Loefflers syndrome CT
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
Löffler's syndrome Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Loefflers syndrome CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Loefflers syndrome CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Soroush Seifirad, M.D.[2]
Overview
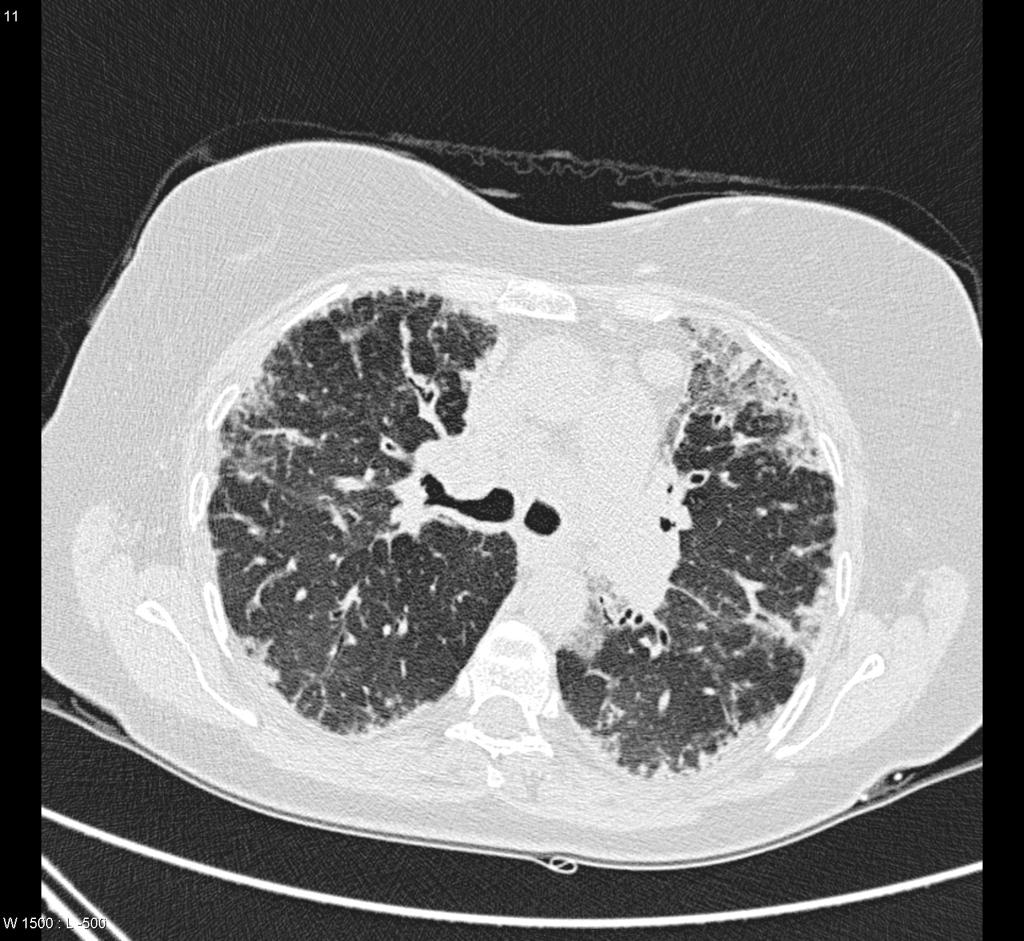
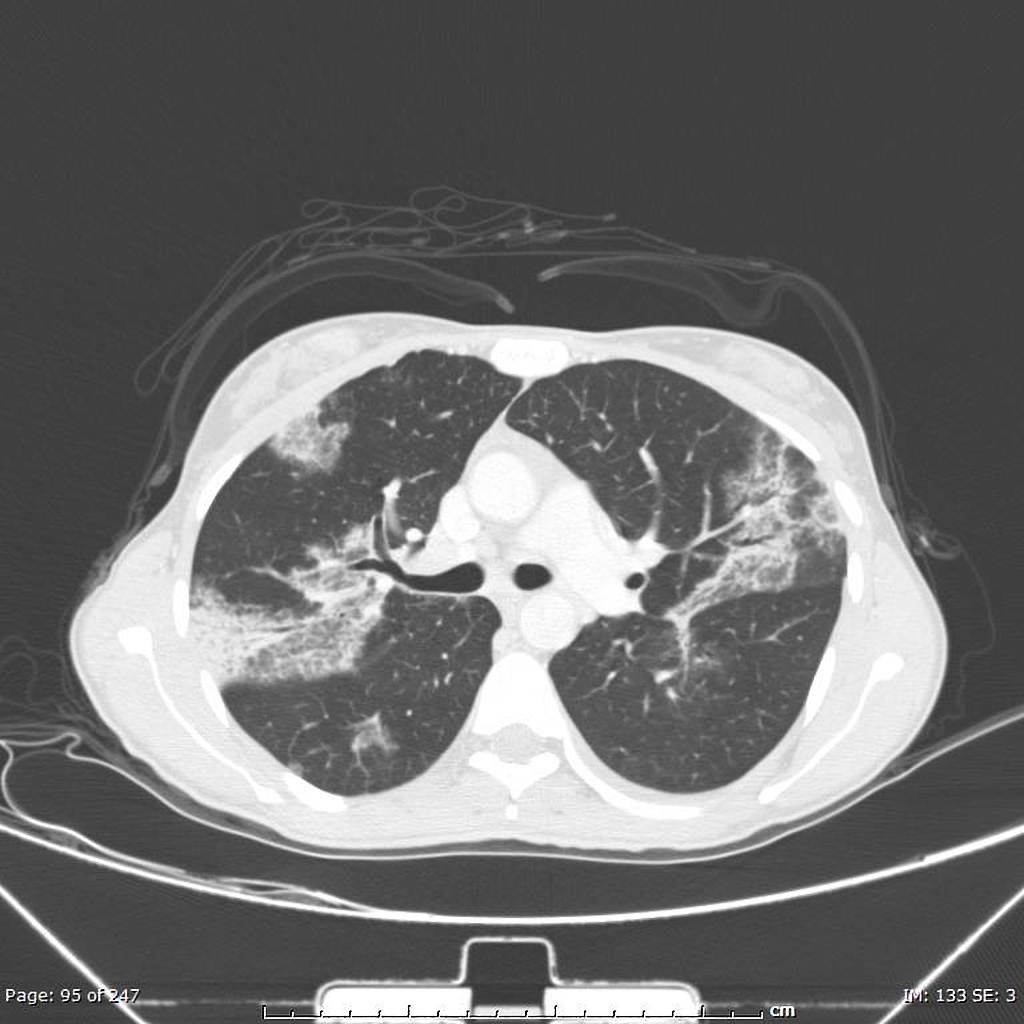
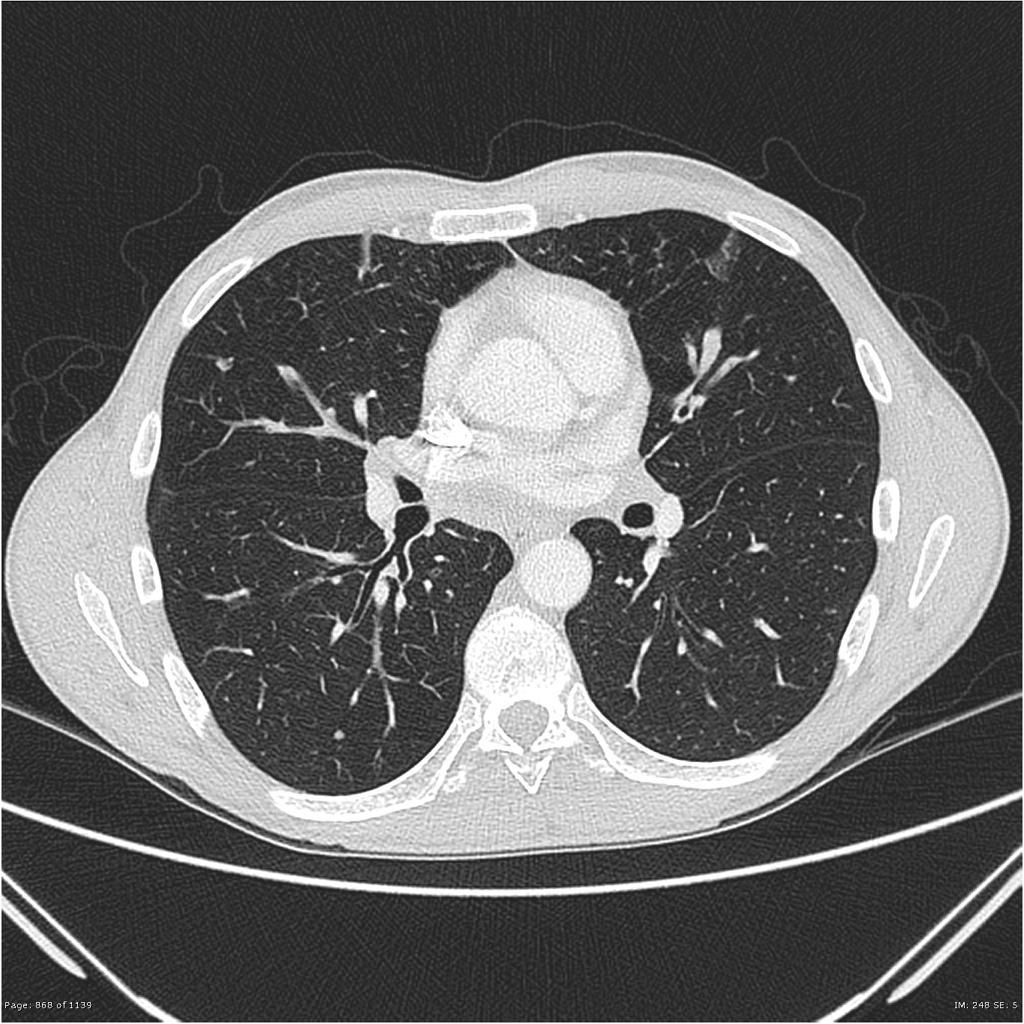
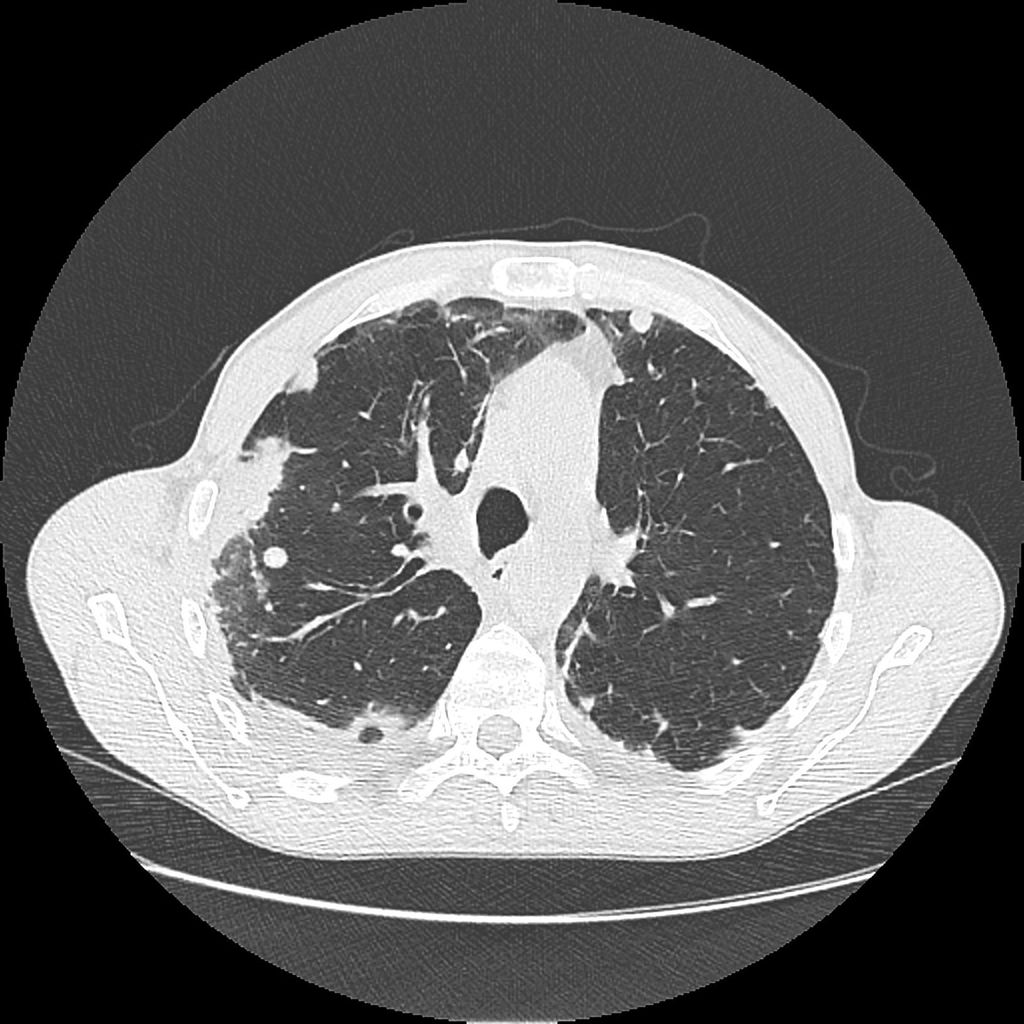
Chest CT scan may be helpful in the diagnosis of Löffler syndrome. Findings on CT scan suggestive of Löffler syndrome include areas of ground-glass opacity (halo) around consolidation, nodules, and dilated airways within the lesion.
CT scan
Chest CT scan may be helpful in the diagnosis of Löffler syndrome. Findings on CT scan suggestive of/diagnostic of Löffler syndrome include:[1][2][1][3] [4][5][6][7][8]
- Areas of ground-glass opacity (halo) around consolidation
- Nodules
- Dilated airways within the lesion.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Te Booij M, de Jong E, Bovenschen HJ (2010) Löffler syndrome caused by extensive cutaneous larva migrans: a case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J 16 (10):2. PMID: 21062596
- ↑ Chitkara RK, Krishna G (2006) Parasitic pulmonary eosinophilia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 27 (2):171-84. DOI:10.1055/s-2006-939520 PMID: 16612768
- ↑ Ekin S, Sertogullarindan B, Gunbatar H, Arisoy A, Yildiz H (2016) Loeffler's syndrome: an interesting case report. Clin Respir J 10 (1):112-4. DOI:10.1111/crj.12173 PMID: 24931460
- ↑ Caulet T (1957) [Loffler syndrome and pulmonary eosinophilia.] Gaz Med Fr 64 (20):1737-8 passim. PMID: 13480465
- ↑ (1968) Löffler's syndrome. Br Med J 3 (5618):569-70. PMID: 5667987
- ↑ SASLAW MS, BOWMAN JA (1946) Loeffler's syndrome. J Fla Med Assoc 32 ():373. PMID: 21007279
- ↑ SPECTOR HI (1945) Loeffler's syndrome (transient pulmonary infiltrations with eosinophilia); report of a case and a review of the available literature. Dis Chest 11 ():380-91. PMID: 21025484
- ↑ GREIG ED (1945) On tropical eosinophilia associated with pulmonary signs (Loeffler's syndrome). J Trop Med Hyg 48 ():149-51. PMID: 21010826