Molluscum contagiosum differential diagnosis
|
Molluscum contagiosum Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mahshid Mir, M.D. [2], João André Alves Silva, M.D. [3]
Overview
Molluscum contagiosum must be differentiated from other diseases that cause inflammatory or ulcertive skin , genital, or mucosal lesions including chicken pox, herpes zoster, erythema multiforme, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pyogenic granuloma.
Differential Diagnosis
Molluscum contagiosum must be differentiated from other inflammatory, ulcerative skin, mucosal or genital lesions
| Disease | Features | Images |
|---|---|---|
| Cryptococcosis |
|
|
| Histoplasmosis [1][2][3][4] |
|
|
| Penicillium marneffei[5] |
|
|
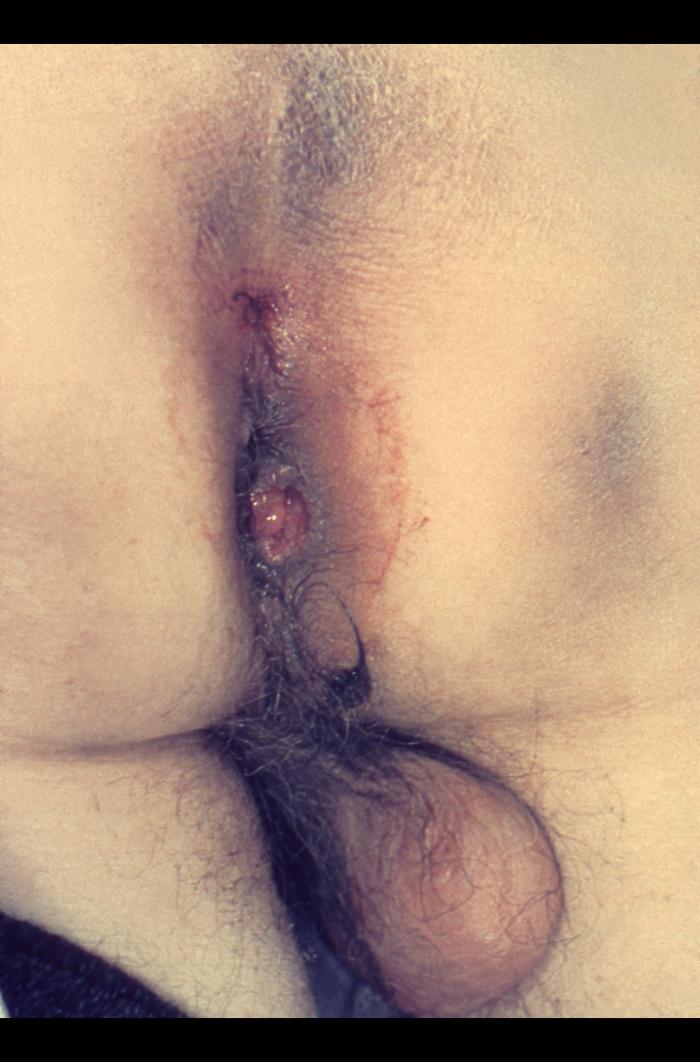
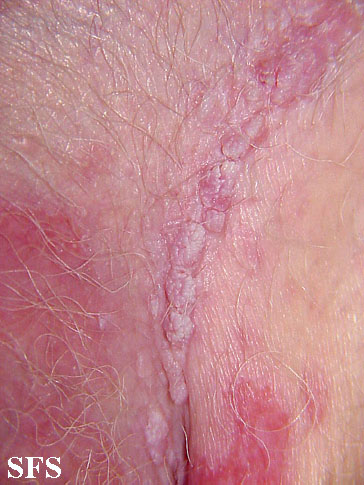
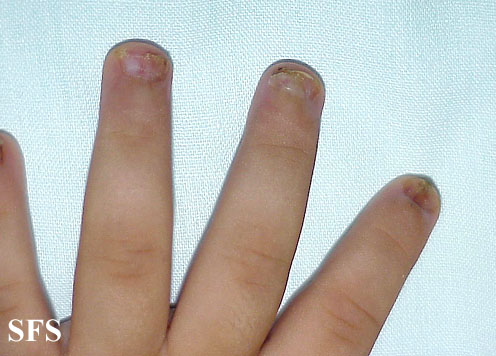
| Condyloma acuminatum [6] |
|
|
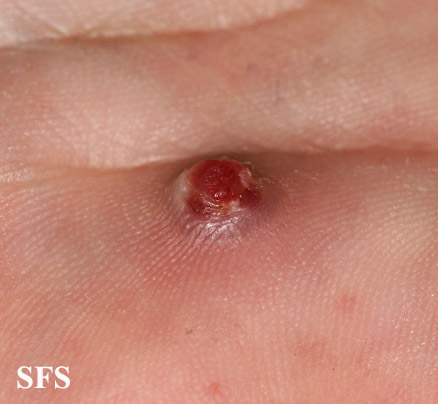
| Pyogenic granuloma |
|
|
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
|
|
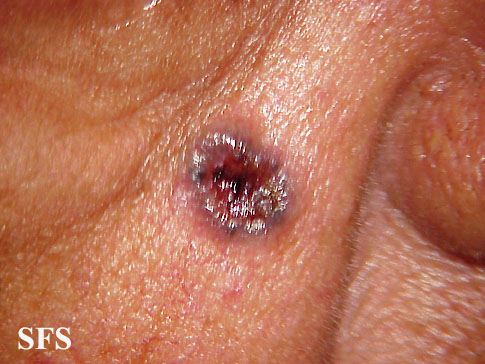
| Basal cell carcinoma[16] |
|
|
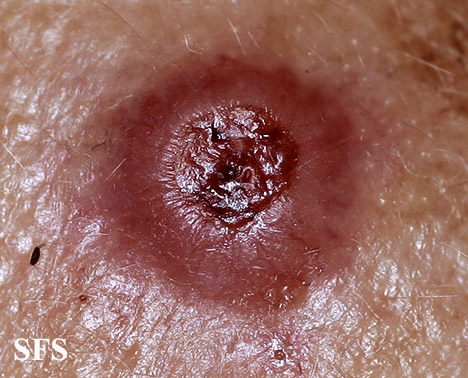
| Amelanotic melanoma |
|
Different conditions that cause a rash must be differentiated from molluscum contagiosum based on the appearance of the lesions such as:[17][18][19][20][21][22][23]
| Disease | Features |
|---|---|
| Impetigo | |
| Insect bites |
|
| Kawasaki disease |
|
| Measles |
|
| Monkeypox |
|
| Rubella |
|
| Atypical measles |
|
| Coxsackievirus |
|
| Acne |
|
| Syphilis | It commonly presents with gneralized systemic symptoms such as malaise, fatigue, headache and fever. Skin eruptions may be subtle and asymptomatic It is classically described as:
|
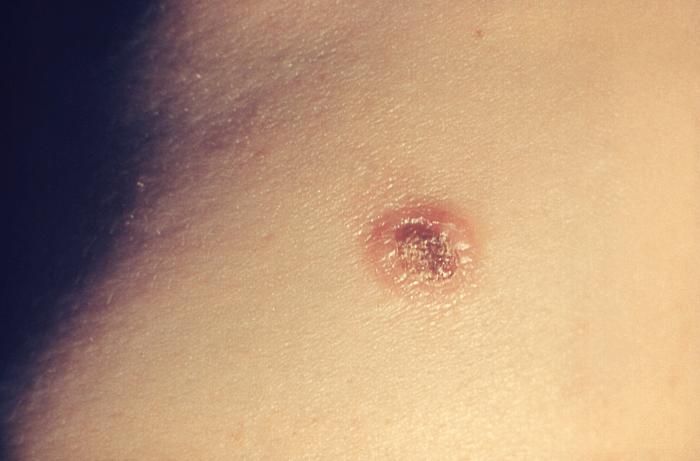
| Molluscum contagiosum |
|
| Mononucleosis |
|
| Toxic erythema | |
| Rat-bite fever | |
| Parvovirus B19 | |
| Cytomegalovirus |
|
| Scarlet fever |
|
| Rocky Mountain spotted fever |
|
| Stevens-Johnson syndrome |
|
| Varicella-zoster virus | |
| Chickenpox |
|
| Meningococcemia | |
| Rickettsial pox | |
| Meningitis |
|
References
- ↑ Knox KS, Hage CA (2010). "Histoplasmosis". Proc Am Thorac Soc. 7 (3): 169–72. doi:10.1513/pats.200907-069AL. PMID 20463244.
- ↑ Kauffman CA (2009). "Histoplasmosis". Clin Chest Med. 30 (2): 217–25, v. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2009.02.002. PMID 19375629.
- ↑ Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL (2008). "Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008". Critical Care Medicine. 36 (1): 296–327. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000298158.12101.41. PMID 18158437. Retrieved 2012-09-16. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992 Jun;101(6):1644-55. PMID 1303622.
- ↑ Supparatpinyo K, Chiewchanvit S, Hirunsri P, Baosoung V, Uthammachai C, Chaimongkol B; et al. (1992). "An efficacy study of itraconazole in the treatment of Penicillium marneffei infection". J Med Assoc Thai. 75 (12): 688–91. PMID 1339213.
- ↑ Cortez, Michelle Fay and Pettypiece, Shannon. "Merck Cancer Shot Cuts Genital Warts, Lesions in Men". Bloomberg News. (Bloomberg.com) 13 Nov 2008.
- ↑ Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ↑ Jafarzadeh H, Sanatkhani M, Mohtasham N (December 2006). "Oral pyogenic granuloma: a review" (– Scholar search). J Oral Sci. 48 (4): 167–75. doi:10.2334/josnusd.48.167. PMID 17220613. Retrieved 2009-01-04.[dead link]
- ↑ Nthumba PM (2008). "Giant pyogenic granuloma of the thigh: a case report". J Med Case Reports. 2 (1): 95. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-2-95. PMC 2329656. PMID 18377654.
- ↑ DiCaprio MR, Roberts TT (2014). "Diagnosis and Management of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis". J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 22 (10): 643–652. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-22-10-643. PMID 25281259.
- ↑ Grana N (2014). "Langerhans cell histiocytosis". Cancer Control. 21 (4): 328–34. PMID 25310214.
- ↑ Harmon CM, Brown N (2015). "Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A Clinicopathologic Review and Molecular Pathogenetic Update". Arch Pathol Lab Med. 139 (10): 1211–4. doi:10.5858/arpa.2015-0199-RA. PMID 26414464.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Wikipedia (2015) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Langerhans_cell_histiocytosis Accessed on February, 2 2016
- ↑ Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Radiopeadia (2015) http://radiopaedia.org/articles/langerhans-cell-histiocytosis Accessed on February, 3 2016
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Treatment (PDQ®): Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute (2015) http://www.cancer.gov/types/langerhans/hp/langerhans-treatment-pdq Accessed on February, 3 2016
- ↑ Epstein EH, Shepard JA, Flotte TJ (2008). "Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 3-2008. An 80-year-old woman with cutaneous basal-cell carcinomas and cysts of the jaws". N Engl J Med. 358 (4): 393–401. doi:10.1056/NEJMcpc0707893. PMID 18216361. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Hartman-Adams H, Banvard C, Juckett G (2014). "Impetigo: diagnosis and treatment". Am Fam Physician. 90 (4): 229–35. PMID 25250996.
- ↑ Mehta N, Chen KK, Kroumpouzos G (2016). "Skin disease in pregnancy: The approach of the obstetric medicine physician". Clin Dermatol. 34 (3): 320–6. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2016.02.003. PMID 27265069.
- ↑ Moore, Zack S; Seward, Jane F; Lane, J Michael (2006). "Smallpox". The Lancet. 367 (9508): 425–435. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68143-9. ISSN 0140-6736.
- ↑ Ibrahim F, Khan T, Pujalte GG (2015). "Bacterial Skin Infections". Prim Care. 42 (4): 485–99. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2015.08.001. PMID 26612370.
- ↑ Ramoni S, Boneschi V, Cusini M (2016). "Syphilis as "the great imitator": a case of impetiginoid syphiloderm". Int J Dermatol. 55 (3): e162–3. doi:10.1111/ijd.13072. PMID 26566601.
- ↑ Kimura U, Yokoyama K, Hiruma M, Kano R, Takamori K, Suga Y (2015). "Tinea faciei caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes (molecular type Arthroderma benhamiae ) mimics impetigo : a case report and literature review of cases in Japan". Med Mycol J. 56 (1): E1–5. doi:10.3314/mmj.56.E1. PMID 25855021.
- ↑ CEDEF (2012). "[Item 87--Mucocutaneous bacterial infections]". Ann Dermatol Venereol. 139 (11 Suppl): A32–9. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2012.01.002. PMID 23176858.
Categories:
- Pages with citations using unsupported parameters
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al.
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from March 2009
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Disease
- Infectious disease
- Dermatology
- Poxviruses
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Primary care