Metolazone: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
* [[Alcohol]], [[Barbiturates]], And [[Narcotics]] | * [[Alcohol]], [[Barbiturates]], And [[Narcotics]] | ||
:* The [[hypotensive]] effects of these drugs may be potentiated by the volume contraction that may be associated with metolazone therapy. | :* The [[hypotensive]] effects of these drugs may be potentiated by the volume contraction that may be associated with metolazone therapy. | ||
* Digitalis Glycosides | * [[Digitalis|Digitalis Glycosides]] | ||
:* Diuretic-induced hypokalemia can increase the sensitivity of the myocardium to digitalis. Serious | :* [[Diuretic]]-induced [[hypokalemia]] can increase the sensitivity of the [[myocardium]] to [[digitalis]]. Serious [[arrhythmia]]s can result. | ||
* Corticosteroids Or ACTH | * [[Corticosteroids]] Or [[ACTH]] | ||
:* May increase the risk of hypokalemia and increase salt and water retention. | :* May increase the risk of [[hypokalemia]] and increase salt and water retention. | ||
* Lithium | * [[Lithium]] | ||
:* Serum lithium levels may increase. | :* Serum [[lithium]] levels may increase. | ||
* Curariform Drugs | * Curariform Drugs | ||
:* Diuretic-induced hypokalemia may enhance neuromuscular blocking effects of curariform drugs (such as tubocurarine) – the most serious effect would be respiratory depression which could proceed to apnea. Accordingly, it may be advisable to discontinue ZAROXOLYN three days before elective surgery. | :* [[Diuretic]]-induced hypokalemia may enhance neuromuscular blocking effects of curariform drugs (such as [[tubocurarine]]) – the most serious effect would be [[respiratory depression]] which could proceed to [[apnea]]. Accordingly, it may be advisable to discontinue ZAROXOLYN three days before elective surgery. | ||
* | * [[Salicylate]]s And Other [[NSAID|Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs]] | ||
:* May decrease the antihypertensive effects of ZAROXOLYN Tablets. | :* May decrease the antihypertensive effects of ZAROXOLYN Tablets. | ||
* | * [[Sympathomimetic]]s | ||
:* Metolazone may decrease arterial responsiveness to norepinephrine, but this diminution is not sufficient to preclude effectiveness of the pressor agent for therapeutic use. | :* Metolazone may decrease arterial responsiveness to norepinephrine, but this diminution is not sufficient to preclude effectiveness of the pressor agent for therapeutic use. | ||
* Insulin And Oral Antidiabetic Agents | * [[Insulin]] And Oral Antidiabetic Agents | ||
* Methenamine | * [[Methenamine]] | ||
:* Efficacy may be decreased due to urinary alkalizing effect of metolazone. | :* Efficacy may be decreased due to urinary alkalizing effect of metolazone. | ||
* Anticoagulants | * [[Anticoagulants]] | ||
:* Metolazone, as well as other thiazide-like diuretics, may affect the hypoprothrombinemic response to anticoagulants; dosage adjustments may be necessary. | :* Metolazone, as well as other [[thiazide]]-like [[diuretics]], may affect the hypoprothrombinemic response to [[anticoagulants]]; dosage adjustments may be necessary. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 5 July 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
DO NOT INTERCHANGE:
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Do not interchange Zaroxolyn tablets and other formulations of metolazone that share its slow and incomplete bioavailability and are not therapeutically equivalent at the same doses to Mykrox® tablets, a more rapidly available and completely bioavailable metolazone product. Formulations bioequivalent to Zaroxolyn and formulations bioequivalent to Mykrox should not be interchanged for one another.
|
Overview
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of edema associated with congestive heart failure or renal disease. Metolazone is also indicated for the treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include orthostatic hypotension, electrolyte disturbances, hyperuricemia, dizziness, and fatigue.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Effective dosage of ZAROXOLYN should be individualized according to indication and patient response. A single daily dose is recommended. Therapy with ZAROXOLYN should be titrated to gain an initial therapeutic response and to determine the minimal dose possible to maintain the desired therapeutic response.
Edema
- Dosing Information
- 5–20 mg PO qd
- The time interval required for the initial dosage to produce an effect may vary. Diuresis and saluresis usually begin within one hour and persist for 24 hours or longer. When a desired therapeutic effect has been obtained, it may be advisable to reduce the dose if possible. The daily dose depends on the severity of the patient's condition, sodium intake, and responsiveness. A decision to change the daily dose should be based on the results of thorough clinical and laboratory evaluations. If antihypertensive drugs or diuretics are given concurrently with ZAROXOLYN, more careful dosage adjustment may be necessary. For patients who tend to experience paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, it may be advisable to employ a larger dose to ensure prolongation of diuresis and saluresis for a full 24-hour period.
Mild to Moderate Essential Hypertension
- Dosing Information
- 2.5–5 mg PO qd
- The time interval required for the initial dosage regimen to show effect may vary from three or four days to three to six weeks in the treatment of elevated blood pressure. Doses should be adjusted at appropriate intervals to achieve maximum therapeutic effect.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Metolazone in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Calcium Renal Calculus
- Dosing Information
- 2.5–10 mg PO qd[1]
Edema Associated with Liver Disease
- Dosing Information
- 5–20 mg PO qd[2]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Edema
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established in controlled clinical trials.
- There is limited experience with the use of ZAROXOLYN in pediatric patients with congestive heart failure, hypertension, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, nephrotic syndrome and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
- Doses used generally ranged from 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg administered once daily and usually resulted in a 1 to 2.8 kg weight loss and 150 to 300 cc increase in urine output. Not all patients responded and some gained weight. Those patients who did respond did so in the first few days of treatment. Prolonged use (beyond a few days) was generally associated with no further beneficial effect or a return to baseline status and is not recommended.
- Dosing Information
- 0.05–0.1 mg/kg qd
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Metolazone in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Metolazone in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Anuria
- Hepatic coma or precoma
- Allergy or hypersensitivity to metolazone
Warnings
|
DO NOT INTERCHANGE:
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Do not interchange Zaroxolyn tablets and other formulations of metolazone that share its slow and incomplete bioavailability and are not therapeutically equivalent at the same doses to Mykrox® tablets, a more rapidly available and completely bioavailable metolazone product. Formulations bioequivalent to Zaroxolyn and formulations bioequivalent to Mykrox should not be interchanged for one another.
|
- Rapid Onset Hyponatremia And/Or Hypokalemia
- Rarely, the rapid onset of severe hyponatremia and/or hypokalemia has been reported following initial doses of thiazide and non-thiazide diuretics. When symptoms consistent with severe electrolyte imbalance appear rapidly, drug should be discontinued and supportive measures should be initiated immediately. Parenteral electrolytes may be required. Appropriateness of therapy with this class of drugs should be carefully reevaluated.
- Hypokalemia may occur with consequent weakness, cramps, and cardiac dysrhythmias. Serum potassium should be determined at regular and appropriate intervals, and dose reduction, potassium supplementation or addition of a potassium-sparing diuretic instituted whenever indicated. Hypokalemia is a particular hazard in patients who are digitalized or who have or have had a ventricular arrhythmia; dangerous or fatal arrhythmias may be precipitated. Hypokalemia is dose related.
- Concomitant Therapy
-
- Unusually large or prolonged losses of fluids and electrolytes may result when ZAROXOLYN is administered concomitantly to patients receiving furosemide.
- Other Antihypertensive Drugs
- When ZAROXOLYN is used with other antihypertensive drugs, particular care must be taken to avoid excessive reduction of blood pressure, especially during initial therapy.
- Cross-Allergy
- Cross-allergy may occur when ZAROXOLYN is given to patients known to be allergic to sulfonamide-derived drugs, thiazides, or quinethazone.
- Sensitivity Reactions
- Sensitivity reactions (e.g., angioedema, bronchospasm) may occur with or without a history of allergy or bronchial asthma and may occur with the first dose of ZAROXOLYN.
Precautions
- Fluid And Electrolytes
- All patients receiving therapy with ZAROXOLYN Tablets should have serum electrolyte measurements done at appropriate intervals and be observed for clinical signs of fluid and/or electrolyte imbalance: namely, hyponatremia, hypochloremic alkalosis, and hypokalemia. In patients with severe edema accompanying cardiac failure or renal disease, a low-salt syndrome may be produced, especially with hot weather and a low-salt diet. Serum and urine electrolyte determinations are particularly important when the patient has protracted vomiting, severe diarrhea, or is receiving parenteral fluids. Warning signs of imbalance are: dryness of mouth, thirst, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, muscle pains or cramps, muscle fatigue, hypotension, oliguria, tachycardia, and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting. Hyponatremia may occur at any time during long term therapy and, on rare occasions, may be life threatening.
- The risk of hypokalemia is increased when larger doses are used, when diuresis is rapid, when severe liver disease is present, when corticosteroids are given concomitantly, when oral intake is inadequate or when excess potassium is being lost extrarenally, such as with vomiting or diarrhea.
- Thiazide-like diuretics have been shown to increase the urinary excretion of magnesium; this may result in hypomagnesemia.
- Glucose Tolerance
- Metolazone may raise blood glucose concentrations possibly causing hyperglycemia and glycosuria in patients with diabetes or latent diabetes.
- ZAROXOLYN regularly causes an increase in serum uric acid and can occasionally precipitate gouty attacks even in patients without a prior history of them.
- Renal Impairment
- Use caution when administering ZAROXOLYN Tablets to patients with severely impaired renal function. As most of the drug is excreted by the renal route, accumulation may occur.
- Orthostatic hypotension may occur; this may be potentiated by alcohol, barbiturates, narcotics, or concurrent therapy with other antihypertensive drugs.
- Hypercalcemia may infrequently occur with metolazone, especially in patients taking high doses of vitamin D or with high bone turnover states, and may signify hidden hyperparathyroidism. Metolazone should be discontinued before tests for parathyroid function are performed.
- Thiazide diuretics have exacerbated or activated systemic lupus erythematosus and this possibility should be considered with ZAROXOLYN Tablets.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Metolazone in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
- ZAROXOLYN is usually well tolerated, and most reported adverse reactions have been mild and transient. Many ZAROXOLYN related adverse reactions represent extensions of its expected pharmacologic activity and can be attributed to either its antihypertensive action or its renal/metabolic actions. The following adverse reactions have been reported. Several are single or comparably rare occurrences. Adverse reactions are listed in decreasing order of severity within body systems.
Cardiovascular
Chest pain/discomfort, orthostatic hypotension, excessive volume depletion, hemoconcentration, venous thrombosis, palpitations.
Neurologic
Syncope, neuropathy, vertigo, paresthesias, psychotic depression, impotence, dizziness/lightheadedness, drowsiness, fatigue, weakness, restlessness (sometimes resulting in insomnia), headache.
Hypersensitivity
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, necrotizing angiitis (cutaneous vasculitis), skin necrosis, purpura, petechiae, dermatitis (photosensitivity), urticaria, pruritus, skin rashes.
Gastrointestinal
Hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice, pancreatitis, vomiting, nausea, epigastric distress, diarrhea, constipation, anorexia, abdominal bloating, abdominal pain.
Hematologic
Aplastic/hypoplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Metabolic
Hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hyperuricemia, hypochloremia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hyperglycemia, glycosuria, increase in serum urea nitrogen (BUN) or creatinine, hypophosphatemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia.
Musculoskeletal
Joint pain, acute gouty attacks, muscle cramps or spasm.
Miscellaneous
Transient blurred vision, chills, dry mouth.
- In addition, adverse reactions reported with similar antihypertensive-diuretics, but which have not been reported to date for ZAROXOLYN include: bitter taste, sialadenitis, xanthopsia, respiratory distress (including pneumonitis), and anaphylactic reactions. These reactions should be considered as possible occurrences with clinical usage of ZAROXOLYN.
- Whenever adverse reactions are moderate or severe, ZAROXOLYN dosage should be reduced or therapy withdrawn.
Drug Interactions
- Furosemide and probably other loop diuretics given concomitantly with metolazone can cause unusually large or prolonged losses of fluid and electrolytes.
- Other Antihypertensives
- When ZAROXOLYN Tablets are used with other antihypertensive drugs, care must be taken, especially during initial therapy. Dosage adjustments of other antihypertensives may be necessary.
- Alcohol, Barbiturates, And Narcotics
- The hypotensive effects of these drugs may be potentiated by the volume contraction that may be associated with metolazone therapy.
- Diuretic-induced hypokalemia can increase the sensitivity of the myocardium to digitalis. Serious arrhythmias can result.
- May increase the risk of hypokalemia and increase salt and water retention.
- Serum lithium levels may increase.
- Curariform Drugs
- Diuretic-induced hypokalemia may enhance neuromuscular blocking effects of curariform drugs (such as tubocurarine) – the most serious effect would be respiratory depression which could proceed to apnea. Accordingly, it may be advisable to discontinue ZAROXOLYN three days before elective surgery.
- May decrease the antihypertensive effects of ZAROXOLYN Tablets.
- Metolazone may decrease arterial responsiveness to norepinephrine, but this diminution is not sufficient to preclude effectiveness of the pressor agent for therapeutic use.
- Insulin And Oral Antidiabetic Agents
- Methenamine
- Efficacy may be decreased due to urinary alkalizing effect of metolazone.
- Metolazone, as well as other thiazide-like diuretics, may affect the hypoprothrombinemic response to anticoagulants; dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Metolazone in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Metolazone during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Metolazone in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Metolazone in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Metolazone in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Metolazone in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Metolazone in the drug label.
Pharmacology
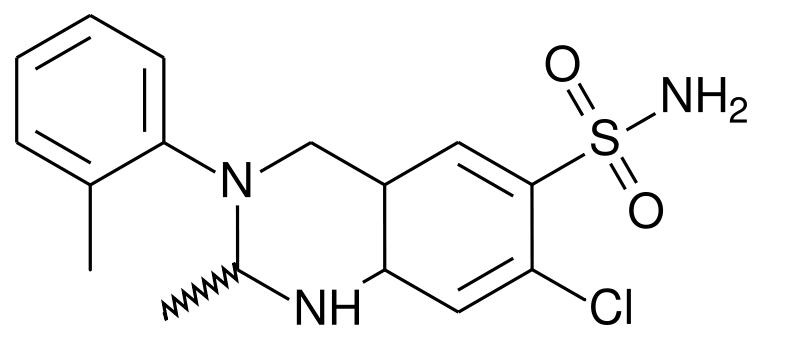
| |
Metolazone
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 7-chloro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)- 4-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinazoline-6-sulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C03 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 365.835 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~65% |
| Metabolism | minimal |
| Half life | 14 hours |
| Excretion | primarily urine |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
B |
| Legal status |
Prescription only |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Metolazone in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Metolazone in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Metolazone in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Metolazone in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Metolazone Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Metolazone |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Metolazone |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients should be informed of possible adverse effects, advised to take the medication as directed, and promptly report any possible adverse reactions to the treating physician.
Precautions with Alcohol
- The hypotensive effects of alcohol may be potentiated by the volume contraction associated with metolazone therapy.
Brand Names
- Mykrox®
- Zaroxolyn®[3]
Look-Alike Drug Names
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Cunningham, E. (1982-11). "Metolazone therapy of active calcium nephrolithiasis". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 32 (5): 642–645. ISSN 0009-9236. PMID 7128005. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Hillenbrand, P. (1971-10-30). "Use of metolazone in the treatment of ascites due to liver disease". British Medical Journal. 4 (5782): 266–270. ISSN 0007-1447. PMC 1799533. PMID 5123909. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ "ZAROXOLYN (metolazone) tablet".
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Metolazone |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Metolazone |Label Name=Metolazone11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Metolazone |Label Name=Metolazone11.png
}}
