Chondrosarcoma surgery: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Farima Kahe (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Chondrosarcoma}} | {{Chondrosarcoma}} | ||
{{CMG}} | |||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Rohan}} | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[Surgery]] is the mainstay of treatment for chondrosarcoma. Adjunctive [[chemotherapy]] and [[radiation]] may be required. Recurrence rate depends on the grade of chondrosarcoma. | |||
==Surgery== | ==Surgery== | ||
*Surgery is the mainstay treatment for chondrosarcoma.<ref>{{cite book | last = Peabody | first = Terrance | title = Orthopaedic oncology : primary and metastatic tumors of the skeletal system | publisher = Springer | location = Cham | year = 2014 | isbn = 9783319073224 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Czerniak | first = Bogdan | title = Dorfman and Czerniak's bone tumors | publisher = Elsevier/Saunders | location = Philadelphia, PA | year = 2016 | isbn = 9780323023962 }}</ref><ref name="pmid30559960">{{cite journal| author=Lex JR, Evans S, Stevenson JD, Parry M, Jeys LM, Grimer RJ| title=Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma of the pelvis: clinical outcomes and current treatment. | journal=Clin Sarcoma Res | year= 2018 | volume= 8 | issue= | pages= 23 | pmid=30559960 | doi=10.1186/s13569-018-0110-1 | pmc=6293503 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30559960 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8608505">{{cite journal| author=Ozaki T, Lindner N, Hillmann A, Rödl R, Blasius S, Winkelmann W| title=Influence of intralesional surgery on treatment outcome of chondrosarcoma. | journal=Cancer | year= 1996 | volume= 77 | issue= 7 | pages= 1292-7 | pmid=8608505 | doi=10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960401)77:7<1292::AID-CNCR10>3.0.CO;2-X | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8608505 }} </ref><ref name="pmid11029557">{{cite journal| author=Marco RA, Gitelis S, Brebach GT, Healey JH| title=Cartilage tumors: evaluation and treatment. | journal=J Am Acad Orthop Surg | year= 2000 | volume= 8 | issue= 5 | pages= 292-304 | pmid=11029557 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11029557 }} </ref> | |||
===Intra-Lesional Curettage=== | |||
'''Indications''' | |||
*Grade 1 chondrosarcoma involving the [[extremities]]. | |||
===Wide Surgical Excision=== | |||
'''Indications''' | |||
*Grade 2 or 3 chondrosarcoma anywhere in the body. | |||
*Grade 1 chondrosarcoma in [[pelvis]]. | |||
===Wide Surgical Excision Combined with Multi-Agent Chemotherapy=== | |||
'''Indications''' | |||
*Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma. | |||
===Limb-salvage through Pelvic Resection with or without Reconstruction=== | |||
* | '''Indications''' | ||
*Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma involving the [[pelvis]].<ref name="pmid15523011">{{cite journal| author=Dickey ID, Rose PS, Fuchs B, Wold LE, Okuno SH, Sim FH et al.| title=Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma: the role of chemotherapy with updated outcomes. | journal=J Bone Joint Surg Am | year= 2004 | volume= 86-A | issue= 11 | pages= 2412-8 | pmid=15523011 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15523011 }} </ref> | |||
* | |||
===Limb-sacrifice with Hindquarter Amputation=== | |||
'''Indications''' | |||
*Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma involving the [[pelvis]]<ref name="pmid15523011">{{cite journal| author=Dickey ID, Rose PS, Fuchs B, Wold LE, Okuno SH, Sim FH et al.| title=Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma: the role of chemotherapy with updated outcomes. | journal=J Bone Joint Surg Am | year= 2004 | volume= 86-A | issue= 11 | pages= 2412-8 | pmid=15523011 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15523011 }} </ref> | |||
===Recurrence Rate=== | |||
'''Grade 1 chondrosarcoma''' | |||
*It is rare after wide [[resection]] with negative margins. | |||
*5-15% is the recurrence rate after [[curettage]] with [[adjuvant treatment]]. | |||
'''Grade 2 chondrosarcoma''' | |||
*The recurrence rate varies depending on [[resection]] margins. | |||
'''Grade 3 chondrosarcoma''' | |||
*The local recurrence rate is 25% and >30% chances of [[metastasis]]. | |||
{| | |||
|[[File:Chondrosarcoma clinical image.gif|500px|thumb|Chondrosarcoma of glenoid and scapula. Source: Case courtesy by: [[User:Rohan Bhimani|Dr. Rohan A. Bhimani]]]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br style="clear:left" /> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{ | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:04, 13 March 2019
|
Chondrosarcoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Chondrosarcoma surgery On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Chondrosarcoma surgery |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Chondrosarcoma surgery |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rohan A. Bhimani, M.B.B.S., D.N.B., M.Ch.[2]
Overview
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for chondrosarcoma. Adjunctive chemotherapy and radiation may be required. Recurrence rate depends on the grade of chondrosarcoma.
Surgery
Intra-Lesional Curettage
Indications
- Grade 1 chondrosarcoma involving the extremities.
Wide Surgical Excision
Indications
- Grade 2 or 3 chondrosarcoma anywhere in the body.
- Grade 1 chondrosarcoma in pelvis.
Wide Surgical Excision Combined with Multi-Agent Chemotherapy
Indications
- Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma.
Limb-salvage through Pelvic Resection with or without Reconstruction
Indications
Limb-sacrifice with Hindquarter Amputation
Indications
Recurrence Rate
Grade 1 chondrosarcoma
- It is rare after wide resection with negative margins.
- 5-15% is the recurrence rate after curettage with adjuvant treatment.
Grade 2 chondrosarcoma
- The recurrence rate varies depending on resection margins.
Grade 3 chondrosarcoma
- The local recurrence rate is 25% and >30% chances of metastasis.
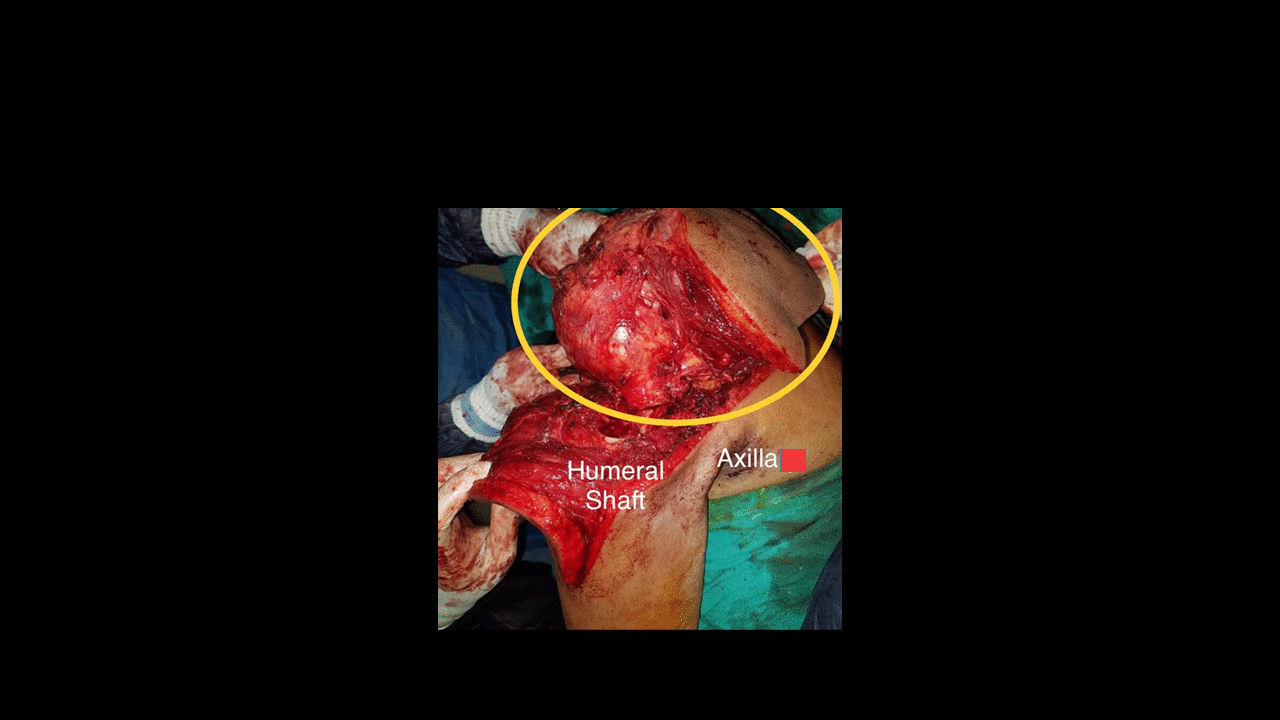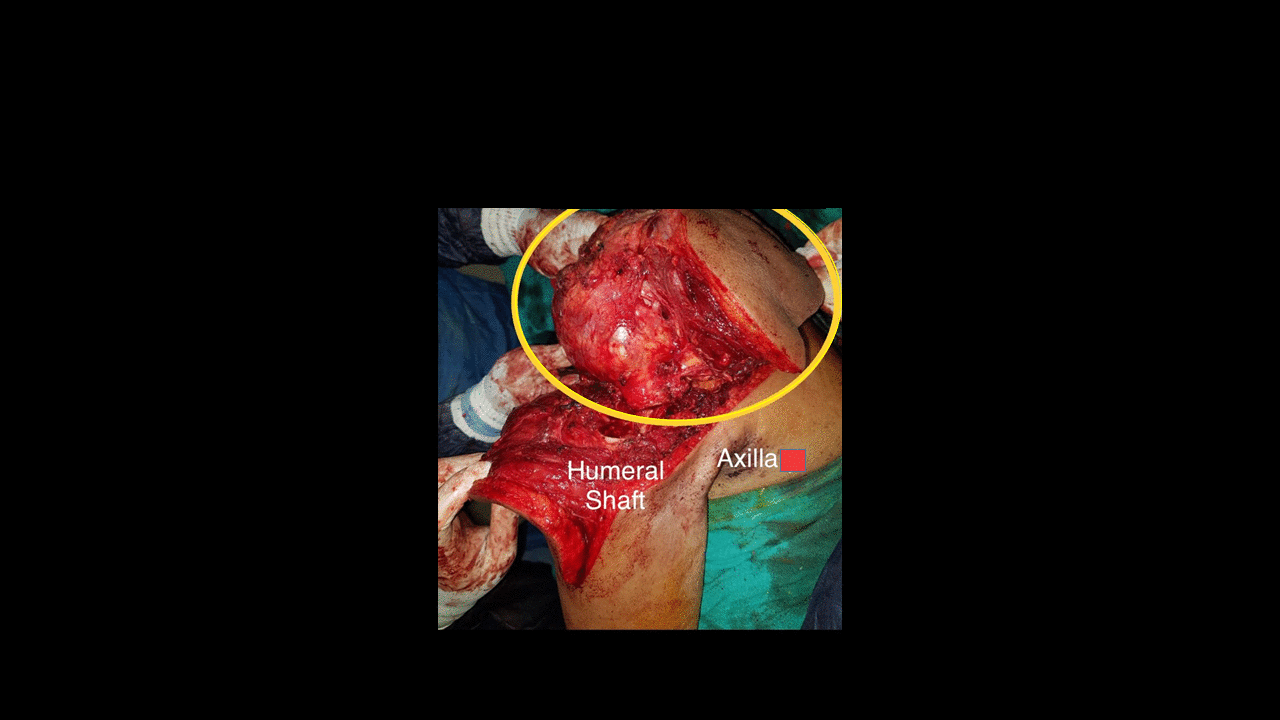 |
References
- ↑ Peabody, Terrance (2014). Orthopaedic oncology : primary and metastatic tumors of the skeletal system. Cham: Springer. ISBN 9783319073224.
- ↑ Czerniak, Bogdan (2016). Dorfman and Czerniak's bone tumors. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. ISBN 9780323023962.
- ↑ Lex JR, Evans S, Stevenson JD, Parry M, Jeys LM, Grimer RJ (2018). "Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma of the pelvis: clinical outcomes and current treatment". Clin Sarcoma Res. 8: 23. doi:10.1186/s13569-018-0110-1. PMC 6293503. PMID 30559960.
- ↑ Ozaki T, Lindner N, Hillmann A, Rödl R, Blasius S, Winkelmann W (1996). "Influence of intralesional surgery on treatment outcome of chondrosarcoma". Cancer. 77 (7): 1292–7. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960401)77:7<1292::AID-CNCR10>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 8608505.
- ↑ Marco RA, Gitelis S, Brebach GT, Healey JH (2000). "Cartilage tumors: evaluation and treatment". J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 8 (5): 292–304. PMID 11029557.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Dickey ID, Rose PS, Fuchs B, Wold LE, Okuno SH, Sim FH; et al. (2004). "Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma: the role of chemotherapy with updated outcomes". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 86-A (11): 2412–8. PMID 15523011.