Cortisone: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Protected "Cortisone": Bot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|genericName=cortisone | |genericName=cortisone | ||
|aOrAn=a | |aOrAn=a | ||
|drugClass=hormone | |drugClass=[[hormone]] | ||
|indicationType=treatment | |indicationType=treatment | ||
|indication=primary and secondary adrenocortical deficiency, rheumatic disorders, [[psoriasis]], [[exfoliative dermatitis]], [[bronchial asthma]], allergic conjunctivitis, [[hemolytic anemia]], [[enteritis]], [[tuberculosis]], [[trichnosis]] | |indication=primary and secondary adrenocortical deficiency, rheumatic disorders, [[psoriasis]], [[exfoliative dermatitis]], [[bronchial asthma]], allergic [[conjunctivitis]], [[hemolytic anemia]], [[enteritis]], [[tuberculosis]], [[trichnosis]] | ||
|adverseReactions=[[convulsions]], increased intracranial pressure with [[papilledema]], [[vertigo]], [[headache]], [[psychic disturbances]], [[hirsuitism]], [[glaucoma]], [[exophthalmos]] | |adverseReactions=[[convulsions]], increased intracranial pressure with [[papilledema]], [[vertigo]], [[headache]], [[psychic disturbances]], [[hirsuitism]], [[glaucoma]], [[exophthalmos]] | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle=<span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span> | |blackBoxWarningTitle=<span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* Primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency (hydrocortisone or cortisone is the first choice; synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance). | * Primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency (hydrocortisone or cortisone is the first choice; synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance). | ||
* Congenital adrenal hyperplasia | * Congenital adrenal hyperplasia | ||
* Nonsuppurative thyroiditis | * Nonsuppurative [[thyroiditis]] | ||
* Hypercalcemia associated with cancer | * Hypercalcemia associated with [[cancer]] | ||
=====Rheumatic Disorders===== | =====Rheumatic Disorders===== | ||
* As adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in the following conditions | * As adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in the following conditions | ||
:* Psoriatic arthritis | :* [[Psoriatic arthritis]] | ||
:* Rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy) | :* [[Rheumatoid arthritis]], including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy) | ||
:* Ankylosing spondylitis | :* [[Ankylosing spondylitis]] | ||
:* Acute and subacute bursitis | :* Acute and subacute [[bursitis]] | ||
:* Acute nonspecific tenosynovitis | :* Acute nonspecific [[tenosynovitis]] | ||
:* Acute gouty arthritis | :* Acute gouty [[arthritis]] | ||
:* Post-traumatic osteoarthritis | :* Post-traumatic [[osteoarthritis]] | ||
:* Synovitis of osteoarthritis | :* [[Synovitis]] of [[osteoarthritis]] | ||
:* Epicondylitis | :* [[Epicondylitis]] | ||
=====Collagen Diseases===== | =====Collagen Diseases===== | ||
* During an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of following conditions. | * During an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of following conditions. | ||
:* Systemic lupus erythematosus | :* [[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] | ||
:* Acute rheumatic carditis | :* Acute rheumatic [[carditis]] | ||
:* Systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis) | :* [[Systemic dermatomyositis]] (polymyositis) | ||
:* Dermatologic Diseases | :* Dermatologic Diseases | ||
:* Pemphigus | :* [[Pemphigus]] | ||
:* Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis | :* Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis | ||
:* Severe erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) | :* Severe erythema multiforme ([[Stevens-Johnson syndrome]]) | ||
:* Exfoliative dermatitis | :* [[Exfoliative dermatitis]] | ||
:* Mycosis fungoides | :* [[Mycosis fungoides]] | ||
:* Severe psoriasis | :* Severe [[psoriasis]] | ||
:* Severe seborrheic dermatitis | :* Severe [[seborrheic dermatitis]] | ||
=====Allergic States===== | =====Allergic States===== | ||
* Control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment of following conditions. | * Control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment of following conditions. | ||
:* Seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis | :* Seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis | ||
:* Bronchial asthma | :* [[Bronchial asthma]] | ||
:* Contact dermatitis | :* Contact [[dermatitis]] | ||
:* Atopic dermatitis | :* [[Atopic dermatitis]] | ||
:* Serum sickness | :* [[Serum sickness]] | ||
:* Drug hypersensitivity reactions | :* Drug hypersensitivity reactions | ||
=====Ophthalmic Diseases===== | =====Ophthalmic Diseases===== | ||
* Severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa, such as: | * Severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa, such as: | ||
* Allergic conjunctivitis | * [[Allergic conjunctivitis]] | ||
* Keratitis | * [[Keratitis]] | ||
* Allergic corneal marginal ulcers | * Allergic corneal marginal ulcers | ||
* Herpes zoster ophthalmicus | * [[Herpes zoster ophthalmicus]] | ||
* Iritis and iridocyclitis | * [[Iritis]] and [[iridocyclitis]] | ||
* Chorioretinitis | * [[Chorioretinitis]] | ||
* Anterior segment inflammation | * Anterior segment inflammation | ||
* Diffuse posterior uveitis and choroiditis | * Diffuse posterior [[uveitis]] and [[choroiditis]] | ||
* Optic neuritis | * [[Optic neuritis]] | ||
* Sympathetic ophthalmia | * Sympathetic ophthalmia | ||
* Respiratory Diseases | * Respiratory Diseases | ||
* Symptomatic sarcoidosis | * Symptomatic [[sarcoidosis]] | ||
* Loeffler's syndrome not manageable by other means | * [[Loeffler's syndrome]] not manageable by other means | ||
* Berylliosis | * [[Berylliosis]] | ||
* Fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculosis chemotherapy | * Fulminating or disseminated pulmonary [[tuberculosis]] when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculosis chemotherapy | ||
* Aspiration pneumonitis | * Aspiration [[pneumonitis]] | ||
=====Hematologic Disorders===== | =====Hematologic Disorders===== | ||
* Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults | * Idiopathic thrombocytopenic [[purpura]] in adults | ||
* Secondary thrombocytopenia in adults | * Secondary [[thrombocytopenia]] in adults | ||
* Acquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia | * Acquired (autoimmune) [[hemolytic anemia]] | ||
* Erythroblastopenia (RBC anemia) | * [[Erythroblastopenia]] (RBC anemia) | ||
* Congenital (erythroid) hypoplastic anemia | * Congenital (erythroid) hypoplastic anemia | ||
=====Neoplastic Diseases===== | =====Neoplastic Diseases===== | ||
* For palliative management of following conditions. | * For palliative management of following conditions. | ||
:* Leukemias and lymphomas in adults | :* [[Leukemias]] and [[lymphomas]] in adults | ||
:* Acute leukemia of childhood | :* Acute leukemia of childhood | ||
:* Edematous States | :* Edematous States | ||
:* To induce a diuresis or remission of proteinuria in the nephrotic syndrome, without uremia, of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus | :* To induce a diuresis or remission of proteinuria in the [[nephrotic syndrome]], without [[uremia]], of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus | ||
=====Gastrointestinal Diseases===== | =====Gastrointestinal Diseases===== | ||
* To tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in the follwoing conditions. | * To tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in the follwoing conditions. | ||
:* Ulcerative colitis | :* [[Ulcerative colitis]] | ||
:* Regional enteritis | :* Regional [[enteritis]] | ||
=====Miscellaneous===== | =====Miscellaneous===== | ||
* Tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy | * Tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy | ||
* Trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement. | * [[Trichinosis]] with neurologic or myocardial involvement. | ||
====For Oral Administration===== | ====For Oral Administration===== | ||
* DOSAGE REQUIREMENTS ARE VARIABLE AND MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED ON THE BASIS OF THE DISEASE AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT. | * DOSAGE REQUIREMENTS ARE VARIABLE AND MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED ON THE BASIS OF THE DISEASE AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT. | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | ||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=* Carcinoma of breast | |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=* Carcinoma of breast | ||
* Carcinoma of prostate | * Carcinoma of [[prostate]] | ||
* Fever, due to malignancy; treatment adjunct | * Fever, due to[[malignancy]]; treatment adjunct | ||
* Intracranial tumor | * [[Intracranial tumor]] | ||
* Multiple myeloma | * [[Multiple myeloma]] | ||
|fdaLIADPed= | |fdaLIADPed=There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | ||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | <!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | ||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | <!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | ||
| Line 121: | Line 119: | ||
* Corticosteroids may mask some signs of infection, and new infections may appear during their use. There may be decreased resistance and inability to localize infection when corticosteroids are used. | * Corticosteroids may mask some signs of infection, and new infections may appear during their use. There may be decreased resistance and inability to localize infection when corticosteroids are used. | ||
* Moreover, corticosteroids may affect the nitroblue-tetrazolium test for bacterial infection and produce false negative results. | * Moreover, corticosteroids may affect the nitroblue-tetrazolium test for bacterial infection and produce false negative results. | ||
* In cerebral malaria, a double-blind trial has shown that the use of corticosteroids is associated with prolongation of coma and a higher incidence of pneumonia and gastrointestinal bleeding. | * In cerebral [[malaria]], a double-blind trial has shown that the use of corticosteroids is associated with prolongation of coma and a higher incidence of [[pneumonia]] and gastrointestinal bleeding. | ||
* Corticosteroids may activate latent amebiasis. Therefore, it is recommended that latent or active amebiasis be ruled out before initiating corticosteroid therapy in any patient who has time in the tropics or any patient with unexplained diarrhea. | * Corticosteroids may activate latent [[amebiasis]]. Therefore, it is recommended that latent or active [[amebiasis]] be ruled out before initiating corticosteroid therapy in any patient who has time in the tropics or any patient with unexplained [[diarrhea]]. | ||
* Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subsapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses. | * Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subsapsular [[cataracts]], [[glaucoma]] with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to [[fungi]] or [[viruses]]. | ||
* Average and large doses of hydrocortisone or cortisone can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased excretion of potassium. These effects are less likely to occur with the synthetic derivatives except when used in large doses. | * Average and large doses of hydrocortisone or cortisone can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased excretion of potassium. These effects are less likely to occur with the synthetic derivatives except when used in large doses. | ||
* Dietary salt restriction and potassium supplementation may be necessary. All corticosteroids increase calcium excretion. | * Dietary salt restriction and potassium supplementation may be necessary. All corticosteroids increase calcium excretion. | ||
* Administration of live virus vaccines, including smallpox, is contraindicated in individuals receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids. If inactivated viral or bacterial vaccines are administered to individuals receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids, the expected serum antibody response may not be obtained. | * Administration of live virus vaccines, including [[smallpox]], is contraindicated in individuals receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids. If inactivated viral or bacterial vaccines are administered to individuals receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids, the expected serum antibody response may not be obtained. | ||
* However, immunization procedures may be undertaken in patients who are receiving corticosteroids as replacement therapy, e.g., for Addison's disease. | * However, immunization procedures may be undertaken in patients who are receiving corticosteroids as replacement therapy, e.g., for Addison's disease. | ||
* Persons who are on drugs which suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals. Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have more serious or even fatal course in non-immune children or adults on corticosteroids. | * Persons who are on drugs which suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals. Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have more serious or even fatal course in non-immune children or adults on corticosteroids. | ||
* In such children or adults who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route and duration of corticosteroid administration affects the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. | * In such children or adults who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route and duration of corticosteroid administration affects the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. | ||
* If exposed to chickenpox, prophylaxis with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information). If chickenpox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered. | * If exposed to chickenpox, prophylaxis with [[varicella zoster]] immune globulin (VZIG) may be indicated. If exposed to [[measles]], prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information). If [[chickenpox]] develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered. | ||
* The use of cortisone acetate tablets in active tuberculosis should be restricted to those cases of fulminating or disseminated tuberculosis in which the corticosteroid is used for the management of the disease in conjunction with an appropriate antituberculous regimen. | * The use of cortisone acetate tablets in active tuberculosis should be restricted to those cases of fulminating or disseminated tuberculosis in which the corticosteroid is used for the management of the disease in conjunction with an appropriate antituberculous regimen. | ||
* If corticosteroids are indicated in patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity, close observation is necessary as reactivation of the disease may occur. During prolonged corticosteroid therapy, these patients should receive chemoprophylaxis. | * If corticosteroids are indicated in patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity, close observation is necessary as reactivation of the disease may occur. During prolonged corticosteroid therapy, these patients should receive chemoprophylaxis. | ||
* Literature reports suggest an apparent association between use of corticosteroids and left ventricular free wall rupture after a recent myocardial infarction; therefore, therapy with corticosteroids should be used with great caution in these patients. | * Literature reports suggest an apparent association between use of corticosteroids and left ventricular free wall rupture after a recent [[myocardial infarction]]; therefore, therapy with corticosteroids should be used with great caution in these patients. | ||
|clinicalTrials=There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Trial Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |clinicalTrials=There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Trial Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
|postmarketing======Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances===== | |postmarketing======Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances===== | ||
* Sodium retention | * Sodium retention | ||
| Line 146: | Line 142: | ||
=====Musculoskeletal===== | =====Musculoskeletal===== | ||
* Muscle weakness | * Muscle weakness | ||
* Steroid myopathy | * Steroid [[myopathy]] | ||
* Loss of muscle mass | * Loss of muscle mass | ||
* Osteoporosis | * [[Osteoporosis]] | ||
* Vertebral compression fractures | * Vertebral compression fractures | ||
* Aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads | * [[Aseptic necrosis]] of femoral and humeral heads | ||
* Pathologic fracture of long bones | * Pathologic fracture of long bones | ||
* Tendon rupture | * [[Tendon rupture]] | ||
=====Gastrointestinal===== | =====Gastrointestinal===== | ||
* Peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage | * [[Peptic ulcer]] with possible perforation and hemorrhage | ||
* Perforation of the small and large bowel, particularly in patients with inflammatory bowel disease | * Perforation of the small and large bowel, particularly in patients with inflammatory bowel disease | ||
* Pancreatitis | * [[Pancreatitis]] | ||
* Abdominal distention | * Abdominal distention | ||
* Ulcerative esophagitis | * [[Ulcerative esophagitis]] | ||
=====Dermatologic===== | =====Dermatologic===== | ||
* Impaired wound healing | * Impaired wound healing | ||
* Thin fragile skin | * Thin fragile skin | ||
* Petechiae and ecchymoses | * [[Petechiae]] and [[ecchymoses]] | ||
* Erythema | * [[Erythema]] | ||
* Increased sweating | * Increased sweating | ||
* May suppress reactions to skin tests | * May suppress reactions to skin tests | ||
* Other cutaneous reactions, such as allergic dermatitis, urticaria, angioneurotic edema | * Other cutaneous reactions, such as allergic dermatitis, [[urticaria]], angioneurotic edema | ||
=====Neurologic===== | =====Neurologic===== | ||
* Convulsions | * [[Convulsions]] | ||
* Increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudotumor cerbri) usually after treatment | * Increased intracranial pressure with [[papilledema]] (pseudotumor cerbri) usually after treatment | ||
* Vertigo | * [[Vertigo]] | ||
* Headache | * [[Headache]] | ||
* Psychic disturbances | * Psychic disturbances | ||
=====Endocrine===== | =====Endocrine===== | ||
| Line 179: | Line 175: | ||
* Secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery, or illness | * Secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery, or illness | ||
* Decreased carbohydrate tolerance | * Decreased carbohydrate tolerance | ||
* Manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus | * Manifestations of latent [[diabetes mellitus]] | ||
* Increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics | * Increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics | ||
* Hirsutism | * [[Hirsutism]] | ||
=====Ophthalmic===== | =====Ophthalmic===== | ||
* Posterior subcapsular cataracts | * Posterior subcapsular [[cataracts]] | ||
* Increased intraocular pressure | * Increased intraocular pressure | ||
* Glaucoma | * [[Glaucoma]] | ||
* Exophthalmos | * [[Exophthalmos]] | ||
=====Metabolic===== | =====Metabolic===== | ||
* Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism | * Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism | ||
=====Cardiovascular===== | =====Cardiovascular===== | ||
* Myocardial rupture following recent myocardial infarctions | * Myocardial rupture following recent myocardial infarctions | ||
* Thromboembolism | * [[Thromboembolism]] | ||
* Weight gain | * Weight gain | ||
* Increased appetite | * Increased appetite | ||
* Nausea | * [[Nausea]] | ||
* Malaise | * [[Malaise]] | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions=<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
|FDAPregCat=D | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA=* Since adequate human reproduction studies have not been done with corticosteroids, use of these drugs in pregnancy or in women of childbearing potential requires that the anticipated benefits be weighed against the possible hazards to the mother and embryo or fetus. | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | * Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be carefully observed for signs of hypoadrenalism. | ||
|useInPregnancyFDA=* | * Corticosteroids appear in breast milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other unwanted effects. Mothers taking pharmacologic doses of corticosteroids should be advised not to nurse. | ||
|AUSPregCat=A | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS=* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |useInPregnancyAUS=* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | ||
| Line 220: | Line 217: | ||
* Intravenous | * Intravenous | ||
|monitoring=There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |monitoring=There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | <!--IV Compatibility--> | ||
| Line 227: | Line 222: | ||
<!--Overdosage--> | <!--Overdosage--> | ||
|overdose==== | |overdose=* Reports of acute toxicity and/or death following overdosage of glucocorticoids are rare. In the event of overdosage, no specific antidote is available; treatment is supportive and symptomatic. | ||
* The intraperitoneal LD50 of cortisone acetate in female mice was 1405 mg/kg. | |||
==== | |drugBox= | ||
<div style="float: left;"> | |||
{{chembox new | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
==== | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| verifiedrevid = 456660597 | |||
| ImageFile = Cortison.svg.png | |||
| ImageSize = 200px | |||
=== | | ImageFile1 = 800px-Cortisone-3D-balls.png | ||
| ImageSize1 = 200px | |||
| IUPACName = (8''S'',9''S'',10''R'',13''S'',14''S'',17''R'')-17-Hydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,9,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,11-dione | |||
| OtherNames = | |||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = V27W9254FZ | |||
| | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | ||
|mechAction=* | | ChEMBL = 111861 | ||
| InChI = 1/C21H28O5/c1-19-7-5-13(23)9-12(19)3-4-14-15-6-8-21(26,17(25)11-22)20(15,2)10-16(24)18(14)19/h9,14-15,18,22,26H,3-8,10-11H2,1-2H3/t14-,15-,18+,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1 | |||
| InChIKey = MFYSYFVPBJMHGN-ZPOLXVRWBW | |||
|structure=* | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| StdInChI = 1S/C21H28O5/c1-19-7-5-13(23)9-12(19)3-4-14-15-6-8-21(26,17(25)11-22)20(15,2)10-16(24)18(14)19/h9,14-15,18,22,26H,3-8,10-11H2,1-2H3/t14-,15-,18+,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1 | |||
: [[File: | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| StdInChIKey = MFYSYFVPBJMHGN-ZPOLXVRWSA-N | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 193441 | |||
| CASNo = 53-06-5 | |||
| PubChem = 222786 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D07749 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 16962 | |||
| ATCCode_prefix = H02 | |||
| ATCCode_suffix = AB10 | |||
| ATC_Supplemental = {{ATC|S01|BA03}} | |||
| SMILES = O=C(CO)[C@@]3(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]4CC\C1=C\C(=O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@H]4C(=O)C[C@@]23C | |||
| MeSHName = Cortisone | |||
}} | |||
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | |||
| C=21|H=28|O=5 | |||
| Appearance = | |||
| Density = | |||
| MeltingPtC = 220 | |||
| MeltingPtCH = 224 | |||
| BoilingPt = | |||
}} | |||
| Section3 = {{Chembox Hazards | |||
| Solubility = | |||
| MainHazards = | |||
| FlashPt = | |||
| Autoignition = | |||
}} | |||
}}</div>{{clr}} | |||
|mechAction=* Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and cortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. They are also used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems. | |||
* Glucocorticoids cause profound and varied metabolic effects. In addition, they modify the body's immune responses to diverse stimuli. | |||
|structure=* Glucocorticoids are adrenocortical steroids, both naturally occurring and synthetic, which are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. | |||
* Cortisone acetate is a white or practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It is stable in air. It is insoluble in water. The molecular weight is 402.49. It is designated chemically as 21-(acetyloxy)-17-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione. The molecular formula is C23H30O6 and the structural formula is | |||
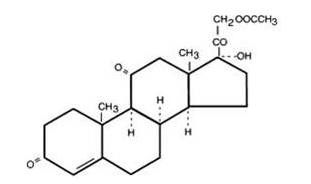
: [[File:Cortisone.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
* Cortisone Acetate tablets contain 25 mg of cortisone acetate in each tablet. | |||
* Inactive ingredients are Anhydrous Lactose, Colloidal Silicon Dioxide, Magnesium Stearate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, and Sodium Starch Glycolate. | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
| Line 265: | Line 298: | ||
<!--How Supplied--> | <!--How Supplied--> | ||
|howSupplied=* | |howSupplied=*Cortisone Acetate Tablets USP 25 mg: White, Round, Scored Tablet; Imprinted "West-ward 202." | ||
| | * Bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 60429-015-01). | ||
|storage=* Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light and moisture. | |||
* Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure. | |||
|packLabel=[[File:Cortisone 01.jpg|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
[[File:DailyMed - CORTISONE ACETATE- cortisone acetate tablet .png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
|fdaPatientInfo=There is limited information regarding <i>Patient Counseling Information</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |fdaPatientInfo=There is limited information regarding <i>Patient Counseling Information</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
| Line 273: | Line 310: | ||
<!--Brand Names--> | <!--Brand Names--> | ||
|brandNames=* ®<ref>{{Cite web | title = | |brandNames=*CORTISONE ACETATE ®<ref>{{Cite web | title =CORTISONE ACETATE- cortisone acetate tablet | url = http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=105133d9-2991-4dd2-8d99-beb81aed8aad }}</ref> | ||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | <!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | ||
|drugShortage= | |drugShortage= | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{LabelImage | {{LabelImage | ||
|fileName= | |fileName=Cortisone 01.jpg | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{LabelImage | {{LabelImage | ||
|fileName= | |fileName=DailyMed - CORTISONE ACETATE- cortisone acetate tablet .png | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--Pill Image--> | <!--Pill Image--> | ||
| Line 298: | Line 332: | ||
<!--Category--> | <!--Category--> | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
[[Category:Corticosteroids]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:25, 18 August 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Cortisone is a hormone that is FDA approved for the treatment of primary and secondary adrenocortical deficiency, rheumatic disorders, psoriasis, exfoliative dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, hemolytic anemia, enteritis, tuberculosis, trichnosis. Common adverse reactions include convulsions, increased intracranial pressure with papilledema, vertigo, headache, psychic disturbances, hirsuitism, glaucoma, exophthalmos.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Endocrine Disorders
- Primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency (hydrocortisone or cortisone is the first choice; synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance).
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Nonsuppurative thyroiditis
- Hypercalcemia associated with cancer
Rheumatic Disorders
- As adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in the following conditions
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy)
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Acute and subacute bursitis
- Acute nonspecific tenosynovitis
- Acute gouty arthritis
- Post-traumatic osteoarthritis
- Synovitis of osteoarthritis
- Epicondylitis
Collagen Diseases
- During an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of following conditions.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Acute rheumatic carditis
- Systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis)
- Dermatologic Diseases
- Pemphigus
- Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis
- Severe erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
- Exfoliative dermatitis
- Mycosis fungoides
- Severe psoriasis
- Severe seborrheic dermatitis
Allergic States
- Control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment of following conditions.
- Seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis
- Bronchial asthma
- Contact dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Serum sickness
- Drug hypersensitivity reactions
Ophthalmic Diseases
- Severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa, such as:
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Keratitis
- Allergic corneal marginal ulcers
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Iritis and iridocyclitis
- Chorioretinitis
- Anterior segment inflammation
- Diffuse posterior uveitis and choroiditis
- Optic neuritis
- Sympathetic ophthalmia
- Respiratory Diseases
- Symptomatic sarcoidosis
- Loeffler's syndrome not manageable by other means
- Berylliosis
- Fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculosis chemotherapy
- Aspiration pneumonitis
Hematologic Disorders
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults
- Secondary thrombocytopenia in adults
- Acquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia
- Erythroblastopenia (RBC anemia)
- Congenital (erythroid) hypoplastic anemia
Neoplastic Diseases
- For palliative management of following conditions.
- Leukemias and lymphomas in adults
- Acute leukemia of childhood
- Edematous States
- To induce a diuresis or remission of proteinuria in the nephrotic syndrome, without uremia, of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus
Gastrointestinal Diseases
- To tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in the follwoing conditions.
- Ulcerative colitis
- Regional enteritis
Miscellaneous
- Tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy
- Trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement.
For Oral Administration=
- DOSAGE REQUIREMENTS ARE VARIABLE AND MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED ON THE BASIS OF THE DISEASE AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.
- The initial dosage varies from 25 to 300 mg a day depending on the disease being treated. In less severe diseases doses lower than 25 mg may suffice, while in severe diseases doses higher than 300 mg may be required. The initial dosage should be maintained or adjusted until the patient's response is satisfactory. If satisfactory clinical response does not occur after a reasonable period of time, discontinue cortisone acetate tablets and transfer the patient to other therapy.
- After a favorable initial response, the proper maintenance dosage should be determined by decreasing the initial dosage in small amounts to the lowest dosage that maintains an adequate clinical response.
- Patients should be observed closely for signs that might require dosage adjustment, including changes in clinical status resulting from remissions or exacerbations of the disease, individual drug responsiveness, and the effect of stress (e.g., surgery, infection, trauma). During stress it may be necessary to increase dosage temporarily.
- If the drug is to be stopped after more than a few days of treatment, it usually should be withdrawn gradually.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Cortisone in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- Carcinoma of breast
- Carcinoma of prostate
- Fever, due tomalignancy; treatment adjunct
- Intracranial tumor
- Multiple myeloma
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Cortisone in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Cortisone in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- Adrenal insufficiency: 0.5-0.75 mg/kg/day or 20-25 mg/m(2)/day ORALLY divided every 8 hr
- Adrenal insufficiency: 0.25-0.35 mg/kg/day or 12.5 mg/m(2)/day IM
Contraindications
- Systemic fungal infections
- Hypersensitivity to this product
Warnings
- In patients on corticosteroid therapy subjected to unusual stress, increased dosage of rapidly acting corticosteroids before, during, and after the stressful situation is indicated.
- Drug-induced secondary adrenocortical insufficiency may result from too rapid withdrawal of corticosteroids and may be minimized by gradual reduction of dosage.
- This type of relative insufficiency may persist for months after discontinuation of therapy; therefore, in any situation of stress occurring during that period, hormone therapy should be reinstituted.
- If the patient is receiving steroids already, dosage may have to be increased. Since mineralocorticoid secretion may be impaired, salt and/or a mineralocorticoid should be administered concurrently.
- Corticosteroids may mask some signs of infection, and new infections may appear during their use. There may be decreased resistance and inability to localize infection when corticosteroids are used.
- Moreover, corticosteroids may affect the nitroblue-tetrazolium test for bacterial infection and produce false negative results.
- In cerebral malaria, a double-blind trial has shown that the use of corticosteroids is associated with prolongation of coma and a higher incidence of pneumonia and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Corticosteroids may activate latent amebiasis. Therefore, it is recommended that latent or active amebiasis be ruled out before initiating corticosteroid therapy in any patient who has time in the tropics or any patient with unexplained diarrhea.
- Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subsapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses.
- Average and large doses of hydrocortisone or cortisone can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased excretion of potassium. These effects are less likely to occur with the synthetic derivatives except when used in large doses.
- Dietary salt restriction and potassium supplementation may be necessary. All corticosteroids increase calcium excretion.
- Administration of live virus vaccines, including smallpox, is contraindicated in individuals receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids. If inactivated viral or bacterial vaccines are administered to individuals receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids, the expected serum antibody response may not be obtained.
- However, immunization procedures may be undertaken in patients who are receiving corticosteroids as replacement therapy, e.g., for Addison's disease.
- Persons who are on drugs which suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals. Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have more serious or even fatal course in non-immune children or adults on corticosteroids.
- In such children or adults who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route and duration of corticosteroid administration affects the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known.
- If exposed to chickenpox, prophylaxis with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information). If chickenpox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
- The use of cortisone acetate tablets in active tuberculosis should be restricted to those cases of fulminating or disseminated tuberculosis in which the corticosteroid is used for the management of the disease in conjunction with an appropriate antituberculous regimen.
- If corticosteroids are indicated in patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity, close observation is necessary as reactivation of the disease may occur. During prolonged corticosteroid therapy, these patients should receive chemoprophylaxis.
- Literature reports suggest an apparent association between use of corticosteroids and left ventricular free wall rupture after a recent myocardial infarction; therefore, therapy with corticosteroids should be used with great caution in these patients.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Cortisone in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances
- Sodium retention
- Fluid retention
- Congestive heart failure in susceptible patients
- Potassium loss
- Hypokalemic alkalosis
- Hypertension
Musculoskeletal
- Muscle weakness
- Steroid myopathy
- Loss of muscle mass
- Osteoporosis
- Vertebral compression fractures
- Aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads
- Pathologic fracture of long bones
- Tendon rupture
Gastrointestinal
- Peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage
- Perforation of the small and large bowel, particularly in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
- Pancreatitis
- Abdominal distention
- Ulcerative esophagitis
Dermatologic
- Impaired wound healing
- Thin fragile skin
- Petechiae and ecchymoses
- Erythema
- Increased sweating
- May suppress reactions to skin tests
- Other cutaneous reactions, such as allergic dermatitis, urticaria, angioneurotic edema
Neurologic
- Convulsions
- Increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudotumor cerbri) usually after treatment
- Vertigo
- Headache
- Psychic disturbances
Endocrine
- Menstrual irregularities
- Development of cushingoid state
- Suppression of growth in children
- Secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery, or illness
- Decreased carbohydrate tolerance
- Manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus
- Increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics
- Hirsutism
Ophthalmic
- Posterior subcapsular cataracts
- Increased intraocular pressure
- Glaucoma
- Exophthalmos
Metabolic
- Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism
Cardiovascular
- Myocardial rupture following recent myocardial infarctions
- Thromboembolism
- Weight gain
- Increased appetite
- Nausea
- Malaise
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Cortisone Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Since adequate human reproduction studies have not been done with corticosteroids, use of these drugs in pregnancy or in women of childbearing potential requires that the anticipated benefits be weighed against the possible hazards to the mother and embryo or fetus.
- Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be carefully observed for signs of hypoadrenalism.
- Corticosteroids appear in breast milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other unwanted effects. Mothers taking pharmacologic doses of corticosteroids should be advised not to nurse.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Cortisone in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Cortisone during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cortisone in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Cortisone in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Cortisone in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Cortisone in the drug label.
Overdosage
- Reports of acute toxicity and/or death following overdosage of glucocorticoids are rare. In the event of overdosage, no specific antidote is available; treatment is supportive and symptomatic.
- The intraperitoneal LD50 of cortisone acetate in female mice was 1405 mg/kg.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and cortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. They are also used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems.
- Glucocorticoids cause profound and varied metabolic effects. In addition, they modify the body's immune responses to diverse stimuli.
Structure
- Glucocorticoids are adrenocortical steroids, both naturally occurring and synthetic, which are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Cortisone acetate is a white or practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It is stable in air. It is insoluble in water. The molecular weight is 402.49. It is designated chemically as 21-(acetyloxy)-17-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione. The molecular formula is C23H30O6 and the structural formula is
- Cortisone Acetate tablets contain 25 mg of cortisone acetate in each tablet.
- Inactive ingredients are Anhydrous Lactose, Colloidal Silicon Dioxide, Magnesium Stearate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, and Sodium Starch Glycolate.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Cortisone in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Cortisone in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Cortisone in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Cortisone in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Cortisone Acetate Tablets USP 25 mg: White, Round, Scored Tablet; Imprinted "West-ward 202."
- Bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 60429-015-01).
Storage
- Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light and moisture.
- Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Cortisone |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Cortisone |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Cortisone in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Cortisone interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- CORTISONE ACETATE ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Cortisone Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Cortisone |Label Name=Cortisone 01.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Cortisone |Label Name=DailyMed - CORTISONE ACETATE- cortisone acetate tablet .png
}}