Esophageal cancer other diagnostic studies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Esophageal cancer}} | {{Esophageal cancer}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
==Other Diagnostic Studies== | |||
== | |||
[[FDG-PET]] (positron emission tomography) scan is also being used to estimate whether enlarged masses are metabolically active, indicating faster-growing cells that might be expected in cancer. Esophageal [[endoscopic ultrasound]] (EUS) can provide staging information regarding the level of tumor invasion, and possible spread to regional lymph nodes. | [[FDG-PET]] (positron emission tomography) scan is also being used to estimate whether enlarged masses are metabolically active, indicating faster-growing cells that might be expected in cancer. Esophageal [[endoscopic ultrasound]] (EUS) can provide staging information regarding the level of tumor invasion, and possible spread to regional lymph nodes. | ||
[[Image:Mid esophageal mass.jpg|left|300px|thumb|Endoscopy and radial endoscopic ultrasound images of submucosal tumour in mid-esophagus]] | |||
The location of the tumor is generally measured by the distance from the teeth. The esophagus (25 cm or 10 inches long) is commonly divided into three parts for purposes of determining the location. Adenocarcinomas tend to occur distally and squamous cell carcinomas proximally, but the converse may also be the case. | The location of the tumor is generally measured by the distance from the teeth. The esophagus (25 cm or 10 inches long) is commonly divided into three parts for purposes of determining the location. Adenocarcinomas tend to occur distally and squamous cell carcinomas proximally, but the converse may also be the case. | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 14 September 2012
|
Esophageal cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Esophageal cancer other diagnostic studies On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Esophageal cancer other diagnostic studies |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Esophageal cancer other diagnostic studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Other Diagnostic Studies
FDG-PET (positron emission tomography) scan is also being used to estimate whether enlarged masses are metabolically active, indicating faster-growing cells that might be expected in cancer. Esophageal endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can provide staging information regarding the level of tumor invasion, and possible spread to regional lymph nodes.
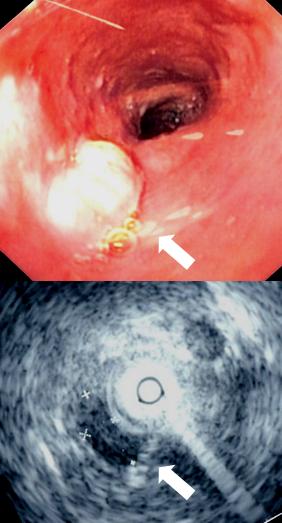
The location of the tumor is generally measured by the distance from the teeth. The esophagus (25 cm or 10 inches long) is commonly divided into three parts for purposes of determining the location. Adenocarcinomas tend to occur distally and squamous cell carcinomas proximally, but the converse may also be the case.