duration is 10 days.
- For patients not requiring invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, total treatment duration is 5 days. If a patient does not demonstrate clinical improvement, treatment may be extended for up to 5 additional days (i.e., up to a total of 10 days).
- Administer remdesivir via IV infusion in a total volume of up to 250 mL 0.9% sodium chloride over 30 to 120 minutes.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Remdesivir in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Remdesivir in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Suspected or Laboratory Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severe Disease
Remdesivir is authorized for use under an EUA for treatment of patients hospitalized with suspected or laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe disease. Severe disease is defined as patients with an oxygen saturation (SpO2) ≤94% on room air or requiring supplemental oxygen or requiring mechanical ventilation or requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Specifically, remdesivir is only authorized for hospitalized adult and pediatric patients for whom use of an intravenous (IV) agent is clinically appropriate.
Dosage
For pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg, the dose should be calculated using the mg/kg dose according to the patient’s weight.
- For pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg, use remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, lyophilized powder only. Do not use remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), for pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg due to the higher amount of sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin sodium salt (SBECD) present and resulting higher tonicity of the solution concentrate compared to the lyophilized formulation.
- Refer to the table below for recommended dosage form and dosage in pediatric patients according to weight.
| Body weight | Recommended Dosage Form | Loading dose on Day 1 | Maintenance dose from Day 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 kg to <40 kg | Lyophilized Powder for Injection Only | 5 mg/kg | 2.5 mg/kg |
| ≥40 kg | Lyophilized Powder for Injection OR Injection | 200 mg | 100 mg |
- For pediatric patients requiring invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, total treatment duration is 10 days.
- For pediatric patients not requiring invasive mechanical ventilation and/or ECMO, total treatment duration is 5 days. If a patient does not demonstrate clinical improvement, treatment may be extended for up to 5 additional days (i.e., up to a total of 10 days).
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Remdesivir in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Remdesivir in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
Remdesivir is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any ingredient of remdesivir.
Warnings
There are limited clinical data available for remdesivir. Serious and unexpected adverse events may occur that have not been previously reported with remdesivir use.
Hypersensitivity Including Infusion-Related and Anaphylactic Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions including infusion-related and anaphylactic reactions have been observed during and following administration of remdesivir. Signs and symptoms may include hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia, dyspnea, wheezing, angioedema, rash, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and shivering. Slower infusion rates, with a maximum infusion time of up to 120 minutes, can be considered to potentially prevent these signs and symptoms. If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. The use of remdesivir is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to remdesivir.
Increased Risk of Transaminase Elevations
Transaminase elevations have been observed in healthy volunteers who received 200 mg of remdesivir followed by 100 mg doses for 5-10 days. Transaminase elevations have also been reported in patients with COVID-19 who received remdesivir in clinical trials. As transaminase elevations have been reported as a component of COVID-19, including in patients receiving placebo in clinical trials of remdesivir, discerning the contribution of remdesivir to transaminase elevations in this patient population is challenging.
Hepatic laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to starting remdesivir and daily while receiving remdesivir.
- Remdesivir should not be initiated in patients with ALT greater than or equal to 5 times the upper limit of normal at baseline.
- Remdesivir should be discontinued in patients who develop:
- ALT greater than or equal to 5 times the upper limit of normal during treatment with remdesivir. Remdesivir may be restarted when ALT is less than 5 times the upper limit of normal.
- OR
- ALT elevation accompanied by signs or symptoms of liver inflammation or increasing conjugated bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, or INR.
Risk of Reduced Antiviral Activity When Coadministered with Chloroquine or Hydroxychloroquine
Coadministration of remdesivir and chloroquine phosphate or hydroxychloroquine sulfate is not recommended based on in vitro data demonstrating an antagonistic effect of chloroquine on the intracellular metabolic activation and antiviral activity of remdesivir.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
1. Overall Safety Summary
In healthy subjects and hospitalized patients with PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, graded elevations in ALT and AST have been observed with a loading dose of remdesivir 200 mg administered intravenously on Day 1 followed by 100 mg administered intravenously once daily for up to 9 days. The mechanism of these elevations is unknown.
Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. The decision to continue or discontinue remdesivir after development of an adverse event should be made based on the clinical risk benefit assessment for the individual.
1.1 Clinical Studies in Healthy Adults
Remdesivir was evaluated in four Phase 1 studies in 138 healthy adult volunteers (Studies GS-US-399-1812, GS-US-399-1954, GS-US-399-4231, and GS-US-399-5505). In these studies, transient graded elevations in ALT and AST were observed at repeated once-daily doses of remdesivir.
1.2 NIAID ACTT-1 Trial
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-1) of remdesivir in 1,063 hospitalized subjects with COVID-19 treated with remdesivir (n=541) or placebo (n=522) for 10 days, serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported in 21% and 27% of subjects, respectively, and Grade ≥3 non-serious adverse events were reported in 29% and 33% of subjects, respectively. The most common SAE was respiratory failure reported in 5% of subjects treated with remdesivir and 8% of subjects treated with placebo. The most common Grade ≥3 non-serious adverse events in the remdesivir treatment arm are shown below.
| Grade ≥3 Non-Serious Adverse Events | Remdesivir (N=538) | Placebo (N=521) |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia or decreased hemoglobin | 43 (8%) | 47 (9%) |
| Acute kidney injury, decreased eGFR or creatinine clearance, or increased blood creatinine | 40 (7%) | 38 (7%) |
| Pyrexia | 27 (5%) | 17 (3%) |
| Hyperglycemia or increased blood glucose | 22 (4%) | 17 (3%) |
| Increased transaminases, including ALT and/or AST | 22 (4%) | 31 (6%) |
1.3 Study GS-US-540-5773
In a randomized, open-label clinical trial (Study GS-US-540-5773) of remdesivir in 397 hospitalized subjects with severe COVID-19 treated with remdesivir for 5 (n=200) or 10 days (n=197), adverse events were reported in 70% and 74% of subjects, respectively, SAEs were reported in 21% and 35% of subjects, respectively, and Grade ≥3 adverse events were reported in 30% and 43% of subjects, respectively. The most common adverse events were nausea (10% in the 5-day group vs 9% in the 10-day group), acute respiratory failure (6% vs 11%), ALT increased (6% vs 8%), and constipation (7% in both groups). Nine (4%) subjects in the 5-day group and 20 (10%) subjects in the 10-day group discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. All-cause mortality at Day 28 was 10% vs 13% in the 5- and 10-day treatment groups, respectively.
2. Hepatic Adverse Reactions
2.1 Experience in Healthy Volunteers
Grade 1 and 2 transaminase elevations were observed in healthy volunteers in Study GS-US-399-5505 (200 mg followed by 100 mg dosing for 5–10 days) and Study GS-US-399-1954 (150 mg daily for 7 or 14 days), which resolved after discontinuation of remdesivir.
2.2 NIAID ACTT-1 trial
Grade ≥3 non-serious adverse events of increased aminotransferase levels including ALT, AST, or both were reported in 4% of subjects receiving remdesivir compared with 6% receiving placebo.
2.3 Study GS-US-540-5773
Grade ≥3 hepatic laboratory abnormalities reported in subjects treated with remdesivir for 5 (n=200) or 10 days (n=197) are shown below.
| Hepatic Laboratory Abnormalities | Remdesivir for 5 Days | Remdesivir for 10 Days | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT Increased | Grade 3 | 8/194 (4%) | 11/191 (6%) | 19/385 (5%) |
| Grade 4 | 4/194 (2%) | 5/191 (3%) | 9/385 (2%) | |
| AST Increased | Grade 3 | 11/194 (6%) | 7/190 (4%) | 18/384 (5%) |
| Grade 4 | 3/194 (2%) | 4/190 (2%) | 7/384 (2%) | |
| Total Bilirubin Increased | Grade 3 | 1/193 (1%) | 3/190 (2%) | 4/383 (1%) |
| Grade 4 | 0 | 1/190 (1%) | 1/383 (<1%) | |
2.4 Compassionate Use Experience
In the compassionate use program in patients with severe or critical illness with COVID-19, liver function test abnormalities were reported in 12% (19/163) of patients. Time to onset from first dose ranged from 1-16 days. Four of these patients discontinued remdesivir treatment with elevated transaminases occurring on Day 5 of remdesivir treatment as per protocol.
Seven cases of serious liver-related laboratory abnormality were identified. There was one SAE of blood bilirubin increased in a critically ill patient with septic shock and multiorgan failure. None of the other cases had reported adverse events suggestive of hyperbilirubinemia or symptoms of hepatitis.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Remdesivir Postmarketing Experience.
Drug Interactions
Drug-drug interaction trials of remdesivir and other concomitant medications have not been conducted in humans. Due to antagonism observed in vitro, concomitant use of remdesivir with chloroquine phosphate or hydroxychloroquine sulfate is not recommended.
In vitro, remdesivir is a substrate for drug metabolizing enzymes CYP2C8, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, and is a substrate for Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides 1B1 (OATP1B1) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporters. In vitro, remdesivir is an inhibitor of CYP3A4, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, BSEP, MRP4, and NTCP. The clinical relevance of these in vitro assessments has not been established.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
No adequate and well-controlled studies of remdesivir use in pregnant women have been conducted. Remdesivir should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk for the mother and the fetus.
In nonclinical reproductive toxicity studies, remdesivir demonstrated no adverse effect on embryofetal development when administered to pregnant animals at systemic exposures (AUC) of the predominant circulating metabolite of remdesivir (GS-441524) that were 4 times (rats and rabbits) the exposure in humans at the recommended human dose (RHD).
Animal Data
Remdesivir was administered via intravenous injection to pregnant rats and rabbits (up to 20 mg/kg/day) on Gestation Days 6 through 17, and 7 through 20, respectively, and also to rats from Gestation Day 6 to Lactation/Post-partum Day 20. No adverse effects on embryo-fetal (rats and rabbits) or pre/postnatal (rats) development were observed in rats and rabbits at nontoxic doses in pregnant animals. During organogenesis, exposures to the predominant circulating metabolite (GS-441524) were 4 (rats and rabbits) times higher than the exposure in humans at the RHD. In a pre/postnatal development study, exposures to the predominant circulating metabolite of remdesivir (GS-441524) were similar to the human exposures at the RHD.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Remdesivir in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Remdesivir during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of remdesivir in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. In animal studies, remdesivir and metabolites have been detected in the nursing pups of mothers given remdesivir, likely due to the presence of remdesivir in milk. Because of the potential for viral transmission to SARS-CoV-2-negative infants and adverse reactions from the drug in breastfeeding infants, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for remdesivir and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from remdesivir or from the underlying maternal condition.
Animal Data
Remdesivir and its metabolites were detected in the plasma of nursing rat pups, likely due to the presence of remdesivir and/or its metabolites in milk, following daily intravenous administration of remdesivir to pregnant mothers from Gestation Day 6 to Lactation Day 20. Exposures in nursing pups were approximately 1% that of maternal exposure on lactation day 10.
Pediatric Use
The safety, effectiveness, or pharmacokinetics of remdesivir for treatment of COVID-19 have not been assessed in pediatric patients. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetics (PBPK) modeling of pharmacokinetic data from healthy adults was used to derive pediatric doses. Pediatric doses are expected to result in comparable steady-state exposures of remdesivir and metabolites as observed in healthy adults following administration of the recommended dosage regimen.
For pediatric patients with weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg, use remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, lyophilized powder only. Remdesivir injection, 100/20 mL (5 mg/mL), should not be used for pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg due to the higher amount of SBECD present and resulting higher tonicity of the solution concentrate compared to the lyophilized formulation.
Pediatric patients (older than 28 days) must have eGFR determined and full-term neonates (at least 7 days to less than or equal to 28 days) must have serum creatinine determined before dosing and daily while receiving remdesivir. Pediatric patients should be monitored for renal function and consideration given for stopping therapy in the setting of substantial decline.
Because the excipient SBECD is renally cleared and accumulates in patients with decreased renal function, administration of drugs formulated with SBECD (such as remdesivir) is not recommended in adults and pediatric patients (older than 28 days old) with eGFR less than 30 mL/min or in full-term neonates (at least 7 days and less than or equal to 28 days old) with serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1 mg/dL unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Geriatic Use
The pharmacokinetics of remdesivir have not been evaluated in patients >65 years of age. In general, appropriate caution should be exercised in the administration of remdesivir and monitoring of elderly patients, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Remdesivir with respect to specific gender.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Remdesivir with respect to specific race.
Renal Impairment
Patients with eGFR greater than or equal to 30 mL/min have received remdesivir for treatment of COVID-19 with no dose adjustment. The safety and efficacy of remdesivir have not been assessed in patients with severe renal impairment or ESRD. The pharmacokinetics of remdesivir have not been evaluated in patients with renal impairment. Remdesivir is not recommended in adults and pediatric patients (at least 28 days old) with eGFR less than 30 mL/min or in full-term neonates (at least 7 days and less than or equal to 28 days old) with serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1 mg/dL unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Adult and pediatric patients (greater than 28 days old) must have an eGFR determined and full-term neonates (at least 7 days to less than or equal to 28 days old) must have serum creatinine determined before dosing and daily while receiving remdesivir.
Adults
- eGFR, Male: (140 – age in years) × (weight in kg) / 72 × (serum creatinine in mg/dL)
- eGFR, Female: (140 – age in years) × (weight in kg) × 0.85 / 72 × (serum creatinine in mg/dL)
Pediatric patients (greater than 28 days old to less than 1 year of age)
- eGFR: 0.45 × (height in cm) / serum creatinine in mg/dL
Pediatric patients (at least 1 year of age to less than 18 years of age)
- eGFR = 0.413 x (height or length)/Scr) if height/length is expressed in centimeters OR 41.3 x (height or length)/Scr) if height/length is expressed in meters
Because the excipient SBECD is renally cleared and accumulates in patients with decreased renal function, administration of drugs formulated with SBECD [such as remdesivir is not recommended in adults and pediatric patients (greater than 28 days old) with eGFR less than 30 mL/min or in full-term neonates (at least 7 days and less than or equal to 28 days old)] with serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1 mg/dL unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of remdesivir have not been evaluated in patients with hepatic impairment.
It is not known if dosage adjustment is needed in patients with hepatic impairment, and remdesivir should only be used in patients with hepatic impairment if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Hepatic laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to starting remdesivir and daily while receiving remdesivir.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Remdesivir in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Remdesivir in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Important Testing Prior to and During Treatment and Route of Administration
- Adult and pediatric patients (greater than 28 days old) must have an eGFR determined and full-term neonates (at least 7 days to less than or equal to 28 days old) must have serum creatinine determined before dosing of remdesivir and daily while receiving remdesivir.
- Hepatic laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to starting remdesivir and daily while receiving remdesivir.
- Remdesivir should be administered via IV infusion only. Do not administer as an intramuscular (IM) injection.
Dose Preparation and Administration, Adults and Pediatric Patients Weighing 40 kg and Higher
Adults and pediatric patients weighing 40 kg and higher can use remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, lyophilized powder and remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), solution. See below for different preparation and administration instructions for the two dosage formulations.
A. Remdesivir for Injection, 100 mg, Lyophilized Powder
Reconstitution Instructions
Remove the required number of single-dose vial(s) from storage. For each vial:
- Aseptically reconstitute remdesivir lyophilized powder by addition of 19 mL of Sterile Water for Injection using a suitably sized syringe and needle per vial.
- Discard the vial if a vacuum does not pull the Sterile Water for Injection into the vial.
- Immediately shake the vial for 30 seconds.
- Allow the contents of the vial to settle for 2 to 3 minutes. A clear solution should result.
- If the contents of the vial are not completely dissolved, shake the vial again for 30 seconds and allow the contents to settle for 2 to 3 minutes. Repeat this procedure as necessary until the contents of the vial are completely dissolved.
- Following reconstitution, each vial contains 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) of remdesivir solution.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
• After reconstitution, the total storage time before administration should not exceed 4 hours at room temperature or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]).
Dilution Instructions
Care should be taken during admixture to prevent inadvertent microbial contamination. As there is no preservative or bacteriostatic agent present in this product, aseptic technique must be used in preparation of the final parenteral solution. It is always recommended to administer IV medication immediately after preparation when possible.
- The reconstituted remdesivir lyophilized powder for injection, containing 100 mg/20 mL remdesivir solution, should be further diluted in 100 mL or 250 mL 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bags.
- Using the table below, determine the volume of 0.9% sodium chloride to withdraw from the infusion bag.
| Dose | 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag volume to be used | Volume to be withdrawn and discarded from 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag | Required volume of reconstituted remdesivir for injection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg (2 vials) | 250 mL | 40 mL | 40 mL (2 × 20 mL) |
| 100 mL | 40 mL | 40 mL (2 × 20 mL) | |
| 100 mg (1 vial) | 250 mL | 20 mL | 20 mL |
| 100 mL | 20 mL | 20 mL |
- Withdraw and discard the required volume of 0.9% sodium chloride from the bag using an appropriately sized syringe and needle.
- Withdraw the required volume of reconstituted remdesivir for injection from the remdesivir vial using an appropriately sized syringe. Discard any unused portion remaining in the remdesivir vial.
- Transfer the required volume of reconstituted remdesivir for injection to the selected infusion bag.
- Gently invert the bag 20 times to mix the solution in the bag. Do not shake.
- The prepared diluted solution is stable for 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) or 24 hours in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Administration Instructions
The prepared diluted solution should not be administered simultaneously with any other IV medication. The compatibility of remdesivir injection with IV solutions and medications other than 0.9% sodium chloride is not known.
Administer the diluted solution with the infusion rate described in the table below.
| Infusion bag volume | Infusion time | Rate of infusion |
|---|---|---|
| 250 mL | 30 min | 8.33 mL/min |
| 60 min | 4.17 mL/min | |
| 120 min | 2.08 mL/min | |
| 100 mL | 30 min | 3.33 mL/min |
| 60 min | 1.67 mL/min | |
| 120 min | 0.83 mL/min |
B. Remdesivir Injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), Solution
Dilution Instructions
Care should be taken during admixture to prevent inadvertent microbial contamination. As there is no preservative or bacteriostatic agent present in this product, aseptic technique must be used in preparation of the final parenteral solution. It is always recommended to administer IV medication immediately after preparation when possible.
- Remove the required number of single-dose vial(s) from storage. Each vial contains 100 mg of remdesivir. For each vial:
- Equilibrate to room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]). Sealed vials can be stored up to 12 hours at room temperature prior to dilution.
- Inspect the vial to ensure the container closure is free from defects and the solution is free of particulate matter.
- Using the table below, determine the volume of 0.9% sodium chloride to withdraw from the infusion bag
| Dose | 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag volume to be used | Volume to be withdrawn and discarded from 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag | Required volume of reconstituted remdesivir for injection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg (2 vials) | 250 mL | 40 mL | 40 mL (2 × 20 mL) |
| 100 mg (1 vial) | 250 mL | 20 mL | 20 mL |
- Withdraw and discard the required volume of 0.9% sodium chloride from the bag using an appropriately sized syringe and needle.
- Withdraw the required volume of remdesivir injection solution from the remdesivir vial using an appropriately sized syringe.
- Pull the syringe plunger rod back to fill the syringe with approximately 10 mL of air.
- Inject the air into the remdesivir injection vial above the level of the solution.
- Invert the vial and withdraw the required volume of remdesivir injection solution into the syringe. The last 5 mL of solution requires more force to withdraw.
- Discard any unused solution remaining in the remdesivir vial.
- Transfer the required volume of remdesivir injection solution to the infusion bag.
- Gently invert the bag 20 times to mix the solution in the bag. Do not shake.
- The prepared diluted solution is stable for 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) or 24 hours in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Administration Instructions
The prepared diluted solution should not be administered simultaneously with any other medication. The compatibility of remdesivir injection with IV solutions and medications other than 0.9% sodium chloride is not known.
Administer the diluted solution with the infusion rate described in the table below.
| Infusion bag volume | Infusion time | Rate of infusion |
|---|---|---|
| 250 mL | 30 min | 8.33 mL/min |
| 60 min | 4.17 mL/min | |
| 120 min | 2.08 mL/min |
Dose Preparation and Administration, Pediatric Patients Weighing 3.5 kg to Less Than 40 kg
For pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg, use remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, lyophilized powder only. Remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), should not be used for pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg due to the higher amount of SBECD present and resulting higher tonicity of the solution concentrate compared to the lyophilized formulation.
Remdesivir for Injection, 100 mg, Lyophilized Powder
Reconstitution Instructions
Remove the required number of single-dose vial(s) from storage. For each vial:
- Aseptically reconstitute remdesivir lyophilized powder by addition of 19 mL of Sterile Water for Injection using a suitably sized syringe and needle per vial.
- Discard the vial if a vacuum does not pull the Sterile Water for Injection into the vial.
- Immediately shake the vial for 30 seconds.
- Allow the contents of the vial to settle for 2 to 3 minutes. A clear solution should result.
- If the contents of the vial are not completely dissolved, shake the vial again for 30 seconds and allow the contents to settle for 2 to 3 minutes. Repeat this procedure as necessary until the contents of the vial are completely dissolved.
- Following reconstitution, each vial contains 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) of remdesivir solution.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- After reconstitution, the total storage time before administration should not exceed 4 hours at room temperature or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]).
Dilution Instructions
- Care should be taken during admixture to prevent inadvertent microbial contamination. As there is no preservative or bacteriostatic agent present in this product, aseptic technique must be used in preparation of the final parenteral solution. It is always recommended to administer IV medication immediately after preparation when possible. Following reconstitution as instructed above, each vial will contain a 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) remdesivir concentrated solution. For pediatric patients weighing 3.5 kg to less than 40 kg, the 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) remdesivir concentrate should be further diluted to a fixed concentration of 1.25 mg/mL using 0.9% sodium chloride.
- The total required infusion volume of the 1.25 mg/mL remdesivir solution for infusion is calculated from the pediatric weight-based dosing regimens of 5 mg/kg for the Loading Dose and 2.5 mg/kg for each Maintenance Dose.
- Small 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bags (e.g., 25, 50, or 100 mL) or an appropriately sized syringe should be used for pediatric dosing. The recommended dose is administered via IV infusion in a total volume dependent on the dose to yield the target remdesivir concentration of 1.25 mg/mL.
- A syringe may be used for delivering volumes less than 50 mL.
Infusion with IV Bag
- Prepare an IV bag of 0.9% sodium chloride with volume equal to the total infusion volume minus the volume of reconstituted remdesivir solution that will be diluted to achieve a 1.25 mg/mL solution.
- Withdraw the required volume of reconstituted solution containing remdesivir for injection into an appropriately sized syringe.
- Transfer the required volume of reconstituted remdesivir for injection to the 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag.
- Gently invert the bag 20 times to mix the solution in the bag. Do not shake.
Infusion with Syringe
- Select an appropriately sized syringe equal to or larger than the calculated total infusion volume of 1.25 mg/mL remdesivir solution needed.
- Withdraw the required volume of 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) reconstituted remdesivir solution from the vial into the syringe followed by the required volume of 0.9% sodium chloride needed to achieve a 1.25 mg/mL remdesivir solution.
- Mix the syringe by inversion 20 times.
- The prepared diluted solution is stable for 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) or 24 hours in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) (including any time before dilution into intravenous infusion fluids).
Administration Instructions
The prepared diluted solution should not be administered simultaneously with any other medication. The compatibility of remdesivir injection with IV solutions and medications other than 0.9% sodium chloride is not known.
Administer the diluted solution with the infusion rate described in the table below.
| Infusion bag volume | Infusion time | Rate of infusion † |
|---|---|---|
| 100 mL | 30 min | 3.33 mL/min |
| 60 min | 1.67 mL/min | |
| 120 min | 0.83 mL/min | |
| 50 mL | 30 min | 1.67 mL/min |
| 60 min | 0.83 mL/min | |
| 120 min | 0.42 mL/min | |
| 25 mL | 30 min | 0.83 mL/min |
| 60 min | 0.42 mL/min | |
| 120 min | 0.21 mL/min |
† Rate of infusion may be adjusted based on total volume to be infused.
Storage of Prepared Dosages
Lyophilized Powder
After reconstitution, vials can be stored up to 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) prior to administration or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]). Dilute within the same day as administration.
Injection Solution
Prior to dilution, equilibrate remdesivir injection to room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]). Sealed vials can be stored up to 12 hours at room temperature prior to dilution.
Diluted Infusion Solution
Store diluted remdesivir solution for infusion up to 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]).
IMPORTANT: This product contains no preservative. Any unused portion of a single-dose remdesivir vial should be discarded after a diluted solution is prepared. Maintain adequate records showing receipt, use, and disposition of remdesivir. For unused intact vials, maintain adequate records showing disposition of remdesivir; do not discard unused intact vials
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Remdesivir for injection, 100 mg: Each single-dose vial of remdesivir for injection,100 mg, contains a sterile, preservative-free white to off-white to yellow lyophilized powder that is to be reconstituted with 19 mL of Sterile Water for Injection and further diluted into 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag prior to administration by intravenous infusion. Following reconstitution, each vial contains 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) remdesivir reconcentrated solution.
- Remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL): Each single-dose vial of remdesivir injection contains 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) of remdesivir as a clear, colorless to yellow, aqueous-based concentrated solution that is to be diluted into 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag prior to administration by intravenous infusion.
Monitoring
Patient Monitoring Recommendations
Given the limited experience with remdesivir at the recommended dose and duration, patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events while receiving remdesivir. Additionally, completion of FDA MedWatch Form to report all medication errors and serious adverse events is mandatory.
For mandatory reporting requirements, please see MANDATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR REMDESIVIR ADMINISTRATION UNDER EMERGENCY USE AUTHORIZATION below.
ADVERSE REACTIONS AND MEDICATION ERRORS REPORTING REQUIREMENTS AND INSTRUCTIONS
The prescribing health care provider and/or the provider’s designee are/is responsible for the mandatory reporting of all medication errors and the following selected adverse events occurring during remdesivir use and considered to be potentially attributable to remdesivir. These adverse events must be reported within 7 calendar days from the onset of the event:
- Deaths
- Serious Adverse Events
Serious Adverse Events are defined as:
- death;
- a life-threatening adverse event;
- inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization;
- a persistent or significant incapacity or substantial disruption of the ability to conduct normal life functions;
- a congenital anomaly/birth defect;
- a medical or surgical intervention to prevent death, a life-threatening event, hospitalization, disability, or congenital anomaly.
If a serious and unexpected adverse event occurs and appears to be associated with the use of remdesivir, the prescribing health care provider and/or the provider’s designee should complete and submit a MedWatch form to FDA using one of the following methods:
- Complete and submit the report online: www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm, or
- Use a postage-paid Form FDA 3500 (available at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AboutFDA/ReportsManualsForms/Forms/UCM163919.pdf) and returning by mail (MedWatch, 5600 Fishers Lane, Rockville, MD 20852-9787), or by fax (1-800-FDA-0178), or
- Call 1-800-FDA-1088 to request a reporting form
IMPORTANT: When reporting adverse events or medication errors to MedWatch, please complete the entire form with detailed information. It is important that the information reported to FDA be as detailed and complete as possible. Information to include:
- Patient demographics (e.g., patient initials, date of birth)
- Pertinent medical history
- Pertinent details regarding admission and course of illness
- Concomitant medications
- Timing of adverse event(s) in relationship to administration of remdesivir
- Pertinent laboratory and virology information
- Outcome of the event and any additional follow-up information if it is available at the time of the MedWatch report. Subsequent reporting of follow-up information should be completed if additional details become available.
The following steps are highlighted to provide the necessary information for safety tracking:
- In section A, box 1, provide the patient’s initials in the Patient Identifier
- In section A, box 2, provide the patient’s date of birth
- In section B, box 5, description of the event:
- Write “Remdesivir EUA” as the first line
- Provide a detailed report of medication error and/or adverse event. It is important to provide detailed information regarding the patient and adverse event/medication error for ongoing safety evaluation of this unapproved drug. Please see information to include listed above.
- In section G, box 1, name and address:
- Provide the name and contact information of the prescribing health care provider or institutional designee who is responsible for the report.
- Provide the address of the treating institution (NOT the health care provider’s office address).
INSTRUCTIONS FOR HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS
As the health care provider, you must communicate to your patient or parent/caregiver information consistent with the Fact Sheet for Patients and Parents/Caregivers (and provide a copy of the Fact Sheet) prior to the patient receiving remdesivir, including:
- FDA has authorized the emergency use of remdesivir, which is not an FDA approved drug.
- The patient or parent/caregiver has the option to accept or refuse remdesivir.
- The significant known and potential risks and benefits of remdesivir, and the extent to which such risks and benefits are unknown.
- Information on available alternative treatments and the risks and benefits of those alternatives.
If providing this information will delay the administration of remdesivir to a degree that would endanger the lives of patients, the information must be provided to the patients as soon as practicable after remdesivir is administered.
For information on clinical trials that are testing the use of remdesivir for COVID-19, please see http://www.clinicaltrials.gov.
MANDATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR REMDESIVIR ADMINISTRATION UNDER EMERGENCY USE AUTHORIZATION
In order to mitigate the risks of using this unapproved product under EUA and to optimize the potential benefit of remdesivir, the following items are required. Use of unapproved remdesivir under this EUA is limited to the following (all requirements must be met):
- Treatment of suspected or laboratory confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in adults and pediatric patients hospitalized with severe disease. Severe disease is defined as patients with an oxygen saturation (SpO2) ≤94% on room air or requiring supplemental oxygen or requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, or requiring ECMO. Specifically, remdesivir is authorized only for the following patients who are admitted to a hospital and under the care or consultation of a licensed clinician (skilled in the diagnosis and management of patients with potentially life-threatening illness and the ability to recognize and manage medication-related adverse events):
- Adult patients for whom use of an IV agent is clinically appropriate.
- Pediatric patients for whom use of an IV agent is clinically appropriate.
- As the health care provider, communicate to your patient or parent/caregiver information consistent with the Fact Sheet for Patients and Parents/Caregivers prior to the patient receiving remdesivir. Health care providers (to the extent practicable given the circumstances of the emergency) must document in the patient’s medical record that the patient/caregiver has been:
- Given the Fact Sheet for Patients and Parents/Caregivers,
- Informed of alternatives to receiving remdesivir, and
- Informed that remdesivir is an unapproved drug that is authorized for use under EUA.
- Adult and pediatric patients (greater than 28 days old) must have an eGFR determined and full-term neonates (at least 7 days to less than or equal to 28 days old) must have serum creatinine determined prior to remdesivir first administration and daily while receiving remdesivir.
- Hepatic laboratory testing should be performed in all patients prior to starting remdesivir and daily while receiving remdesivir.
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to any ingredient of remdesivir must not receive remdesivir.
- The prescribing health care provider and/or the provider’s designee are/is responsible for mandatory responses to requests from FDA for information about adverse events and medication errors following receipt of remdesivir.
- The prescribing health care provider and/or the provider’s designee are/is responsible for mandatory reporting of all medication errors and adverse events (death, serious adverse events*) considered to be potentially related to remdesivir occurring during remdesivir treatment within 7 calendar days from the onset of the event. The reports should include unique identifiers and the words “Remdesivir under Emergency Use Authorization (EUA)” in the description section of the report.
- Submit adverse event reports to FDA MedWatch using one of the following methods:
- Complete and submit the report online: www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm, or
- By using a postage-paid Form FDA 3500 (available at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AboutFDA/ReportsManualsForms/Forms/UCM163919.pdf) and returning by mail (MedWatch, 5600 Fishers Lane, Rockville, MD 20852-9787), or by fax (1-800-FDA-0178), or
- Call 1-800-FDA-1088 to request a reporting form
- Submitted reports should include in the field name, “Describe Event, Problem, or Product Use/Medication Error” a statement “Remdesivir under Emergency Use Authorization (EUA).”
OTHER REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
In addition please provide a copy of all FDA MedWatch forms to:
Gilead Pharmacovigilance and Epidemiology Fax: 1-650-522-5477 E-mail: Safety_fc@gilead.com
APPROVED AVAILABLE ALTERNATIVES
There is no approved available alternative product. There are EUAs for other COVID-19 treatments. Additional information on COVID-19 treatments can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/index.html. The health care provider should visit https://clinicaltrials.gov/ to determine whether the patient may be eligible for enrollment in a clinical trial.
AUTHORITY FOR ISSUANCE OF THE EUA
The Secretary of HHS has declared a public health emergency that justifies the emergency use of remdesivir to treat COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2. In response, the FDA has issued an EUA for the unapproved product, remdesivir, for the treatment of COVID-19.† As a health care provider, you must comply with the MANDATORY REQUIREMENTS of the EUA (see above).
FDA issued this EUA, requested by Gilead Sciences, Inc. and based on their submitted data.
Although limited scientific information is available, based on the totality of the scientific evidence available to date, it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective for the treatment of COVID-19 in patients as specified in this Fact Sheet. You may be contacted and asked to provide information to help with the assessment of the use of the product during this emergency.
This EUA for remdesivir will end when the Secretary determines that the circumstances justifying the EUA no longer exist or when there is a change in the approval status of the product such that an EUA is no longer needed.
† The health care provider should visit clinicaltrials.gov to determine whether there is an active clinical trial for the product in this disease/condition and whether enrollment of the patient(s) in a clinical trial is more appropriate than product use under this EUA.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Remdesivir and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is no human experience of acute overdosage with remdesivir. Treatment of overdose with remdesivir should consist of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. There is no specific antidote for overdose with remdesivir.
Pharmacology
| |
| |
Remdesivir
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
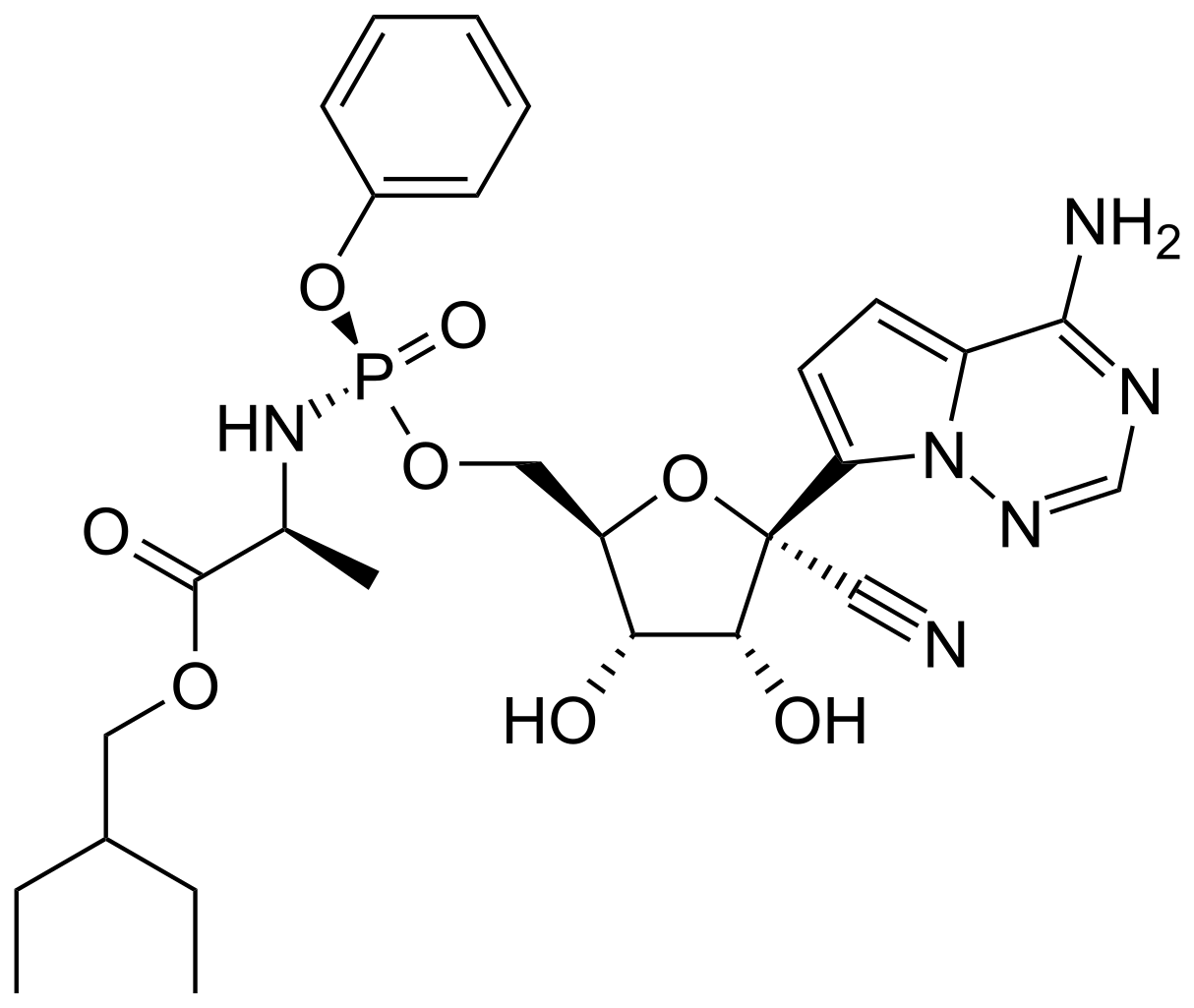
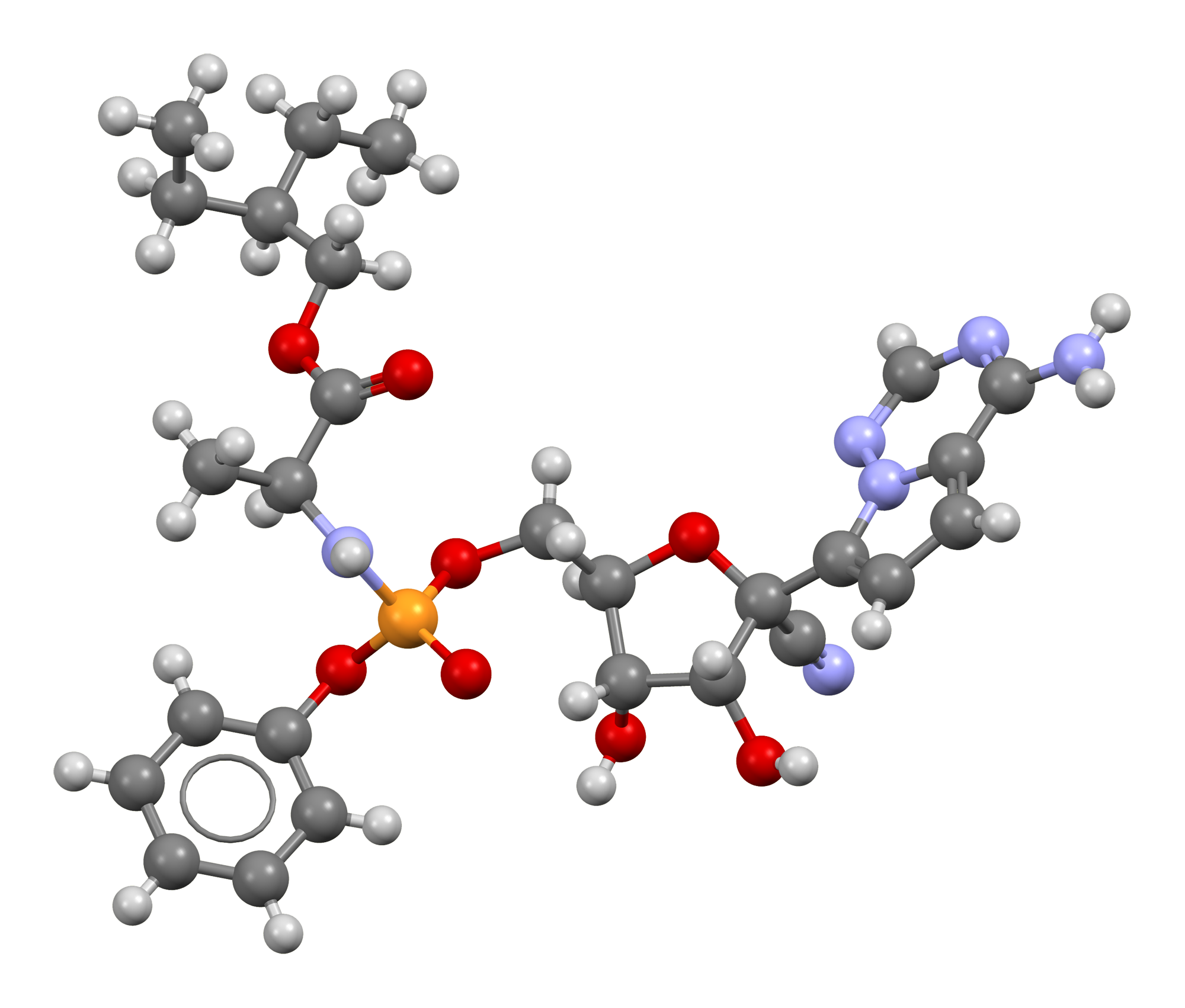
| (2S)-2-{(2R,3S,4R,5R)-[5-(4-Aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxy-tetrahydro-furan-2-ylmethoxy]phenoxy-(S)-phosphorylamino}propionic acid 2-ethyl-butyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | None |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Synonyms | GS-5734 |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
Investigational / Rx-only |
| Routes | Intravenous |
Mechanism of Action
Remdesivir is an adenosine nucleotide prodrug that distributes into cells where it is metabolized to form the pharmacologically active nucleoside triphosphate metabolite. Metabolism of remdesivir to remdesivir triphosphate has been demonstrated in multiple cell types. Remdesivir triphosphate acts as an analog of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and competes with the natural ATP substrate for incorporation into nascent RNA chains by the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which results in delayed chain termination during replication of the viral RNA. Remdesivir triphosphate is a weak inhibitor of mammalian DNA and RNA polymerases with low potential for mitochondrial toxicity.
Structure
Remdesivir is a nucleoside ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase inhibitor.
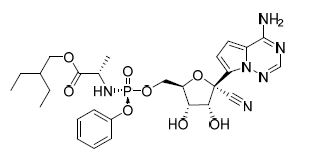
The chemical name for remdesivir is 2-ethylbutyl N-{(S)-[2-C-(4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-2,5-anhydro-d-altrononitril-6-O-yl]phenoxyphosphoryl}-L-alaninate. It has a molecular formula of C27H35N6O8P and a molecular weight of 602.6 g/mol. Remdesivir has the following structural formula:
Physical Appearance
Lyophilized Powder
Remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, is a sterile, preservative-free lyophilized powder that is to be reconstituted with 19 mL of Sterile Water for Injection and further diluted into 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag prior to administration by intravenous infusion. Remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, is supplied in a single-dose clear glass vial.
The appearance of the lyophilized powder is white to off-white to yellow.
Injection Solution
Remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), is a sterile, preservative-free, clear, colorless to yellow, aqueous-based concentrated solution that is to be diluted into 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag prior to administration by intravenous infusion. Remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), is supplied in a single-dose clear glass vial. 13.2 Inactive Ingredients The inactive ingredients are sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin sodium salt (SBECD), Water for Injection, USP, and may include hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. Remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, contains 3 g SBECD, and remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), contains 6 g SBECD.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Remdesivir Pharmacodynamics.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of remdesivir have been evaluated in adults in several Phase 1 trials.
- The pharmacokinetics of remdesivir and metabolites have not been in evaluated in patients with COVID-19.
- Following single-dose, 2-hour IV administration of remdesivir solution formulation at doses ranging from 3 to 225 mg, remdesivir exhibited a linear PK profile.
- Following single-dose, 2-hour IV administration of remdesivir at doses of 75 and 150 mg, both the lyophilized and solution formulations provided comparable PK parameters (AUCinf, AUClast, and Cmax), indicating similar formulation performance.
- Remdesivir 75 mg lyophilized formulation administered IV over 30 minutes provided similar peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) exposure of the active triphosphate metabolite GS-443902 as remdesivir 150 mg lyophilized formulation administered IV over 2 hours.
- Following a single 150 mg intravenous dose of [14C]-remdesivir, mean total recovery of the dose was >92%, consisting of approximately 74% and 18% recovered in urine and feces, respectively. The majority of remdesivir dose recovered in urine was metabolite GS-441524 (49%), while 10% was recovered as remdesivir.
Specific Populations
Sex, Race and Age
Pharmacokinetic differences based on sex, race, and age have not been evaluated.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of remdesivir in pediatric patients has not been evaluated.
PBPK modeling of pharmacokinetic data from healthy adults was used to derive pediatric doses. PBPK modeling incorporated in vitro data for remdesivir and other similar compounds along with age-dependent changes in physiology (e.g., organ volume/function, blood flow), metabolism, distribution, and elimination of remdesivir. Pediatric doses are expected to result in comparable steady-state exposures of remdesivir and metabolites as observed in healthy adults following administration of the recommended dosage regimen.
Renal Impairment
Because the excipient SBECD is renally cleared and accumulates in patients with decreased renal function, administration of drugs formulated with SBECD (such as remdesivir) is not recommended in adult and pediatric patients (greater than 28 days old) with eGFR less than 30 mL/min or in full-term neonates (at least 7 days and less than or equal to 28 days old) with serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1 mg/dL unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Microbiology/Resistance Information
Antiviral Activity
Remdesivir exhibited cell culture antiviral activity against a clinical isolate of SARS-CoV-2 in primary human airway epithelial (HAE) cells with a 50% effective concentration (EC50) of 9.9 nM after 48 hours of treatment. The EC50 values of remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 in Vero cells was 137 nM at 24 hours and 750 nM at 48 hours post-treatment. The antiviral activity of remdesivir was antagonized by chloroquine phosphate in a dose-dependent manner when the two drugs were co-incubated at clinically relevant concentrations in HEp-2 cells infected with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Higher remdesivir EC50 values were observed with increasing concentrations of chloroquine phosphate. Increasing concentrations of chloroquine phosphate reduced formation of remdesivir triphosphate in normal human bronchial epithelial cells.
Resistance
No clinical data are available on the development of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to remdesivir. The cell culture development of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to remdesivir has not been assessed to date.
Cell culture resistance profiling of remdesivir using the rodent CoV murine hepatitis virus identified 2 substitutions (F476L and V553L) in the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase at residues conserved across CoVs that conferred a 5.6-fold reduced susceptibility to remdesivir. The mutant viruses showed reduced viral fitness in cell culture and introduction of the corresponding substitutions (F480L and V557L) into SARS-CoV resulted in 6-fold reduced susceptibility to remdesivir in cell culture and attenuated SARS-CoV pathogenesis in a mouse model.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis
Given the short-term administration of remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19, long-term animal studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of remdesivir are not required.
Mutagenesis
Remdesivir was not genotoxic in a battery of assays, including bacterial mutagenicity, chromosome aberration using human peripheral blood lymphocytes and in vivo rat micronucleus assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Nonclinical toxicity studies in rats demonstrated no adverse effect on male fertility at exposures of the predominant circulating metabolite (GS-441524) approximately 2 times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Reproductive toxicity, including decreases in corpora lutea, numbers of implantation sites, and viable embryos, was seen when remdesivir was administered intravenous daily at a systemically toxic dose (10 mg/kg) in female rats 14 days prior to mating and during conception; exposures of the predominant circulating metabolite (GS-441524) were 1.3 times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Intravenous administration (slow bolus) of remdesivir to male rhesus monkeys at dosage levels of 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg/day for 7 days resulted, at all dose levels, in increased mean urea nitrogen and increased mean creatinine, renal tubular atrophy, and basophilia and casts.
Intravenous administration (slow bolus) of remdesivir to rats at dosage levels of ≥3 mg/kg/day for up to 4 weeks resulted in findings indicative of kidney injury and/or dysfunction.
Animal Pharmacologic and Efficacy Data
It is unknown, at present, how the observed antiviral activity of remdesivir in animal models of SARS-CoV-2 infection will translate into clinical efficacy in patients with symptomatic disease. Key attributes of the remdesivir nonclinical profile supporting its development for the treatment of COVID-19 are provided below:
- Remdesivir showed cell culture antiviral activity against a clinical isolate of SARS-CoV-2 in primary HAE cells (EC50 value= 9.9 nM). The EC50 values of remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 in Vero cells has been reported to be 137 nM at 24 hours and 750 nM at 48 hours post-treatment.
- Remdesivir showed antiviral activity in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus monkeys. Administration of remdesivir at 10/5 mg/kg (10 mg/kg first dose, followed by 5 mg/kg once daily thereafter) using IV bolus injection initiated 12 hours post-inoculation with SARS-CoV-2 resulted in a reduction in clinical signs of respiratory disease, lung pathology and gross lung lesions, and lung viral RNA levels compared with vehicle-treated animals.
Clinical Studies
Remdesivir is an unapproved antiviral drug with available data from two randomized clinical trials in patients with COVID-19.
Clinical Trials in Subjects with COVID-19
NIAID ACTT-1 Trial in Subjects with Mild/Moderate and Severe COVID-19
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated remdesivir 200 mg once daily for 1 day followed by remdesivir 100 mg once daily for 9 days (for a total of up to 10 days of intravenously administered therapy) in hospitalized adult subjects with COVID-19 with evidence of lower respiratory tract involvement. The trial enrolled 1,063 subjects: 120 [11.3%] subjects with mild/moderate disease and 943 [88.7%] subjects with severe disease. A total of 272 subjects (25.6%) (n=125 received remdesivir) were on mechanical ventilation/ECMO. Subjects were randomized in a 1:1 manner, stratified by disease severity at enrollment, to receive remdesivir (n=541) or placebo (n=522), plus standard of care. The primary clinical endpoint was time to recovery within 28 days after randomization, defined as either discharged from the hospital or hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care. In a preliminary analysis of the primary endpoint performed after 607 recoveries were attained (n=1,059; 538 remdesivir, 521 placebo), the median time to recovery was 11 days in the remdesivir group compared to 15 days in the placebo group (recovery rate ratio 1.32; 95% CI 1.12 to 1.55, p<0.001); 14-day mortality was 7.1% for the remdesivir group versus 11.9% for the placebo group (hazard ratio 0.70 [95% CI 0.47, 1.04], p=0.07). Among subjects with mild/moderate disease at enrollment (n=119), the median time to recovery was 5 days in both the remdesivir and placebo groups (recovery rate ratio 1.09; [95% CI 0.73 to 1.62]). Among subjects with severe disease at enrollment (n=940), the median time to recovery was 12 days in the remdesivir group compared to 18 days in the placebo group (recovery rate ratio, 1.37; [95% CI, 1.15 to 1.63]; p<0.001; n=940) and 14-day mortality was 7.7% and 13%, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.71; [95% CI, 0.48 to 1.05]).
Overall, the odds of improvement in the ordinal scale were higher in the remdesivir group at Day 15 when compared to the placebo group (odds ratio, 1.50; [95% CI, 1.18 to 1.91], p=0.001; n=844).
Study GS-US-540-5773 in Subjects with Severe COVID-19
A randomized, open-label multi-center clinical trial (Study GS-US-540-5773) of hospitalized subjects at least 12 years of age with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, oxygen saturation of ≤94% on room air, and radiological evidence of pneumonia compared 197 subjects who received IV remdesivir for 5 days with 200 subjects who received IV remdesivir for 10 days. Patients on mechanical ventilation at screening were excluded. All subjects received 200 mg of remdesivir on Day 1 and 100 mg once daily on subsequent days, plus standard of care. The primary endpoint was clinical status on Day 14 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale ranging from hospital discharge to increasing levels of oxygen and ventilatory support to death. After adjusting for between-group differences at baseline, patients receiving a 10-day course of remdesivir had similar clinical status at Day 14 as those receiving a 5-day course (odds ratio for improvement: 0.75; [95% CI 0.51 to 1.12]).
Clinical improvement was defined as an improvement of two or more points from baseline on the 7-point ordinal scale. Subjects achieved clinical recovery if they no longer required oxygen support or were discharged from the hospital. At Day 14, observed rates between the 5- and 10-day treatment groups were 65% vs 54% for clinical improvement, 70% vs 59% for clinical recovery, and 8% vs 11% for mortality.
How Supplied
How Supplied
Lyophilized Powder
Remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, is supplied as a single-dose vial containing a sterile, preservative-free white to off-white to yellow lyophilized powder that is to be reconstituted with 19 mL of Sterile Water for Injection and further diluted into 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag prior to administration by intravenous infusion. Following reconstitution, each vial contains 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) remdesivir reconcentrated solution.
Discard unused portion.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Injection Solution
Remdesivir injection is supplied as a single dose vial containing 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL) of remdesivir per vial for dilution into 0.9% sodium chloride infusion bag.
Discard unused portion.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
Do not reuse or save unused remdesivir lyophilized powder, injection solution, or diluted solution for infusion for future use. This product contains no preservative.
Lyophilized Powder
Store remdesivir for injection, 100 mg, vials below 30°C (below 86°F) until required for use. Do not use after expiration date.
After reconstitution, vials can be stored up to 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) prior to administration or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]). Dilute within the same day as administration.
Injection Solution
Store remdesivir injection, 100 mg/20 mL (5 mg/mL), vials at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]) until required for use. Do not use after expiration date. Dilute within the same day as administration.
Prior to dilution, equilibrate remdesivir injection to room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]). Sealed vials can be stored up to 12 hours at room temperature prior to dilution.
Diluted Solution for Infusion
Store diluted remdesivir solution for infusion up to 4 hours at room temperature (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F]) or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature (2°C to 8°C [36°F to 46°F]).
Patient Counseling Information
Source: Fact Sheet for Patients and Parents/Caregivers
You are being given a medicine called remdesivir for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
This Fact Sheet contains information to help you understand the potential risks and potential benefits of taking remdesivir, which you have received or may receive.
There is no U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved product available to treat COVID-19. Receiving remdesivir may benefit certain people in the hospital with COVID-19.
Read this Fact Sheet for information about remdesivir. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions. It is your choice to receive remdesivir or stop it at any time.
What is COVID-19?
COVID-19 is caused by a virus called a coronavirus. This type of coronavirus has not been seen before.
This new coronavirus was first found in people in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China in December 2019. Person-to-person spread was reported outside Hubei and in countries outside China, including in the United States. You can get COVID-19 through contact with another person who has the virus.
COVID-19 illnesses have ranged from very mild (including some with no reported symptoms) to severe, including illness resulting in death. While information so far suggests that most COVID-19 illness is mild, serious illness can happen and may cause some of your other medical conditions to become worse. Older people and people of all ages with severe, long-lasting (chronic) medical conditions like heart disease, lung disease, and diabetes, for example, seem to be at higher risk of being hospitalized for COVID-19.
What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
The symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, cough, and shortness of breath, which may appear 2 to 14 days after exposure. Serious illness including breathing problems can occur and may cause your other medical conditions to become worse.
What is remdesivir?
Remdesivir is an investigational antiviral medicine used for the treatment of certain people in the hospital with COVID-19. Remdesivir is investigational because it is still being studied. There is limited information known about the safety and effectiveness of using remdesivir to treat people in the hospital with COVID-19. Remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to shorten the time to recovery in some people. There are no medicines approved by the FDA as safe and effective to treat people in the hospital who have COVID-19. Therefore, the FDA has authorized the emergency use of remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19 under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA).
For more information on EUA, see the What is an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) section at the end of this Fact Sheet.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before I receive remdesivir?
Tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- Have any allergies
- Have kidney or liver problems
- Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed
- Have any serious illnesses
- Are taking any medicines (prescription, over-the-counter, vitamins, or herbal products). Remdesivir may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how remdesivir works.
- Especially tell your healthcare provider if you are taking the medicines chloroquine phosphate or hydroxychloroquine sulfate.
How will I receive remdesivir?
Remdesivir is given to you through a vein (intravenous or IV) one time each day for up to 10 days depending on what your healthcare provider thinks is best for you. Remdesivir may help decrease the amount of the coronavirus in your body. This may help you to get better faster.
What are the important possible side effects of remdesivir?
Possible side effects of remdesivir are:
- Allergic reactions. Remdesivir can cause allergic reactions, including serious reactions, during and after infusion. Tell your healthcare provider or nurse, or get medical help right away if you get any of the following signs and symptoms of allergic reactions: low blood pressure, changes in your heartbeat, shortness of breath, wheezing, swelling of your lips, face, or throat, rash, nausea, vomiting, sweating, or shivering.
- Increases in levels of liver enzymes. Increases in levels of liver enzymes have been seen in people who have received remdesivir, which may be a sign of inflammation or damage to cells in the liver. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before you receive remdesivir and daily while receiving remdesivir.
These are not all the possible side effects of remdesivir. Remdesivir is still being studied so it is possible that all of the risks are not known at this time.
Not a lot of people have taken remdesivir. Serious and unexpected side effects may happen. The side effects of getting any medicine by vein may include brief pain, bleeding, bruising of the skin, soreness, swelling, and possible infection at the injection site.
What other treatment choices are there?
Like remdesivir, FDA may allow for the emergency use of other medicines to treat people in the hospital with COVID-19. Go to http://www.cdc.gov/COVID19 for information on the emergency use of other medicines that are not approved by FDA to treat people in the hospital with COVID-19. Your healthcare provider may talk with you about clinical trials you may be eligible for.
It is your choice to be treated or not to be treated with remdesivir. Should you decide not to receive it or stop it at any time, it will not change your standard medical care.
What if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
There is limited experience giving remdesivir to pregnant women or breastfeeding mothers. For a mother and unborn baby, the benefit of receiving remdesivir may be greater than the risk from the treatment. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, discuss your options and specific situation with your healthcare provider.
How do I report side effects with remdesivir?
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. Report side effects to FDA MedWatch at http://www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
How can I learn more?
- Ask your healthcare provider.
- Visit http://www.cdc.gov/COVID19
- Contact your local or state public health department.
What is an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA)
The United States FDA has made remdesivir available under an emergency access mechanism called an EUA. The EUA is supported by a Secretary of Health and Human Service (HHS) declaration that circumstances exist to justify the emergency use of drugs and biological products during the COVID-19 pandemic. Remdesivir has not undergone the same type of review as an FDA-approved or cleared product. FDA may issue an EUA when certain criteria are met, which includes that there are no adequate, approved, available alternatives. In addition, the FDA decision is based on the totality of scientific evidence available showing that it is reasonable to believe that the product meets certain criteria for safety, performance, and labeling and may be effective in treatment of patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. All of these criteria must be met to allow for the product to be used in the treatment of patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The EUA for remdesivir is in effect for the duration of the COVID-19 declaration justifying emergency use of these products, unless terminated or revoked (after which the products may no longer be used)
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Remdesivir interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
Veklury®
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Remdesivir Look-Alike Drug Names.
Drug Shortage Status
References
The contents are provided by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.