Pegaspargase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
*[[Hepatotoxicity]] and abnormal [[liver function]], including elevations of [[AST]] ([[SGOT]]), [[ALT]] ([[SGPT]]), [[alkaline phosphatase]], [[bilirubin]] (direct and indirect), and depression of serum [[albumin]], and plasma [[fibrinogen]] can occur. Perform appropriate monitoring. | *[[Hepatotoxicity]] and abnormal [[liver function]], including elevations of [[AST]] ([[SGOT]]), [[ALT]] ([[SGPT]]), [[alkaline phosphatase]], [[bilirubin]] (direct and indirect), and depression of serum [[albumin]], and plasma [[fibrinogen]] can occur. Perform appropriate monitoring. | ||
|clinicalTrials='''The following serious adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections of the label:''' | |clinicalTrials='''The following serious adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections of the label:''' | ||
*Anaphylaxis and serious allergic reactions. | *[[Anaphylaxis]] and serious [[allergic reactions]]. | ||
*Serious thrombosis. | *Serious [[thrombosis]]. | ||
*Pancreatitis. | *[[Pancreatitis]]. | ||
*Glucose intolerance. | *[[Glucose intolerance]]. | ||
*Coagulopathy. | *[[Coagulopathy]]. | ||
*Hepatotoxicity and abnormal liver function. | *[[Hepatotoxicity]] and abnormal [[liver function]]. | ||
The most common adverse reactions with Oncaspar® are allergic reactions (including [[anaphylaxis]]), [[hyperglycemia]], [[pancreatitis]], central nervous system (CNS) [[thrombosis]], [[coagulopathy]], [[hyperbilirubinemia]], and elevated [[transaminases]]. | The most common adverse reactions with Oncaspar® are allergic reactions (including [[anaphylaxis]]), [[hyperglycemia]], [[pancreatitis]], central nervous system (CNS) [[thrombosis]], [[coagulopathy]], [[hyperbilirubinemia]], and elevated [[transaminases]]. [[Hyperlipidemia]] ([[hypercholesterolemia]] and [[hypertriglyceridemia]]) has been reported in patients exposed to Oncaspar®. | ||
====Clinical Trials Experience==== | ====Clinical Trials Experience==== | ||
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice. | |||
=====First-Line ALL===== | =====First-Line ALL===== | ||
*The data presented below are derived from 2 studies in patients with standard-risk ALL who received Oncaspar® as a component of first-line multi-agent chemotherapy. Study 1 was a randomized (1:1), active-controlled study that enrolled 118 patients, with a median age of 4.7 years (1.1-9.9 years), of whom 54% were males and 65% White, 14% Hispanic, 8% Black, 8% Asian, and 6% other. Of the 59 patients in Study 1 who were randomized to Oncaspar®, 48 patients (81%) received all 3 planned doses of Oncaspar®, 6 (10%) received 2 doses, 4 (7%) received 1 dose, and 1 patient (2%) did not receive the assigned treatment. Study 2 is an ongoing, multi-factorial design study in which all patients received Oncaspar® as a component of various multi-agent chemotherapy regimens; interim safety data are available for 2,770 patients. Study participants had a median age of 4 years (1-10 years), and were 55% male, 68% White, 18% Hispanic, 4% Black, 3% Asian, and 7% other. Per protocol, the schedule of Oncaspar® varied by treatment arm, with intermittent doses of Oncaspar® for up to 10 months. | *The data presented below are derived from 2 studies in patients with standard-risk ALL who received Oncaspar® as a component of first-line multi-agent chemotherapy. Study 1 was a randomized (1:1), active-controlled study that enrolled 118 patients, with a median age of 4.7 years (1.1-9.9 years), of whom 54% were males and 65% White, 14% Hispanic, 8% Black, 8% Asian, and 6% other. Of the 59 patients in Study 1 who were randomized to Oncaspar®, 48 patients (81%) received all 3 planned doses of Oncaspar®, 6 (10%) received 2 doses, 4 (7%) received 1 dose, and 1 patient (2%) did not receive the assigned treatment. Study 2 is an ongoing, multi-factorial design study in which all patients received Oncaspar® as a component of various multi-agent chemotherapy regimens; interim safety data are available for 2,770 patients. Study participants had a median age of 4 years (1-10 years), and were 55% male, 68% White, 18% Hispanic, 4% Black, 3% Asian, and 7% other. Per protocol, the schedule of Oncaspar® varied by treatment arm, with intermittent doses of Oncaspar® for up to 10 months. | ||
*In Study 1, detailed safety information was collected for pre-specified adverse reactions identified as [[asparaginase]]-induced adverse reactions and for grade 3 and 4 non-hematologic adverse reactions according to the Children’s Cancer Group (CCG) Toxicity and Complication Criteria. The per-patient incidence, by treatment arm, for these selected adverse reactions occurring at a severity of grade 3 or 4 are presented in TABLE 1 below: | |||
[[file:Pegasparginase AR1.png|none|300px]] | |||
*Safety data were collected in Study 2 only for National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI CTC) version 2.0, grade 3 and 4 non-hematologic toxicities. In this study, the per-patient incidence for the following adverse reactions occurring during treatment courses in which patients received Oncaspar® were: elevated [[transaminases]], 11%; [[coagulopathy]], 7%; [[hyperglycemia]], 5%; CNS [[thrombosis]]/[[hemorrhage]], 2%; [[pancreatitis]], 2%; clinical [[allergic reaction]], 1%; and [[hyperbilirubinemia]], 1%. There were 3 deaths due to pancreatitis. | |||
=====Previously Treated ALL===== | |||
*Adverse reaction information was obtained from 5 clinical trials that enrolled a total of 174 patients with relapsed ALL who received Oncaspar® as a single agent or in combination with multi-agent chemotherapy. The toxicity profile of Oncaspar® in patients with previously treated relapsed ALL is similar to that reported above with the exception of clinical allergic reactions (see TABLE 2). The most common adverse reactions of Oncaspar® were clinical allergic reactions, elevated [[transaminases]], [[hyperbilirubinemia]], and [[coagulopathies]]. The most common serious adverse events due to Oncaspar® treatment were thrombosis (4%), [[hyperglycemia]] requiring [[insulin]] therapy (3%), and [[pancreatitis]] (1%). | |||
====Allergic Reactions==== | |||
Allergic reactions include the following: [[bronchospasm]], [[hypotension]], [[laryngeal edema]], [[local erythema]] or [[swelling]], systemic [[rash]], and [[urticaria]]. | |||
=====First-Line ALL===== | |||
*Among 58 Oncaspar®-treated patients enrolled in Study 1, clinical allergic reactions were reported in 2 patients (3%). One patient experienced a grade 1 allergic reaction and the other grade 3 hives; both occurred during the first delayed intensification phase of the study (see TABLE 2). | |||
=====Previously Treated ALL===== | |||
*Among 62 patients with relapsed ALL and prior hypersensitivity reactions to asparaginase, 35 patients (56%) had a history of clinical allergic reactions to native Escherichia (E.) coli [[L-asparaginase]], and 27 patients (44%) had history of clinical allergic reactions to both native [[E. coli]] and native [[Erwinia]] [[L-asparaginase]]. Twenty (32%) of these 62 patients experienced clinical allergic reactions to Oncaspar® (see TABLE 2). | |||
*Among 112 patients with relapsed ALL with no prior hypersensitivity reactions to asparaginase, 11 patients (10%) experienced clinical allergic reactions to Oncaspar® (see TABLE 2). | |||
[[file:Pegasparginase AR2.png|none|400px]] | |||
====Immunogenicity==== | |||
*As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity, defined as development of binding and/or neutralizing antibodies to the product. | |||
*In Study 1, Oncaspar®-treated patients were assessed for evidence of binding antibodies using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The incidence of protocol-specified “high-titer” antibody formation was 2% in Induction (n=48), 10% in Delayed Intensification 1 (n=50), and 11% in Delayed Intensification 2 (n=44). There is insufficient information to determine whether the development of antibodies is associated with an increased risk of clinical allergic reactions, altered pharmacokinetics, or loss of anti-leukemic efficacy. | |||
*The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay, and the observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including sample handling, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. Therefore, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to Oncaspar® with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading. | |||
|postmarketing=(Description) | |postmarketing=(Description) | ||
Revision as of 13:56, 17 February 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Pegaspargase is an asparginase that is FDA approved for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia and hypersensitivity to asparaginase. Common adverse reactions include allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis), central nervous system thrombosis, coagulopathy, elevated transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, hyperglycemia, and pancreatitis.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
- History of serious allergic reactions to Oncaspar.
- History of serious thrombosis with prior L-asparaginase therapy.
- History of pancreatitis with prior L-asparaginase therapy.
- History of serious hemorrhagic events with prior L-asparaginase therapy.
Warnings
Anaphylaxis and Serious Allergic Reactions
- Anaphylaxis and serious allergic reactions can occur in patients receiving Oncaspar®. The risk of serious allergic reactions is higher in patients with known hypersensitivity to other forms of L-asparaginase. Observe patients for 1 hour after administration of Oncaspar® in a setting with resuscitation equipment and other agents necessary to treat anaphylaxis (for example, epinephrine, oxygen, intravenous steroids, antihistamines). Discontinue Oncaspar® in patients with serious allergic reactions.
Thrombosis
- Serious thrombotic events, including sagittal sinus thrombosis can occur in patients receiving Oncaspar®. Discontinue Oncaspar® in patients with serious thrombotic events.
Pancreatitis
- Pancreatitis can occur in patients receiving Oncaspar®. Evaluate patients with abdominal pain for evidence of pancreatitis. Discontinue Oncaspar® in patients with pancreatitis.
Glucose Intolerance
- Glucose intolerance can occur in patients receiving Oncaspar®. In some cases, glucose intolerance is irreversible. Monitor serum glucose.
Coagulopathy
- Increased prothrombin time, increased partial thromboplastin time, and hypofibrinogenemia can occur in patients receiving Oncaspar®. Monitor coagulation parameters at baseline and periodically during and after treatment. Initiate treatment with fresh-frozen plasma to replace coagulation factors in patients with severe or symptomatic coagulopathy.
Hepatotoxicity and Abnormal Liver Function
- Hepatotoxicity and abnormal liver function, including elevations of AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin (direct and indirect), and depression of serum albumin, and plasma fibrinogen can occur. Perform appropriate monitoring.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
The following serious adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Anaphylaxis and serious allergic reactions.
- Serious thrombosis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Glucose intolerance.
- Coagulopathy.
- Hepatotoxicity and abnormal liver function.
The most common adverse reactions with Oncaspar® are allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis), hyperglycemia, pancreatitis, central nervous system (CNS) thrombosis, coagulopathy, hyperbilirubinemia, and elevated transaminases. Hyperlipidemia (hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia) has been reported in patients exposed to Oncaspar®.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
First-Line ALL
- The data presented below are derived from 2 studies in patients with standard-risk ALL who received Oncaspar® as a component of first-line multi-agent chemotherapy. Study 1 was a randomized (1:1), active-controlled study that enrolled 118 patients, with a median age of 4.7 years (1.1-9.9 years), of whom 54% were males and 65% White, 14% Hispanic, 8% Black, 8% Asian, and 6% other. Of the 59 patients in Study 1 who were randomized to Oncaspar®, 48 patients (81%) received all 3 planned doses of Oncaspar®, 6 (10%) received 2 doses, 4 (7%) received 1 dose, and 1 patient (2%) did not receive the assigned treatment. Study 2 is an ongoing, multi-factorial design study in which all patients received Oncaspar® as a component of various multi-agent chemotherapy regimens; interim safety data are available for 2,770 patients. Study participants had a median age of 4 years (1-10 years), and were 55% male, 68% White, 18% Hispanic, 4% Black, 3% Asian, and 7% other. Per protocol, the schedule of Oncaspar® varied by treatment arm, with intermittent doses of Oncaspar® for up to 10 months.
- In Study 1, detailed safety information was collected for pre-specified adverse reactions identified as asparaginase-induced adverse reactions and for grade 3 and 4 non-hematologic adverse reactions according to the Children’s Cancer Group (CCG) Toxicity and Complication Criteria. The per-patient incidence, by treatment arm, for these selected adverse reactions occurring at a severity of grade 3 or 4 are presented in TABLE 1 below:
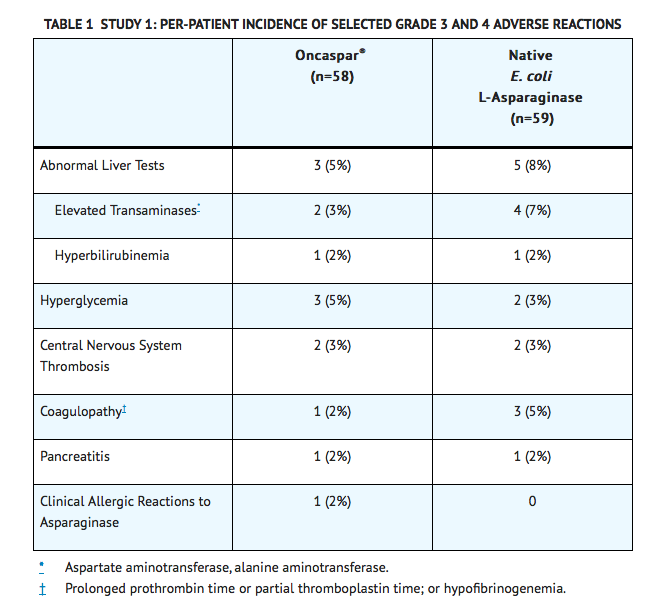
- Safety data were collected in Study 2 only for National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI CTC) version 2.0, grade 3 and 4 non-hematologic toxicities. In this study, the per-patient incidence for the following adverse reactions occurring during treatment courses in which patients received Oncaspar® were: elevated transaminases, 11%; coagulopathy, 7%; hyperglycemia, 5%; CNS thrombosis/hemorrhage, 2%; pancreatitis, 2%; clinical allergic reaction, 1%; and hyperbilirubinemia, 1%. There were 3 deaths due to pancreatitis.
Previously Treated ALL
- Adverse reaction information was obtained from 5 clinical trials that enrolled a total of 174 patients with relapsed ALL who received Oncaspar® as a single agent or in combination with multi-agent chemotherapy. The toxicity profile of Oncaspar® in patients with previously treated relapsed ALL is similar to that reported above with the exception of clinical allergic reactions (see TABLE 2). The most common adverse reactions of Oncaspar® were clinical allergic reactions, elevated transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, and coagulopathies. The most common serious adverse events due to Oncaspar® treatment were thrombosis (4%), hyperglycemia requiring insulin therapy (3%), and pancreatitis (1%).
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions include the following: bronchospasm, hypotension, laryngeal edema, local erythema or swelling, systemic rash, and urticaria.
First-Line ALL
- Among 58 Oncaspar®-treated patients enrolled in Study 1, clinical allergic reactions were reported in 2 patients (3%). One patient experienced a grade 1 allergic reaction and the other grade 3 hives; both occurred during the first delayed intensification phase of the study (see TABLE 2).
Previously Treated ALL
- Among 62 patients with relapsed ALL and prior hypersensitivity reactions to asparaginase, 35 patients (56%) had a history of clinical allergic reactions to native Escherichia (E.) coli L-asparaginase, and 27 patients (44%) had history of clinical allergic reactions to both native E. coli and native Erwinia L-asparaginase. Twenty (32%) of these 62 patients experienced clinical allergic reactions to Oncaspar® (see TABLE 2).
- Among 112 patients with relapsed ALL with no prior hypersensitivity reactions to asparaginase, 11 patients (10%) experienced clinical allergic reactions to Oncaspar® (see TABLE 2).
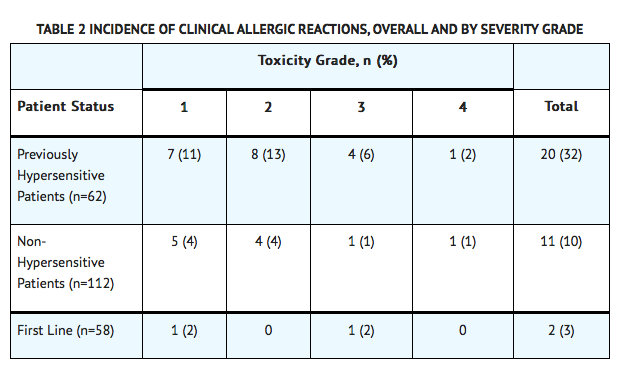
Immunogenicity
- As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity, defined as development of binding and/or neutralizing antibodies to the product.
- In Study 1, Oncaspar®-treated patients were assessed for evidence of binding antibodies using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The incidence of protocol-specified “high-titer” antibody formation was 2% in Induction (n=48), 10% in Delayed Intensification 1 (n=50), and 11% in Delayed Intensification 2 (n=44). There is insufficient information to determine whether the development of antibodies is associated with an increased risk of clinical allergic reactions, altered pharmacokinetics, or loss of anti-leukemic efficacy.
- The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay, and the observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including sample handling, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. Therefore, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to Oncaspar® with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
(Description)
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
Solution
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Y-Site
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Admixture
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Syringe
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
TPN/TNA
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Pegaspargase
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
(Description)
Structure
(Description with picture)
Pharmacodynamics
(Description)
Pharmacokinetics
(Description)
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
Condition 1
(Description)
Condition 2
(Description)
Condition 3
(Description)
How Supplied
(Description)
Storage
There is limited information regarding Pegaspargase Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Pegaspargase |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Pegaspargase |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
(Patient Counseling Information)
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Pegaspargase interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Pegaspargase Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
- (Paired Confused Name 1a) — (Paired Confused Name 1b)
- (Paired Confused Name 2a) — (Paired Confused Name 2b)
- (Paired Confused Name 3a) — (Paired Confused Name 3b)
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.