Tuberculous pericarditis: Difference between revisions
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
===Electrocardiogram=== | ===Electrocardiogram=== | ||
[[ECG]] may show non-specific ST-T–wave changes<ref name="pmid14443596">{{cite journal| author=SCHRIRE V| title=Experience with pericarditis at Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town: an analysis of one hundred and sixty cases studied over a six-year period. | journal=S Afr Med J | year= 1959 | volume= 33 | issue= | pages= 810-7 | pmid=14443596 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref><ref name="pmid11447490">{{cite journal| author=Smedema JP, Katjitae I, Reuter H, Burgess L, Louw V, Pretorius M et al.| title=Twelve-lead electrocardiography in tuberculous pericarditis. | journal=Cardiovasc J S Afr | year= 2001 | volume= 12 | issue= 1 | pages= 31-4 | pmid=11447490 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref>. Characteristic EKG finding of acute pericarditis, PR-segment deviation and diffuse ST-segment elevation are found in only 9-11% of cases<ref name="pmid5410398">{{cite journal| author=Rooney JJ, Crocco JA, Lyons HA| title=Tuberculous pericarditis. | journal=Ann Intern Med | year= 1970 | volume= 72 | issue= 1 | pages= 73-81 | pmid=5410398 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref><ref name="pmid11447490">{{cite journal| author=Smedema JP, Katjitae I, Reuter H, Burgess L, Louw V, Pretorius M et al.| title=Twelve-lead electrocardiography in tuberculous pericarditis. | journal=Cardiovasc J S Afr | year= 2001 | volume= 12 | issue= 1 | pages= 31-4 | pmid=11447490 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref>. | [[ECG]] may show non-specific ST-T–wave changes<ref name="pmid14443596">{{cite journal| author=SCHRIRE V| title=Experience with pericarditis at Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town: an analysis of one hundred and sixty cases studied over a six-year period. | journal=S Afr Med J | year= 1959 | volume= 33 | issue= | pages= 810-7 | pmid=14443596 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref><ref name="pmid11447490">{{cite journal| author=Smedema JP, Katjitae I, Reuter H, Burgess L, Louw V, Pretorius M et al.| title=Twelve-lead electrocardiography in tuberculous pericarditis. | journal=Cardiovasc J S Afr | year= 2001 | volume= 12 | issue= 1 | pages= 31-4 | pmid=11447490 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref>. Characteristic EKG finding of acute pericarditis, PR-segment deviation and diffuse ST-segment elevation are found in only 9-11% of cases<ref name="pmid5410398">{{cite journal| author=Rooney JJ, Crocco JA, Lyons HA| title=Tuberculous pericarditis. | journal=Ann Intern Med | year= 1970 | volume= 72 | issue= 1 | pages= 73-81 | pmid=5410398 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref><ref name="pmid11447490">{{cite journal| author=Smedema JP, Katjitae I, Reuter H, Burgess L, Louw V, Pretorius M et al.| title=Twelve-lead electrocardiography in tuberculous pericarditis. | journal=Cardiovasc J S Afr | year= 2001 | volume= 12 | issue= 1 | pages= 31-4 | pmid=11447490 | doi= | pmc= | url= }} </ref>. The presence of micro-voltage and [[electrical alternans]] suggests pericardial effusion and tamponade. | ||
[[Image:12leadpericarditis.png|thumb|500px|left|ECG in acute pericarditis showing diffuse ST elevation]][[Image:PulsusAlternans.jpg|thumb|500px|center|Electrical alternans]] | [[Image:12leadpericarditis.png|thumb|500px|left|ECG in acute pericarditis showing diffuse ST elevation]][[Image:PulsusAlternans.jpg|thumb|500px|center|Electrical alternans]] | ||
<br clear="left"/> | <br clear="left"/> | ||
===Echocardiography=== | ===Echocardiography=== | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 29 June 2011
|
Pericarditis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Surgery |
|
Case Studies |
|
Tuberculous pericarditis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Tuberculous pericarditis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Tuberculous pericarditis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.
Overview
The incidence of tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its complications has significantly decreased in developed nations while it remains high in developing countries. Approximately one third of the world population is believed to be infected with tuberculosis(TB)[1]. In 2006, the WHO estimated the global prevalence of active TB[2] to be 14.4 million cases. TB accounts for 1.7 million deaths worldwide. One of the important complications of TB is pericarditis which is inflammation of the pericardial sac that encases the heart.
Epidemiology and demographics
Tuberculous pericarditis is found in approximately 1-2% of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis[3][4]. It is the most common cause of pericarditis in Africa and other developing countries where TB is a major public health problem[5]. The incidence is increasing rapidly in the presence of HIV[6].
In a study at Western Cape Province of South Africa, tuberculous pericarditis was noted in 69.5% of patients who were referred for diagnostic pericardiocentesis. It should noted that one half of the patients were infected with HIV[7]. In contrast, the incidence of tuberculous pericarditis is 4% in developed countries[8].
Natural history and complications
Tuberculous pericarditis often has a complicated course and poor clinical outcomes. It can lead to pericardial effusion and subsequently, cardiac tamponade which may require urgent intervention including pericardiocentesis. The mortality rate of tuberculous pericarditis in the preantibiotic era was 80-90%[9]. The mortality rate in the modern era is currently 8-17%[10][11] and is 17-34% if the TB is associated with HIV[12].
Tuberculous pericarditis can also cause heart failure as observed in Eastern Cape and Zimbabwe where it is a common cause, but less common than rheumatic heart disease. In this region, TB pericarditis is a more common cause of heart failure than hypertensive heart disease and cardiomyopathy[13][14]
Constrictive pericarditis is another complication of tuberculous pericarditis occurring in 30-60% of patients despite prompt antituberculosis treatment and the use of corticosteroids[15][8]
Pathophysiology
Tuberculous pericarditis develops as a result of lymphatic spread from peritracheal, peribronchial or mediastinal lymphnodes or by contiguous spread from a focus of infection in the lung or pleura. This causes acute inflammation of the pericardium with infiltration of polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes and pericardial vascularization. This may lead to pericardial effusion and fibrinous changes of the pericardium. There are four pathologic stages of involvement:[16][17][18]
- Stage 1: Presence of diffuse fibrin deposition, granulomas and abundant mycobacterium
- Stage 2: Development of serous or serosanguineous pericardial effusion with a predominantly lymphocytic exudate with monocytes and foam cells
- Stage 3: Absorption of effusion with organization of granulomatous caseation and thickening of pericardium secondary to deposition of fibrin and collagen.
- Stage 4: Development of constrictive pericarditis. Pericardial space is obliterated by dense adhesions with marked thickening of parietal layer and replacement of granulomas by fibrous tissue.
Effusive constrictive pericarditis[19] may be seen in some patients. The visceral pericardium thickens with fibrin deposition (changes of constrictive pericarditis) and concomitantly there is presence of pericardial effusion which may present as cardiac tamponade. In this scenario, the diastolic pressure continues to be elevated after pericardiocentesis due to persistent constriction.
Diagnosis
Tuberculous pericarditis has a variable clinical presentation and should be considered in the evaluation of all cases of pericarditis that are not self-limiting[8]. It is one of the difficult disease to diagnose and hence several diagnostic tools are employed[20][21].
History and symptoms
The patient may present with the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- Cough
- breathlessness
- Chest pain which changes with posture
- Malaise
- Ankle edema
The frequency and severity of the above symptoms varies with the stage of the infection, the degree of involvement of the pericardium, and the degree of extrapericardial infection.
Physical examination
Patients present with fever and cachexia.
Vitals: Tachycardia, pulsus paradoxus and hypotension(in cardiac tamponade)
Neck: Jugular venous distension with a prominent Y descent and Kussmaul's sign
Chest: Pleural dullness, decreased breath sounds, pericardial knock, pericardial rub and distant heart sounds
Abdomen: Hepatomegaly, ascites
Extremities: Ankle edema
Chest X-ray
Pulmonary infiltration by the bacterium may be seen in approximately 32% of cases[22], pleural effusion in 40% to 60%, and cardiomegaly in about 90% of patients with tuberculous pericarditis[23][24].
Image shown below is courtesy of Radiopedia

Electrocardiogram
ECG may show non-specific ST-T–wave changes[15][25]. Characteristic EKG finding of acute pericarditis, PR-segment deviation and diffuse ST-segment elevation are found in only 9-11% of cases[24][25]. The presence of micro-voltage and electrical alternans suggests pericardial effusion and tamponade.
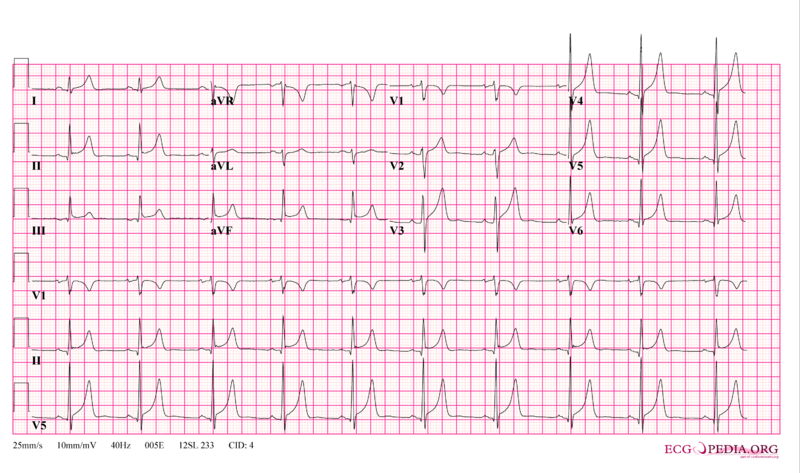
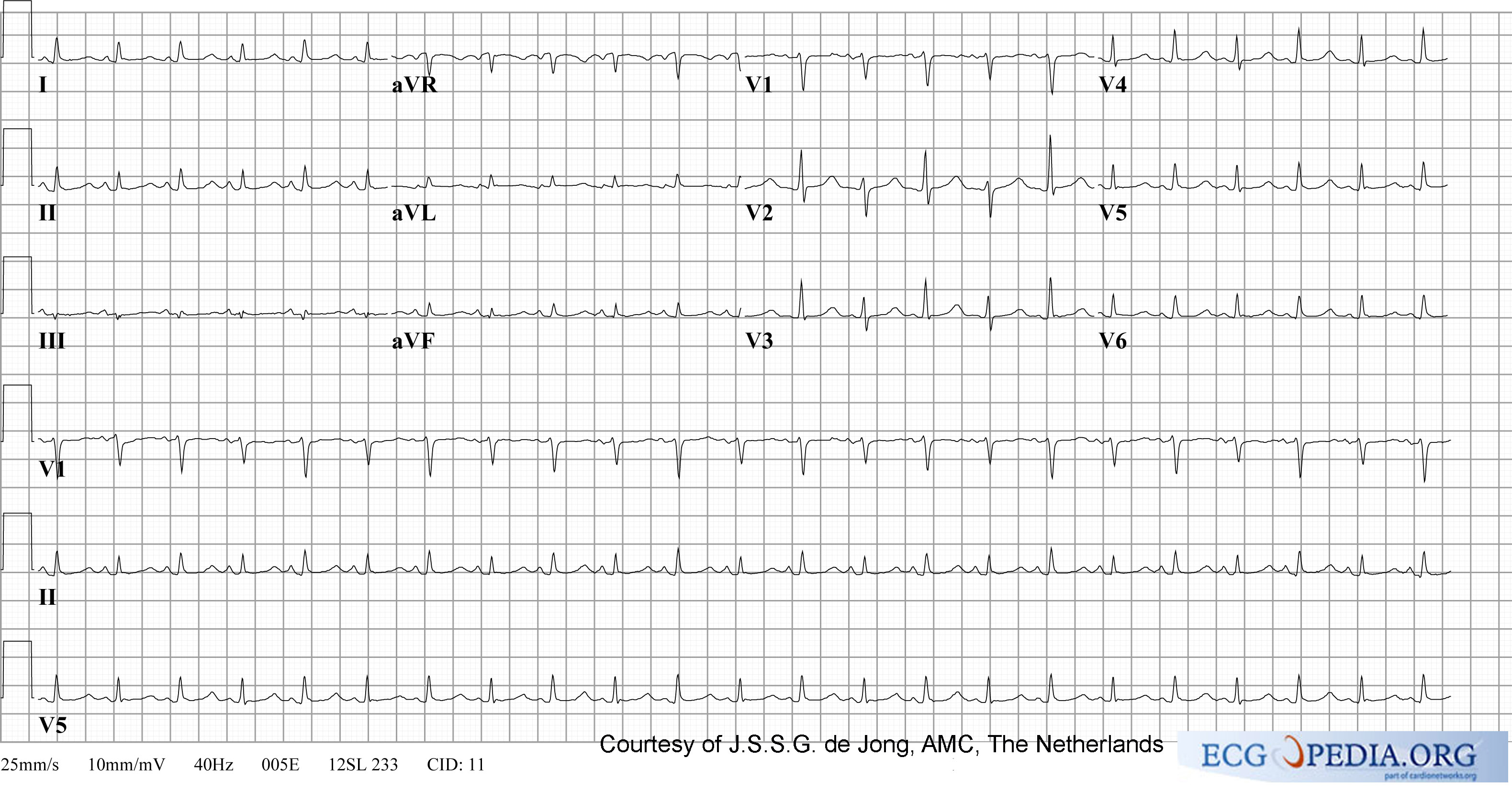
Echocardiography
Echocardiographic findings in constrictive pericarditis include thickened pericardium with dilated atria and venae cavae. In pericardial effusion, large hypoechoic regions are seen surrounding the heart with presence of oscillatory motion of heart. Cardiac tamponade demonstrates right atrial collapse, right ventricular diastolic collapse, and increased variation of mitral and tricuspid flow with respiration.
Below is a video demonstrating echocardiographic features of cardiac tamponade <youtube v=YWVI6rRTIzU/>
MRI
Below is a video demonstrating MR findings of constrictive pericarditis where, in mid-diastole, the thickened pericardium begins to restrict right ventricular filling, causing a rapid increase in ventricular pressure. Early changes of septal flattening and bowing of the interventricular septum toward the left ventricle (normally concave in shape toward the left ventricle during diastolic filling) are seen. This pressure change results in diastolic septal dysfunction, the septal bounce described in echocardiography. <youtube v=5srXVJdWIAM/>
Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac tamponade: Pressures in all four chambers of heart are in equilibrium.
- Constrictive pericarditis: Equalization of elevated right atrial and pulmonary artery wedge pressures may be noted with a diastolic dip and plateau in the right ventricular tracing.
- Effusive constrictive pericarditis: Cardiac tamponade findings are noted initially. Findings of constrictive pericarditis are unmasked following pericardiocentesis.
Tuberculin skin test
Patients with tuberculous pericarditis most often have positive PPD test[24]. However immunocompromised patients such as those with HIV infection may have false negative tuberculin test[26]. In developing countries where TB is endemic, tuberculin skin test may be of little value secondary to high prevalence of TB and BCG vaccination[27].
Pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis should be performed in patients with pericardial effusion. Fluid may be blood-stained in approximately 80% of patients[28]. Tuberculous pericardial fluid is often exudative with high protein, LDH and leukocyte levels[29]. This fluid can be used for testing the presence of acid-fast bacilli which may be detected in upto approximately 40% of patients[3]. Culturing the sample may increase the bacterial yield. If pericardiocentesis is not diagnostic, pericardial biopsy may be done. However, lesser invasive studies such as sputum examination, gastric washings, urine culture, and right scalene lymph node biopsy may be tried before biopsy.
- Polymerase chain reaction(PCR) is another test that helps in detecting presence of DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[30][31][32]. However PCR is found to have low sensitivity and high false positive results in detection of mycobacterium in pericardial fluid[32][33][34].
- Adenosine deaminase(ADA) is an enzyme produced by leukocytes. Measurement of ADA levels in pericardial fluid is found to be of diagnostic value in tuberculous pericardial disease[20][18]. ADA levels of ≥40units/liter in pericardial fluid has a good sensitivity and specificity of 87% and 89% respectively[33].
- Measurement of interferon-gamma in pericardial fluid is another diagnostic modality with a high sensitivity and specificity of 100%, using a cutoff level of >200pg/L as observed in a series with sample size of 30[35]. Sensitivity and specificity and positive predective value of 92%, 100% and 100% respectively were noted in another series in South Africa[33] where prevalence of TB is high. Further studies with a larger sample size may provide substantial evidence for routine use of this test in diagnosis of TB pericarditis.
Pericardial biopsy
Pericardial biopsy may cause marked morbidity and prolongation of the hospital stay depending on the approach adopted[36]. Sensitivity of this test in diagnosing TB ranges between 10-64%[37][38]. Therefore, normal biopsy finding does not exclude TB. The probability of obtaining a definitive bacteriological result is greatest when pericardial fluid and biopsy specimens are examined early in the effusive stage[39][40].
Treatment
Anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy
With the use of antituberculosis chemotherapy, survival rate in tuberculous pericarditis has improved dramatically. Mortality rate in preantibiotic era was 80-90%[41]. At present it is 8-17%[10][11] and 17-34% if associated with HIV[12]. A 2months course of isoniazid, pyrazinamide, rifampicin, and ethambutol followed by 4months course of isoniazid and rifampicin is shown to be effective[42]. Short course chemotherapy is beneficial in HIV infected patients[43].
American Thoracic Society, CDC, and Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends use of corticosteroids(prednisone) as adjunctive therapy for tuberculous pericarditis during the first 11 weeks of antituberculosis therapy[44]. Following are the dosage recommendations:
- Adults: Prednisone 60 mg/day (or the equivalent dose of prednisolone) given for 4 weeks, followed by 30 mg/day for 4 weeks, 15 mg/day for 2 weeks, and finally 5 mg/day for week 11 (the final week)
- Children: doses should be proportionate to their weight, beginning with about 1 mg/kg body weight and decreasing the dose as described for adults.
Approach to patients with suspected tuberculous pericarditis[18]
| “ |
|
” |
References
- ↑ Lönnroth K, Raviglione M (2008). "Global epidemiology of tuberculosis: prospects for control". Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 29 (5): 481–91. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1085700. PMID 18810682.
- ↑ WHO. Global Tuberculosis control. WHO/HTM/TB/2008.393. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008. Available online at http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2008/en/index.html (Accessed June 27, 2011)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Fowler NO (1991). "Tuberculous pericarditis". JAMA. 266 (1): 99–103. PMID 2046135.
- ↑ Larrieu AJ, Tyers GF, Williams EH, Derrick JR (1980). "Recent experience with tuberculous pericarditis". Ann Thorac Surg. 29 (5): 464–8. PMID 7377888.
- ↑ Mayosi BM, Volmink JA, Commerford PJ. Pericardial disease: an evidence-based approach to diagnosis and treatment. In: Yusuf S, Cairns JA, Camm AJ, Fallen BJ, eds. Evidence-Based Cardiology. 2nd ed. London: BMJ Books; 2003: 735–748.
- ↑ Cegielski JP, Ramiya K, Lallinger GJ, Mtulia IA, Mbaga IM (1990). "Pericardial disease and human immunodeficiency virus in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania". Lancet. 335 (8683): 209–12. PMID 1967676.
- ↑ Reuter H, Burgess LJ, Doubell AF (2005). "Epidemiology of pericardial effusions at a large academic hospital in South Africa". Epidemiol Infect. 133 (3): 393–9. PMC 2870262. PMID 15962545.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Sagristà-Sauleda J, Permanyer-Miralda G, Soler-Soler J (1988). "Tuberculous pericarditis: ten year experience with a prospective protocol for diagnosis and treatment". J Am Coll Cardiol. 11 (4): 724–8. PMID 3351140.
- ↑ Harvey AM, Whitehill MR. Tuberculous pericarditis. Medicine. 1937; 16: 45–94
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Desai HN (1979). "Tuberculous pericarditis. A review of 100 cases". S Afr Med J. 55 (22): 877–80. PMID 472922.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Bhan GL (1980). "Tuberculous pericarditis". J Infect. 2 (4): 360–4. PMID 7185934.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Hakim JG, Ternouth I, Mushangi E, Siziya S, Robertson V, Malin A (2000). "Double blind randomised placebo controlled trial of adjunctive prednisolone in the treatment of effusive tuberculous pericarditis in HIV seropositive patients". Heart. 84 (2): 183–8. PMC 1760932. PMID 10908256.
- ↑ Strang JI (1984). "Tuberculous pericarditis in Transkei". Clin Cardiol. 7 (12): 667–70. PMID 6509811.
- ↑ Hakim JG, Manyemba J (1998). "Cardiac disease distribution among patients referred for echocardiography in Harare, Zimbabwe". Cent Afr J Med. 44 (6): 140–4. PMID 9810393.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 SCHRIRE V (1959). "Experience with pericarditis at Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town: an analysis of one hundred and sixty cases studied over a six-year period". S Afr Med J. 33: 810–7. PMID 14443596.
- ↑ Peel AA (1948). "TUBERCULOUS PERICARDITIS". Br Heart J. 10 (3): 195–207. PMC 481044. PMID 18610109.
- ↑ Permanyer-Miralda G, Sagristá-Sauleda J, Soler-Soler J (1985). "Primary acute pericardial disease: a prospective series of 231 consecutive patients". Am J Cardiol. 56 (10): 623–30. PMID 4050698.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Mayosi BM, Burgess LJ, Doubell AF (2005). "Tuberculous pericarditis". Circulation. 112 (23): 3608–16. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.543066. PMID 16330703.
- ↑ Sagristà-Sauleda J, Angel J, Sánchez A, Permanyer-Miralda G, Soler-Soler J (2004). "Effusive-constrictive pericarditis". N Engl J Med. 350 (5): 469–75. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035630. PMID 14749455.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Maisch B, Seferović PM, Ristić AD, Erbel R, Rienmüller R, Adler Y; et al. (2004). "Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases executive summary; The Task force on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases of the European society of cardiology". Eur Heart J. 25 (7): 587–610. doi:10.1016/j.ehj.2004.02.002. PMID 15120056.
- ↑ Maisch B, Ristić AD (2003). "Practical aspects of the management of pericardial disease". Heart. 89 (9): 1096–103. PMC 1767862. PMID 12923044.
- ↑ Fowler NO, Manitsas GT (1973). "Infectious pericarditis". Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 16 (3): 323–36. PMID 4593515.
- ↑ Reuter H, Burgess LJ, Doubell AF (2005). "Role of chest radiography in diagnosing patients with tuberculous pericarditis". Cardiovasc J S Afr. 16 (2): 108–11. PMID 15915278.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Rooney JJ, Crocco JA, Lyons HA (1970). "Tuberculous pericarditis". Ann Intern Med. 72 (1): 73–81. PMID 5410398.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Smedema JP, Katjitae I, Reuter H, Burgess L, Louw V, Pretorius M; et al. (2001). "Twelve-lead electrocardiography in tuberculous pericarditis". Cardiovasc J S Afr. 12 (1): 31–4. PMID 11447490.
- ↑ Cegielski JP, Lwakatare J, Dukes CS, Lema LE, Lallinger GJ, Kitinya J; et al. (1994). "Tuberculous pericarditis in Tanzanian patients with and without HIV infection". Tuber Lung Dis. 75 (6): 429–34. PMID 7718831.
- ↑ Ng TT, Strang JI, Wilkins EG (1995). "Serodiagnosis of pericardial tuberculosis". QJM. 88 (5): 317–20. PMID 7796085.
- ↑ Mayosi BM, Volmink JA, Commerford PJ. Pericardial disease: an evidence-based approach to diagnosis and treatment. In: Yusuf S, Cairns JA, Camm AJ, Fallen BJ, eds. Evidence-Based Cardiology. 2nd ed. London: BMJ Books; 2003: 735–748.
- ↑ Burgess LJ, Reuter H, Carstens ME, Taljaard JJ, Doubell AF (2002). "Cytokine production in patients with tuberculous pericarditis". Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 6 (5): 439–46. PMID 12019920.
- ↑ Brisson-Noël A, Gicquel B, Lecossier D, Lévy-Frébault V, Nassif X, Hance AJ (1989). "Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples". Lancet. 2 (8671): 1069–71. PMID 2572798.
- ↑ Rana BS, Jones RA, Simpson IA (1999). "Recurrent pericardial effusion: the value of polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of tuberculosis". Heart. 82 (2): 246–7. PMC 1729120. PMID 10409547.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Cegielski JP, Devlin BH, Morris AJ, Kitinya JN, Pulipaka UP, Lema LE; et al. (1997). "Comparison of PCR, culture, and histopathology for diagnosis of tuberculous pericarditis". J Clin Microbiol. 35 (12): 3254–7. PMC 230157. PMID 9399529.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 Reuter H, Burgess L, van Vuuren W, Doubell A (2006). "Diagnosing tuberculous pericarditis". QJM. 99 (12): 827–39. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcl123. PMID 17121764.
- ↑ Lee JH, Lee CW, Lee SG, Yang HS, Hong MK, Kim JJ; et al. (2002). "Comparison of polymerase chain reaction with adenosine deaminase activity in pericardial fluid for the diagnosis of tuberculous pericarditis". Am J Med. 113 (6): 519–21. PMID 12427503.
- ↑ Burgess LJ, Reuter H, Carstens ME, Taljaard JJ, Doubell AF (2002). "The use of adenosine deaminase and interferon-gamma as diagnostic tools for tuberculous pericarditis". Chest. 122 (3): 900–5. PMID 12226030.
- ↑ Reuter H, Burgess LJ, Louw VJ, Doubell AF (2007). "The management of tuberculous pericardial effusion: experience in 233 consecutive patients". Cardiovasc J S Afr. 18 (1): 20–5. PMID 17392991.
- ↑ Komsuoğlu B, Göldelï O, Kulan K, Komsuoğlu SS (1995). "The diagnostic and prognostic value of adenosine deaminase in tuberculous pericarditis". Eur Heart J. 16 (8): 1126–30. PMID 8665976.
- ↑ SCHEPERS GW (1962). "Tuberculous pericarditis". Am J Cardiol. 9: 248–76. PMID 14498251.
- ↑ BARR JF (1955). "The use of pericardial biopsy in establishing etiologic diagnosis in acute pericarditis". AMA Arch Intern Med. 96 (5): 693–6. PMID 13257965.
- ↑ Strang G, Latouf S, Commerford P, Roditi D, Duncan-Traill G, Barlow D; et al. (1991). "Bedside culture to confirm tuberculous pericarditis". Lancet. 338 (8782–8783): 1600–1. PMID 1684009.
- ↑ Harvey AM, Whitehill MR. Tuberculous pericarditis. Medicine. 1937; 16: 45–94
- ↑ Cohn DL, Catlin BJ, Peterson KL, Judson FN, Sbarbaro JA (1990). "A 62-dose, 6-month therapy for pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis. A twice-weekly, directly observed, and cost-effective regimen". Ann Intern Med. 112 (6): 407–15. PMID 2106816.
- ↑ Perriëns JH, St Louis ME, Mukadi YB, Brown C, Prignot J, Pouthier F; et al. (1995). "Pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients in Zaire. A controlled trial of treatment for either 6 or 12 months". N Engl J Med. 332 (12): 779–84. doi:10.1056/NEJM199503233321204. PMID 7862181.
- ↑ American Thoracic Society. CDC. Infectious Diseases Society of America (2003). "Treatment of tuberculosis". MMWR Recomm Rep. 52 (RR-11): 1–77. PMID 12836625.