Niacin/lovastatin adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sheng Shi, M.D. [2]
Adverse Reactions
Overview
In controlled clinical studies, 40/214 (19%) of patients randomized to ADVICOR discontinued therapy prior to study completion. Of the 214 patients enrolled 18 (8%) discontinued due to flushing. In the same controlled studies, 9/94 (10%) of patients randomized to lovastatin and 19/92 (21%) of patients randomized to NIASPAN also discontinued treatment prior to study completion secondary to adverse events. flushing episodes (i.e., warmth, redness, itching and/or tingling) were the most common treatment-emergent adverse events, and occurred in 53% to 83% of patients treated with ADVICOR. Spontaneous reports with NIASPAN and clinical studies with ADVICOR suggest that flushing may also be accompanied by symptoms of dizziness or syncope, tachycardia, palpitations, shortness of breath, sweating, burning sensation/skin burning sensation, chills, and/or edema.
Adverse Reactions Information
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice. The adverse reaction information from clinical studies does, however provide a basis for identifying the adverse events that appear to be related to drug use and for approximating rates.
The data described in this section reflect the exposure to ADVICOR in two double-blind, controlled clinical studies of 400 patients. The population was 28 to 86 years-of-age, 54% male, 85% Caucasian, 9% Black, and 7% Other, and had mixed dyslipidemia.
In addition to flushing, other adverse events occurring in 5% or greater of patients treated with ADVICOR are shown in Table 10 below.
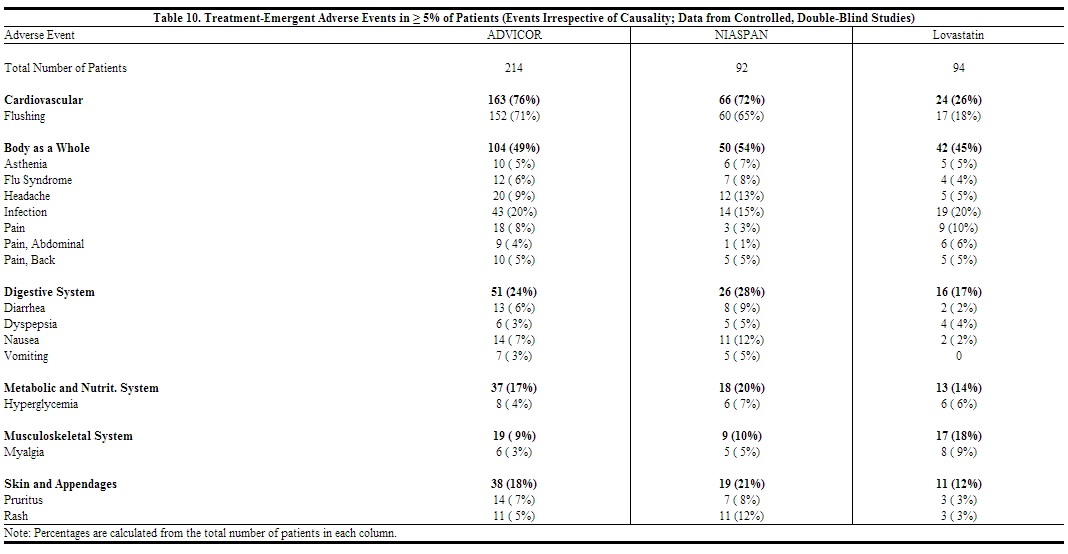 |
See also the full prescribing information for niacin extended release (Niaspan) and lovastatin products.
The following adverse events have also been reported with niacin, lovastatin, and/or other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, but not necessarily with ADVICOR, either during clinical studies or in routine patient management.
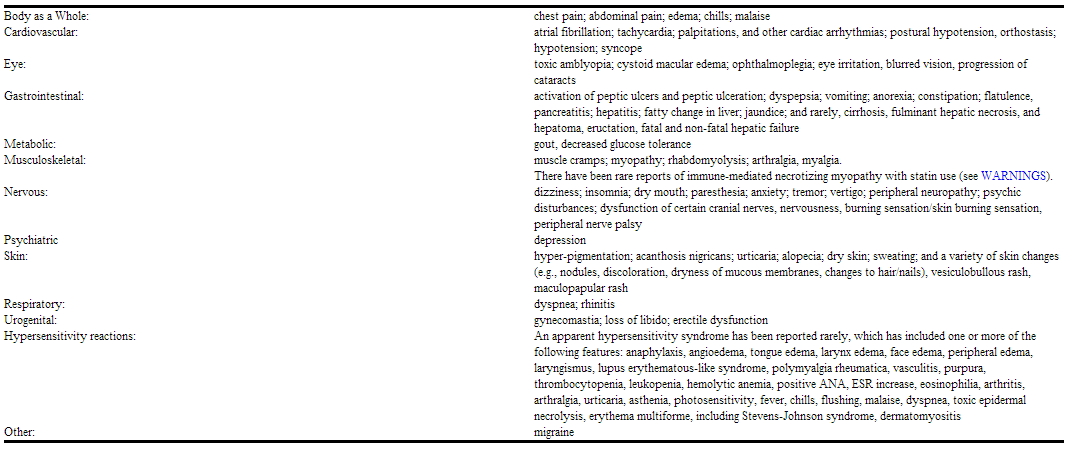 |
There have been rare postmarketing reports of cognitive impairment (e.g., memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion) associated with statin use. These cognitive issues have been reported for all statins. The reports are generally nonserious, and reversible upon statin discontinuation, with variable times to symptom onset (1 day to years) and symptom resolution (median of 3 weeks).
Clinical Laboratory Abnormalities
Chemistry
Elevations in serum transaminases (see WARNINGS - Liver Dysfunction), CPK and fasting glucose, and reductions in phosphorus. Niacin extended-release tablets have been associated with slight elevations in LDH, uric acid, total bilirubin, amylase and creatine kinase. Lovastatin and/or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have been associated with elevations in alkaline phosphatase, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and bilirubin, and thyroid function abnormalities.
Hematology
Niacin extended-release tablets have been associated with slight reductions in platelet counts and prolongation in PT (see WARNINGS).[1]
References
- ↑ "ADVICOR (NIACIN AND LOVASTATIN) TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE [ABBVIE INC.]". Retrieved 18 February 2014.