|
|
| (98 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
|
| |
|
| I{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}}
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==new== |
|
| |
|
| ==Differential diagnosis of mediastinal mass==
| |
| Wide variety of medical conditions can present as a mediastinal mass on [[Radiology|radiological imaging]].
| |
| * Mediastinal mass may cause [[obstruction]], [[entrapment]] or [[Infiltration (medical)|infiltration]] of other [[Mediastinum|mediastinal organs]] such as: [[Trachea]], [[Bronchus|bronchi]], [[esophagus]], [[aorta]], [[SVC|superior vena cava (SVC)]] or [[heart]].<ref name="pmid27698718">{{cite journal |vauthors=Zardi EM, Pipita ME, Afeltra A |title=Mediastinal syndrome: A report of three cases |journal=Exp Ther Med |volume=12 |issue=4 |pages=2237–2240 |date=October 2016 |pmid=27698718 |pmc=5038184 |doi=10.3892/etm.2016.3596 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * Disorder caused by any kind of [[mediastinal mass]] is collectively known as: [[Mediastinal syndromes]]
| |
| * '''Mediastinal syndrome''' includes:
| |
| ** Compression of the [[trachea]]: [[Dyspnea]] and [[respiratory insufficiency]].
| |
| ** Compression of the [[esophagus]]: [[Dysphagia]].
| |
| ** Compression of [[SVC]] causes [[superior vena cava syndrome]]: [[Vein]] distention, [[edema]] of the face or [[Upper limb|upper extremities]] and a positive [[Pemberton's sign]].
| |
| *** [[Pemberton's sign]]: Development of suffusion, [[plethora]], or duskiness upon elevation of the arms above the head in patient
| |
| *** [[Superior vena cava syndrome]] is the most severe [[Complication (medicine)|complication]] of [[mediastinal syndrome]] and a [[medical emergency]].
| |
|
| |
|
| {|
| |
| | colspan="10" |'''<small>ABBREVIATIONS''': '''N/A''': Not available, '''SOB''': Shortness of breath, '''M/C''': Most common, '''RI''': Respiratory insufficiency, '''NM''': Neuromuscular system, '''SVCS''': Superior vena cava syndrome, '''SLE''': Systemic lupus erythematosus disease, '''T3:''' Triiodothyronine, '''T4:''' Thyroxine, '''TSH:''' Thyroid stimulating hormone, '''TFT:''' Thyroid function test</small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small>
| |
| |-
| |
| ! rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Class'''
| |
| ! rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! colspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Clinical presentation
| |
| ! colspan="3" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Paraclinical findings
| |
| |-
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''General symptoms'''
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Mediastinal syndrome
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="10" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Anterior mediastinal mass
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="6" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |'''Tumors'''
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Thymoma|'''Thymoma''']]
| |
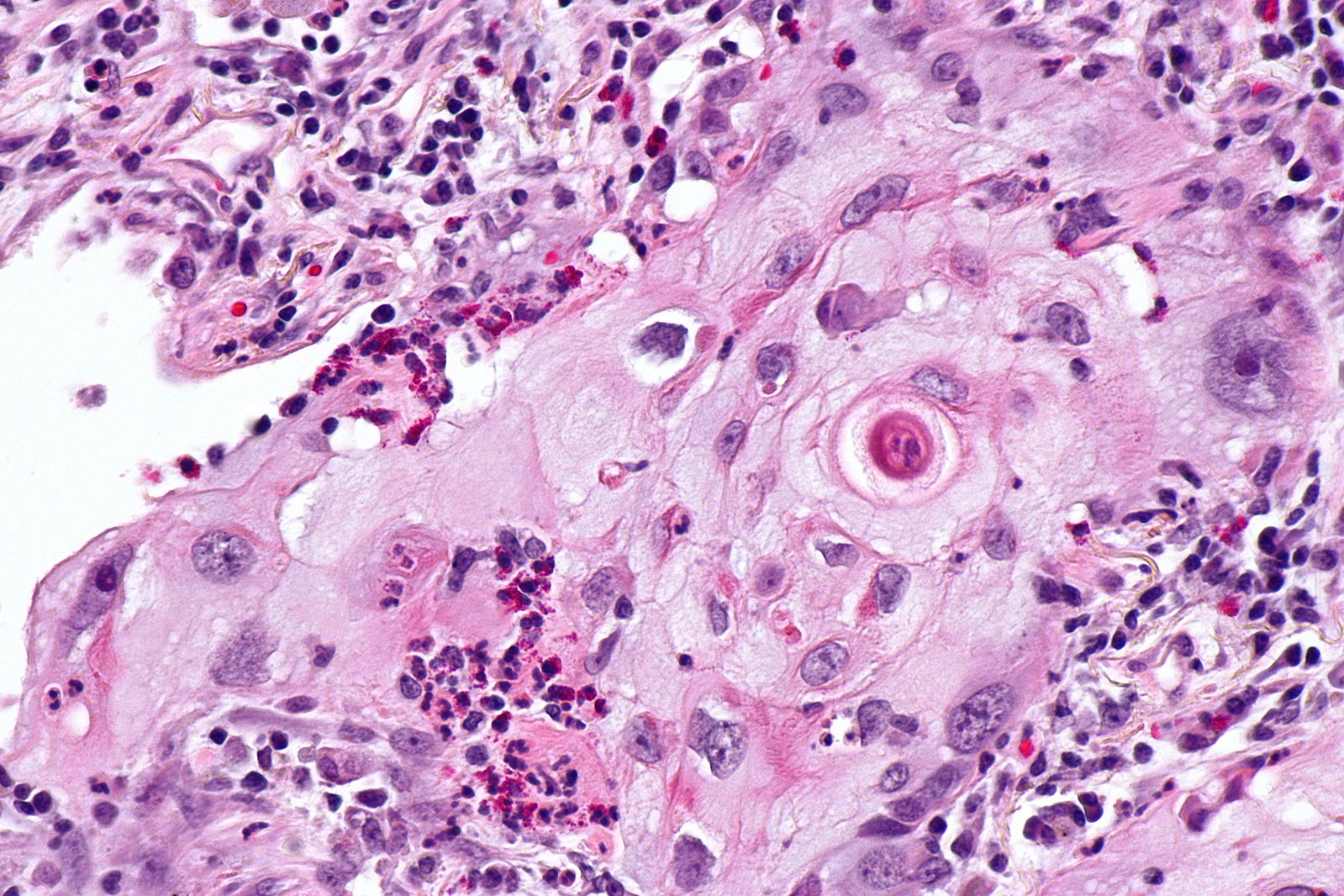
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Human foamy virus]]
| |
| * [[Epstein-Barr virus]]
| |
| * Human T-cell lymphotropic virus
| |
| * [[MEN 1 syndrome]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[wheezing]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Muscle weakness]] ([[Myasthenia gravis|MG]])
| |
| * [[Anemia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Biopsy]]:
| |
| * [[Epithelium|Epithelial cells]]
| |
| * [[Lymphoblasts|Immature lymphocytes]]
| |
| * Immature T cells
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |'''Associated condition'''
| |
| * NM
| |
| ** [[Myasthenia gravis]]
| |
| ** [[Neuromyotonia]]
| |
| ** [[Rippling muscle disease]]
| |
| ** [[Polymyositis and dermatomyositis|Polymyositis/dermatomyositis]]
| |
| ** [[Encephalitis]] (limbic, cortical and brain stem)
| |
| ** [[Intestinal pseudoobstruction]]
| |
| * Hematological
| |
| ** [[Anemia]]: [[pure red cell aplasia]], [[pernicious anemia]], [[hemolytic anemia]], [[aplastic anemia]]
| |
| ** Other isolated [[Cytopenia|cytopenias]]: [[eosinophils]], [[basophils]] [[neutrophils]]
| |
| ** Immunodeficiencies: [[Hypogammaglobulinaemia|hypogammaglobulinemia]]/- T-cell deficiencies [[Good syndrome|(Good syndrome)]]
| |
| * Dermatological
| |
| ** [[Pemphigus]] ([[Pemphigus foliaceus|foliaceus]] or [[Paraneoplastic syndrome|paraneoplastic]])
| |
| ** [[Lichen planus]]
| |
| ** [[Alopecia areata]]
| |
| * Endocrine
| |
| ** [[Addison's disease|Addison disease]]
| |
| ** [[Graves' disease|Grave's disease]]
| |
| ** [[Cushing's disease]]
| |
| * Hepato-renal
| |
| ** [[Glomerulonephritis]]
| |
| ** [[Autoimmune hepatitis]]
| |
| * Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
| |
| ** [[SLE]]
| |
| ** [[Sjögren's syndrome]]
| |
| ** [[Systemic sclerosis]]
| |
| ** [[Graft-versus-host disease]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''Fatty mass'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22021525">{{cite journal |vauthors=Molinari F, Bankier AA, Eisenberg RL |title=Fat-containing lesions in adult thoracic imaging |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=197 |issue=5 |pages=W795–813 |date=November 2011 |pmid=22021525 |doi=10.2214/AJR.11.6932 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Steroid use
| |
| * Cushing's syndrome
| |
| * Obeses
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Mostly asymptomatic
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |MRI:
| |
| * Well-defined encapsulated mas
| |
| * Extensive fat content
| |
| * Small amounts of solid areas
| |
| * Fibrous septa
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Fatty mass can be:
| |
| * Lipoma
| |
| * Liposarcoma
| |
| * Thymolipoma
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma|'''Non-Hodgkin lymphoma''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26174528">{{cite journal| author=Sandlund JT| title=Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children. | journal=Curr Hematol Malig Rep | year= 2015 | volume= 10 | issue= 3 | pages= 237-43 | pmid=26174528 | doi=10.1007/s11899-015-0277-y | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26174528 }}</ref><ref name="pmid28153383">{{cite journal| author=Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F| title=Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. | journal=Lancet | year= 2017 | volume= 390 | issue= 10091 | pages= 298-310 | pmid=28153383 | doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32407-2 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28153383 }}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Age (above 60 years)
| |
| * Caucasians > African and Asian Americans
| |
| * Positive family history of first degree relative
| |
| * B-cell activating autoimmune disorders
| |
| * Radiation exposure
| |
| * Infections
| |
| (HIV, Hep C, HTLV-1, EBV, HHV-8, H. pylori, psittacosis, Campylobacter jejuni)
| |
| * Previous cancer treatment
| |
| * Exposure to chemicals and drugs
| |
| (pesticides, methotrexate, TNF inhibitors, trichloroethylene)
| |
| * Cigarette smoking for ≥ 40 years
| |
| * BMI ≥30 kg/m2
| |
| * Diet
| |
| * Hair dyes
| |
| * Breast implants
| |
|
| |
|
| *
| | {| align="right" |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | | |
| * Painless [[lymphadenopathy]]
| | [[Image:Squamous cell mircopathology2.jpeg|x200px|thumb| Micropathology: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. H&E stain, By Nephron [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ALung_squamous_carcinoma_--_high_mag.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] |
| * [[Fever]]
| | |} |
| * [[Weight loss]] and [[Anorexia (symptom)|anorexia]]
| | {| align="right" |
| * [[Night sweats]]
| | | |
| * Constant [[Fatigue (physical)|fatigue]]
| | [[Image:Bronchial cancer.jpeg|x200px|thumb|Gross pathology: Bronchial squamous lung cell cancer By John Hayman [Public domain], (Image source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACa_bronchus.jpg Wikimedia Commons])]] |
| * [[Pruritis|Itchy skin]]
| | |} |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Shortness of breath]]
| |
| * [[Abdominal pain]] or swelling
| |
| * [[Constipation]]
| |
| * [[Nausea]]
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
| * [[Headache]]
| |
| * Personality changes
| |
| * [[Seizures]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/- | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/- | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Excisional lymph node biopsy with immunohistochemical study
| |
| * CD 20+ cells
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * [[Anemia|Anemia:]]
| |
| **Involvement of [[bone marrow]]
| |
| **[[Autoimmune hemolytic anemia|Autoimmune hemolysis]] and [[bleeding]]
| |
|
| |
|
| * [[Thrombocytopenia]], [[leukopenia]], or [[pancytopenia]]
| | {| |
| * [[Lymphocytosis]] with [[malignant]] cell
| |
| * [[Thrombocytosis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Teratoma|'''Teratoma''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24426558">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yalagachin GH |title=Anterior mediastinal teratoma- a case report with review of literature |journal=Indian J Surg |volume=75 |issue=Suppl 1 |pages=182–4 |date=June 2013 |pmid=24426558 |doi=10.1007/s12262-012-0569-6 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26251691">{{cite journal |vauthors=No TH, Seol SH, Seo GW, Kim DI, Yang SY, Jeong CH, Hwang YH, Kim JY |title=Benign Mature Teratoma in Anterior Mediastinum |journal=J Clin Med Res |volume=7 |issue=9 |pages=726–8 |date=September 2015 |pmid=26251691 |pmc=4522994 |doi=10.14740/jocmr2270w |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Benign equal in men and women
| |
| * Malignant more common in men
| |
| * Pediatric population higher risk
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Benign
| |
| * Asymptomatic
| |
| Malignant
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Trichoptysis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Chest CT scan:
| |
| * Location
| |
| * Metastasis
| |
| * Intrinsic structure
| |
| * Soft tissue
| |
| * Fat
| |
| * Calcification
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |N/A
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |'''Thyroid disease'''
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Thyroid cancer]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Hx of [[goiter]]
| |
| * Family Hx of thyroid disease
| |
| * Female gender
| |
| * Asian race
| |
| * [[Radiation exposure]]
| |
| * [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia|MEN syndrome]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Lump]] in the neck
| |
| * [[Dysphonia]]
| |
| * [[Lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Sore throat]]
| |
| * [[Neck pain]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |US guided biopsy:
| |
| * [[Papillary thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Follicular thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Medullary thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Anaplastic thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Primary thyroid lymphoma|Lymphoma]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Thyroid function tests|TFT]]
| |
| * Elevated [[Triiodothyronine|T3]]
| |
| * Elevated [[Thyroxine|T4]]
| |
| * Low [[Thyroid-stimulating hormone|TSH]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Goitre|'''Goiter''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlBenign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview">{{cite web |url=http://endocrinediseases.org/thyroid/goiter.shtml |title=Benign thyroid enlargement (non-toxic multinodular goiter): Overview |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Iodine]] deficiency
| |
| * Female gender
| |
| * Age over 50 years
| |
| * Personal or family history
| |
| * Certain medications
| |
| ** [[Immunosuppressant|Immunosuppressants]]
| |
| ** [[Antiretroviral|Antiretrovirals]]
| |
| ** [[Amiodarone]]
| |
| ** [[Lithium]]
| |
| * [[Radiation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * A visible swelling at the base of your neck
| |
| * Tight feeling in throat
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Hoarseness]]
| |
| * [[Fatigue]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Radioactive iodine scan:
| |
| * Nodules
| |
| * Size
| |
| * Function of the gland: ↑ or ↓
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Hyperavtive gland (hyperthyroid):
| |
| * Grave's disease
| |
| Hypoactive gland (hypothyroid):
| |
| * Hashimoto thyroiditis
| |
| Normal functioning gland (euthyroid):
| |
| * Benign thyroid enlargement (non toxic multinodular goiter)
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Class'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="10" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Middle mediastinal mass
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="5" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |'''CVS disease'''
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pericardial effusion|'''Pericardial effusion''']]
| |
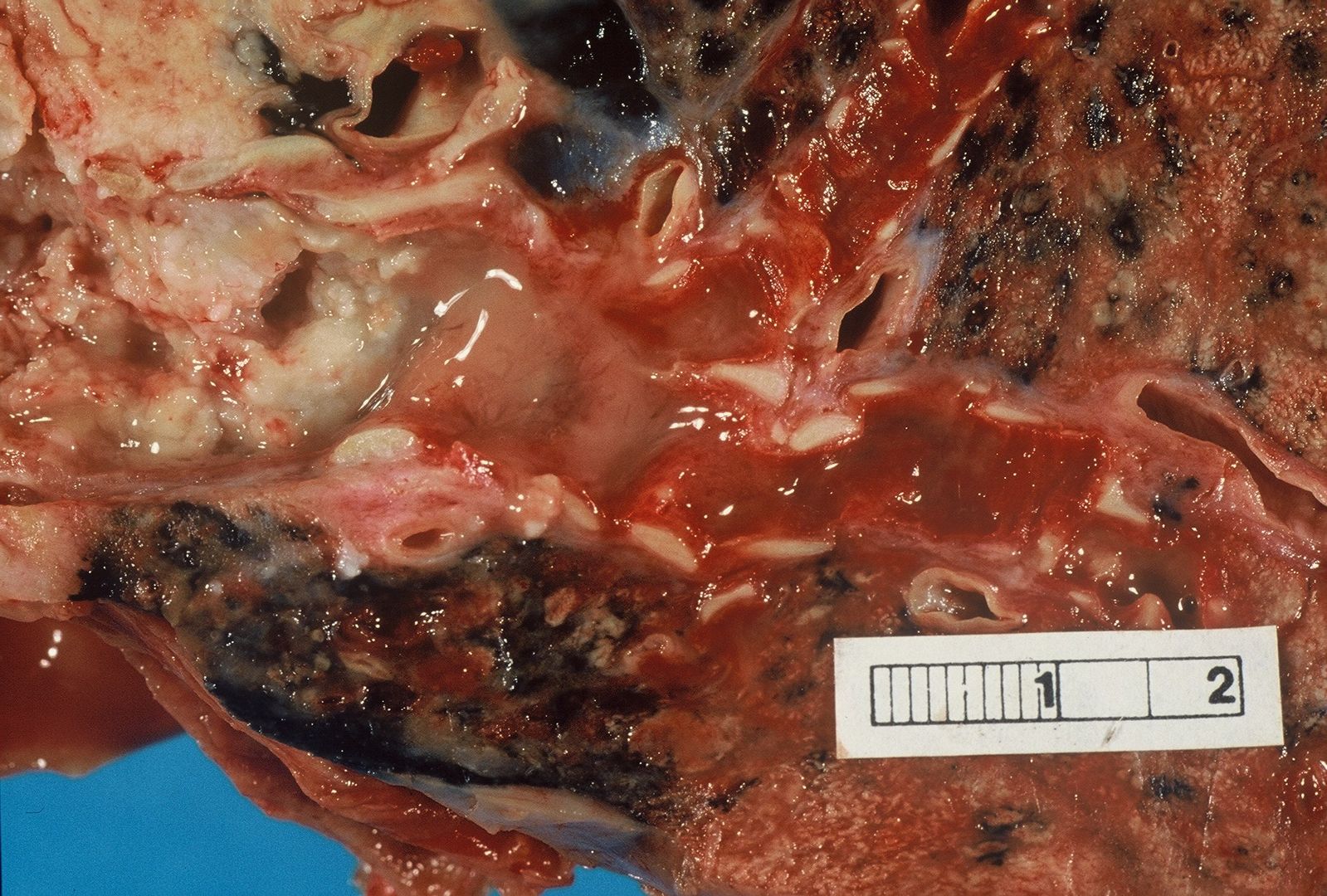
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26317273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Vanneman MW, Fikry K, Quraishi SA, Schoenfeld W |title=A Young Man with a Mediastinal Mass and Sudden Cardiac Arrest |journal=Ann Am Thorac Soc |volume=12 |issue=8 |pages=1235–9 |date=August 2015 |pmid=26317273 |doi=10.1513/AnnalsATS.201504-212CC |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid10579740">{{cite journal |vauthors=Salem K, Mulji A, Lonn E |title=Echocardiographically guided pericardiocentesis - the gold standard for the management of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade |journal=Can J Cardiol |volume=15 |issue=11 |pages=1251–5 |date=November 1999 |pmid=10579740 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Acute myocardial infarction]]
| |
| * [[Aortic dissection]]
| |
| * [[Aortic rupture]]
| |
| * [[Myocardial rupture]]
| |
| * [[Ventricular aneurysm|Rupture of ventricular aneurysm]]
| |
| * [[Uremic pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Rheumatic fever|Rheumatic pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Tuberculous pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Uremic pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Pericarditis|Viral pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Dressler's syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Cardiac catheterization]]
| |
| * [[Cardiomyopathy]]
| |
| * [[Chemotherapy]]
| |
| * [[Chest trauma]]
| |
| * [[Collagen vascular disease]]
| |
| * [[Congestive heart failure]]
| |
| * [[Neoplasm]]
| |
| * [[Postpericardiotomy syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Radiation injury|Postirradiation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * The positional change affecting the [[chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Orthopnea]]
| |
| * [[Fever]]
| |
| * symptoms of [[infection]], [[injury]] or systemic disease causing the [[Pericardial effusion|effusion]]
| |
| | |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | +/-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Echocardiography]] guided [[pericardiocentesis]]:
| |
| * [[Therapy|Therapeutic]]
| |
| * [[Diagnostic]]
| |
| * [[Pericarditis|pericardial disease]]
| |
| * [[Hemodynamic]] parameters
| |
| * Volume
| |
| * Effusion content
| |
| ([[blood]]/[[exudate]]/[[transudate]])
| |
| * [[Microbial culture]]
| |
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Physical findings:
| |
| * [[Pulsus paradoxus]]
| |
| * [[Hypotension]] in [[cardiac tamponade]]
| |
| * [[Jugular venous distension]] with a prominent Y descent
| |
| * [[Kussmaul's sign]]
| |
| EKG:
| |
| * [[Electrical alternans]]
| |
| Echo:
| |
| * Presence of effusion
| |
| * Reversal of [[Right atrium|RA]] and [[Right ventricle|RV]] [[Diastole|diastolic]] trans-mural pressures
| |
| * [[Heart|Cardiac chamber]] indentation or [[Collapse (medical)|collapse]]
| |
| * [[Respiratory]] variation of [[Heart valve|atrioventricular valves]] increased.
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Aortic dissection]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15121626">{{cite journal| author=Weissmann-Brenner A, Schoen R, Divon MY| title=Aortic dissection in pregnancy. | journal=Obstet Gynecol | year= 2004 | volume= 103 | issue= 5 Pt 2 | pages= 1110-3 | pmid=15121626 | doi=10.1097/01.AOG.0000124984.82336.43 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15121626 }}</ref><ref name="pmid22829842">{{cite journal| author=Brooke V, Goswami S, Mohanty A, Kasi PM| title=Aortic dissection and renal failure in a patient with severe hypothyroidism. | journal=Case Rep Med | year= 2012 | volume= 2012 | issue= | pages= 842562 | pmid=22829842 | doi=10.1155/2012/842562 | pmc=PMC3399550 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=22829842 }}</ref><ref name="pmid2062514">{{cite journal| author=| title=Classification of diabetic retinopathy from fluorescein angiograms. ETDRS report number 11. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. | journal=Ophthalmology | year= 1991 | volume= 98 | issue= 5 Suppl | pages= 807-22 | pmid=2062514 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2062514 }}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| *[[Atherosclerosis]]
| |
| *[[Chest trauma]]
| |
| | |
| * [[Chronic hypertension]]
| |
| * [[Iatrogenic|Complication of cardiac procedures]]
| |
| | |
| *[[Connective tissue disorders]]
| |
| *[[Vasculitis]]
| |
| *Advanced age
| |
| *[[Smoking]]
| |
| *[[Lipoprotein disorders|Dyslipidaemia]]
| |
| *[[Cocaine]]
| |
| *[[Connective tissue disease|Connective tissue disorders]]
| |
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Severe acute [[chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Back pain]]
| |
| * Pain radiating to neck, throat, jaw, and/or unilateral face
| |
| | |
| * [[Abdominal pain]]
| |
| * [[Claudication]]
| |
| * [[Hemoptysis]]
| |
| * [[Horner syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Oliguria]]/ [[Anuria]]
| |
| * [[Paraplegia]], [[paralysis]]
| |
| * [[Hoarseness]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +/-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]]:
| |
| * Location of the [[Intima|intimal]] tear
| |
| * Involvement of branches of [[aorta]]
| |
| * Other vascular pathology
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)|TEE]]:
| |
| * Identify true and [[False lumen|false lumens]]
| |
| * [[Intima|Intimal]] flap
| |
| * [[Thrombosis]] in the [[false lumen]]
| |
| * [[Pericardial effusion]]
| |
| * [[AI|Aortic regurgitation]]
| |
| * [[Proximal]] [[Coronary artery|coronaries]]
| |
| [[CT angiography|CTA]]:
| |
| * Beak sign: An [[acute]] angle between the dissection flap and the [[Artery|arterial]] wall
| |
| * [[Aortic]] cobwebs: Fibroelastic bands
| |
| * Size: [[False lumen]] larger than the true [[lumen]]
| |
| * Displaced [[Intima|intimal]] [[calcification]]: True lumen
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Superior vena cava obstruction]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16502166">{{cite journal |vauthors=Uberoi R |title=Quality assurance guidelines for superior vena cava stenting in malignant disease |journal=Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=319–22 |year=2006 |pmid=16502166 |doi=10.1007/s00270-005-0284-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22477372">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cohen R, Mena D, Carbajal-Mendoza R, Matos N, Karki N |title=Superior vena cava syndrome: A medical emergency? |journal=Int. J. Angiol. |volume=17 |issue=1 |pages=43–6 |date=2008 |pmid=22477372 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Compression of [[SVC]] from:
| |
| * [[Aortic aneurysm]]
| |
| * [[Bronchogenic carcinoma]]
| |
| * [[Breast cancer]]
| |
| * [[Cystic hygroma]]
| |
| * [[Goiter]]
| |
| * [[Histoplasmosis]]
| |
| * [[Central venous catheter|Indwelling catheter]]
| |
| * [[Lung cancer]]
| |
| * [[Lymphoma]]
| |
| * [[Non Hodgkin's lymphoma]]
| |
| * [[Small cell lung cancer]]
| |
| * [[Thymoma]]
| |
| * [[Tuberculosis]]
| |
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| | |
| * [[Hoarseness]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * Problems [[swallowing]] and/or talking
| |
| * [[Hemoptysis]]
| |
| * [[Headache]]
| |
| * [[Lightheadedness|Dizziness]]
| |
| * [[Decreased alertness]]
| |
| * [[Dizziness]]
| |
| * [[Fainting]]
| |
| * Sensation of [[head]] or [[ear]] "fullness"
| |
| * Vision changes
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | ++
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|Contrast-enhanced CT scan:]]
| |
| * Location and severity of the [[obstruction]]
| |
| * Superimposed [[thrombosis]]
| |
| * Mediastinal mass or [[lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| * Collateral vessels and associated lung masses
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Invasive [[contrast]] [[venography]]:
| |
| * Etiology of obstruction
| |
| * Exact location of the obstruction
| |
| | |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22837866">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sears EH, Aliotta JM, Klinger JR |title=Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return presenting with adult-onset pulmonary hypertension |journal=Pulm Circ |volume=2 |issue=2 |pages=250–5 |date=2012 |pmid=22837866 |pmc=3401879 |doi=10.4103/2045-8932.97637 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18595412">{{cite journal |vauthors=Broy C, Bennett S |title=Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return |journal=Mil Med |volume=173 |issue=6 |pages=523–4 |date=June 2008 |pmid=18595412 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Uncommon [[congenital abnormality]]
| |
| * Associated with an [[Atrial septal defect|ASD]]
| |
| * [[Turner's syndrome|Turner's syndrome (monosomy X)]]
| |
| * The [[scimitar syndrome]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Asymptomatic]]
| |
| * Episodic exertional [[dizziness]]
| |
| * Neck pain
| |
| * [[Diaphoresis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI with contrast]]:
| |
| * Provide better anatomic definition
| |
| * Associated defects
| |
| * Condition of heart chambers
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Associated with
| |
| * Adult onset [[Pulmonary hypertension|pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)]]
| |
| * [[Right ventricle|Right ventricular]] [[volume overload]] ([[Right heart failure|RV failure)]]
| |
| [[Cardiac catheterization|Cardiac catheter]]:
| |
| * Pressure and [[Oxygen saturation|O2 Sat]] in heart chambers
| |
| [[Spirometry|PFT]]:
| |
| * Normal despite of severe [[Dyspnea|SOB]]
| |
|
| |
|
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="5" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |GI disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Esophageal achalasia|'''Esophageal achalasia''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid22532812">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gockel I, Müller M, Schumacher J |title=Achalasia--a disease of unknown cause that is often diagnosed too late |journal=Dtsch Arztebl Int |volume=109 |issue=12 |pages=209–14 |year=2012 |pmid=22532812 |pmc=3329145 |doi=10.3238/arztebl.2012.0209 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22791940">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ghoshal UC, Daschakraborty SB, Singh R |title=Pathogenesis of achalasia cardia |journal=World J. Gastroenterol. |volume=18 |issue=24 |pages=3050–7 |year=2012 |pmid=22791940 |pmc=3386318 |doi=10.3748/wjg.v18.i24.3050 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26087861">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ates F, Vaezi MF |title=The Pathogenesis and Management of Achalasia: Current Status and Future Directions |journal=Gut Liver |volume=9 |issue=4 |pages=449–63 |year=2015 |pmid=26087861 |pmc=4477988 |doi=10.5009/gnl14446 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23871090">{{cite journal| author=Boeckxstaens GE, Zaninotto G, Richter JE| title=Achalasia. | journal=Lancet | year= 2013 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=23871090 | doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60651-0 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23871090 }}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| *[[Idiopathic]]
| |
| *[[Chagas disease ]]
| |
|
| |
| *[[Gastric carcinoma]]
| |
| *[[Herpes zoster]]
| |
| *[[HSV-1]]
| |
| *[[Measles virus]]
| |
| *[[Paraneoplastic syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Sarcoidosis ]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]] for solids and liquids of patients respectively
| |
| * [[Regurgitation]] of undigested food
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Aspiration]]
| |
| * [[Weight loss]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]], radiate to the back, jaw, neck, and arms
| |
| * [[Heartburn]]
| |
| * [[Hiccup]]
| |
| * Difficulty [[Burping|belching]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[High resolution manometry|High resolution manometry (HRM)]]:
| |
| * Residual pressure of LES > 10 mmHg
| |
| * Incomplete relaxation of the [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]].
| |
| * Increased resting tone of [[Lower esophageal sphincter|LES]]
| |
| * [[Aperistalsis]]
| |
| * High intra-esophageal pressure (due to stasis of food)
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[X-rays|X ray]]:
| |
| * "Bird's beak image" or "rat tail" appearance
| |
| * Dilated esophageal body
| |
| * Air fluid level due to absent [[peristalsis]]
| |
| * Absence of gastric air bubble
| |
| * In advanced achalasia - sigmoid appearance
| |
| [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]:
| |
| * Dilatation of the esophagus
| |
| * Air fluid levels
| |
| * Exclude [[pseudoachalasia]]
| |
| * Echalasia symptoms resulting from [[esophageal cancer]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Esophageal cancer|'''Esophageal cancer''']]
| |
| <ref>Corley DA, Kerlikowske K, Verma R, Buffler P. Protective association of aspirin/NSAIDs and esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ''Gastroenterology'' 2003;124:47-56. PMID 12512029. See also [http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/prevention/esophageal/healthprofessional#Section_57 NCI - "Esophageal Cancer (PDQ®): Prevention"].</ref><ref>Wong A, Fitzgerald RC. Epidemiologic risk factors for Barrett's esophagus and associated adenocarcinoma. ''Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.'' 2005 Jan;3(1):1-10. PMID 15645398</ref><ref>Ye W, Held M, Lagergren J, Engstrand L, Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Nyren O. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric atrophy: risk of adenocarcinoma and squamous-cell carcinoma of the esophagus and adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia. ''J Natl Cancer Inst.'' 2004 Mar 3;96(5):388-96. PMID 14996860</ref><ref>Nakajima S, Hattori T. Oesophageal adenocarcinoma or gastric cancer with or without eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in chronic atrophic gastritis patients: a hypothetical opinion from a systematic review. ''Aliment Pharmacol Ther.'' 2004 Jul;20 Suppl 1:54-61. PMID 15298606</ref><ref>NCI [http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/prevention/esophageal/healthprofessional#Section_57 Prevention: Dietary Factors], based on Chainani-Wu N. Diet and oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal cancer. ''Nutr Cancer'' 2002;44:104-26. PMID 12734057.</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Age over 60
| |
| * Male gender
| |
| * [[Smoking]]
| |
| * [[Alcohol]] consumption
| |
| * [[Obesity]]
| |
| * [[Lye]] Ingestion
| |
| * [[Nitrosamine]] in food
| |
| * [[Plummer-Vinson syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Tylosis]] or [[Howel-Evans syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Radiation therapy]]
| |
| * [[Gastroesophageal reflux disease|GERD]]
| |
| * [[Barrett's esophagus]]
| |
| * [[Achalasia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]] to solid food
| |
| * [[Heartburn]]
| |
| * [[Weight loss]]
| |
| * Changes in diet
| |
| * [[Anorexia]]
| |
|
| |
| * [[Regurgitation (digestion)|Regurgitation]] of food or saliva
| |
| * [[Dysphonia|Hoarseness]] or loss of voice
| |
| * Intractable [[cough]]
| |
| * [[Melena|Blood in stools]]
| |
| * Frequent [[pneumonia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Endoscopy]] with [[biopsy]]:
| |
| * Friable lesion
| |
| * Superficial [[Plaque|plaques]]
| |
| * Superfcial [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]]
| |
| * Superficial [[Ulcer|ulcerations]]
| |
| * [[Stenosis|Strictures]]
| |
| * [[Ulcer|Ulcerated]] mass
| |
| * Circumferential masses
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Esophagogram|Barium swallow]]:
| |
| * Tapering stricture known as a "rat's tail"
| |
| * Irregular stricture
| |
| * Pre-stricture dilatation
| |
| * Shouldering
| |
| [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]:
| |
| * Eccentric or circumferential wall thickening >5 mm
| |
| * Peri-[[esophageal]] [[soft tissue]] and [[fat]] stranding
| |
| * Dilated fluid and debris filling the esophageal lumen
| |
| * [[Tracheobronchial tree|Tracheobronchial]] invasion
| |
| * [[Aorta|Aortic]] invasion
| |
|
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Esophageal rupture|'''Esophageal rupture''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid1994204">{{cite journal |vauthors=McGovern M, Egerton MJ |title=Spontaneous perforation of the cervical oesophagus |journal=Med. J. Aust. |volume=154 |issue=4 |pages=277–8 |year=1991 |pmid=1994204 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid5112482">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wilson RF, Sarver EJ, Arbulu A, Sukhnandan R |title=Spontaneous perforation of the esophagus |journal=Ann. Thorac. Surg. |volume=12 |issue=3 |pages=291–6 |year=1971 |pmid=5112482 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
| <ref name="pmid3753071">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bladergroen MR, Lowe JE, Postlethwait RW |title=Diagnosis and recommended management of esophageal perforation and rupture |journal=Ann. Thorac. Surg. |volume=42 |issue=3 |pages=235–9 |year=1986 |pmid=3753071 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7089304">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dodds WJ, Stewart ET, Vlymen WJ |title=Appropriate contrast media for evaluation of esophageal disruption |journal=Radiology |volume=144 |issue=2 |pages=439–41 |year=1982 |pmid=7089304 |doi=10.1148/radiology.144.2.7089304 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid1126592">{{cite journal |vauthors=James AE, Montali RJ, Chaffee V, Strecker EP, Vessal K |title=Barium or gastrografin: which contrast media for diagnosis of esophageal tears? |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=68 |issue=5 Pt 1 |pages=1103–13 |year=1975 |pmid=1126592 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid1193339">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schwartz SS |title=Letter: Barium or gastrografin: which contrast media for diagnosis of esophageal tears? |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=69 |issue=6 |pages=1377 |year=1975 |pmid=1193339 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid1115308">{{cite journal |vauthors=Vessal K, Montali RJ, Larson SM, Chaffee V, James AE |title=Evaluation of barium and gastrografin as contrast media for the diagnosis of esophageal ruptures or perforations |journal=Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med |volume=123 |issue=2 |pages=307–19 |year=1975 |pmid=1115308 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Seizures]]
| |
|
| |
| * Severe straining
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
|
| |
| * [[Childbirth]]
| |
| * Prolonged [[coughing]] or laughing
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| [[Mackler's triad]]:
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
| * [[Subcutaneous emphysema]]
| |
| Other:
| |
| * [[Odynophagia]]
| |
| * [[Fever]]
| |
| * [[Tachypnea]]
| |
| * [[Tachycardia]]
| |
| * [[Cyanosis]], and [[hypotension]]
| |
| * [[Pleural effusion]]
| |
| Patients with [[cervical]] perforations can present with
| |
| * Neck pain
| |
| * [[Dysphonia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Esophagogram]]:
| |
| * The location
| |
| * Extent of [[perforation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]:
| |
| * Esophageal wall edema and thickening
| |
| * Peri-esophageal fluid
| |
| * [[Mediastinal widening]]
| |
| * Air and fluid in the [[Pleural space|pleural spaces]], [[retroperitoneum]], or [[lesser sac]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Hiatus hernia|'''Hiatus hernia''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid22320417">{{cite journal |vauthors=Khajanchee YS, Cassera MA, Swanström LL, Dunst CM |title=Diagnosis of Type-I hiatal hernia: a comparison of high-resolution manometry and endoscopy |journal=Dis. Esophagus |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=1–6 |date=January 2013 |pmid=22320417 |doi=10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01314.x |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24503366">{{cite journal| author=Chang P, Friedenberg F| title=Obesity and GERD. | journal=Gastroenterol Clin North Am | year= 2014 | volume= 43 | issue= 1 | pages= 161-73 | pmid=24503366 | doi=10.1016/j.gtc.2013.11.009 | pmc=3920303 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24503366 }}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * 50 or older age
| |
|
| |
| * [[Obesity]]
| |
| * Female > Male
| |
|
| |
| * [[Trauma]]: when undergoing [[surgery]]
| |
| * Frequent [[coughing]]
| |
| * Straining with [[constipation]]
| |
| * Heavy lifting
| |
| * [[Congenital]]
| |
| * [[Tobacco smoking|Smoking]]
| |
| * [[Stress (medicine)|Stress]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Nausea]]
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
| * [[Regurgitation]]
| |
|
| |
| * [[Heart burn]]
| |
| * [[Regurgitation]]
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[High resolution manometry]] with [[Esophageal pressure topography|esophageal pressure topography (EPT)]]:
| |
| * Evidence of separation of the [[Crural hernia|crural]] [[diaphragm]] from the [[lower esophageal sphincter]](LES)
| |
| * Real-time localization of the [[gastroesophageal junction]]
| |
| * Identification of intermittent [[herniation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Ultrasound]]:
| |
| * Location of [[gastroesophageal junction]]
| |
| * Bowel diameter measured at the diaphragmatic hiatus
| |
| [[Ultrasound]] in [[Pediatrics|pediatric]] population:
| |
| * Measurement of intra-abdominal [[esophagus]] which is less than 2 cm in diameter
| |
| * Sign of a beak at the [[gastroesophageal junction]]
| |
| [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]:
| |
| * [[Retrocardiac]] air-fluid level
| |
| * Organs within the [[Hernia|hernia sac]]
| |
|
| |
| * Focal [[fat]] collection in the middle of the [[mediastinum]]
| |
| * Visualise contents, length, orientation of [[Hernia|herniated]] [[stomach]] inside the lower [[thorax]]
| |
| * Herniated contents lie adjoining to the [[esophagus]]
| |
|
| |
| * Widening of [[esophageal hiatus]]
| |
| * [[Dehiscence]] of [[Diaphragm (anatomy)|diaphragmatic]] [[crura]] (>15 mm)
| |
|
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Class'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Pulmonary disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Hilar lymphadenopathy|'''Hilar lymphadenopathy''']]
| |
| <ref name="JashMaji2013">{{cite journal|last1=Jash|first1=Debraj|last2=Maji|first2=Arnab|last3=Patra|first3=Anupam|last4=Sarkar|first4=Supriya|title=Approach to unequal hilum on chest X-ray|journal=The Journal of Association of Chest Physicians|volume=1|issue=2|year=2013|pages=32|issn=2320-8775|doi=10.4103/2320-8775.123204}}</ref><ref name="pmid24753638">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid247536382">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohseni S, Shojaiefard A, Khorgami Z, Alinejad S, Ghorbani A, Ghafouri A |title=Peripheral lymphadenopathy: approach and diagnostic tools |journal=Iran J Med Sci |volume=39 |issue=2 Suppl |pages=158–70 |year=2014 |pmid=24753638 |pmc=3993046 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="radio">Lymph node enlargment. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymph-node-enlargement Accessed on May 9, 2016</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Lymphadenopathy]]:<nowiki/>
| |
| * [[Tuberculosis]]
| |
| * [[Tuberculosis|Tubercular]] [[hilar lymphadenopathy]] in adult particularly in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] ([[HIV AIDS|HIV infection]])
| |
| * [[Lung cancer|Bronchogenic carcinoma]]
| |
| * [[Lymphoma]]
| |
| * [[Sarcoidosis]]
| |
| * [[Infection]] ([[Mycosis|fungal]], [[Nontuberculous mycobacteria|atypical mycobacteria]], [[Virus|viral]], [[tularemia]], and [[anthrax]])
| |
| * Exposure to [[silica]] and certain [[:Category:Drugs|drugs]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Constituitional symptoms like:
| |
| *[[Fatigue]]
| |
| *[[Fever]]
| |
| *[[Malaise]]
| |
| *[[Flu]]- like illness
| |
| *[[Nausea]] and [[vomiting]]
| |
| *[[Night sweats]]
| |
| *[[Weight loss]] and
| |
| *[[Cachexia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Lymph node biopsy]] and [[histopathology]]
| |
|
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]
| |
| * 10 mm in short-axis
| |
| * Loss of fatty hilum
| |
| * Focal [[necrosis]]
| |
| * Cystic necrotic nodes
| |
| * Long-to-short axis ratio (>2cm - usually [[benign]])
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pneumomediastinum|'''Pneumomediastinum''']]
| |
| <ref name="pmid17669882">{{cite journal |author=Utsumi T, Shiono H, Fukai I, Akashi A |title=Artificial pneumomediastinum facilitates thoracoscopic surgery in anterior mediastinum |journal=Interactive cardiovascular and thoracic surgery |volume=6 |issue=3 |pages=411–2 |year=2007 |pmid=17669882 |doi=10.1510/icvts.2006.147355}}</ref><ref>name="pmid18721592">{{cite journal |vauthors=Caceres M, Ali SZ, Braud R, Weiman D, Garrett HE |title=Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature |journal=Ann. Thorac. Surg. |volume=86 |issue=3 |pages=962–6 |date=September 2008 |pmid=18721592 |doi=10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.04.067 |url=}}</ref><ref name="KimYoo2016">{{cite journal|last1=Kim|first1=Hye Rin|last2=Yoo|first2=Seung Min|last3=Lee|first3=Hwa Yeon|last4=Han|first4=Jin Hee|last5=Frazier|first5=Aletta A|last6=White|first6=Charles S|title=Presence of subpleural pulmonary interstitial emphysema as an indication of single or multiple alveolar ruptures on CT in patients with spontaneous pneumomediastinum|journal=Acta Radiologica|volume=57|issue=12|year=2016|pages=1483–1489|issn=0284-1851|doi=10.1177/0284185116629830}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| *[[Endoscopy|Endoscopic procedures]]
| |
| *[[Intubation|Intubation/extubation]]
| |
| *Central vascular access procedure
| |
| *[[Pleural cavity]] instrumentation
| |
| *[[Thoracic surgery|Chest]] or [[abdominal surgery]]
| |
| *Direct [[Chest trauma|chest wall trauma]]
| |
| *[[Tracheostomy]]
| |
| *[[Barotrauma|Pulmonary]] [[barotrauma]] (scuba diver, free diver, airplane passenger)
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Severe, [[Acute chest pain|acute pain in the chest]] (pain may radiate to the [[Shoulder|shoulders]] or [[Back pain|back]])
| |
| * [[Dyspnea|Shortness of breath]]
| |
| * [[Fever]]
| |
| * [[Neck pain|Cervical pain]] ([[Subcutaneous emphysema]])
| |
| * [[Jaw pain/swelling|Jaw pain]] ([[Subcutaneous emphysema]])
| |
| * [[Neck pain|Swelling of neck]], [[Swollen face|face]], [[chest]], [[abdomen]], [[shoulder]] [[Subcutaneous emphysema|(subcutaneous emphysema]])
| |
| * [[Dysphonia]]
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]]
| |
| * [[Nausea and vomiting|Emesis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT scan]]:
| |
| * [[Subcutaneous emphysema]]
| |
| * Naclerio V sign: [[Pneumomediastinum]] secondary to an [[Boerhaave syndrome|esophageal rupture]]
| |
| * [[Pneumopericardium]]: Gas anterior to [[pericardium]]
| |
| * Ring around [[artery]] sign: Gas around [[Pulmonary artery|pulmonary artery and main branches]]
| |
| * Tubular [[artery]] sign: Gas outlining major [[Aorta|aortic branches]]
| |
| * Double bronchial wall sign: Gas outlining [[Bronchus|bronchial wall]]
| |
| * Continuous [[Diaphragm (anatomy)|diaphragm]] sign: Gas trapped posterior to [[pericardium]]
| |
| * Extrapleural sign: Gas between [[parietal pleura]] and [[Thoracic diaphragm|diaphragm]]
| |
| * Gas in [[pulmonary ligament]]
| |
| Pediatric [[pneumomediastinum]]:
| |
| * Thymic wing sign: Elevated [[thymus]]
| |
| * Haystack sign (the [[heart]] appears like a haystack in a Monet painting)
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Physical exam:]]
| |
| *[[Mediastinal crunch]] or click on [[auscultation]] over the [[Apex of the heart|cardiac apex]] and the [[left sternal border]] synchronous with the [[Heart sounds|heart sound]] [[Hamman's sign|(Hamman's sign)]]
| |
| *[[Subcutaneous emphysema physical examination|Subcutaneous crepitation]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Sarcoidosis|'''Sarcoidosis''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Mediastinal tumor
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinal tumor|'''Mediastinal tumor''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Mediastinal germ cell tumor]]'''
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Infection
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinitis|'''Mediastinitis''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Anthrax|'''Anthrax''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Tularemia|'''Tularemia''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Cystic disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Dermoid cyst|'''Dermoid cyst''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Bronchogenic cyst]]'''
| |
| '''<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>'''
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Chronic
| |
| inflammatory
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Churg-Strauss syndrome|'''Churg-Strauss syndrome''']]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Class'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Disease'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Etiology'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dyspnea/
| |
| RI
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Dysphagia
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |SVCS
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Image'''
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Additional findings'''
| |
| |-
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="10" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Posterior mediastinal mass
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |CNS disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Meningocele]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>'''
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |'''[[Neurilemmoma]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>'''
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="10" |'''<small>ABBREVIATIONS''': '''N/A''': Not available, '''SOB''': Shortness of breath, '''M/C''': Most common, '''RI''': Respiratory insufficiency, '''NM''': Neuromuscular system, '''SVCS''': Superior vena cava syndrome, '''SLE''': Systemic lupus erythematosus disease, '''T3:''' Triiodothyronine, '''T4:''' Thyroxine, '''TSH:''' Thyroid stimulating hormone, '''TFT:''' Thyroid function test</small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small><small><nowiki/></small>
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] | | # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] |
| Line 943: |
Line 47: |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
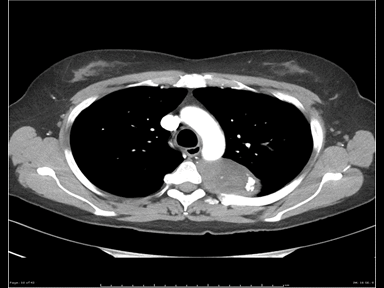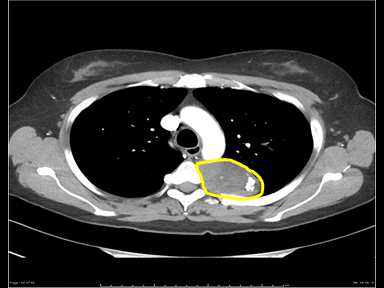
| [[File: name|x300px|thumb| CT scan showing a smooth anterior mediastinal mass, with a mixed internal density of containing both enhancing soft tissue and cystic areas. The outline of the mass is relatively well defined. No lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion or infiltration. Case courtesy of Dr. Abdallah Al Khateeb | | [[File:Mediastinal lymohangioma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows cystic mass which was located on the posterior to the lower esophagus later diagnosed as thoracic duct lymphangioma. [https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.423 Source:Case courtesy of Jin San Bok et al, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital]]] |
| (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/43403 Radiopedia])]] | | |
| | |
| | [[File:Posterior-mediastinal-schwannoma.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a soft tissue density lesion within the left posterior mediastinum, in a paravertebral location. The lesion is closely related to the left neural exit foramen, but there is no definite extension into the spinal canal. The lesion does extend into the intercostal space. |
| | Case courtesy of Dr Paul Leong |
| | (Picture courtesy:[https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26625 Radiopedia])]] |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{SI}} |
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Trusha}}, {{AM}} |
| | |
| | {{SK}} Mediastinal enlargement; mass in the mediastinum |
| | |
| | ==Overview== |
| | |
| | The [[mediastinum]] is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax (chest), surrounded by loose connective tissue. Since it is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, and it contains a lot of important structures, it is the site of involvement of various tumors. |
| | |
| | ==Causes== |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | ==Initial Evaluation== |
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | {{Family tree |border=2|boxstyle=background: WhiteSmoke;| | | | | A01 | | | | |A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 25em; padding: 1em;">'''Mediastinal Mass'''</div>}} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; padding: 1em; "> '''Workups''' |
| | ---- |
| | ❑ CT chest with contrast <br> ❑ Serum beta-HCG, AFP, if appropriate <br> ❑ CBC, platelets <br> ❑ PET-CT scan (optional) <br> ❑ Pulmonary function tests if clinically indicated <br> ❑ MRI chest if clinically indicated |
| | </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |,|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | C01 | | | | | | C02 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Likely''' </div> |C02= <div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Unlikely''' </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | }} |
| | |
| | {{familytree | D01 | | | | | | D02 | | | |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Consider [[Thymoma surgery|surgery]]</div>|D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Disease-specific management</div>}} |
|
| |
|
| | {{familytree/start}} |
|
| |
|
| [[File: name|x300px|thumb| CT scan showing excessive fatty tissue deposition within the posterior mediastinum with anterior displacement of the esophagus. Case courtesy of Dr. Ahmed Abdrabou (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/50447Radiopedia])]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |