Bowel obstruction: Difference between revisions
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The main diagnostic tools are [[blood test]]s, [[X-ray]]s of the abdomen, [[Computed axial tomography|CT scanning]] and/or [[medical ultrasonography|ultrasound]]. If a mass is identified, [[biopsy]] may determine the nature of the mass. | The main diagnostic tools are [[blood test]]s, [[X-ray]]s of the abdomen, [[Computed axial tomography|CT scanning]] and/or [[medical ultrasonography|ultrasound]]. If a mass is identified, [[biopsy]] may determine the nature of the mass. | ||
<div align="left"> | |||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:Small bowel obstruction 001.jpg|CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Small bowel obstruction 002.jpg|CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Small bowel obstruction 003.jpg|CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Small bowel obstruction 004.jpg|CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
Image:Small bowel obstruction 005.jpg|CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium <small>Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted</small> | |||
</div> | |||
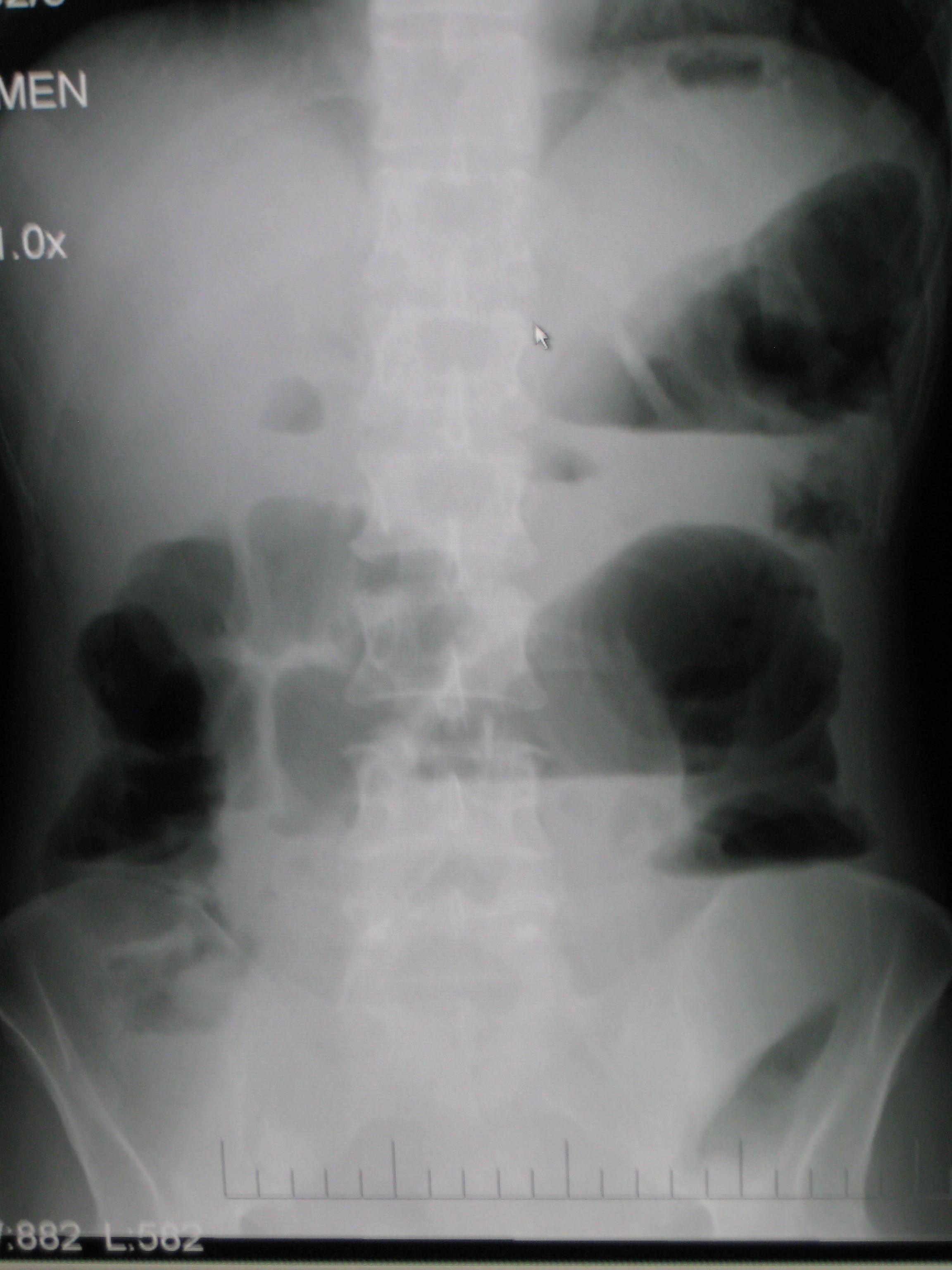
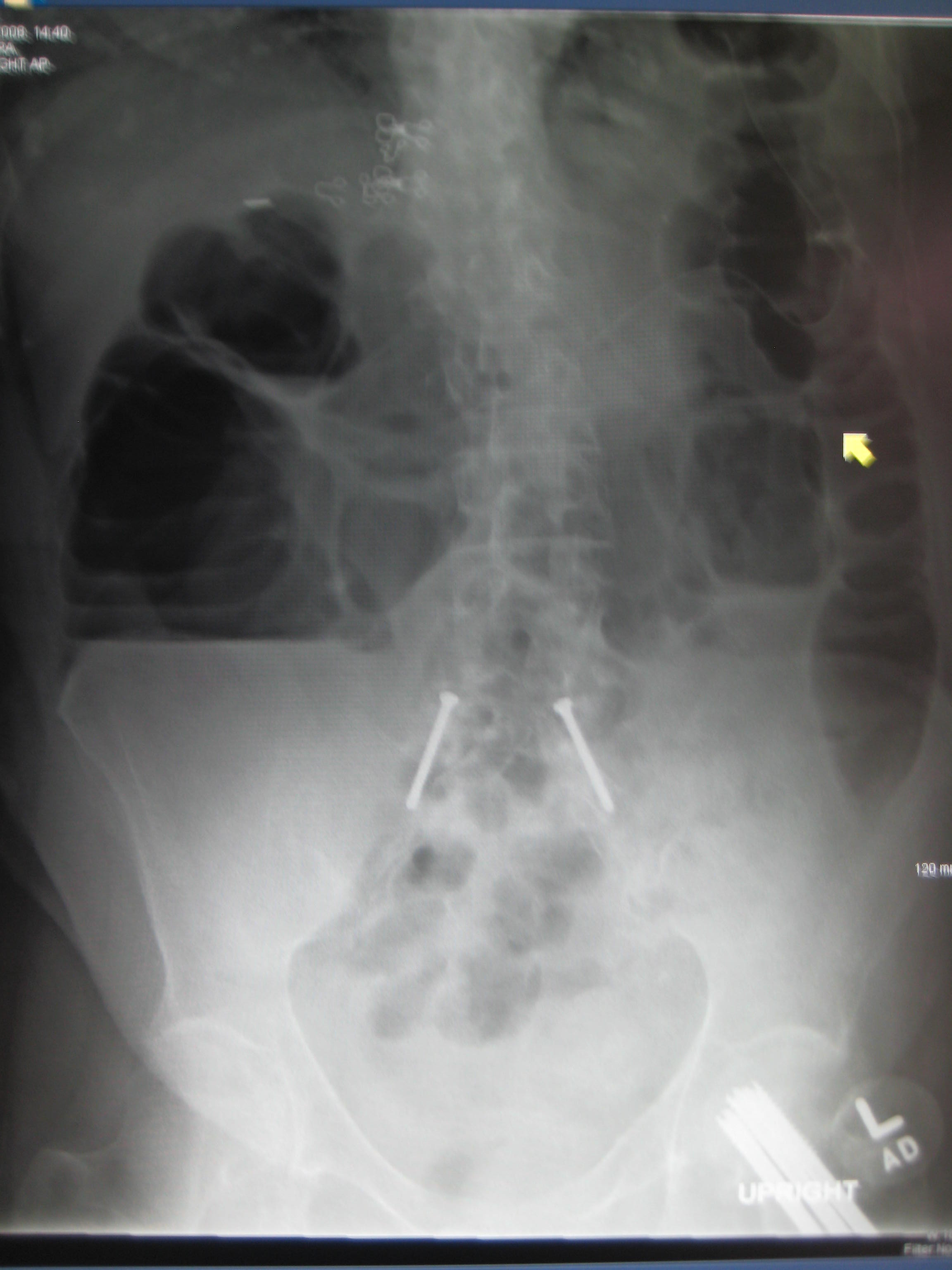
[[Radiology|Radiological]] signs of bowel obstruction include bowel distension and the presence of multiple (more than six) gas-fluid levels on supine and erect abdominal [[Radiography|radiographs]]. | [[Radiology|Radiological]] signs of bowel obstruction include bowel distension and the presence of multiple (more than six) gas-fluid levels on supine and erect abdominal [[Radiography|radiographs]]. | ||
Revision as of 19:46, 31 July 2012
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox For patient information click here
|
WikiDoc Resources for Bowel obstruction |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Bowel obstruction Most cited articles on Bowel obstruction |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Bowel obstruction |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Cochrane Collaboration on Bowel obstruction |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Bowel obstruction at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Bowel obstruction Clinical Trials on Bowel obstruction at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Bowel obstruction NICE Guidance on Bowel obstruction
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Bowel obstruction Discussion groups on Bowel obstruction Patient Handouts on Bowel obstruction Directions to Hospitals Treating Bowel obstruction Risk calculators and risk factors for Bowel obstruction
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Bowel obstruction |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Bowel obstruction is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines, preventing the normal transit of the products of digestion. It can occur at any level distal to the duodenum of the small intestine and is a medical emergency. Although many cases are not treated surgically, it is a surgical problem.
Differential Diagnosis of Causes of Bowel Obstruction
By Localization
Small bowel obstruction
- Adhesions from previous abdominal surgery
- Carcinoid rare, preferred location: ileum
- Crohn's disease causing adhesions or inflammatory strictures
- Foreign bodies (e.g. gallstones in gallstone ileus, swallowed objects)
- Hernias containing bowel
- Intestinal atresia
- Intussusception in children
- Ischaemic strictures
- Neoplasms, benign or malignant
- Volvulus
Large bowel obstruction
Causes of large bowel obstruction include:
- Neoplasms
- Hernias
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Colonic volvulus (sigmoid, caecal, transverse colon)
- Faecal impaction
- Colon atresia
- Benign strictures (Diverticular Disease)
-
Upright abdominal X-ray of a patient with a large bowel obstruction showing multiple air fluid levels and dilated loops of bowel.
By organ system
- Miscellaneous syndromes
- Pseudo-obstruction or Ogilvie's syndrome
- Paralytic Ileus
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Autosomal dominant conditions
- Neurofibromatosis type 1
- Malignant neoplastic conditions
- Trauma, mechanical and physical conditions
- Infectious disorders
- Intra-abdominal sepsis
- Pneumonia or other systemic illness
- Ascariasis
By mechanism
Mechanical Obstruction
- Adenomatous polyps
- Adhesions
- Adhesive bands
- Annular pancreas
- Ascariades
- Atresia
- Biliary calculus
- Bowel duplication
- Carcinomatosis
- Colon Cancer
- Congenital megacolon
- Crohn's Disease
- Cysts
- Diverticular stricture
- Diverticulitis
- Endometriosis
- Foreign body
- Gallstone ileus
- Hematoma of the bowel wall
- Hernia
- Hirschprung's disease
- Iatrogenic
- Imperforate anus
- Incarcerated hernia
- Inflammatory
- Intrabdominal abscess
- Intrabdominal hematoma
- Invagination, intussisception
- Ischemia
- Malrotation
- Meckel's Diverticulum
- Megacolon
- Multiple polyposis syndromes
- Neoplasm
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pneumatosis intestinalis
- Postoperative
- Pregnancy
- Radiation induced stenosis
- Sarcoma
- Scleroderma
- Surgical anastomosis
- Therapy with dietary fiber
- Trauma
- Tuberculosis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Volvulus
Non-Mechanical Obstruction
- Acid-base imbalance
- Acute pancreatitis
- Anticholinergics
- Antihistamines
- Apoplexy
- Brain tumor
- Cancer
- Catecholamines
- Cholecystolithiasis
- Connective tissue disease
- Diabetic coma
- Empyema
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hypokalemia
- Lead poisoning
- Lymphoma
- Mechanical ventilation
- Mesenteric infarction
- Morphine
- Narcotics
- Osteomyelitis of the spine
- Ovarian torsion
- Pancreatitis
- Penetrating wounds
- Perinephric abscess
- Peritoneal carcinomatosis
- Peritonitis
- Pneumonia
- Porphyria
- Postoperative
- Psoas abscess
- Pyelonephritis
- Renal colic
- Retroperitoneal hematoma
- Spinal cord inflammation
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal cord trauma
- Systemic infection
- Testicular torsion
- Ulcer perforation
- Uremia
- Urosepsis
- Vitamin deficiency
Pseudo-Obstruction
- Aerophagia
- Functional bowel disease
Signs, symptoms and causes
Depending on the level of obstruction, bowel obstruction can present with abdominal pain, abdominal distension, vomiting, fecal vomiting, and constipation.
Obstruction may be due to causes within the bowel lumen, within the wall of the bowel, or external to the bowel (such as compression, entrapment or volvulus).
Bowel obstruction may be complicated by dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities due to vomiting; respiratory compromise from pressure on the diaphragm by a distended abdomen, or aspiration of vomitus; bowel ischaemia or perforation from prolonged distension or pressure from a foreign body.
In small bowel obstruction the pain tends to be colicky (cramping and intermittent) in nature, with spasms lasting a few minutes. The pain tends to be central and mid-abdominal. Vomiting occurs before constipation.
In large bowel obstruction the pain is felt lower in the abdomen and the spasms last longer. Constipation occurs earlier and vomiting may be less prominent. Proximal obstruction of the large bowel may present as small bowel obstruction.
Diagnosis
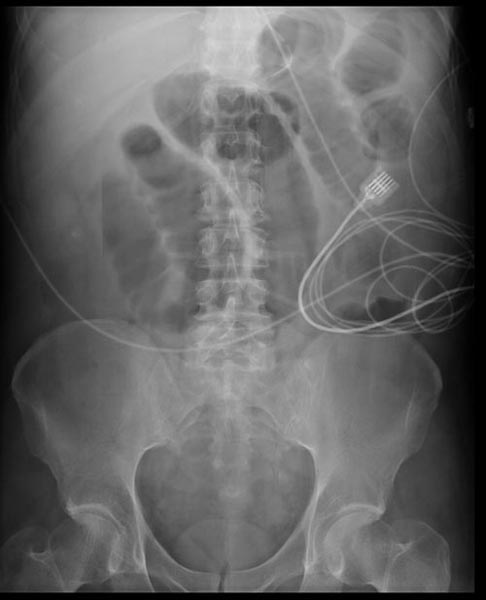
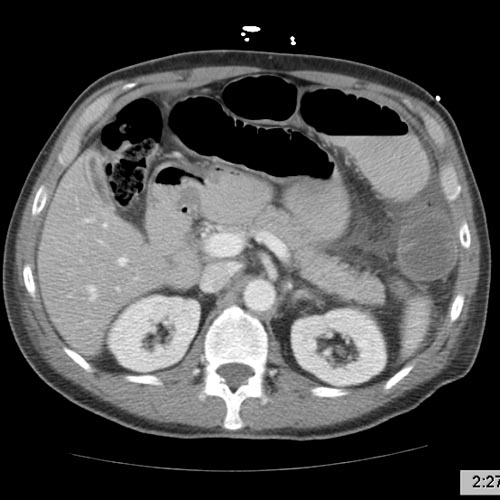
The main diagnostic tools are blood tests, X-rays of the abdomen, CT scanning and/or ultrasound. If a mass is identified, biopsy may determine the nature of the mass.
-
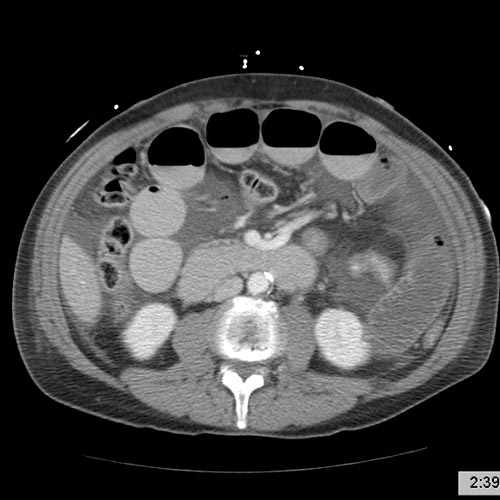
CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
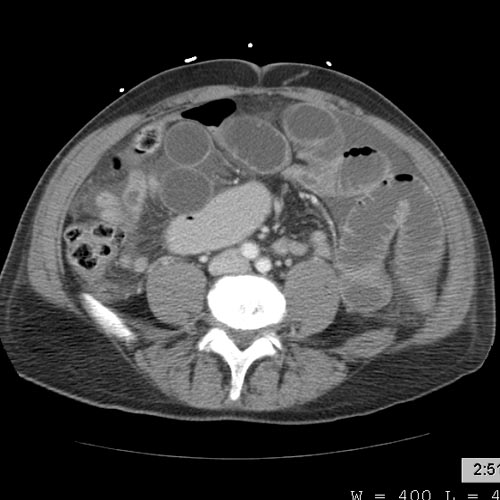
CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
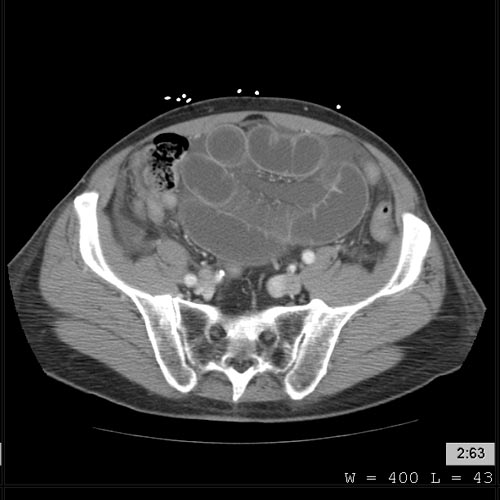
CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
CT demonstrate a cardiac myxoma in the left atrium Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
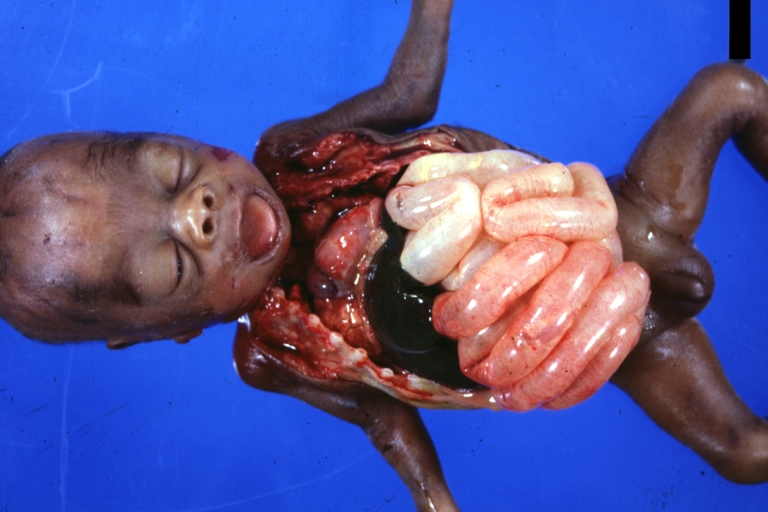
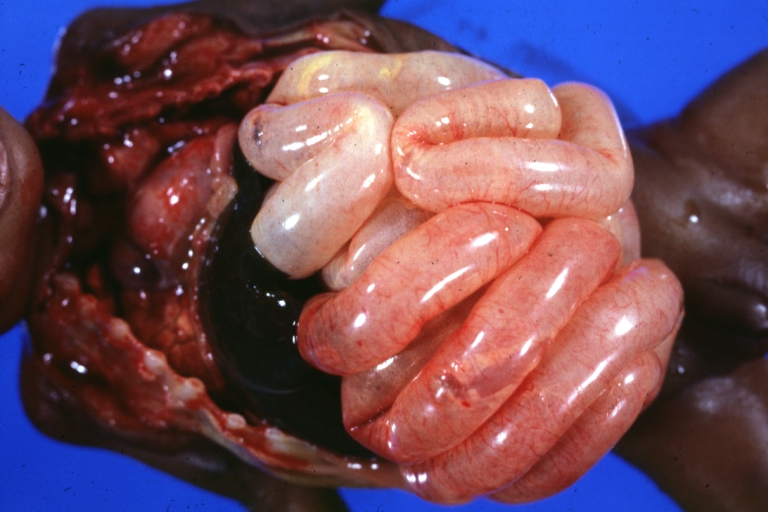
Intestine: Ileus Newborn Cause Unknown: Gross natural color opened body with protruding grossly dilated loops of bowel there was no evidence of necrotizing enteritis
-
Intestine: Ileus Newborn Cause Unknown: Gross natural color close-up view of distended gut loops
References