Diabetic foot physical examination: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
**Note that [[Dorsalis pedis artery|dorsalis pedis]] and [[Posterior tibial artery|posterior tibial]] [[pulses]] are absent in 8% and 3% of normal population, respectively. | **Note that [[Dorsalis pedis artery|dorsalis pedis]] and [[Posterior tibial artery|posterior tibial]] [[pulses]] are absent in 8% and 3% of normal population, respectively. | ||
*[[Capillary]] filling time (venous refilling > 5s) | *[[Capillary]] filling time (venous refilling > 5s) | ||
*[[Muscle strength]] and tone | *[[Muscle strength]] and tone | ||
*[[Sensation]] | *[[Sensation]] | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 28 June 2021
|
Diabetic foot Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Diabetic foot physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Diabetic foot physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Diabetic foot physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Anahita Deylamsalehi, M.D.[2] Vishnu Vardhan Serla M.B.B.S. [3]
Overview
Physical Examination
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with diabetic foot ulcer could appear ill if ulcers are severe or infected.
Vital Signs
- ±Fever (Based on the infection severity can present as high or low grade fever)
- Hypothermia or hyperthermia may be present
- Tachycardia
- Low blood pressure could be seen in septic patients
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal, except for the foot skin.
HEENT
- HEENT examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Abdomen
- Abdominal examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Back
- Back examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal.
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with diabetic foot is usually normal, except in their foot. Examine their foot for the following:
- Motor examination
- Tone
- Power
- Reflexes
- Sensory examination
- Vibration
- Joint position sense
- Motor examination
Neuropathy Assessment
- Using the neuropathy symptoms score (NSS) and neuropathy disability score (NDS) is helpful in physical examination of patients with diabetic foot.[1][2][3]
- Findings that favor the diagnosis of sensory neuropathy:
- Impaired vibration perception and position sense
- Depressed tendon reflexes
- Dull, crushing or cramp-like pain in the bones of the feet
- Sensory ataxia
- Shortening of the achilles tendon
- Abnormal thresholds for warm thermal perception
- Decreased neurovascular function
Extremities
Inspection
The following list is a summary of possible findings in diabetic foot inspection:
- Peeling skin, maceration, fissuring between toes
- Dilated or varicose veins
- Scar
- Sinuses
- Shiny skin
- Decreased hair distribution
- Areas of pigmentation or discoloration
- Ulcers
- Brittle or broken nail
- Fungal infection
- Foot deformities such as charcot foot and hammer toe
- Pink and warm
- Even in ischemic settings due to arteriovenous shunting.
Palpation
The following is a list of recommended examinations in a diabetic foot patients:[3]
- Temperature (increased temperature could be due to deep vein thrombosis while decreased temperature could be an ischemia presentation)
- Tenderness (squeeze calf muscle and achilles tendon for tenderness)
- Pulses such as dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses
- Although even when both dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are present, low perfusion can not be excluded.
- Note that dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are absent in 8% and 3% of normal population, respectively.
- Capillary filling time (venous refilling > 5s)
- Muscle strength and tone
- Sensation
- Light touch
- Filament nerve conduction studies
- Quantitative sensory testing and autonomic testing
Video: Physical Examination Diabetes
{{#ev:youtube|715j6zRZHaA}}
Image: Diabetic Foot Ulcer
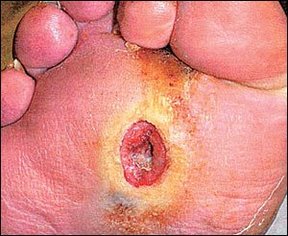
References
- ↑ Meijer JW, Smit AJ, Sonderen EV, Groothoff JW, Eisma WH, Links TP (2002). "Symptom scoring systems to diagnose distal polyneuropathy in diabetes: the Diabetic Neuropathy Symptom score". Diabet Med. 19 (11): 962–5. PMID 12421436.
- ↑ Daousi C, MacFarlane IA, Woodward A, Nurmikko TJ, Bundred PE, Benbow SJ (2004). "Chronic painful peripheral neuropathy in an urban community: a controlled comparison of people with and without diabetes". Diabet Med. 21 (9): 976–82. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01271.x. PMID 15317601.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lepäntalo M, Apelqvist J, Setacci C, Ricco JB, de Donato G, Becker F; et al. (2011). "Chapter V: Diabetic foot". Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 42 Suppl 2: S60–74. doi:10.1016/S1078-5884(11)60012-9. PMID 22172474.