Pyloric stenosis diagnostic study of choice
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohamadmostafa Jahansouz M.D.[2]
|
Pyloric stenosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pyloric stenosis diagnostic study of choice On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pyloric stenosis diagnostic study of choice |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pyloric stenosis diagnostic study of choice |
Overview
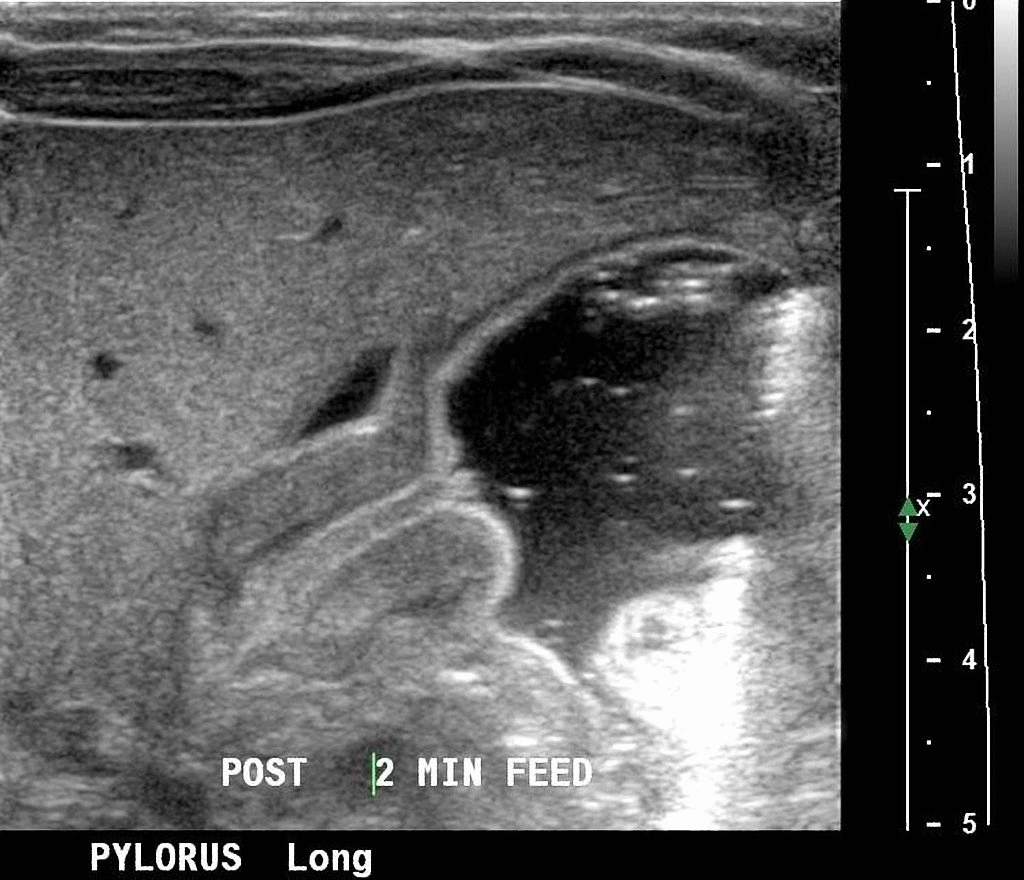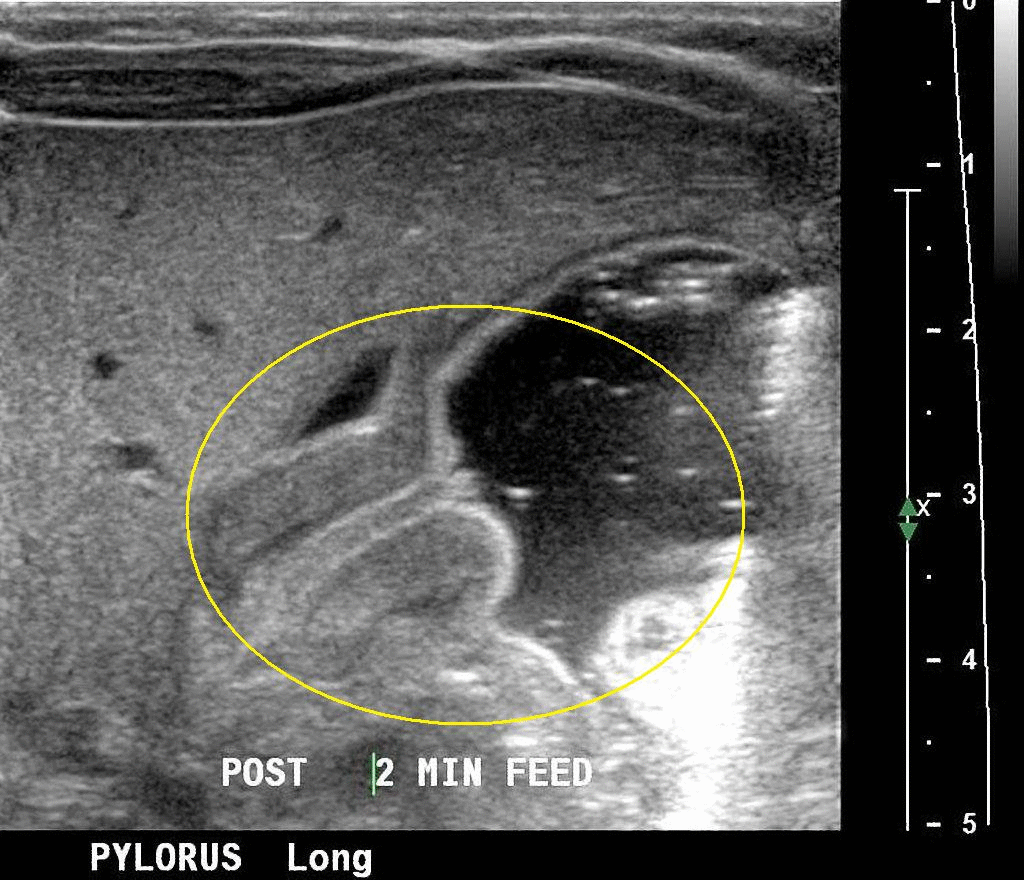
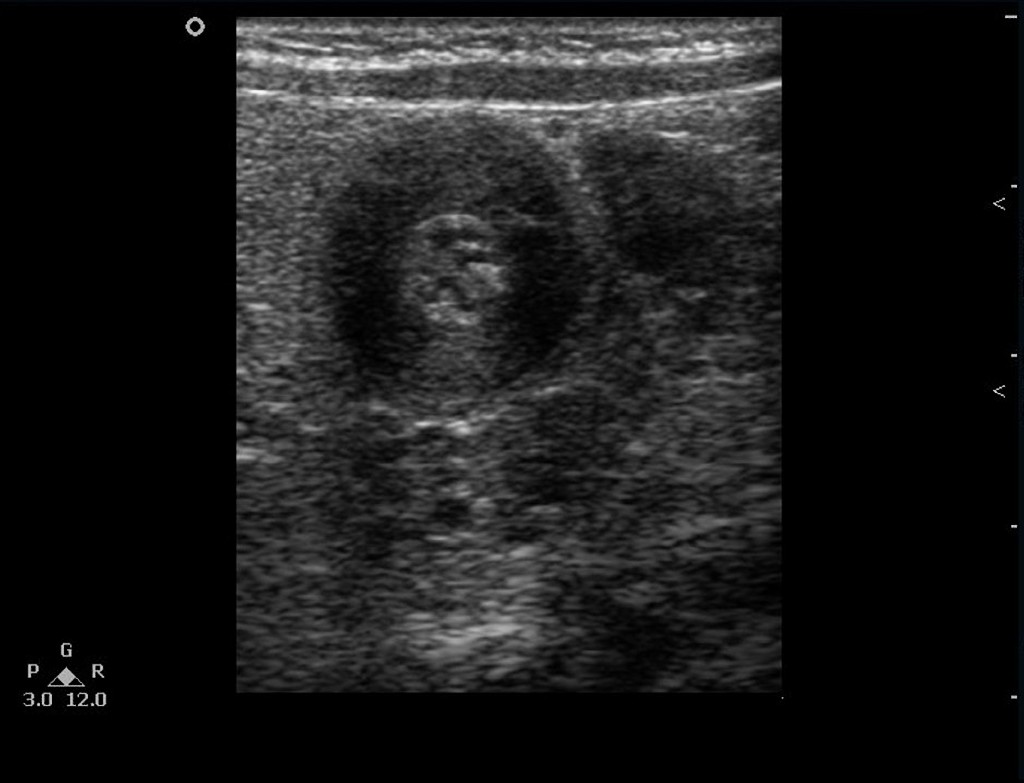
Ultrasonography is the the modality of choice for the diagnosis of infantile pyloric stenosis.The thickened prepyloric antrum bridging the duodenal bulb and distended stomach and crowded intervening mucosa that protrudes into the distended portion of the antrum (nipple sign) may be seen in Ultrasonography of patients with infantyle pyloric stenosis.
Diagnostic Study of Choice
Gold standard of choice:
- Ultrasonography is the modality of choice for the diagnosis of infantile pyloric stenosis.[1]
- The following result of ultrasonography is confirmatory of infantile pyloric stenosis:
- Hypertrophied hypoechoic muscle surrounding echogenic mucosa may be seen in the ultrasound of patients with infantile pyloric stenosis called target sign.[3]
References
- ↑ Costa Dias S, Swinson S, Torrão H, Gonçalves L, Kurochka S, Vaz CP; et al. (2012). "Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: tips and tricks for ultrasound diagnosis". Insights Imaging. 3 (3): 247–50. doi:10.1007/s13244-012-0168-x. PMC 3369120. PMID 22696086.
- ↑ Hernanz-Schulman M, Dinauer P, Ambrosino MM, Polk DB, Neblett WW (1995). "The antral nipple sign of pyloric mucosal prolapse: endoscopic correlation of a new sonographic observation in patients with pyloric stenosis". J Ultrasound Med. 14 (4): 283–7. PMID 7602686.
- ↑ Hussain M (2008). "Sonographic Diagnosis of Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric stenosis- Use of Simultaneous Grey-scale & Colour Doppler Examination". Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2 (2): 134–40. PMC 3068743. PMID 21475495.