|
|
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 5: |
Line 5: |
| ==new== | | ==new== |
|
| |
|
| {|
| |
| ! colspan="9" style="background: #707070; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Cystic mass'''
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Bronchogenic cyst]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215" />
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Abnormal [[ventral]] budding or branching of the [[tracheobronchial tree]] during [[Embryology|embryologic]] development
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Pleurisy|Pleuritic chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Hemoptysis]]
| |
| * [[Fever]]
| |
| * [[Pneumonia]] secondary to [[airway obstruction]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |CT scan:
| |
| * Spherical or oval mass
| |
| * Smooth outline
| |
| * Unilocular
| |
| * Noncalcified
| |
| * Demonstrating the size and shape of the cyst
| |
| * Determining its position in relation to other structures
| |
| * Bronchogenic cysts can mimic hydatid cysts
| |
| * [[Pneumonitis]], [[pneumothorax]], or [[empyema]] may present
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Enteric duplication cysts|Esophageal duplication cysts]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25184121">{{cite journal |vauthors=Liu R, Adler DG |title=Duplication cysts: Diagnosis, management, and the role of endoscopic ultrasound |journal=Endosc Ultrasound |volume=3 |issue=3 |pages=152–60 |date=July 2014 |pmid=25184121 |pmc=4145475 |doi=10.4103/2303-9027.138783 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Rare congenital gastrointestinal malformation
| |
|
| |
|
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Stridor]]
| |
| * [[Cough|Nonproductive cough]]
| |
| * [[Epigastric distress|Epigastric discomfort]]
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
| * [[Cardiac arrhythmia]]
| |
| * [[Retrosternal]] and [[thoracic]] [[back pain]]
| |
| * [[Cyst]] [[ulceration]] and [[bleeding]]
| |
| * [[Cyst]] [[rupture]] with secondary [[mediastinitis]]
| |
|
| |
|
| *
| | {| align="right" |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| | | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
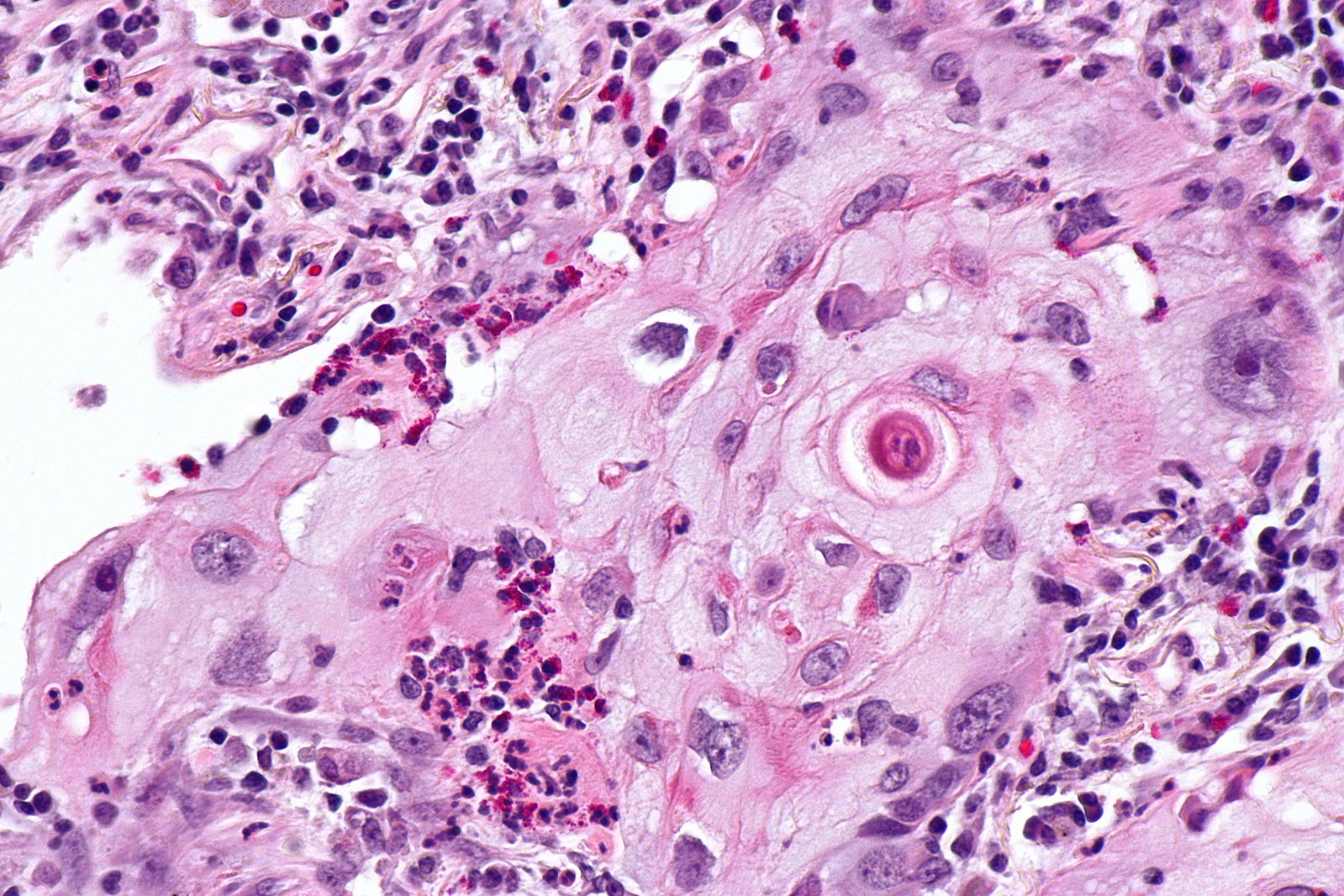
| | [[Image:Squamous cell mircopathology2.jpeg|x200px|thumb| Micropathology: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. H&E stain, By Nephron [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ALung_squamous_carcinoma_--_high_mag.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | - | | |} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Endoscopic ultrasound|Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)]]
| | {| align="right" |
| * Distinguish between solid and [[Cyst|cystic]] lesions
| | | |
| * Periesophageal [[homogeneous]]-hypoechoic mass
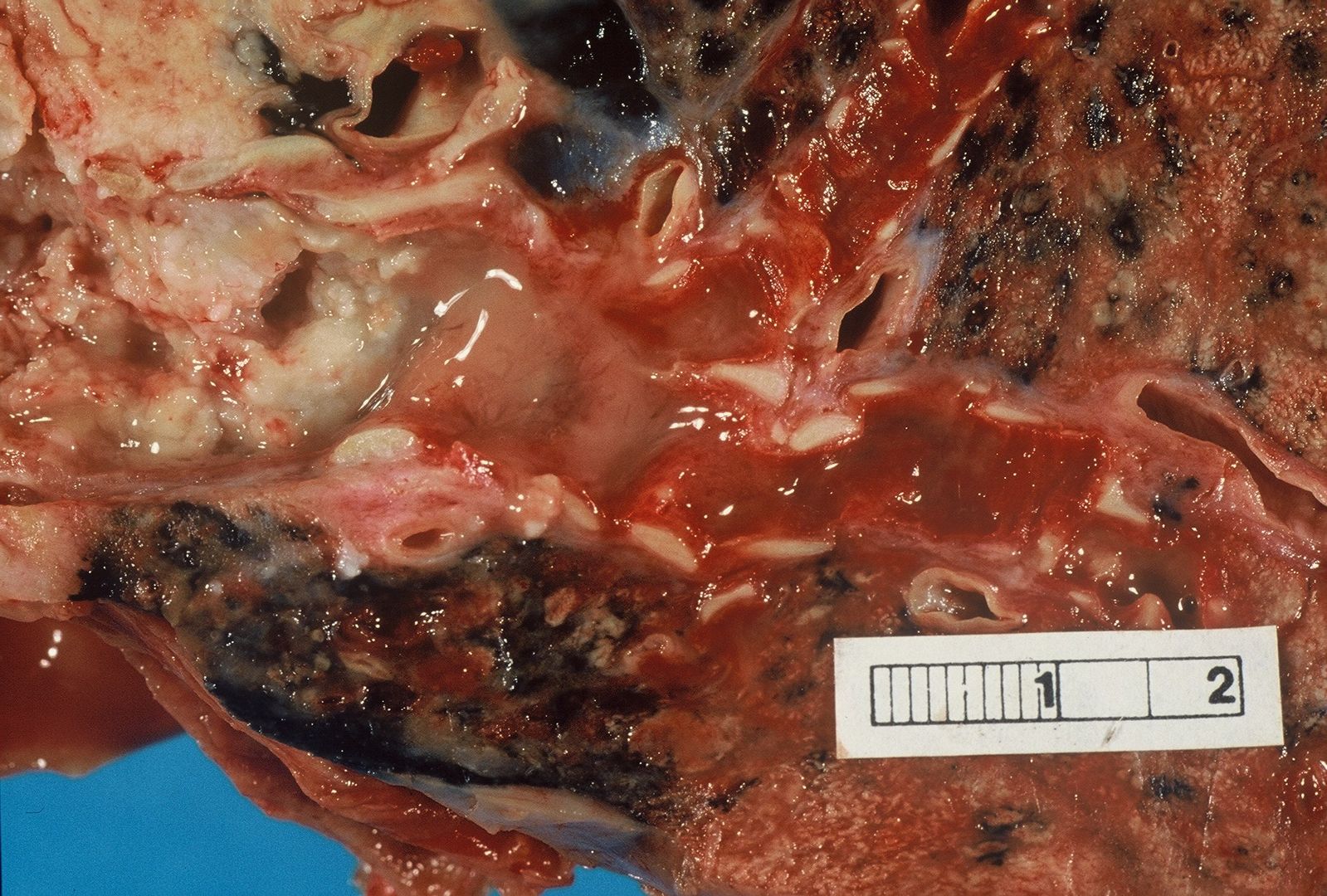
| | [[Image:Bronchial cancer.jpeg|x200px|thumb|Gross pathology: Bronchial squamous lung cell cancer By John Hayman [Public domain], (Image source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACa_bronchus.jpg Wikimedia Commons])]] |
| * Multi-layered wall and well-defined margins
| | |} |
| * [[Anechoic]] [[cyst]] if considerable central fluid present
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Endoscopic ultrasound]]-guided [[Needle aspiration biopsy|FNA]] | |
| * Atypical in appearance for [[Enteric duplication cysts|duplication cysts]]
| |
| * [[Cancer|Malignancy]] suspicion
| |
| [[Endoscopy]]
| |
| * Indistinguishable from a [[lipoma]], [[leiomyoma]], a [[gastrointestinal stromal tumor]] (GIST), or other [[Submucosal|submucosal lesions]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Thymic cyst]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215" /><ref name="KondovKondov2017">{{cite journal|last1=Kondov|first1=Goran|last2=Kondov|first2=Borislav|last3=Srceva|first3=Marija Jovanovska|last4=Damjanovski|first4=Goge|last5=Ferati|first5=Imran|last6=Karapetrov|first6=Ivan|last7=Topuzovska|first7=Irena Kondova|last8=Tanevska|first8=Nikolina|last9=Kokareva|first9=Anita|title=Giant Mediastinal Thymic Cyst|journal=PRILOZI|volume=38|issue=2|year=2017|pages=139–145|issn=1857-8985|doi=10.1515/prilozi-2017-0032}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Congenital
| |
| * Unilocular
| |
| Acquired
| |
| * Multilocular associated with:
| |
| ** [[Teratoma]]
| |
| ** [[Lymphoma]]
| |
| ** [[Thymic carcinoma]]
| |
| ** [[Autoimmune disorders]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * Asymptomatic
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | + | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Biopsy]] with [[histopathology]] and [[Cell biology|cytology]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |CT scan: | |
| * Oval shape
| |
| * Smooth contour
| |
| * Midline location
| |
| * Calcified
| |
| * Septate cyst
| |
| * Fluid attenuation
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Mediastinal neuroenteric cyst|Mediastinal neurenteric cyst]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215" /><ref name="SettyHegde2005">{{cite journal|last1=Setty|first1=HAN|last2=Hegde|first2=KKS|last3=Narvekar|first3=VN|title=Neurenteric cyst of the posterior mediastinum|journal=Australasian Radiology|volume=49|issue=2|year=2005|pages=151–153|issn=0004-8461|doi=10.1111/j.1440-1673.2005.01360.x}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Developmental abnormality|Developmental foregut anomaly]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Neurological disorder|Neurologic impairment]]
| |
| ** [[Back pain]]
| |
| ** [[Gait abnormality|Gait disturbance]]
| |
| ** [[Sensory|Sensory deficit]]
| |
| ** [[Motor neuron disease|Motor deficit]]
| |
| * [[Stridor]]
| |
| * [[Cough|Persistent cough]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]:
| |
| * [[Cyst|Cystic]] nature of the [[Tumor|mass]]
| |
| * Extent of the [[Tumor|mass]]
| |
| * [[Congenital anomalies of spine|Vertebral anomalies]]
| |
|
| |
|
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| | {| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Postnatal]] [[chest X-ray]]:
| |
| * [[Posterior mediastinum|Posterior mediastinal]] [[Tumor|mass]] with associated [[Congenital anomalies of spine|vertebral anomalies]]
| |
| [[Ultrasound]]:
| |
| * [[Cyst|Cystic]] nature of the [[Tumor|mass]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Lymphangioma]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215" /><ref name="pmid3706240">{{cite journal |vauthors=Carr RF, Ochs RH, Ritter DA, Kenny JD, Fridey JL, Ming PM |title=Fetal cystic hygroma and Turner's syndrome |journal=Am. J. Dis. Child. |volume=140 |issue=6 |pages=580–3 |date=June 1986 |pmid=3706240 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Turner syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Down syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Noonan syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Chronic (medical)|Chronic]] [[lymphatic obstruction]] such as after [[surgery]], [[Infection|infections]] or [[radiotherapy]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Constipation]]
| |
| * [[Failure to thrive]]
| |
| * Signs and symptoms of genetic defects
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Histopathology]] and [[Cell biology|cytology]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| MRI:
| |
| * Degree of involvement and extent of lesion
| |
| * MRI can prevent extensive, incomplete surgical resection
| |
| CT scan:
| |
| * [[Homogenization|Homogeneous]], [[cystic]] [[Tumor|mass]]
| |
| * Intrinsic [[Septa|septations]]
| |
| * Compression of adjacent organs
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Pancreatic pseudocyst]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215" /><ref name="EltaEnestvedt2018">{{cite journal|last1=Elta|first1=Grace H|last2=Enestvedt|first2=Brintha K|last3=Sauer|first3=Bryan G|last4=Marie Lennon|first4=Anne|title=ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts|journal=The American Journal of Gastroenterology|volume=113|issue=4|year=2018|pages=464–479|issn=0002-9270|doi=10.1038/ajg.2018.14}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Acute pancreatitis]]
| |
| * [[Chronic pancreatitis]]
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal pain]] - constant pain or deep ache in the abdomen, which may also be felt in the back
| |
| * [[Abdominal mass]]
| |
| * [[Bloating]] of the abdomen
| |
| * Difficulty eating and digesting food
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Histopathology]] and [[Cell biology|cytology]] of cyst and fluid content
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]
| |
| * Thin-walled
| |
| * Fluid-containing cyst within the posterior mediastinum
| |
| * In continuity with the intrapancreatic or peripancreatic fluid collections
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="9" style="background: #707070; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Chronic inflammatory disease'''
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Churg-Strauss syndrome|'''Churg-Strauss syndrome''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid14740430">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hellmich B, Ehlers S, Csernok E, Gross WL |title=Update on the pathogenesis of Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. |volume=21 |issue=6 Suppl 32 |pages=S69–77 |date=2003 |pmid=14740430 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid29240526">{{cite journal |vauthors=Safran T, Masckauchan M, Maj J, Green L |title=Wells syndrome secondary to influenza vaccination: A case report and review of the literature |journal=Hum Vaccin Immunother |volume= |issue= |pages=1–3 |date=December 2017 |pmid=29240526 |doi=10.1080/21645515.2017.1417714 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Human leukocyte antigen|HLA]]-DRB1*04 and *07
| |
| * [[Human leukocyte antigen|HLA]] - DRB4
| |
| * [[Allergen|Allergens]]
| |
| * [[Infection|Infections]]
| |
| * [[Vaccination|Vaccinations]] (eg, [[influenza]])
| |
| * [[:Category:Drugs|Drugs]]:
| |
| ** [[Leukotriene antagonist|Leukotriene receptor antagonists]]/ leukotriene modifying agents
| |
| ** Anti [[Immunoglobulin E|IgE]] [[antibodies]] (eg, [[omalizumab]])
| |
| ** [[Mesalazine]]
| |
| ** [[Propylthiouracil]]
| |
| ** [[Methimazole]]
| |
| ** [[Silica|Exposure to silica]]
| |
| ** [[Cocaine]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Lung]] [[biopsy]]
| |
| | |
| 4 out of 6 positive :
| |
| * [[Asthma]]
| |
| * [[Eosinophilia]]
| |
| * [[Polyneuropathy]] or [[Mononeuropathy]]
| |
| * Non fixed pulmonary infiltrates
| |
| * [[Paranasal sinus]] that is abnormal
| |
| * [[Eosinophil granulocyte|Eosinophils]] that are extravascular
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
|
| |
|
| [[High-resolution CT|High-resolution computerized tomography]] ([[High Resolution CT|HRCT]]):
| |
| * [[Alveolar lung disease|Airspace]] consolidations mostly bilateral and [[Lobe (anatomy)|lobular]]
| |
| * [[Ground glass opacification on CT|Ground-glass opacities]] in a patchy or [[subpleural]] distribution
| |
| * [[Centrilobular]] [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]]
| |
| * [[Bronchial wall]] thickening and/or dilatation
| |
| * [[Pleural effusion|Pleural effusions]]
| |
| * Hilar or [[mediastinal lymph node]] enlargement
| |
| * Interlobular septal thickening
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Dyspnea/'''
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Dysphagia'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''SVCS'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="9" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Posterior mediastinal mass
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="9" style="background: #707070; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Central nervous system disease
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Meningocele]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Neurilemmoma]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="10" |'''<small>ABBREVIATIONS''': '''N/A''': Not available, '''SOB''': Shortness of breath, '''M/C''': Most common, '''RI''': Respiratory insufficiency, '''NM''': Neuromuscular system, '''SVCS''': Superior vena cava syndrome, '''SLE''': Systemic lupus erythematosus disease, '''T3:''' Triiodothyronine, '''T4:''' Thyroxine, '''TSH:''' Thyroid stimulating hormone, '''TFT:''' Thyroid function test</small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small>
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] | | # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] |
| Line 277: |
Line 47: |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
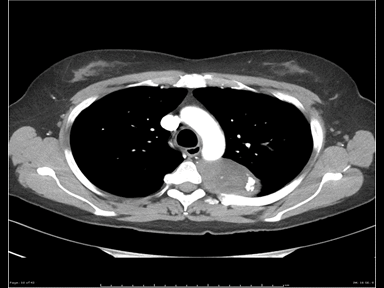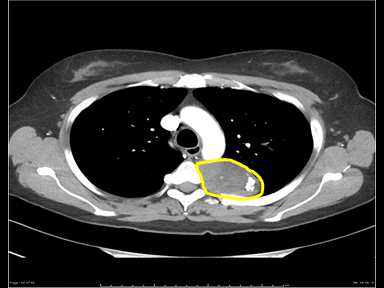
| [[File: name|x300px|thumb| CT scan showing a smooth anterior mediastinal mass, with a mixed internal density of containing both enhancing soft tissue and cystic areas. The outline of the mass is relatively well defined. No lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion or infiltration. Case courtesy of Dr. Abdallah Al Khateeb | | [[File:Mediastinal lymohangioma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows cystic mass which was located on the posterior to the lower esophagus later diagnosed as thoracic duct lymphangioma. [https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.423 Source:Case courtesy of Jin San Bok et al, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital]]] |
| (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/43403 Radiopedia])]] | | |
| | |
| | [[File:Posterior-mediastinal-schwannoma.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a soft tissue density lesion within the left posterior mediastinum, in a paravertebral location. The lesion is closely related to the left neural exit foramen, but there is no definite extension into the spinal canal. The lesion does extend into the intercostal space. |
| | Case courtesy of Dr Paul Leong |
| | (Picture courtesy:[https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26625 Radiopedia])]] |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{SI}} |
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Trusha}}, {{AM}} |
| | |
| | {{SK}} Mediastinal enlargement; mass in the mediastinum |
| | |
| | ==Overview== |
| | |
| | The [[mediastinum]] is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax (chest), surrounded by loose connective tissue. Since it is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, and it contains a lot of important structures, it is the site of involvement of various tumors. |
| | |
| | ==Causes== |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | ==Initial Evaluation== |
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | {{Family tree |border=2|boxstyle=background: WhiteSmoke;| | | | | A01 | | | | |A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 25em; padding: 1em;">'''Mediastinal Mass'''</div>}} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; padding: 1em; "> '''Workups''' |
| | ---- |
| | ❑ CT chest with contrast <br> ❑ Serum beta-HCG, AFP, if appropriate <br> ❑ CBC, platelets <br> ❑ PET-CT scan (optional) <br> ❑ Pulmonary function tests if clinically indicated <br> ❑ MRI chest if clinically indicated |
| | </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |,|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | C01 | | | | | | C02 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Likely''' </div> |C02= <div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Unlikely''' </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | }} |
| | |
| | {{familytree | D01 | | | | | | D02 | | | |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Consider [[Thymoma surgery|surgery]]</div>|D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Disease-specific management</div>}} |
|
| |
|
| | {{familytree/start}} |
|
| |
|
| [[File: name|x300px|thumb| CT scan showing excessive fatty tissue deposition within the posterior mediastinum with anterior displacement of the esophagus. Case courtesy of Dr. Ahmed Abdrabou (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/50447Radiopedia])]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |