Posterior cerebral artery
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
In human anatomy, the posterior cerebral artery is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the posterior aspect of the brain (occipital lobe). It arises from the basilar artery and connects with the ipsilateral middle cerebral artery and internal carotid artery via the posterior communicating artery.
Branches
The branches of the posterior cerebral artery are divided into two sets, ganglionic and cortical:
Ganglionic branches
- The postero-medial ganglionic branches are a group of small arteries which arise at the commencement of the posterior cerebral artery: these, with similar branches from the posterior communicating, pierce the posterior perforated substance, and supply the medial surfaces of the thalami and the walls of the third ventricle.
- The posterior choroidal branches run forward beneath the splenium of the corpus callosum, and supply the tela chorioidea of the third ventricle and the choroid plexus.
- The postero-lateral ganglionic branches are small arteries which arise from the posterior cerebral artery after it has turned around the cerebral peduncle; they supply a considerable portion of the thalamus.
Cortical branches
The cortical branches are:
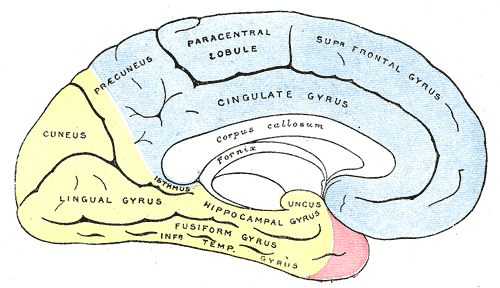
- the anterior temporal, distributed to the uncus and the anterior part of the fusiform gyrus
- the posterior temporal, to the fusiform and the inferior temporal gyri
- the calcarine, to the cuneus and gyrus lingualis and the back part of the convex surface of the occipital lobe
- the parietoöccipital, to the cuneus and the precuneus
Pathology
Because the artery supplies much of the occipital lobe, occlusions can lead to deficiencies in visual perception.
See also
Additional images
-
Location of the cerebral cortex
-
Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere, showing areas supplied by cerebral arteries.
External links
- neuro/322 at eMedicine - Posterior Cerebral Artery Stroke
- Template:UMichAtlas
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs
- Template:RocheLexicon
- Overview at strokecenter.org
- Angiography at State University of New York Upstate Medical University
- Diagram at psyweb.com
- Blood supply at neuropat.dote.hu