Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis
|
Melanoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis |
|
FDA on Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis |
|
CDC on Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis |
|
Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis in the news |
|
Blogs on Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Melanoma natural history, complications and prognosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Features that affect prognosis are tumor thickness in millimeters (Breslow's depth), depth related to skin structures (Clark level), type of melanoma, presence of ulceration, presence of lymphatic/perineural invasion, presence of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (if present, prognosis is better), location of lesion, presence of satellite lesions, and presence of regional or distant metastasis.[1] Between 2004 and 2010, the 5-year relative survival of patients with melanoma was 92.9%.[2]
Complications
- Bone metastases
- Cerebral metastases
- Cutaneous metastasis
- Lung metastases
- Renal metastases
Prognosis
Features that affect prognosis are tumor thickness in millimeters (Breslow's depth), depth related to skin structures (Clark level), type of melanoma, presence of ulceration, presence of lymphatic/perineural invasion, presence of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (if present, prognosis is better), location of lesion, presence of satellite lesions, and presence of regional or distant metastasis.[3]
Certain types of melanoma have worse prognoses but this is explained by their thickness. Interestingly, less invasive melanomas even with lymph node metastases carry a better prognosis than deep melanomas without regional metastasis at time of staging. Local recurrences tend to behave similarly to a primary unless they are at the site of a wide local excision (as opposed to a staged excision or punch/shave excision) since these recurrences tend to indicate lymphatic invasion.
When melanomas have spread to the lymph nodes, one of the most important factors is the number of nodes with malignancy. Extent of malignancy within a node is also important; micro-metastases in which malignancy is only microscopic have a more favorable prognosis than macrometastases. In some cases micrometastases may only be detected by special staining, and if malignancy is only detectable by a rarely-employed test known as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the prognosis is better. Macrometastases in which malignancy is clinically apparent (in some cases cancer completely replaces a node) have a far worse prognosis, and if nodes are matted or if there is extracapsular extension, the prognosis is still worse.
When there is distant metastasis, the cancer is generally considered incurable. The five year survival rate is less than 10%.[4] The median survival is 6 to 12 months. Treatment is palliative, focusing on life-extension and quality of life. In some cases, patients may live many months or even years with metastatic melanoma (depending on the aggressiveness of the treatment). Metastases to skin and lungs have a better prognosis. Metastases to brain, bone and liver are associated with a worse prognosis.
There is not enough definitive evidence to adequately stage, and thus give a prognosis for ocular melanoma and melanoma of soft parts, or mucosal melanoma (e.g. rectal melanoma), although these tend to metastasize more easily. Even though regression may increase survival, when a melanoma has regressed, it is impossible to know its original size and thus the original tumor is often worse than a pathology report might indicate.
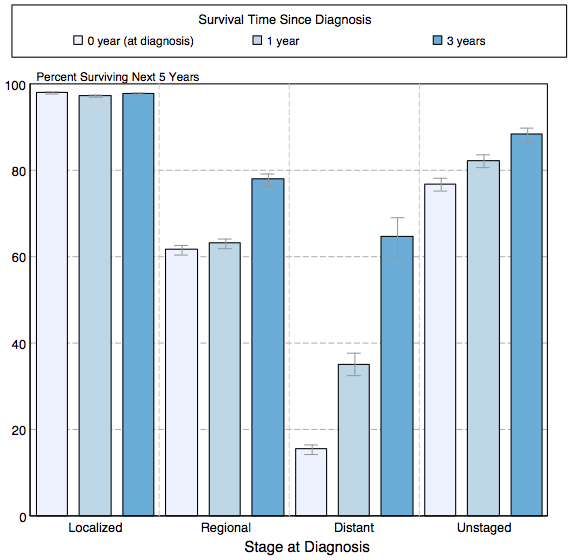
5-Year Survival
- Between 2004 and 2010, the 5-year relative survival of patients with melanoma was 92.9%.[2]
- When stratified by age, the 5-year relative survival of patients with melanoma was 92.7% and 88.2% for patients <65 and ≥ 65 years of age respectively.[2]
- The survival of patients with melanoma varies with the stage of the disease. Shown below is a table depicting the 5-year relative survival by the stage of melanoma:[2]
| Stage | 5-year relative survival (%), (2004-2010) |
| All stages | 91.3% |
| Localized | 98.1% |
| Regional | 62.6% |
| Distant | 16.1% |
| Unstaged | 78.4% |
- Shown below is an image depicting the 5-year conditional relative survival (probability of surviving in the next 5-years given the cohort has already survived 0, 1, 3 years) between 1998 and 2010 of melanoma by stage at diagnosis according to SEER. These graphs are adapted from SEER: The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program of the National Cancer Institute.[2]
References
- ↑ Homsi J, Kashani-Sabet M, Messina J, Daud A (2005). "Cutaneous melanoma: prognostic factors". Cancer Control. 12 (4): 223–9. PMID 16258493.Full text (PDF)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z,Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2011, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/, based on November 2013 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2014.
- ↑ Homsi J, Kashani-Sabet M, Messina J, Daud A (2005). "Cutaneous melanoma: prognostic factors". Cancer Control. 12 (4): 223–9. PMID 16258493.Full text (PDF)
- ↑ Balch C, Buzaid A, Soong S, Atkins M, Cascinelli N, Coit D, Fleming I, Gershenwald J, Houghton A, Kirkwood J, McMasters K, Mihm M, Morton D, Reintgen D, Ross M, Sober A, Thompson J, Thompson J (2001). "Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma". J Clin Oncol. 19 (16): 3635–48. PMID 11504745.Full text